- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 06-RMON Troubleshooting Guide | 46.69 KB |
Troubleshooting network management & monitoring
RMON issues
Failure of the NMS to receive RMON alarm messages
Symptom
The network management system (NMS) fails to receive RMON alarm messages.
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· The device and the NMS are not reachable to reach other.
· SNMP notification configuration error.
· The RMON statistics table has not been created.
· The RMON event table has not been created.
· The RMON alarm table has not been created.
· Alarm variable configuration error.
Troubleshooting flowchart
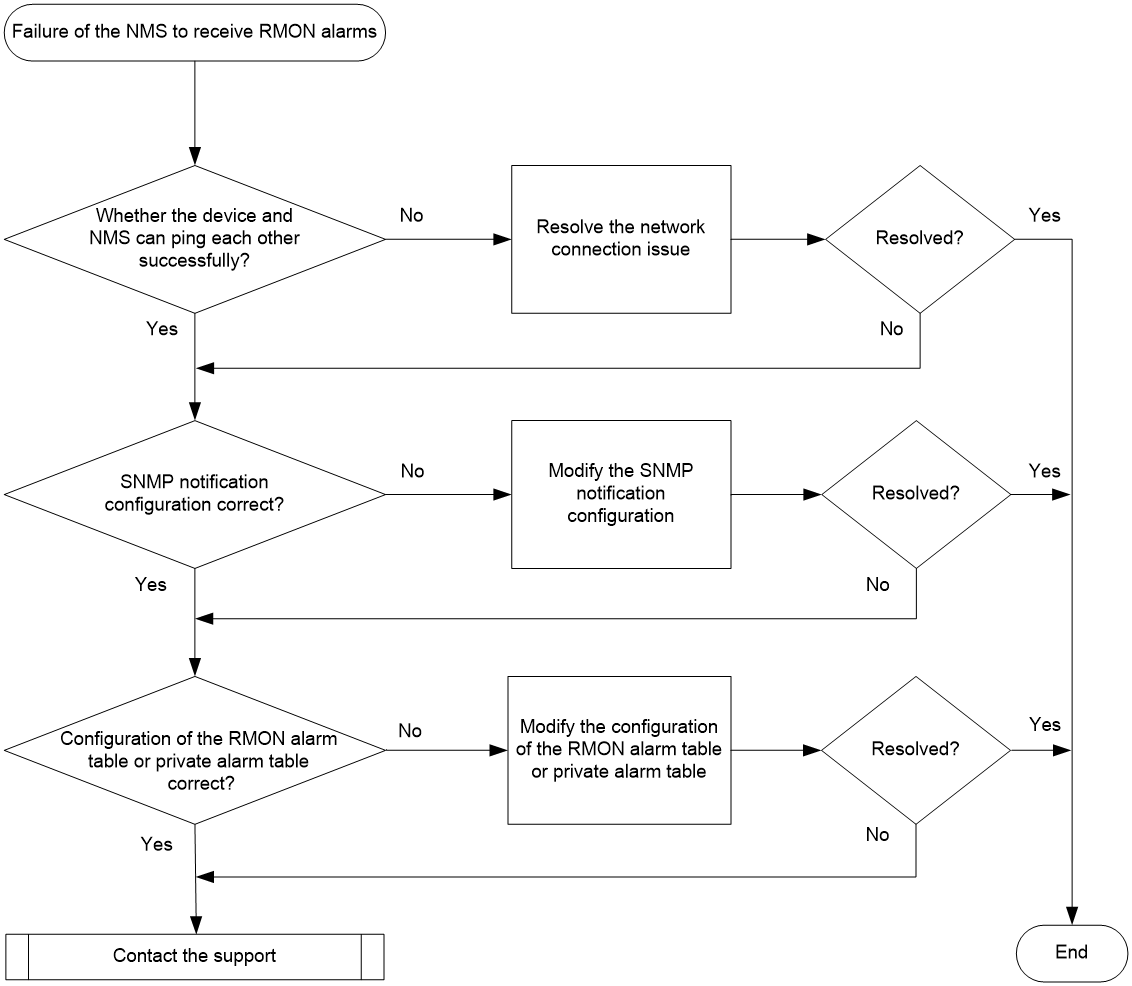
Figure 1 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 1 Flowchart for troubleshooting failure of the NMS to receive RMON alarms
Solution
1. Execute the ping command to test the reachability between the device and NMS.
¡ If the ping is successful, the device and NMS are reachable to each other. Proceed to step 2.
