- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-H3C WLAN Products FAQ | 840.37 KB |
|
H3C WLAN Products FAQ |
|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2023 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Contents
Q. What is the most recent wireless networking standard?
Q. What are the frequency, compatibility, and maximum rate of 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax/be?
Q. Is wireless networking protocol 802.11 a Layer 2 networking protocol?
Q. Which techniques does 802.11ac use to increase channel bandwidth and expand the signal coverage?
Q. Which techniques does 802.11ax use to increase channel bandwidth and expand the signal coverage?
Q. What are the relationships among WPA, WPA2, WPA3, PSK, 802.1X, TKIP, CCMP, GCMP, and AES?
Q. What interference might exist in a WLAN and how seriously can they affect a WLAN?
Q. Does the rate of a WLAN represent the uplink rate or the downlink rate?
Q. What are the functions of fit APs?
Q. How can I view the serial ID of a fit AP? What are the functions of a serial ID?
Q. Do I need to configure ACs' IP addresses for a fit AP?
Q. Do fit APs support PoE power supply?
Q. Does a fit AP have a console port? Can I log in from the console port to configure the AP?
Q. Under what circumstances can I return an AP for repair?
Q. Can a fit AP cooperate with a third-party AC?
Q. Can a radio bound to different SSIDs operate on different channels?
Q. Why is the transmit rate dynamically adjusted in a WLAN?
Q. How can I associate fit APs with an AC?
Q. Why can't I configure an auto AP?
Q. Do fit APs save configuration? How do I upgrade a large number of fit APs in batch?
Q. Can ACs provide services to wired users?
Q. How many AC IP addresses does a fit AP support in Option 43?
Q. Can an AP operate in fat AP mode?
Q. How can I view the software version of a fit AP?
Q. What are the functions of an AC?
Q. How can I connect a fit AP to an AC physically?
Q. How does an AC communicate with a fit AP?
Q. Can an AC act as a local DHCP server?
Q. How can I view detailed information about manual APs and online auto APs on an AC?
Q. How can I view the association status of APs on an AC?
Q. How can I view the version of an AC?
Q. How can I view channel and power adjustment information on an AC?
Q. How can I separate services of different APs with the same SSID?
Q. How can I view information about APs that went offline recently on an AC?
Q. Which UDP ports does a CAPWAP tunnel use?
Q. Why can't I view newly created manual APs in the system-defined AP group?
Q. Do ACs support IRF? How many ACs does an IRF fabric support?
Q. Do ACs support third-party APs?
Q. What are the advantages of local forwarding? When do I need to configure local forwarding?
Q. How do I configure online automatic license installation
Q. How do I uninstall a license?
Q. How do I transfer a license?
Q. What is WLAN IRF license sharing?
Q. How do I identify license compatibility with multiple devices?
Q. How do I view the installed licenses on a device?
Q. How do I view the license usage?
Q. How do I export a DID file?
Q. How do I identify whether a device comes with default licenses?
Q. How do I retrieve a lost license key?
Q. How do I retrieve an activation file?
Q. How do I troubleshoot a license installation error?
Q. How do I obtain the licensing guide?
Q. How do I increase the number of APs that an AC can manage?
Q. How do I know which features require licenses?
Q. How can I register and activate a license?
Q. How can I view the remaining days of AP licenses?
Q. How can I view the number of AP licenses?
Q. Do I need to restart the device for the license to take effect after installing a license?
Q. Will the installed licenses be deleted when the file system is formatted?
Q. How can I register Comware 5 licenses on an AC upgraded from Comware 5 to Comware 7?
Q. How is an AP associated with an AC in different fit AP+AC networking environments?
Q. At which layer can I deploy an AC in a fit AP+AC network?
Q. Do I need to change the wired backbone network for WLAN devices?
Q. How are packets forwarded by default in a fit AP+AC network?
Q. Which authentication methods does an AC support?
Q. Does an AC support portal authentication?
Q. Can an AC cooperate with a third-party LDAP server for authentication?
Q. In a wireless network, which device acts as an AAA authenticator?
Q. Can an AC detect rogue APs?
Q. What is WLAN roaming? How many types of WLAN roaming are available?
Q. Can wireless clients perform Layer 3 roaming?
Q. Do clients need to be reauthenticated or log in again after roaming?
Q. Does the IP address of a client remain unchanged during WLAN roaming?
Q. How can I adjust the sensitivity of a wireless NIC?
Q. Do I need to change the switch or router configuration to enable WLAN roaming?
Q. Do I need to install new client software for WLAN roaming?
Q. Can I configure a mandatory rate for an AC to increase the wireless network performance?
Q. How can I determine whether memory leakage has occurred?
Q. How can I view process state information?
Q. How can I view memory usage for all processes?
Q. Is there an upper limit on the number of member devices of an IRF fabric?
Q. Does an IRF fabric have requirements on the software versions of its member devices?
Q. Are there any requirements on IRF bridge MAC addresses when two IRF fabrics merge?
Q. Under what circumstances do I need to use a switching device to form a star-topology IRF fabric?
Q. What restrictions and guidelines do I need to follow after an IRF fabric is formed?
WLAN products FAQ
Introduction
This document contains the most frequently asked questions about wireless products.
Protocols and standards
This section contains the most frequently asked questions about wireless networking standards and protocols.
Q. What is the most recent wireless networking standard?
A. 802.11 is a set of specifications created and maintained by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for WLAN communication. The 802.11 family includes 802.11, 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11ac, 802.11ax, and 802.11be. The most recent wireless networking standard is 802.11be.
Q. What are the frequency, compatibility, and maximum rate of 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax/be?
A. The following table describes the frequency, compatibility, and maximum rate of 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax/be:
|
Protocols |
Frequency |
Compatibility |
Maximum rate supported by H3C devices |
|
802.11a |
5 GHz |
N/A |
54 Mbps |
|
802.11b |
2.4 GHz |
N/A |
11 Mbps |
|
802.11g |
2.4 GHz |
Compatible with 802.11b |
54 Mbps |
|
802.11n |
2.4 GHz, 5 GHz |
Compatible with 802.11a/b/g |
600 Mbps |
|
802.11ac |
5 GHz |
Compatible with 802.11a/an |
1.733 Gbps |
|
802.11ax |
2.4 GHz, 5 GHz |
Compatible with 802.11a/b/g/n/ac |
4.8 Gbps |
|
802.11be |
2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, 6 GHz |
Compatible with 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax |
11.53 Gbps |
Q. Is wireless networking protocol 802.11 a Layer 2 networking protocol?
A. Yes. 802.11 defines only contents of the PHY layer and the MAC layer of the data link layer in the OSI model. Other layers of a wireless network are the same as those of a wired network.
Q. How many channels are available in the 2.4 GHz band in China? What is the bandwidth for each channel? Why only three channels are used in WLAN deployment?
A. 13 channels are available in the 2.4 GHz band in China. Each channel has a bandwidth of 22 MHz. To avoid interference caused by overlapping channels, only the three non-overlapping channels (typically channels 1, 6, and 11) in the 2.4 GHz band can be used in WLAN deployment.
Q. Which techniques does 802.11ac use to increase channel bandwidth and expand the signal coverage?
A. 802.11ac uses the following techniques:
· Increased spatial streams and high-density modulation.
· Multi-User Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MU-MIMO), which increases data rates.
· A-MPDU, which improves channel usage.
Q. Which techniques does 802.11ax use to increase channel bandwidth and expand the signal coverage?
A. 802.11ax uses the following techniques:
· 1024-QAM—Carries 10 bits of information per symbol, which improves the physical layer data rate by 25% compared with 256-QAM used by 802.11ac.
· Uplink and downlink MU-MIMO—Enables concurrent receiving and transmission of large data packets, which greatly improves data transmission efficiency and system capacity.
· OFDMA—Enables simultaneous multi-user transmission of small data packets, which improves channel usage and transmission efficiency for each single spatial stream.
· Spatial multiplexing—Assigns a different color per BSS to help devices fast identify co-channel interference and stop transmission in time.
· TWT—Improves power efficiency and reduces contention by increasing client sleep time and allowing negotiation of the number of client accesses to the medium.
Q. What key technologies does the 802.11be protocol use to significantly improve the throughput and reliability of wireless networks?
· New 6 GHz frequency band—The 6 GHz frequency band has a total bandwidth of 1200 MHz, which is twice as wide as the previous 2.4GHz + 5GHz bandwidth, greatly alleviating the shortage of Wi-Fi spectrum resources.
· 320 MHz bandwidth—Under the same number of streams and the same encoding, the peak theoretical throughput is directly doubled compared to Wi-Fi 6's 160 MHz bandwidth.
· Higher-order modulation scheme 4096-QAM—Upgraded from 802.11ax's 1024-QAM to 4096-QAM, the physical layer negotiation rate is increased by 20%.
