- Table of Contents
-
- 18-Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Information center configuration
- 02-Flow log configuration
- 03-Fast log output configuration
- 04-NetStream configuration
- 05-Sampler configuration
- 06-Mirroring configuration
- 07-Packet capture configuration
- 08-NQA configuration
- 09-Track configuration
- 10-BFD configuration
- 11-Error code detection configuration
- 12-Monitor Link configuration
- 13-Smart Link configuration
- 14-Interface backup configuration
- 15-Interface collaboration configuration
- 16-System maintenance and debugging configuration
- 17-NTP configuration
- 18-EAA configuration
- 19-Process monitoring and maintenance configuration
- 20-gRPC configuration
- 21-NETCONF configuration
- 22-CWMP configuration
- 23-SNMP configuration
- 24-RMON configuration
- 25-Event MIB configuration
- 26-GOLD configuration
- 27-Process placement configuration
- 28-Cloud connection configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 28-Cloud connection configuration | 125.39 KB |
Cloud connection establishment
Unbinding the device from the cloud server
Display and maintenance commands for cloud connections
Cloud connection configuration examples
Example: Configuring a cloud connection
Cloud connection configuration examples
Example: Configuring a cloud connection
Configuring cloud connections
About cloud connections
A cloud connection is a management tunnel established between a local device and the cloud server. It enables you to manage the local device from the cloud server without accessing the network where the device resides.
Multiple subconnections
After a local device establishes a connection with the cloud server, service modules on the local device can establish multiple subconnections with the microservices on the cloud server. These subconnections are independent from each other and provide separate communication channels for different services. This mechanism avoids interference among different services.
Cloud connection establishment
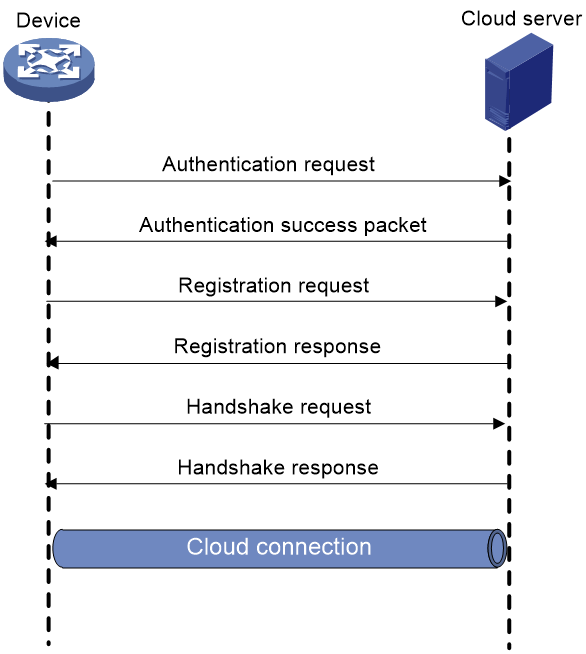
As shown in Figure 1, the cloud connection between the device and the cloud server is established as follows:
1. The device sends an authentication request to the cloud server.
2. The cloud server sends an authentication success packet to the device.
The device passes the authentication only if the serial number of the device has been added to the cloud server. If the authentication fails, the cloud server sends an authentication failure packet to the device.
3. The device sends a registration request to the cloud server.
4. The cloud server sends a registration response to the device.
The registration response contains the uniform resource locator (URL) used to establish a cloud connection.
5. The device uses the URL to send a handshake request (changing the protocol from HTTP to WebSocket) to the cloud server.
6. The cloud server sends a handshake response to the device to finish establishing the cloud connection.
7. After the cloud connection is established, the device automatically obtains the subconnection URLs and establishes subconnections with the cloud server based on the service needs.
Figure 1 Establishing a cloud connection
Configuring the cloud server
For a successful cloud connection establishment, add the serial number of the device to be managed to the cloud server. For more information about the cloud server settings, see the installation guide for the cloud server.
Configuring the local device
About this task
You can specify a cloud server by its domain name and log in to the server through the domain name on a remote PC to manage the local device.
For a device to establish a cloud connection to the cloud server, perform either of the following tasks:
· Manual configuration: Use cloud-management server domain or cloud-management backup-server domain to specify the domain name of the cloud server on the device through CLI.
