- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 04-NTP Troubleshooting Guide | 54.75 KB |
Troubleshooting network management & monitoring
NTP issues
NTP clock synchronization failure
Symptom
The device, acting as an NTP client, fails to synchronize the clock with the NTP server. The output from the display ntp-service status command on the device shows that the value of the Clock status field is unsynchronized, indicating that the NTP clock has not been synchronized.
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· NTP configuration error.
· NTP clock synchronization link disconnected.
· Link flapping and unstable latency.
· Time synchronization anomaly at the NTP server side.
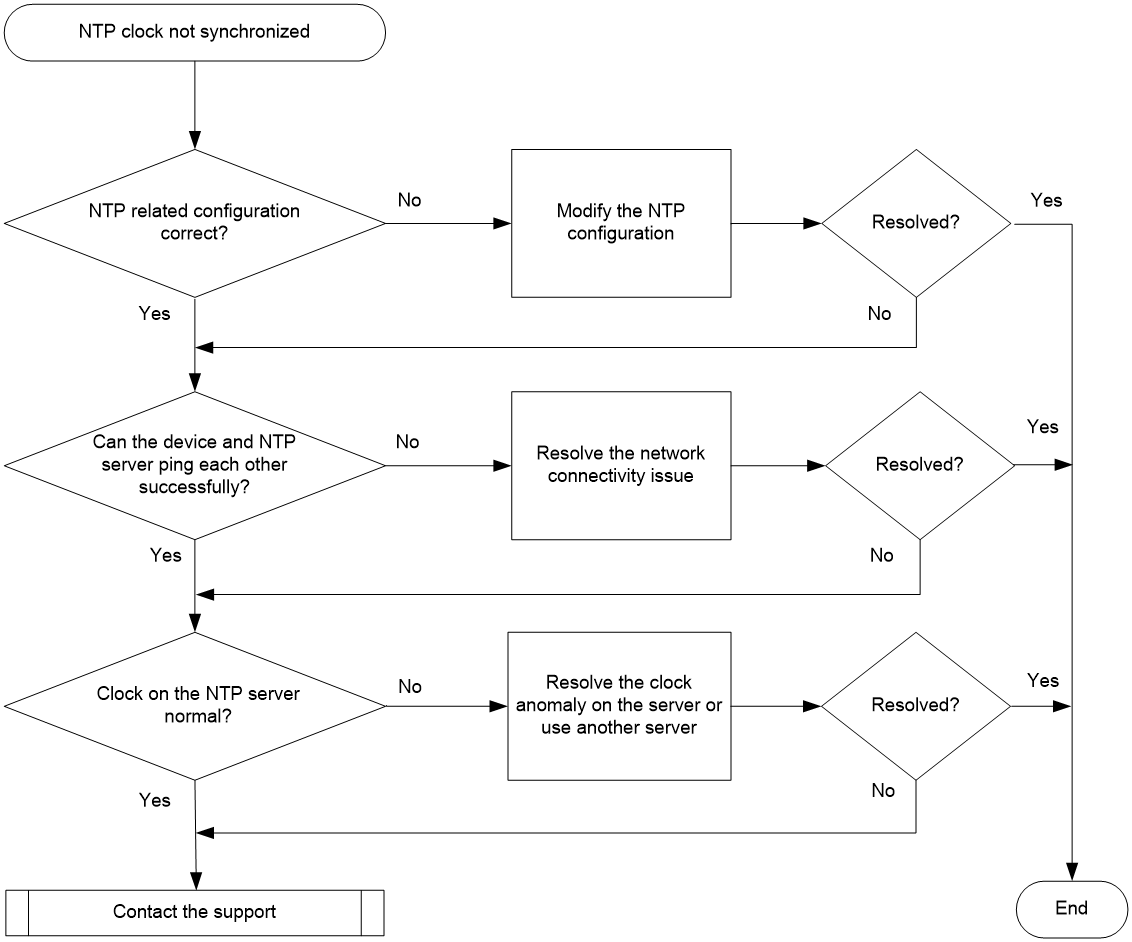
Troubleshooting flow
Figure 1 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 1 Flowchart for troubleshooting NTP clock synchronization failure
Solution
NTP can operate in the following association modes:
· Client/server mode
· Symmetric active/passive peer mode
· Broadcast mode
· Multicast mode
The client/server mode, broadcast mode, and multicast mode all derive from the client/server (C/S) model. The following information is the troubleshooting procedure for NTP time synchronization failure in the C/S model. If you are synchronizing local time with a peer using the symmetric active/passive mode, you can also use this procedure by treating the local end as the client in the C/S model.