Q. What are the relationships among WPA, WPA2, WPA3, PSK, 802.1X, TKIP, CCMP, GCMP, and AES?
A. The 802.11i standard specifies security mechanisms for wireless networks.
· WPA, WPA2, and WPA3 are all security modes for WLANs. WPA uses the TKIP encryption algorithm. WPA2 introduced the AES-based CCMP encryption algorithm, which has significantly improved security compared to TKIP. In recent years, because of the continuous exposure of new security vulnerabilities in WPA2, the more secure WPA3 security mode has been introduced, which requires the use of AES-based authentication encryption algorithms.
· PSK and 802.1X are two authentication methods for wireless networks. PSK is simple and is intended for personal use. 802.1X is complex, more secure, and is intended for enterprise use.
· TKIP, CCMP, and GCMP are encryption algorithms. AES is the core algorithm of CCMP and GCMP and also the most secure encryption algorithm.
Q. What interference might exist in a WLAN and how seriously can they affect a WLAN?
A. WLAN devices operate in the 2.4 GHz industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) band or 5 GHz band.
2.4 GHz ISM band is reserved for the use in industrial, scientific and medical fields other than telecommunications. Devices that can use the 2.4 GHz band include microwave ovens, cordless phones, and Bluetooth devices. Interference severity of cordless phones, microwave ovens (within 3 meters), and Bluetooth devices such as laptop and PDA are in descending order.
Compared with the 2.4 GHz band, the 5 GHz band has less interference. Interference in the 5 GHz band includes radar, wireless sensors, digital satellites, wireless ATMs, and software-defined radios.
Q. Does the rate of a WLAN represent the uplink rate or the downlink rate?
A. WLANs work in half duplex mode and cannot receive and send packets at the same time. The rate of a WLAN typically refers to the sum of the uplink and downlink rates.
Access points (APs)
This section contains the most frequently asked questions about APs.
Q. What are the functions of fit APs?
A. A fit AP provides the following functions:
· Provides communications from wireless clients to a wired network.
· Transfers packet formats between 802.3 and 802.11.
· Encrypts data frames and control frames through WEP, TKIP, or CCMP.
· Buffers data and forwards packets based on QoS configuration.
· Scans working channels to locate wireless clients and detect rogue APs and ad hoc clients.
· Automatically obtains configurations from the associated AC.
Q. How can I view the serial ID of a fit AP? What are the functions of a serial ID?
A. You can view the serial ID of an AP on the rear panel of the AP, or you can display AP information on the AC to view an AP's serial ID.
A serial ID uniquely identifies an AP and must be specified when you create an AP on an AC.
Q. Do I need to configure ACs' IP addresses for a fit AP?
A. You can configure ACs' IP addresses for a fit AP, or the fit AP can obtain ACs' IP addresses automatically.
Q. Do fit APs support PoE power supply?
A. Fit APs that have PoE ports support PoE power supply. For APs with high power consumption, PoE+ power sourcing equipment conforming to 802.3at protocol is required.
Q. How does a fit AP select a channel when starting up? Can the fit AP change its channel while operating?
A. By default, a fit AP automatically selects a channel when starting up. The selected channel does not change when the AP is operating unless radar signals are detected on the working channel or DFS is configured.
Q. Does a fit AP have a console port? Can I log in from the console port to configure the AP?
A. Yes. By default, fit APs do not have any configuration and do not need to be configured. For management purposes, you can log in and configure the AP before it is associated with an AC. To configure a fit AP from the console after it is associated with an AC, you must enable the AP automatically disables the login function unless the function is enabled for the AP on the AC.
Q. Under what circumstances can I return an AP for repair?
A. You can return an AP for repair if any of the following events occur:
· The AP cannot start up, even if from the BootWare menu.
· An error message occurs when the AP starts up, and you cannot press Ctrl+B to enter the Boot menu to upgrade the AP.
· The Ethernet port on the AP cannot communicate with the switch even if you replace the cable or connect the Ethernet port to another port on the switch.
· The output from the display current-configuration command shows that no radio exists on the AP after the AP starts up.
Q. Can a fit AP cooperate with a third-party AC?
A. No.
Q. Can a radio bound to different SSIDs operate on different channels?
A. No. A radio can operate only on one channel.
Q. Why is the transmit rate dynamically adjusted in a WLAN?
A. When wireless signal strength gets worse, the transmit rate will be reduced to decrease the error code ratio.
Q. How can I associate fit APs with an AC?
A. You can create manual APs or enable auto AP on the AC.
If auto AP is disabled, only APs with manual AP configuration can be associated with the AC.
If auto AP is enabled, APs can be associated with the AC without manual AP configuration. The AC names auto APs by their MAC addresses. This feature simplifies configuration when you deploy a large number of APs in a WLAN.
Q. Can a manual AP download a version from the AC and then connect to the AC if it has a different software version than the AC?
A. Yes.
Q. Can an auto AP download a version from the AC and then connect to the AC if it has a different software version than the AC?
A. Yes.
Q. Why can't I configure an auto AP?
A. An auto AP does not have an AP view and cannot be configured. To configure auto APs, you must convert auto APs to manual APs by executing the wlan auto-ap persistent all command.
Q. Do fit APs save configuration? How do I upgrade a large number of fit APs in batch?
A. Fit APs do not save configuration deployed by the AC but save settings configured on the APs. APs automatically upgrade their software versions when connecting to an AC if software upgrade is enabled (default).
Q. Can ACs provide services to wired users?
A. Yes.
Q. How many AC IP addresses does a fit AP support in Option 43?
A. A fit AP supports a maximum of 16 AC IP addresses in Option 43.
Q. Can an AP operate in fat AP mode?
Yes. All H3C Cloud APs can operate as fat APs and can be managed from the Cloudnet platform.
Wi-Fi 6 Cloud APs that operate as fat APs
|
Series |
Models |
|
WA6600 series |
WA6638 WA6638i WA6636 WA6630X WA6628 WA6628X WA6628E-T WA6628XM WA6622 WA6620 WA6620X WA6620X-LI WA6620XE-LI |
|
WA6500 series |
WA6528i |
|
WA6300 series |
WA6338 WA6338-HI WA6338-LI WA6330 WA6330-LI WA6322 WA6322H WA6322H-HI WA6322H-LI WA6320 WA6320-C WA6320-D WA6320-HI WA6320-SI WA6320S-C WA6320S-E WA6320H WA6320H-HI WA6320H-LI WA6320H-XEPON |
|
WAP922 series |
WAP922 WAP922E WAP922H WAP922X |
|
WAP923 series |
WAP923 |
|
Series |
Models |
|
WA6500A series |
WA6520 WA6520-C WA6520-HI WA6520H WA6520H-LI WA6520H-EGPON WA6520S-C WA6520S-D WA6520S-E WA6522 WA6520XS-LI WA6522-C WA6522H-HI WA6522H-LI WA6526 WA6526E WA6526H WA6530 WA6530-LI WA6530i |
|
WA6500-E series |
WA6520-E WA6520H-E WA6520X-E WA6530-E |
|
WAP912 series |
WAP912X |
|
WAP952 series |
WAP952 WAP952E WAP952H |
|
WAP953 series |
WAP953 |
|
WA6100 series |
WA6126 WA6120 WA6120H WA6120X |
Q. How can I view the software version of a fit AP?
A. The software versions of fit APs are saved on the AC. An AP automatically upgrades its software version when connecting to the AC if software upgrade is enabled.
Software upgrade for an AP proceeds as follows:
1. The AP reports the software version and AP model information to the AC.
2. The AC examines the received AP software version.
¡ If a match is found in the APDB, the AC establishes a CAPWAP tunnel with the AP.
¡ If no match is found in the APDB, the AC sends a message that notifies the AP of AP software version inconsistency.
3. Upon receiving the message, the AP requests a software version from the AC.
4. The AC assigns the software version to the AP after receiving the request. By default, the AC assigns the software version in the memory to the AP. You can configure the AC to assigns the software version in the specified folder.
5. The AP upgrades the software version, and restarts to establish a CAPWAP tunnel with the AC.
Access controllers (ACs)
This section contains the most frequently asked questions about ACs.
Q. What are the functions of an AC?
A. An AC is a wireless switch that can provide management and forwarding functions. It can provide client management functions, such as access control and authorization, and AP management functions, such as association, channel selection, and transmit power control.
An AC can also provide additional functions, including traffic classification and marking, QoS functions such as forwarding priority, and multicast services.
Q. How can I connect a fit AP to an AC physically?
A. You can connect an AP to an AC directly or over a Layer 2 network or a Layer 3 network, as long as they can reach each other.
Q. How does an AC communicate with a fit AP?
A. An AC and an AP establish a data tunnel to forward data packets, and they establish a control tunnel to forward control packets for AP configuration and management.