· Auto obtaining: Configure VLAN interface 1 of the device as a DHCP client and the cloud server as the DHCP server. The device obtains the IP address of the DHCP server and parses the option 253 field in the DHCP packets to obtain the domain name of the cloud server. When the domain name obtained through the option 253 field is an IPv4 or IPv6 address, the device uses the IPv4 or IPv6 address to connect to the cloud server. When the domain name obtained through the option 253 field is not an IPv4 or IPv6 address, the device parses the domain name into an IPv4 address. If the device fails to parse the domain name into an IPv4 address, it will not parse the domain name into an IPv6 address. For more information about the option 253 field, see DHCP configuration in Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
To establish cloud connections to the cloud server, a password is required. A device can use either of the following methods to obtain the password for establishing cloud connections to the cloud server:
· Execute the cloud-management server password command on the device to specify the password for establishing cloud connections to the cloud server.
· Configure VLAN interface 1 of the device as a DHCP client and the cloud server as the DHCP server. The device obtains the IP address of the DHCP server and parses the option 252 field in the DHCP packets to obtain the password for connection to the cloud server. For more information about the option 252 field, see DHCP configuration in Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
After establishing the cloud connection, the local device sends keepalive packets to the cloud server at the interval specified by the cloud-management keepalive interval command. If the device does not receive a response from the cloud server after the number of keepalive packets sent reached the limit specified by the cloud-management keepalive count count command, the device sends a registration request to re-establish the cloud connection.
To prevent NAT entry aging, the local device sends ping packets to the cloud server periodically.
If the cloud server verifies the token of a device before establishing a cloud connection to the device, you must configure the token on the device. To avoid authentication failure, make sure the token configured on the device is consistent with that specified for the device on the cloud server.
Restrictions and guidelines
You can specify one primary server by using the cloud-management server domain command and a maximum of eight IPv4 and IPv6 backup servers by repeating the cloud-management backup-server domain command. Each server domain name supports a maximum of three port numbers.
When establishing a cloud connection, the device can connect to only one cloud server at one time according to the sequence in which the servers are stored. The server domain names are stored in alphabet order and port numbers are in descending order. To view the connected server, execute the display cloud-management state command.
If multiple servers exist in the intranet and the NAT device has only one public IP address, you can execute this command to specify different port numbers for one server domain name.
When establishing a cloud connection, the first specified server has the highest priority. When the connected server fails, the device switches to another server and does not switch back to the original server even if the original server recovers.
The password obtained through DHCP has a higher priority than the password configured manually.
If a device obtains the password for connection to the cloud server through DHCP after establishing a cloud connection to the cloud server with the manually configured password, the device performs the following tasks:
· If the automatically obtained and manually configured passwords are identical, the device retains the cloud connection.
· If the automatically obtained and manually configured passwords are different, the device tears down the cloud connection and then establishes a cloud connection to the cloud server with the automatically obtained password.
Reduce the ping interval value if the network condition is poor or the NAT entry aging time is short. When you use the cloud server for cloud connections, you must set the password for establishing cloud connections to the cloud server.
Prerequisites
Before configuring this feature, make sure a DNS server is configured to translate domain names.
To obtain the password for connection to the cloud server automatically, first configure the option 252 field as the password of the cloud server.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable cloud connection.
cloud-management server connect enable
By default, cloud connection is enabled for a device.
3. Specify the primary cloud server by its domain name.
cloud-management server [ ipv6 ] domain domain-name [ port port-number ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ source-ip ip-address ]
By default, the cloud server uses domain name ops.seccloud.h3c.com.
4. (Optional.) Specify a backup cloud server by its domain name.
cloud-management backup-server [ ipv6 ] domain domain-name [ port port-number ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] [ source-ip ip-address ]
By default, no backup cloud server is specified.
5. (Optional.) Set the keepalive interval.
cloud-management keepalive interval
By default, the keepalive interval is 180 seconds.
6. (Optional.) Specify the maximum number of consecutive keepalive packets that the local device can send to the cloud server.
cloud-management keepalive count count
By default, the local device can send three consecutive keepalive packets to the cloud server.
7. (Optional.) Set the ping interval.
cloud-management ping interval
By default, the ping interval is 60 seconds.
8. (Optional.) Specify the TCP port number used by the device to initiate the authentication to the cloud server.
cloud-management server port port-number
By default, TCP port number 19443 is used by the device to initiate the authentication to a cloud server.
9. (Optional.) Set the password for establishing cloud connections to the cloud server.
cloud-management server password { cipher | simple } string
By default, no password is set for establishing cloud connections to the cloud server.
10. (Optional.) Set the token for establishing cloud connections to the cloud server.
cloud-management token { cipher | simple } string
By default, no token is set for establishing cloud connections to the cloud server.
Unbinding the device from the cloud server
About this task
A device can be registered on the cloud server by only one user.