To resolve the issue:
1. Execute the display ntp-service [ ipv6 ] sessions command on the device. If no information is output, NTP is not enabled on the device. Configure NTP settings by referring to the configuration guide for the device. If information is output from the command, locate the issue as follows:
a. Identify whether the value of the source field is the IP address of the intended NTP server. If the source field value is not that of the intended NTP server, proceed to step 2 to modify the NTP configuration.
b. The device, when acting as an NTP client, requires the clock stratum of the NTP server to be in the inclusive range of 0 to 14. If the clock stratum of the NTP server exceeds 14, the device will not synchronize with the NTP server's clock (a higher stratum value indicates lower clock accuracy).
- In IPv4 NTP, the stra field in the command output displays the clock stratum of the NTP server.
- In IPv6 NTP, the Clock stratum field in the command output displays the clock stratum of the server.
To change the clock stratum of the NTP server, log in to the NTP server and execute the ntp-service refclock-master command.
c. Identify the reachability of the client to the clock source. In IPv4 NTP, check the reach field. In IPv6, check the Reachabilities field. If the value of the field is 0, the client and server are not reachable to each other. Go to step 3.
Sample command output about IPv4 NTP sessions:
<Sysname> display ntp-service sessions
source reference stra reach poll now offset delay disper
********************************************************************************
[12345]LOCAL(0) LOCL 0 1 64 - 0.0000 0.0000 7937.9
[5]1.1.1.1 INIT 16 0 64 - 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000
Notes: 1 source(master), 2 source(peer), 3 selected, 4 candidate, 5 configured.
Total sessions: 1
Sample command output about IPv6 NTP sessions:
<Sysname> display ntp-service ipv6 sessions
Notes: 1 source(master), 2 source(peer), 3 selected, 4 candidate, 5 configured.
Source: [12345]3000::32
Reference: 127.127.1.0 Clock stratum: 2
Reachabilities: 1 Poll interval: 64
Last receive time: 6 Offset: -0.0
Roundtrip delay: 0.0 Dispersion: 0.0
Total sessions: 1
2. Identify if the NTP-related configuration is correct.
Determine the NTP association mode used by the device according to the network plan. Based on the NTP association mode, execute the display current-configuration | include ntp-service command on the device to view the NTP-related configuration and identify if the current NTP configuration is correct. For example, when the local end acts as a client for time synchronization in client/server mode, the NTP configuration must meet the following requirements:
¡ The ntp-service [ ipv6 ] unicast-server command has been configured in system view to specify the NTP server IP address correctly.
¡ The clock protocol ntp command has been configured in system view to specify NTP for obtaining the system time.
¡ If NTP authentication is required, make sure the authentication key configured on the device and the NTP server is the same, and the authentication key used on this device is trusted on the server. Verify that the ntp-service authentication-keyid specify an authentication key) and ntp-service reliable authentication-keyid (configure the authentication key as a trust key) commands have been configured in system view correctly.
3. Execute the ping command to verify the reachability between the device and the NTP server.
¡ If the ping is successful, the device and the NTP server are reachable to each other. Proceed to step 4.
¡ If the ping fails, see the ping failure troubleshooting procedure in "Troubleshooting network management and monitoring" to resolve the issue. Proceed to step 4 after the ping succeeds.
4. Execute the debugging ntp-service all command in user view to enable NTP debugging and view NTP debugging information. The local end will not synchronize with the NTP server if the following conditions exist.
¡ If "The packet from ip-address failed the validity tests result" is displayed in the debugging information, the packets from the specified NTP server failed the validity check on the device. The device will not synchronize with the clock of that NTP server.
¡ if delay in rdel: delay > 16000, disper in rdsp: disper > 16000, or delay/2+disper > 16000, the clock provided by the NTP server has a too large offset, and the device will not synchronize the clock with that NTP server.
5. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ Configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
|
|
NOTE: NTP message exchange is slow. After you execute the debugging ntp-service all command to enable NTP debugging, the debugging information might be displayed in 5 to 10 minutes. |
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
· NTP/5/NTP_CLOCK_CHANGE
· NTP/5/NTP_LEAP_CHANGE
· NTP/4/NTP_SOURCE_LOST
· NTP/5/NTP_STRATUM_CHANGE