After an AP starts up without any configuration and is associated with an AC, the AC assigns configuration to the AP. The AP operates with the assigned configuration and is managed by the AC.
Q. Can an AC act as a local DHCP server?
A. Yes.
Q. How can I view detailed information about manual APs and online auto APs on an AC?
A. Execute the display wlan ap name ap-name verbose command.
Q. How can I view the association status of APs on an AC?
A. Execute the display wlan ap all command. APs in R state have been associated with the AC. APs in I state have not been associated with the AC.
Q. How can I view the version of an AC?
A. Execute the display version command.
Q. How can I view channel and power adjustment information on an AC?
A. Execute the display wlan rrm-status ap all command.
Q. How can I separate services of different APs with the same SSID?
A. To separate services of different APs with the same SSID, execute the service-template service-template-name vlan vlan-id command to assign clients accessing different radios to different VLANs.
Q. Can I log off a client?
A. Yes. You can execute the reset wlan client { all | mac-address mac-address } command to log off all or the specified clients.
Q. What's the difference between the online time and the system uptime in the output from the display wlan ap name verbose command?
A. The output from the display wlan ap name verbose command is shown as follows:
<Sysname> display wlan ap name ap1 verbose
AP name : ap1
AP ID : 1
AP group name : default-group
State : Run
Backup Type : Master
Online time : 0 days 1 hours 25 minutes 12 seconds
System uptime : 0 days 2 hours 22
…
Online time shows the duration that the AP has been associated with the AC.
System uptime shows the duration that the AP has operated since the most recent startup.
Q. How can I view information about APs that went offline recently on an AC?
A. Execute the display wlan ap all connection-record command. APs that went offline most recently come first in the output. The command output is shown as follows:
<AC> display wlan ap all connection-record
AP name IP address State Time
ap2 192.168.100.27 Run 01-06 09:06:40
Q. Which UDP ports does a CAPWAP tunnel use?
A. An AC uses UDP ports 5246 and 5247 for the control tunnel and data tunnel, respectively.
An AP uses random UDP ports for the control tunnel and data tunnel.
Q. Why can't I view newly created manual APs in the system-defined AP group?
A. APs in the system-defined AP group are not displayed because all APs belong to the system-defined AP group by default.
Q. Does an AC support backup?
A. Yes. ACs support star-topology IRF and dual-link backup.
Q. Do ACs support IRF? How many ACs does an IRF fabric support?
A. Support for IRF varies by device model. An IRF fabric supports two ACs.
Table 1 Support for IRF
|
Series |
Model |
|
WX3500H series |
WX3508H WX3510H WX3520H WX3520H-F WX3540H |
|
WX3500H-LI series |
WX3508H-WiNet WX3510H-LI WX3520H-LI |
|
WX3800H series |
WX3820H WX3840H |
|
WX5500E series |
WX5510E WX5540E |
|
WX5500H series |
WX5540H WX5560H WX5580H |
|
WX5800H series |
WX5860H |
|
WX5500X series |
WX5540X WX5560X |
|
Access controller modules |
LSUM1WCME0 EWPXM1WCME0 LSQM1WCMX20 LSUM1WCMX20RT LSQM1WCMX40 LSUM1WCMX40RT EWPXM2WCMD0F EWPXM1MAC0F |
Q. How can I configure clients to automatically access another WLAN when the uplink of the associated AC is down?
A. Enable the AC uplink detection function.
Q. Do ACs support third-party APs?
A. No.
Q. What are the advantages of local forwarding? When do I need to configure local forwarding?
A. In local forwarding mode, APs directly forward client packets instead of transferring all packets to the AC. This reduces the AC's load. You can specify a VLAN or a VLAN range to enable APs to forward client data traffic from the specified VLANs.
For example, in a branch+headquarters network where the AC is deployed at the headquarters and APs are deployed in branches, you can configure local forwarding as a best practice.
Licenses
This section contains the most frequently asked questions about licenses.
Q. How do I configure online automatic license installation
|
IMPORTANT: The Web interface in expert mode supports online automatic installation of licenses. If the current device version does not support this feature, upgrade the device to the most recent version as a best practice. |
A. To configure online automatic license installation, use the following procedure:
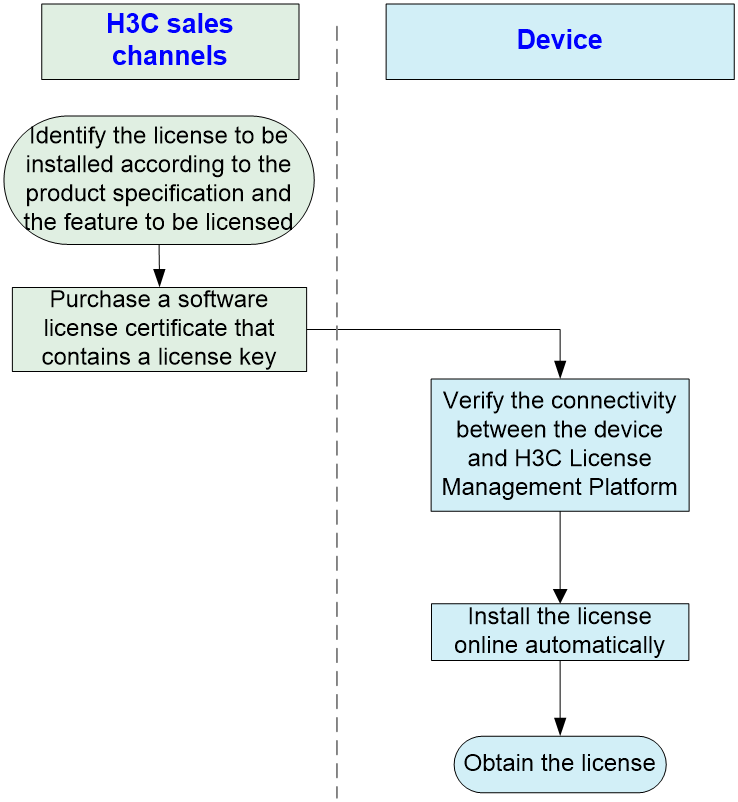
Figure 1 shows the workflow to install a license online automatically.
Figure 1 License installation workflow
1. Purchase a license certificate from an H3C official sales channel. The license key is printed on the license certificate.
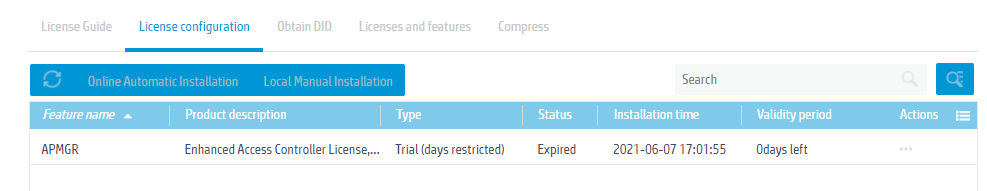
2. Log in to the Web interface of the device, and access the System > System > License Management page. On the License configuration tab, click Online Automatic Installation.
Figure 2 License configuration
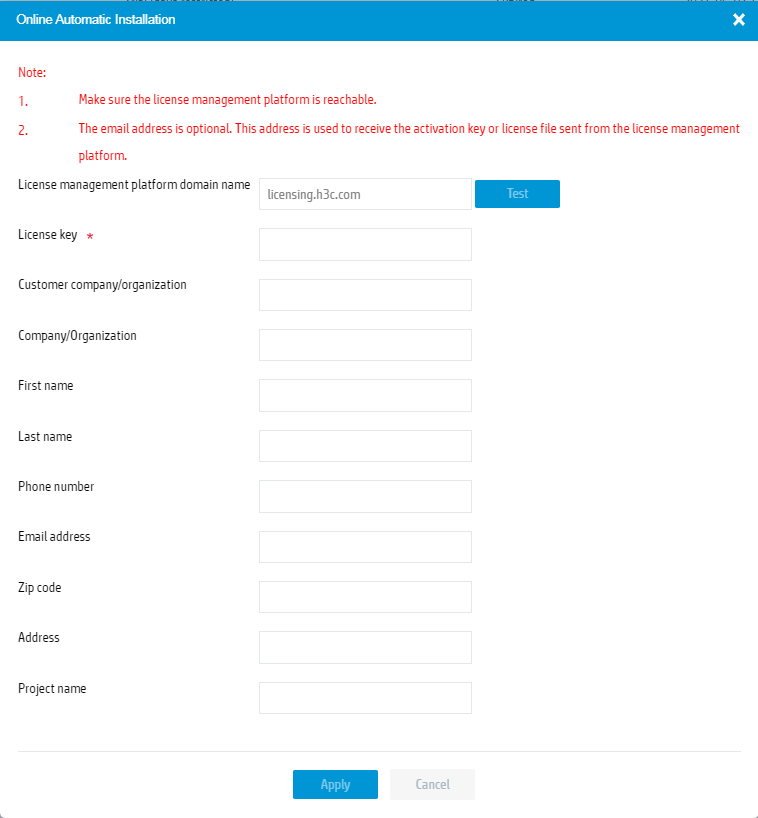
3. In the dialog box that opens, click Test to verify the connectivity between the device and H3C License Management Platform. If they cannot reach each other, resolve the network issue.