¡ If the ping fails, see the ping failure troubleshooting procedure in "Troubleshooting network management and monitoring" to resolve the network connectivity issue. Proceed to step 2 after the ping succeeds.
2. Identify if the SNMP notification configuration is correct.
RMON is an SNMP-based network management protocol, sending RMON alarm messages based on the SNMP notification channel. For the NMS to receive RMON alarm messages, configure SNMP notification on the device, and ensure that the NMS can receive SNMP notifications normally.
If the NMS can receive any of the following SNMP notifications, proceed to step 3. If the NMS cannot receive any of the following notifications, see the troubleshooting procedure for failure of the NMS to receive SNMP notifications in "Troubleshooting network management & monitoring to identify and resolve the issue.
¡ SNMP alive traps. After SNMP is enabled on the device, the device sends Notification hh3cPeriodicalTrap(1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.2.38.1.6.3.0.1) to the NMS by default at intervals of 60 seconds.
|
|
NOTE: The parameters for transmitting SNMP alive traps can be configured by using the snmp-agent trap periodical-interval command. Support for SNMP alive traps depends on the device model. |
¡ Login and logout notifications. You can log in or log out the device via Telnet, triggering the device to automatically generate and send corresponding login and logout notifications. Then verify whether the NMS can receive the notifications sent from the device.
The login notification is as follows:
Notification hh3cLogIn(1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.2.2.1.1.3.0.1) with hh3cTerminalUserName(1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.2.2.1.1.2.1.0)=;hh3cTerminalSource(1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.2.2.1.1.2.2.0)=VTY.
The logout notification is as follows:
Notification hh3cLogOut(1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.2.2.1.1.3.0.2) with hh3cTerminalUserName(1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.2.2.1.1.2.1.0)=;hh3cTerminalSource(1.3.6.1.4.1.25506.2.2.1.1.2.2.0)=VTY.
¡ linkUP and linkDown notifications. Execute the shutdown and undo shutdown commands on an interface that is physically up to trigger the device to generate linkDown and linkUP notifications. Then verify whether the NMS can receive the notifications generated by the device.
The linkup notification is as follows:
Notification linkUp(1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.4) with ifIndex(1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1.961)=961;ifAdminStatus(1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.7.961)=1;ifOperStatus(1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8.961)=1.
The linkdown notification is as follows:
Notification linkDown(1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.3) with ifIndex(1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1.961)=961;ifAdminStatus(1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.7.961)=2;ifOperStatus(1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8.961)=2.
¡ Identify if the configuration of the RMON event table is correct.
Execute the display rmon event command on the device to check if an RMON event table has been created. If the event table is empty, use the rmon event command to create event entries. Make sure actions of these entries include generation of alarm messages.
3. Identify if the configuration of the RMON alarm table or the RMON private alarm table is correct.
Execute the display rmon alarm command on the device to identify whether the RMON alarm table is configured and whether the monitored variables and trigger conditions are consistent with the network plan. If the alarm table is empty, or if the monitored variables and trigger conditions are not consistent with the network plan (for example, the monitored variable does not exist, the monitored variable is configured incorrectly, or the alarm trigger condition cannot be reached), create or modify the alarm table entries using the rmon alarm in system view
Execute the display rmon prialarm on the device to identify whether an RMON private alarm table has been configured and whether the monitored variables and trigger conditions are consistent with the network plan. If the alarm table is empty, or if the monitored variables and trigger conditions are inconsistent with the network plan (such as the monitored variable doesn't exist, the configured variable is configured incorrectly, or the alarm trigger condition can't be reached), execute the rmon prialarm command to create or modify the private alarm entries.
4. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ Configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
· risingAlarm (1.3.6.1.2.1.16.0.1)
· fallingAlarm (1.3.6.1.2.1.16.0.2)
Log messages
N/A