To register a device that has been registered by another user, you need to take the following steps:
1. Obtain a verification code for device unbinding from the cloud server.
2. Execute the command on the device for sending the verification code to the cloud server.
3. Register the device on the cloud server.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Send the verification code for device unbinding to the cloud server.
cloud-management unbinding-code code
Display and maintenance commands for cloud connections
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display cloud connection state information. |
display cloud-management state |
Cloud connection configuration examples
Example: Configuring a cloud connection
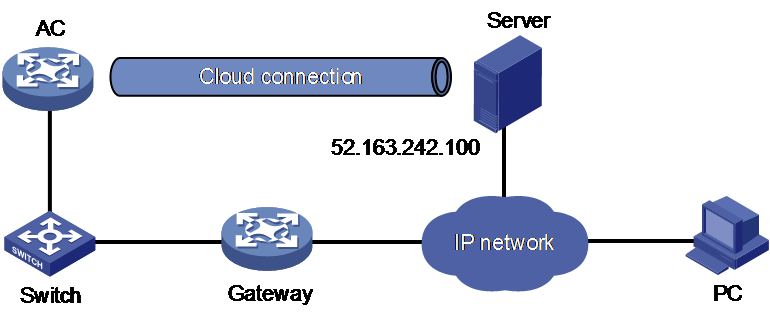
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, configure the AC to establish a cloud connection with the cloud server.
Procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces as shown in Figure 2, and configure a routing protocol to make sure the devices can reach each other. (Details not shown.)
2. Log in to the cloud server to add the serial number of the AC to the server. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure the domain name of the cloud server as oasiscloud.h3c.com.
<AC> system-view
[AC] cloud-management server domain oasiscloud.h3c.com
|
|
NOTE: · The DNS service is provided by the ISP DNS server. · The domain name and IP address of the cloud server used here are for illustration only. |
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the AC and the cloud server have established a cloud connection.
[AC] display cloud-management state
Cloud connection state : Established
Device state : Request_success
Cloud server address : 52.163.242.100
Cloud server domain name : oasiscloud.h3c.com
Cloud connection mode : Https
Cloud server authentication port : 19443
Cloud server connection port : 443
Connected at : Wed Jan 27 14:18:40 2018
Duration : 00d 00h 02m 01s
Process state : Message received
Failure reason : N/A
Last down reason : socket connection error (Details:N/A)
Last down at : Wed Jan 27 13:18:40 2018
Last report failure reason : N/A
Last report failure at : N/A
Dropped packets after reaching buffer limit : 0
Total dropped packets : 1
Last report incomplete reason : N/A
Last report incomplete at : N/A
Buffer full count : 0
Cloud connection configuration examples
Example: Configuring a cloud connection
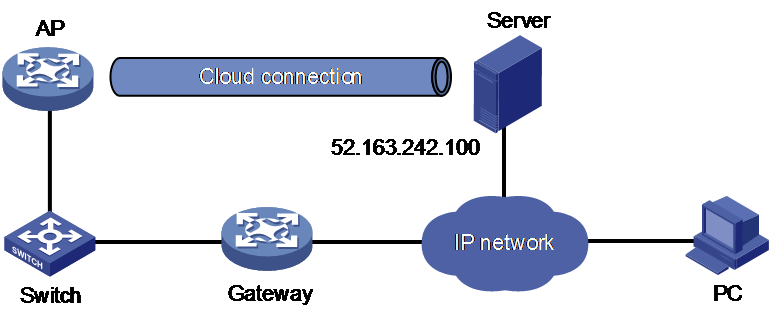
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 3, configure the AP to establish a cloud connection with the cloud server.
Procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces as shown in Figure 3, and configure a routing protocol to ensure that the devices can reach each other. (Details not shown.)
2. Log in to the cloud server to add the serial number of the AP to the server. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure the domain name of the cloud server as oasiscloud.h3c.com.
<AP> system-view
[AP] cloud-management server domain oasiscloud.h3c.com
|
|
NOTE: · The DNS service is provided by the ISP DNS server. · The domain name and IP address of the cloud server used here are for illustration only. |
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the AP and the cloud server have established a cloud connection.
[AP] display cloud-management state
Cloud connection state : Established
Device state : Request_success
Cloud server address : 52.163.242.100
Cloud server domain name : oasiscloud.h3c.com
Cloud connection mode : Https
Cloud server authentication port : 19443
Cloud server connection port : 443
Connected at : Wed Jan 27 14:18:40 2018
Duration : 00d 00h 02m 01s
Process state : Message received
Failure reason : N/A
Last down reason : socket connection error (Details:N/A)
Last down at : Wed Jan 27 13:18:40 2018
Last report failure reason : N/A
Last report failure at : N/A
Dropped packets after reaching buffer limit : 0
Total dropped packets : 1
Last report incomplete reason : N/A
Last report incomplete at : N/A
Buffer full count : 0