4. Enter license key and user information, and then click Apply.
Figure 3 License online automatic installation
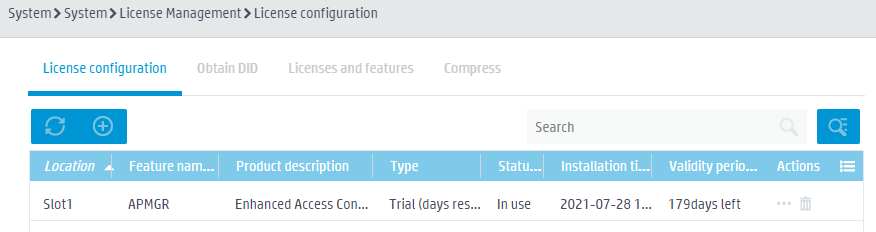
On the License configuration page, you can view license information.
Figure 4 Viewing license information
Q. How do I expand a license?
A. To expand a license, use the following procedure:
Figure 5 License expansion flowchart
1. Identify the expansion demand.
Use the display wlan ap all command to view the number of remaining local AP licenses. If the remaining licenses are insufficient, expand the license based on the service demand.
<Sysname> display wlan ap all
Total number of APs: 127
Total number of connected APs: 1
Total number of connected manual APs: 1
Total number of connected auto APs: 0
Total number of connected common APs: 1
Total number of connected WTUs: 0
Total number of inside APs: 0
Maximum supported APs: 128
Remaining APs: 1
Total AP licenses: 128
Local AP licenses: 128
Server AP licenses: 0
Remaining local AP licenses: 127
Sync AP licenses: 0
AP information
State : I = Idle, J = Join, JA = JoinAck, IL = ImageLoad
C = Config, DC = DataCheck, R = Run M = Master, B = Backup
AP name APID State Model Serial ID
ap1 1 R WA6320 219801A28N819CE0002T
…
2. Identify the device license specifications.
Use the wireless products license info finder to identify the maximum number of AP licenses supported by the device and the compatible licenses. Identify the license code.
If the number of AP licenses will exceed the maximum number of supported APs after expansion, add new ACs.
3. Install a license.
a. Purchase a license certificate from an H3C official sales channel. The license key is printed on the license certificate.
b. Obtain the device SN and DID file from the device.
c. Apply for an activation file from the H3C License Management Platform.
d. Install the activation file on the device.
|
|
NOTE: For more information, see H3C Comware 7 and Comware 9 WLAN Products Local Licensing Guide. |
Q. How do I uninstall a license?
A. To uninstall a license, use the following procedure. You can uninstall only formal licenses that have not expired.
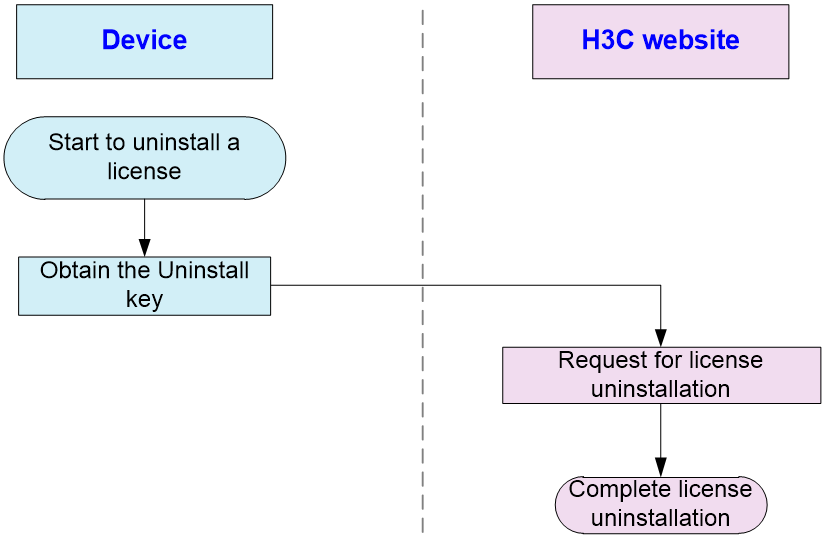
Figure 6 Uninstallation flowchart
1. Obtain an Uninstall key for a license on the device.
To obtain an Uninstall key for a license from the CLI:
a. Execute the display license command to identify the activation file that will be uninstalled.
b. Execute the system-view command to enter system view.
c. Execute the license activation-file uninstall command to uninstall the activation file.
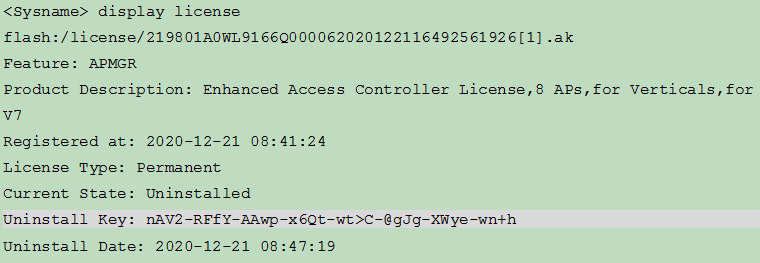
d. Execute the display license command to obtain the Uninstall key. Copy the Uninstall key, and then use the Uninstall key on H3C License Management Platform to request a license transfer or uninstallation.
Figure 7 Sample output from the display license command
To obtain an Uninstall key for a license from the Web interface:
a. Log in to the Web interface of the device, and access the System > System > License Management page.
b. On the License configuration
tab, click the delete icon ![]() in the Actions column for the license
to be uninstalled, and then select Yes in the dialog box that opens.
in the Actions column for the license
to be uninstalled, and then select Yes in the dialog box that opens.
Figure 8 Uninstalling a license
a. Click the ![]() icon to view and copy the Uninstall key.
icon to view and copy the Uninstall key.
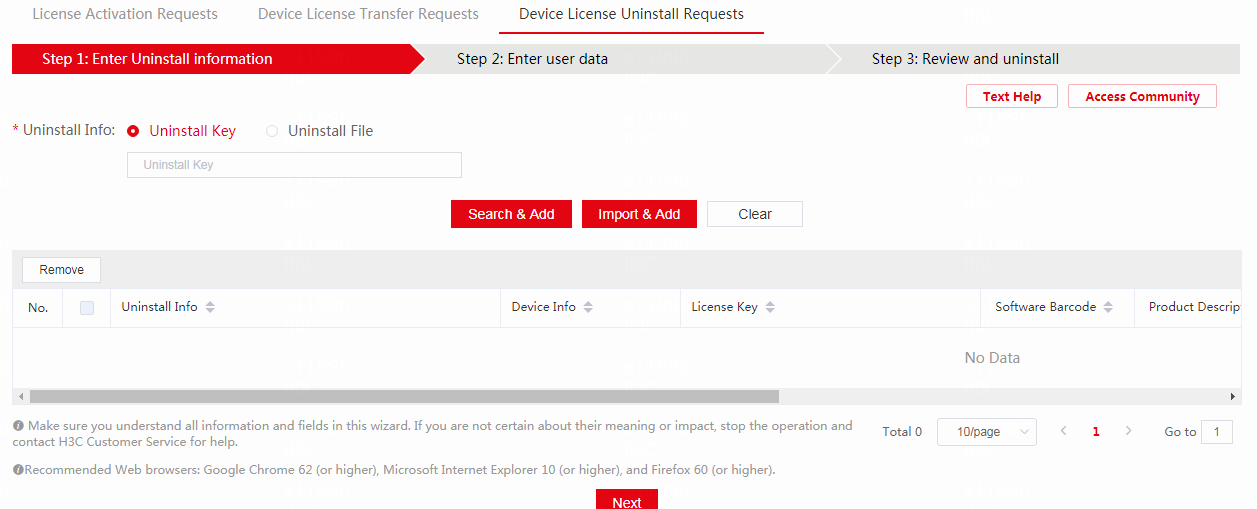
2. Request license uninstallation on H3C License Management Platform.
a. Log in to H3C License Management Platform at https://new-licensing.h3c.com/website/anonymous/navIndex/en-US/activate/input-license. Click the Device License Uninstall Requests tab.
Figure 9 Device License Uninstall Requests page
b. Manually enter Uninstall keys one by one and click Search & Add to obtain uninstallation information. Select the uninstallation information that will be uninstalled, and then click Next.
c. Enter user information, and then click Next. Review the uninstallation information, and then select the option that explicitly states your acceptance of all terms in the legal statement.
d. Click Confirm & Uninstall.
e. Review license and device information, and then click OK. The binding between the device and license key will be removed.
Q. How do I transfer a license?
A. To transfer a license, use the following procedure.
You can perform this task to transfer a formal license that has not expired from one device to another.
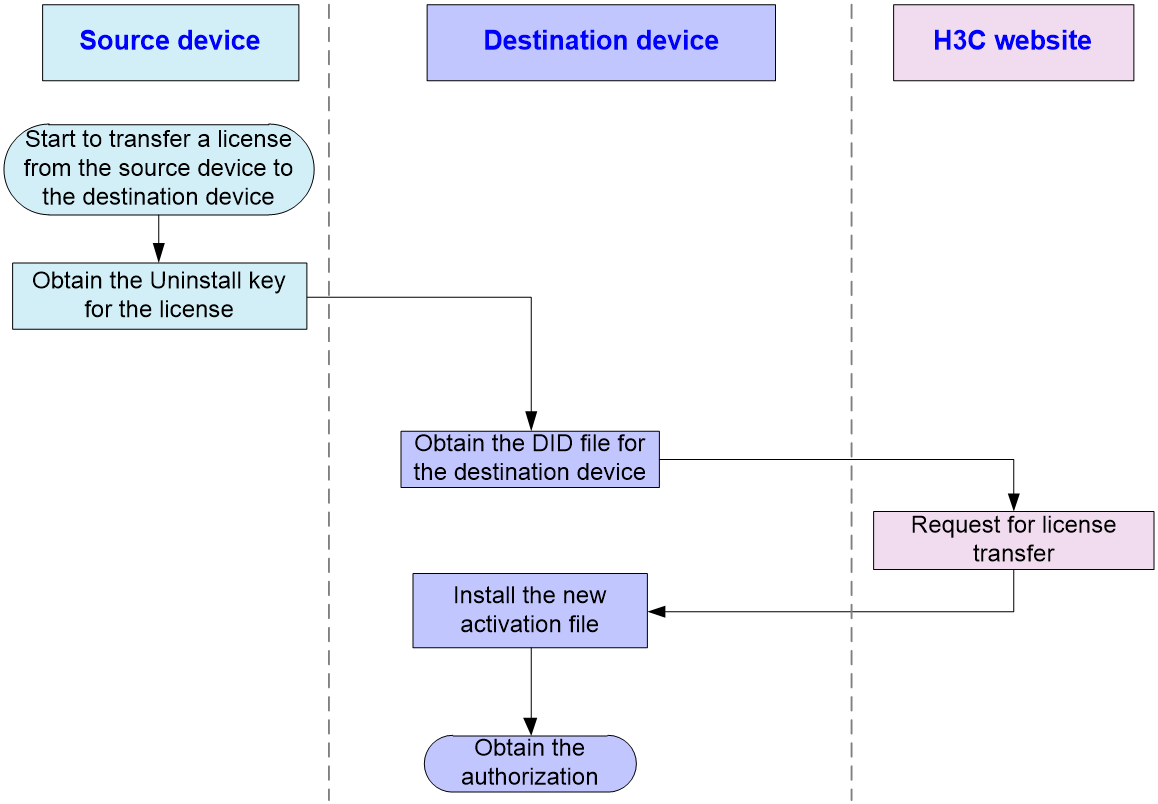
Figure 10 License transfer workflow
1. Obtain an Uninstall key on the source device.
To obtain an Uninstall key for a license from the CLI of the source device:
a. Log in to the CLI of the source device.
b. Execute the display license command to identify the activation file to be uninstalled.
c. Execute the system-view command to enter system view.
d. Execute the license activation-file uninstall command to uninstall the activation file.
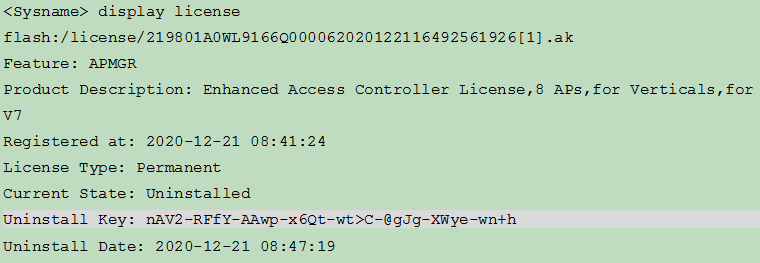
e. Execute the display license command to obtain the Uninstall key. Copy the Uninstall key, and then use the Uninstall key on H3C License Management Platform to request a license transfer or uninstallation.
Figure 11 Sample output from the display license command
To obtain an Uninstall key for a license from the Web interface of the source device:
a. Log in to the Web interface of the device, and access the System > System > License Management page.
b. On the License configuration tab, click the delete icon ![]() in the Actions column
for the license to be uninstalled, and then select Yes in the dialog box
that opens.
in the Actions column
for the license to be uninstalled, and then select Yes in the dialog box
that opens.
Figure 12 Uninstalling a license
c. Click the ![]() icon to view and copy the Uninstall key.
icon to view and copy the Uninstall key.
2. Obtain the device information of the destination device.
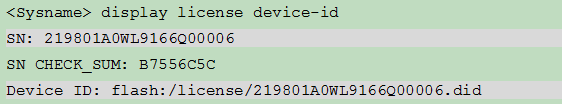
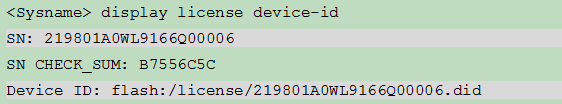
To obtain the device information for the destination device from the CLI of the device, log in to the CLI of the device, and execute the display license device-id command in any view to obtain the device SN and value of the Device ID field. Use FTP or TFTP to upload the DID file to the PC (Web client). If FTP is used to transfer the DID file, use the Binary mode.
Figure 13 Obtaining the DID file
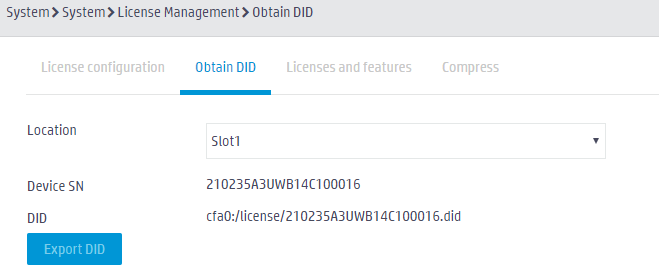
To obtain the device information for the destination device from the Web interface of the device, log in to the Web interface of the device, and access the System > System > License Management page. Click the Obtain DID tab. You can view the device SN and download the DID file.
Figure 14 Obtaining device information
3. Requesting license transfer on H3C License Management Platform.
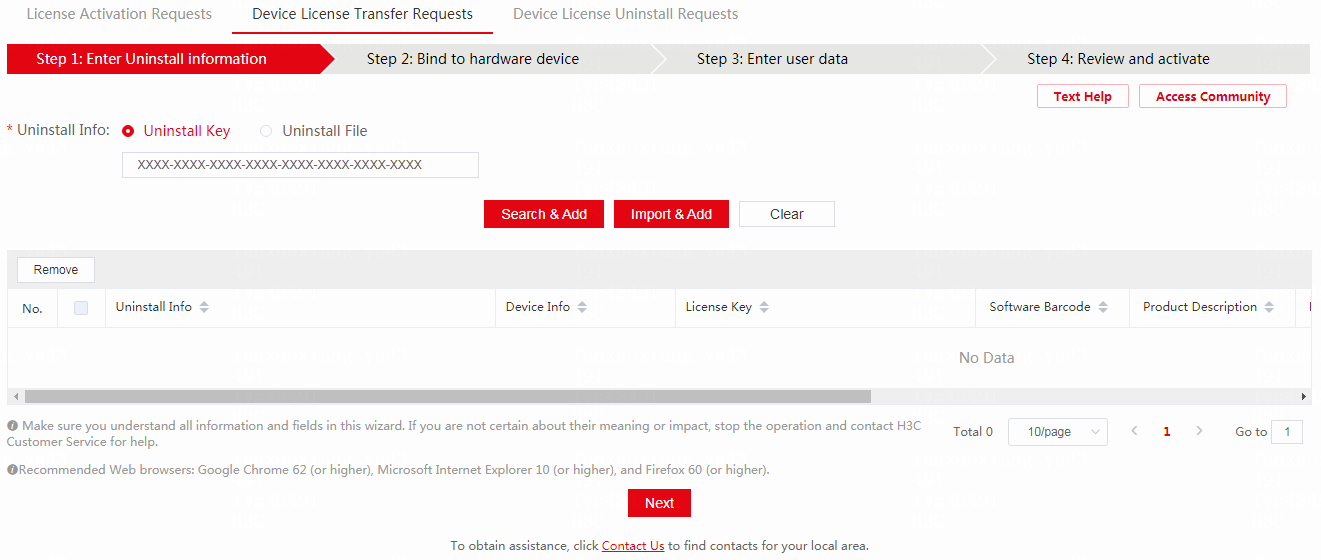
a. Open a Web browser and access H3C License Management Platform at https://new-licensing.h3c.com/website/anonymous/navIndex/en-US/activate/input-license. Click the Device License Transfer Requests tab.
Figure 15 Device License Transfer Requests page
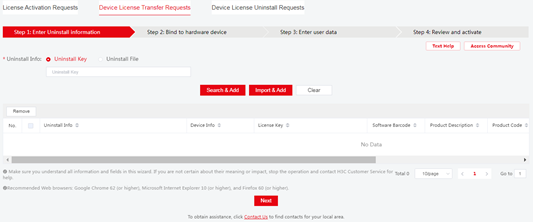
b. Select Uninstall Key, enter the Uninstall key, and then click Search & Add. The platform will automatically obtain the information associated with the Uninstall key.
Figure 16 Uploading Uninstall keys
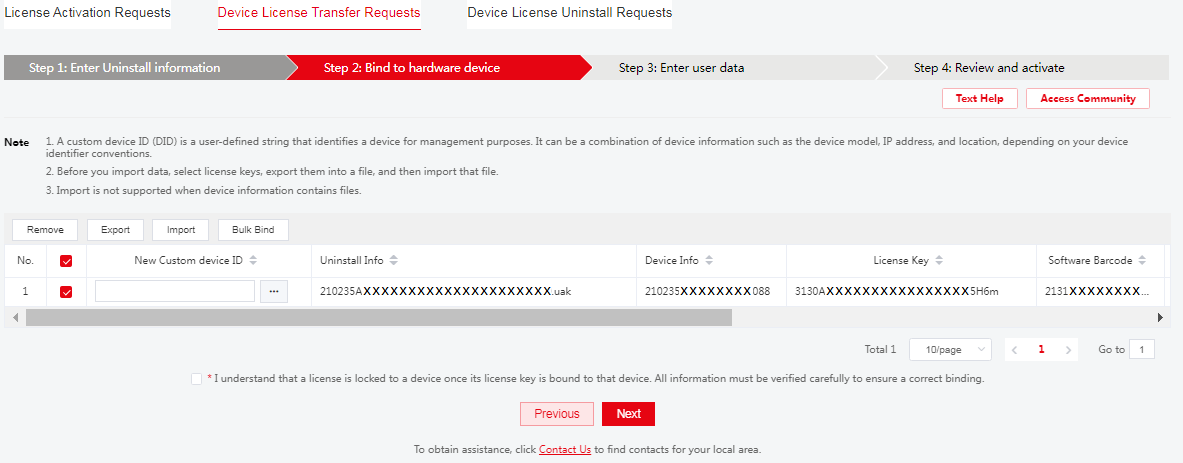
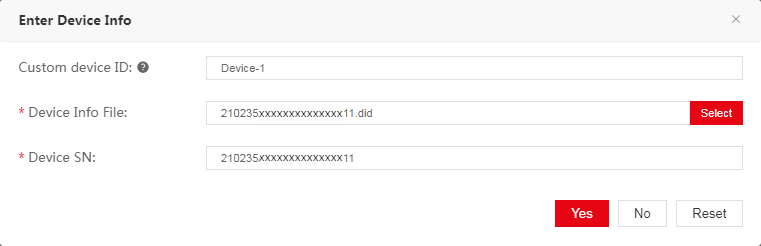
c. Select the target uninstall info, and then
click Next to access the Bind to
hardware device page. Click
the ![]() icon next to the Custom device ID box
in the license key entry. Set
the device ID and upload the device information file as instructed, and then
click Yes to bind the license to the device.
icon next to the Custom device ID box
in the license key entry. Set
the device ID and upload the device information file as instructed, and then
click Yes to bind the license to the device.
Figure 17 Bind to hardware device page
Figure 18 Entering device information
d. Bind the uninstallation information of the source device to the destination device. Make sure you understand the impact of the binding operation, and then select the option that explicitly states so. Click Next.
e. Enter user information, and then click Next.
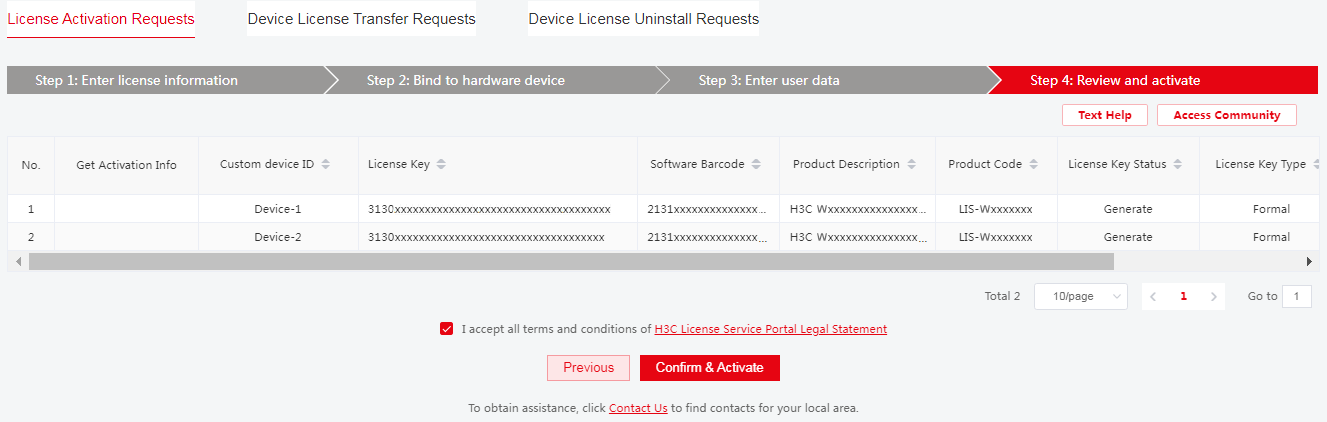
f. Review the license key and device information, select I accept all terms and conditions of H3C License Service Portal Legal Statement, and then click Confirm & Activate.
Figure 19 Reviewing information and activating the licenses
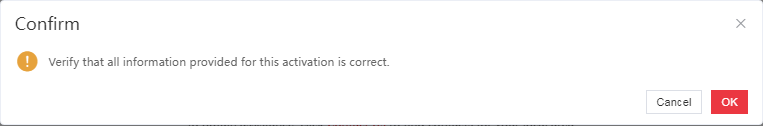
g. Double-check the license key and device information, and then click OK in the dialog box.
Figure 20 Confirmation dialog box
The platform automatically generates an activation file for each binding and sends them to the specified email address.
a. To download the activation file directly, click Get Activation Info in the Get Activation Info column for the license key.
4. Install the new activation file on the destination device.
To install the new activation file from the CLI of the destination device, use FTP or TFTP to upload the activation file to the PC. If FTP is used, use the Binary mode.
To install the activation file on the device from the CLI:
a. Access the CLI of the device.
b. Execute the system-view command to enter system view.
c. Execute the license activation-file install command to install the activation file.
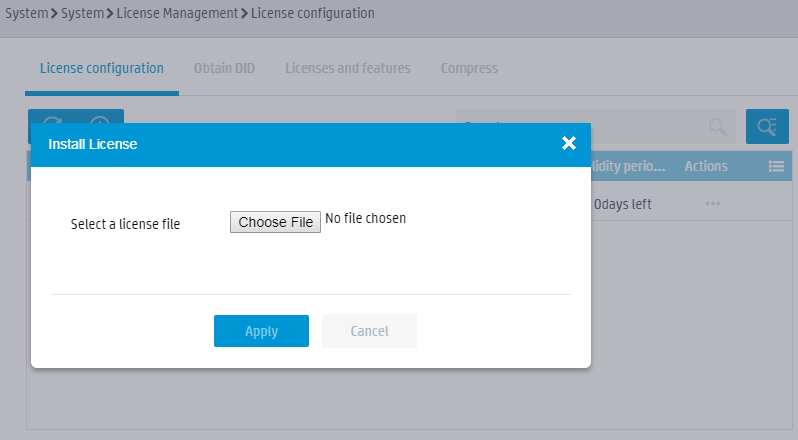
To install the activation file on the device from the Web interface:
a. Log in to the Web interface of the device, and access the System > System > License Management page.
b. On the License configuration tab,
click the ![]() icon.
icon.
c. In the dialog box that opens, click Select File, select a file, and then click Apply.
Figure 21 Installing an activation file
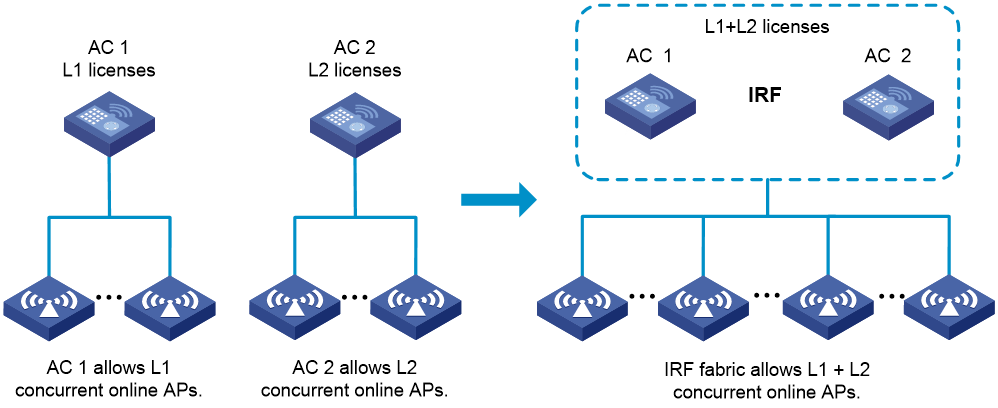
Q. What is WLAN IRF license sharing?
A. WLAN IRF technology virtualizes multiple physical devices into one virtual fabric. AP licenses installed on member devices are shared across the IRF fabric.
The maximum number of concurrent online APs in the entire IRF fabric cannot exceed the following limits:
· The sum of AP count allowed by all licenses on member devices.
· The upper limit on the AP count supported by the connected device.
As shown in Figure 22, AC 1 has L1 licenses installed, allowing L1 concurrent online APs. AC 2 has L2 licenses installed, allowing L2 concurrent online APs.
· After an IRF fabric is formed, it has a total of L1 + L2 licenses, allowing L1 + L2 concurrent online APs.
· If a member device is faulty or leaves the IRF fabric, its licenses continue to function for a 30-day grace period in the IRF fabric to ensure service continuity.
· After the grace period, the licenses on the leaving member device are no longer available. The license capacity reduces to the sum of the remaining licenses in the fabric. The license capacity change will not bring the existing online APs offline even if the number of existing online APs exceeds the license limit. The new limit takes effect after the number of existing online APs goes below the limit.
Figure 22 WLAN IRF license sharing
Q. How do I identify license compatibility with multiple devices?
A. You can use the info finder to identify the license compatibility with multiple devices. If a license code matches multiple device models, the corresponding license can be used on the specific devices.
Q. How do I view the installed licenses on a device?
A. Use the following methods to view the installed licenses on a device:
· Web interface in expert mode
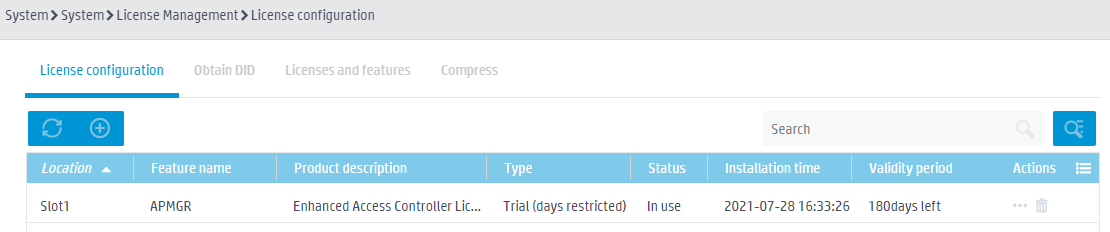
Log in to the Web interface of the device, access the License configuration page. You can view information about the installed licenses on the device.
Figure 23 Viewing information about installed licenses
· CLI
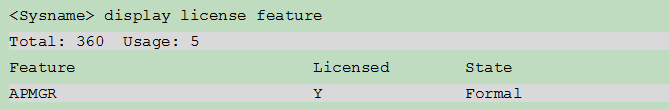
¡ To view information about software feature licenses, execute the display license feature command.
Figure 24 Displaying software feature license information
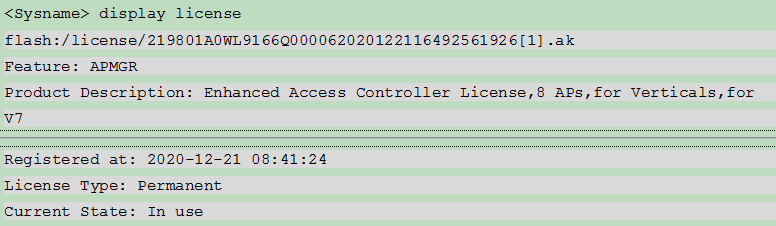
¡ To view information about installed and uninstalled licenses, execute the display license command. The detailed information includes the following:
- Installed licenses—Function description, validity period, installation time.
- Uninstalled licenses—Function description, validity period, uninstallation time, and uninstall key.
Figure 25 Displaying information about installed and uninstalled licenses
Q. How do I view the license usage?
A. To view the number of remaining local AP licenses, execute the display wlan ap all command.
<Sysname> display wlan ap all
Total number of APs: 1
Total number of connected APs: 1
Total number of connected manual APs: 1
Total number of connected auto APs: 0
Total number of connected common APs: 1
Total number of connected WTUs: 0
Total number of inside APs: 0
Maximum supported APs: 2048
Remaining APs: 2047
Total AP licenses: 128
Local AP licenses: 128
Server AP licenses: 0
Remaining local AP licenses: 127
Sync AP licenses: 0
AP information
State : I = Idle, J = Join, JA = JoinAck, IL = ImageLoad
C = Config, DC = DataCheck, R = Run M = Master, B = Backup
AP name APID State Model Serial ID
ap1 1 R WA6320 219801A28N819CE0002T
Q. How do I export a DID file?
A. A DID file is used for requesting for an activation file from the H3C License Management Platform. You can use either of the following methods to export the DID file of a device.
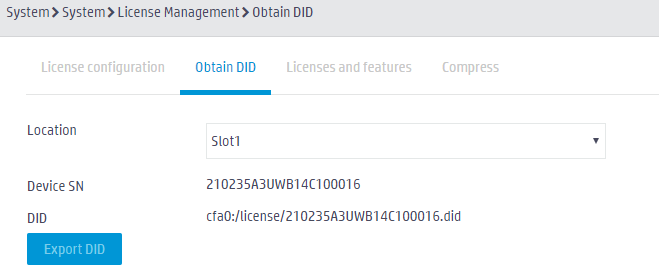
· To export a DID file from the Web interface in expert mode, log in to the Web interface of the device, access the License Management page, click the Obtain DID tab, and then click Export DID.
Figure 26 Exporting the DID file
· To export a DID file from the CLI, execute the display license device-id command in any view to obtain the value in the Device ID field. Use FTP or TFTP to upload the DID file to the PC (Web client). If FTP is used to transfer the DID file, use the Binary mode.
Figure 27 Obtaining the DID file
Q. How do I identify whether a device comes with default licenses?
A. You can use the info finder to view the number of default supported AP licenses and the number of pre-installed AP licenses for the device.
· Default supported AP licenses—Specifies permanent AP licenses that come with the device.
· Pre-installed AP licenses—Specifies 30-day temporary AP licenses that come with the device. The licenses are unavailable if the validity period expires.
Q. How do I retrieve a lost license key?
A. If you lose the license key before obtaining an activation file, contact H3C Support to retrieve the license key based on the license purchase contract.
If you lose the license key after obtaining an activation file, contact H3C Support and provide the activation file or the device information.
Q. How do I retrieve an activation file?
A. You will be unable to use a licensed feature if its activation file is lost or inadvertently deleted. To retrieve an activation file, use one of the following methods:
· Use the backup activation file.
· Find the activation file from the email box of the applicant.
· Contact H3C Support and provide the license key or device information to retrieve the activation file.
Q. How do I troubleshoot a license installation error?
A. If the system prompts an error during license installation or the activation file cannot be decoded, upgrade the device to the most recent version, and try again. If the issue persists, contact H3C Support.
Q. How do I obtain the licensing guide?
Q. You can obtain H3C Comware 7 and Comware 9 WLAN Products Local Licensing Guide at http://www.h3c.com/en/home/qr/default.htm?id=12.
Q. How do I increase the number of APs that an AC can manage?
A. Purchase a license.
Q. How do I know which features require licenses?
A. Execute the display license feature command to display brief license information for features.
Q. How can I register and activate a license?
A. After purchasing a license from H3C, access http://www.h3c.com/en/Support/Online_Help/License_Service/ to register your license. For more information about activating a license on the device, see Managing licenses in H3C Access Controllers Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
Q. How can I view the remaining days of AP licenses?
A. Execute the display license command. The output from this command is displayed as follows:
<AC> display license
Slot 1:
cfa0:/license/210235A1AMB1570000052015091410025584386.ak
Feature: APMGR
Product Description: Enhanced Access Controller License,128 APs,for Verticals,for V7
Registered at: 2018-09-14 10:04:09
License Type: Trial (days restricted)
Trial Time Left (days): 353
Current State: In use
Q. How can I view the number of AP licenses?
A. Execute the display wlan ap all command. The output from this command is displayed as follows:
<AC> display wlan ap all
<Sysname> display wlan ap all
Total number of APs: 1
Total number of connected APs: 1
Total number of connected manual APs: 1
Total number of connected auto APs: 0
Total number of connected common APs: 1
Total number of connected WTUs: 0
Total number of inside APs: 0
Maximum supported APs: 2048
Remaining APs: 2047
Total AP licenses: 128 // Total number of AP licenses.
Local AP licenses: 128
Server AP licenses: 0
Remaining local AP licenses: 127 // The number of remaining AP licenses.
Sync AP licenses: 0
AP information
State : I = Idle, J = Join, JA = JoinAck, IL = ImageLoad
C = Config, DC = DataCheck, R = Run, M = Master, B = Backup
AP name AP ID State Model Serial ID
ap1 1 R/M WA6628 219801A1Q9C123000050
Q. Do I need to restart the device for the license to take effect after installing a license?
A. No. A license takes effect immediately after it is installed.
Q. Will the installed licenses be deleted when the file system is formatted?
A. No. The installed licenses will not be deleted if the file system is formatted from the CLI or the BootWare menu.
Q. Can I edit a license file?
A. No. Do not modify the name of a license file to avoid licensing error, and do not edit a license file to avoid file corruption.
Q. How many licenses can an IRF fabric use and how does the use of licenses change after a member AC leaves the fabric or after the fabric splits?
A. For Comware 7/9 devices:
· An IRF fabric uses the licenses installed on each member AC. For example, if two member ACs exist, one AC has 10 licenses, and the other has 20 licenses, the fabric can use 30 licenses.
· If a member leaves the fabric, the IRF fabric can use the license installed on the device for only 30 days.
· If the IRF fabric splits, the license capacity of the fabric continues to function on each device for 30 days. After 30 days or a restart, a device can use only licenses installed on it.
For Comware 5 devices:
· The number of licenses that an IRF fabric can use depends on the member AC that has the least installed licenses. For example, if two member ACs exist, one AC has 10 licenses, and the other has 20 licenses, the fabric can use only 10 licenses.
· If the fabric splits, the license capacity of the IRF fabric continues to function on each device for 30 days. After 30 days or a restart, a device can use only licenses installed on it.
Q. How can I register Comware 5 licenses on an AC upgraded from Comware 5 to Comware 7?
A. To register Comware 5 licenses on an AC upgraded from Comware 5 to Comware 7:
1. Use the display license device-id command to view the SN check sum of the device.
#
SN: 210235A0VSB151000017
SN CHECK_SUM: 015ACCB8
Device ID: cfa0:/license/210235A0VSB151000017.did
#
2. Follow the Comware 5 license request procedure to obtain the activation key for the license.
3. Use the license activation-key install command to install the activation key on the AC.
Networking
This section contains the most frequently asked questions about networking.
Q. How is an AP associated with an AC in different fit AP+AC networking environments?
A. An AP can be associated with an AC in direct mode, Layer 2 mode, or Layer 3 mode:
· Direct mode and Layer 2 mode—The IP addresses of the AC and AP are in the same subnet.
· Layer 3 mode—The IP addresses of the AC and the AP are in different subnets.
Q. At which layer can I deploy an AC in a fit AP+AC network?
A. An AC can be deployed at the core layer or the aggregation layer. You can connect a fit AP to an AC directly or through an existing wired network. User preference, AP density, and the role of the WLAN in the whole network can affect the location of the AC in the network topology.
Q. Do I need to change the wired backbone network for WLAN devices?
A. No.
Q. How are packets forwarded by default in a fit AP+AC network?
A. All ACs use the centralized forwarding mode by default.
WLAN security
This section contains the most frequently asked questions about WLAN security.
Q. Which authentication methods does an AC support?
A. An AC supports the following authentication methods:
· 802.1X authentication.
· PSK authentication.
· MAC address authentication.
· Portal authentication.
· PPPoE authentication.
Q. Can I configure local forwarding and centralized authentication at the same time when portal authentication is used?
A. Yes.
Q. Does an AC support portal authentication?
A. Yes.
Q. Can an AC cooperate with a third-party LDAP server for authentication?
A. Yes. An AC can cooperate with common LDAP servers, including the Active Directory Server of Microsoft, the Tivoli Directory Server of IBM, and the Sun ONE Directory Server of Sun.
Q. In a wireless network, which device acts as an AAA authenticator?
A. In a wireless network, the AC is the AAA authenticator. You only need to configure the AC, instead of each AP, as the AAA client. This feature reduces network configuration load and operating costs.
Q. Can an AC detect rogue APs?
A. Yes. An AC can detect rogue devices when Wireless Intrusion Prevention System (WIPS) is configured.
WLAN roaming
This section contains the most frequently asked questions about WLAN roaming.
Q. What is WLAN roaming? How many types of WLAN roaming are available?
A. WLAN roaming enables wireless clients to roam between APs in the same Extended Service Set (ESS), keeping their original IP address and privileges unchanged.
WLAN roaming includes the following types:
· Intra-AC roaming—Roaming among APs managed by the same AC.
· Inter-AC roaming—Roaming among APs managed by different ACs.
Q. Can wireless clients perform Layer 3 roaming?
A. Yes.
Q. Do clients need to be reauthenticated or log in again after roaming?
A. No.
Q. During WLAN roaming, will a client keep its subnet attributes such as the assigned VLAN, ACL, and routing policies?
A. Yes. All subnet attributes remain the same during WLAN roaming, including the assigned VLAN, ACL, priority, and other policies.
Q. Does the IP address of a client remain unchanged during WLAN roaming?
A. Yes.
Q. How can I adjust the sensitivity of a wireless NIC?
A. Adjust the roaming sensitivity level of the wireless network card.
Q. Do I need to change the switch or router configuration to enable WLAN roaming?
A. No.
Q. Do I need to install new client software for WLAN roaming?
A. No.
System management
This section contains the most frequently asked questions about system management.
Q. Can I configure a mandatory rate for an AC to increase the wireless network performance?
A. Yes. If the network is not in good condition, you can configure the AC to use the mandatory rate (the maximum rate) to transmit data. This method can increase the bandwidth and network performance. To configure a mandatory rate, use the rate { multicast { auto | rate-value } | { disabled | mandatory | supported } rate-value } command.
Q. How can I determine whether memory leakage has occurred?
A. Execute the display memory command. If the free ratio decreases gradually and cannot recover automatically, memory leakage might have occurred. The output from the command is shown as follows:
<Sysname> display memory
Memory statistics are measured in KB:
Slot 1:
Total Used Free Shared Buffers Cached FreeRatio
Mem: 3775116 2415348 1359768 0 2544 628524 36.0%
-/+ Buffers/Cache: 1784280 1990836
Swap: 0 0 0
Q. How can I view process state information?
A. Execute the display process command.
Q. How can I view memory usage for all processes?
A. Execute the display process memory command.
IRF
This section contains the most frequently asked questions about IRF.
Q. Is there an upper limit on the number of member devices of an IRF fabric?
A. Yes. If the number of member devices in an IRF fabric reaches the limit, no more devices can join the fabric.
Q. Does an IRF fabric have requirements on the software versions of its member devices?
A. All member devices in an IRF fabric must have the same software version. If devices with different software versions are to be added to an IRF fabric, make sure the software auto-update feature is enabled.
Q. Are there any requirements on IRF bridge MAC addresses when two IRF fabrics merge?
A. For a successful IRF merge, make sure the two IRF fabrics have different IRF bridge MAC addresses.
Q. Do I need to disable STP on switch interfaces when member devices are connected through a Layer 2 network?
A. Yes.
Q. Under what circumstances do I need to use a switching device to form a star-topology IRF fabric?
A. If the IRF fabric contains only two member devices, you can connect the member devices directly or through a Layer 2 network. If the IRF fabric contains more than two member devices, you must use a switching device to connect them.
Q. What restrictions and guidelines do I need to follow after an IRF fabric is formed?
A. When you use an IRF fabric, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· To avoid IRF split, do not use the shutdown command on an IRF network interface if the interface is the only control channel available on the IRF standby device.
· IRF uses an IRF domain ID to uniquely identify an IRF fabric. Devices must have the same IRF domain ID to form an IRF fabric.
· In a star-topology IRF fabric that has cross-card aggregation links, do not set the link-aggregation load sharing mode to per-packet.
· NAT is not supported in an IRF fabric.
· If multiple physical IRF links operate correctly between two devices, shut down all interfaces on both devices before you remove an IRF link.