- Table of Contents
-
- 03-Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Examples
- 01-Ethernet Link Aggregation Configuration Examples
- 02-M-LAG Configuration Examples
- 03-MAC Address Table Configuration Examples
- 04-MVRP Configuration Examples
- 05-Port Isolation Configuration Examples
- 06-S-MLAG Configuration Examples
- 07-Spanning Tree Configuration Examples
- 08-VLAN Configuration Examples
- 09-VLAN Tagging Configuration Examples
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 03-MAC Address Table Configuration Examples | 86.73 KB |
Example: Configuring static MAC address entries
Applicable hardware and software versions
Example: Configuring MAC address move suppression
Applicable hardware and software versions
Configuring Device B and Device C
Introduction
This document provides MAC address table configuration examples.
Prerequisites
The configuration examples in this document were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
This document assumes that you have basic knowledge of the MAC address table.
Example: Configuring static MAC address entries
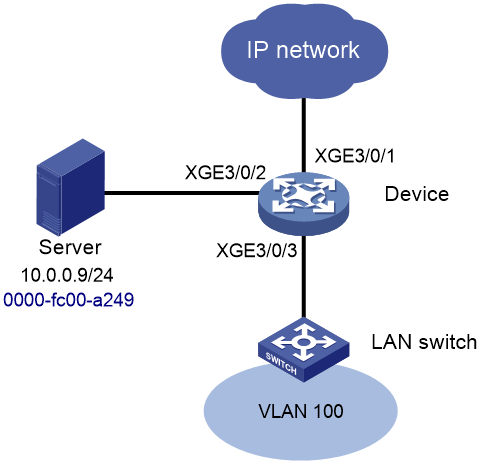
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 1, for secure communication between users in VLAN 100 and the server, perform the following tasks:
· Assign Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 and Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/0/3 to VLAN 100.
· Add a static MAC address entry on Device to bind the server MAC address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/0/2.
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
|
Hardware |
Software version |
|
S12500G-AF |
Release 7753P05 and later |
|
S12500CR |
Release 7753P05 and later |
|
S10500X-G |
Release 7753P05 and later |
|
S7500X-G |
Release 7753P05 and later |
Procedures
# Create VLAN 100, and assign Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 to VLAN 100.
<Device> system-view
[Device] vlan 100
[Device-vlan100] quit
[Device] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/0/2
[Device-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] port access vlan 100
[Device-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] quit
# Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/0/3 (port connected to the LAN switch) as a trunk port, and assign the port to VLAN 100.
[Device] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/0/3
[Device-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/3] port link-type trunk
[Device-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 100
[Device-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/3] quit
# Add a static entry for MAC address 0000-fc00-a249 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 that belongs to VLAN 100.
[Device] mac-address static 0000-fc00-a249 interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/0/2 vlan 100
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that any 10.0.0.0/24 host in VLAN 100 can communicate with the server. (Details not shown.)
# Verify that the static MAC address entry has been added.
[Device] display mac-address
MAC Address VLAN ID State Port/NickName Aging
0000-fc00-a249 100 Static XGE3/0/2 N
7425-8a02-4d00 100 Learned XGE3/0/3 Y
…
Configuration files
#
sysname Device
#
vlan 1
#
vlan 100
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 100
mac-address static 0000-fc00-a249 vlan 100
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 100
#
Example: Configuring MAC address move suppression
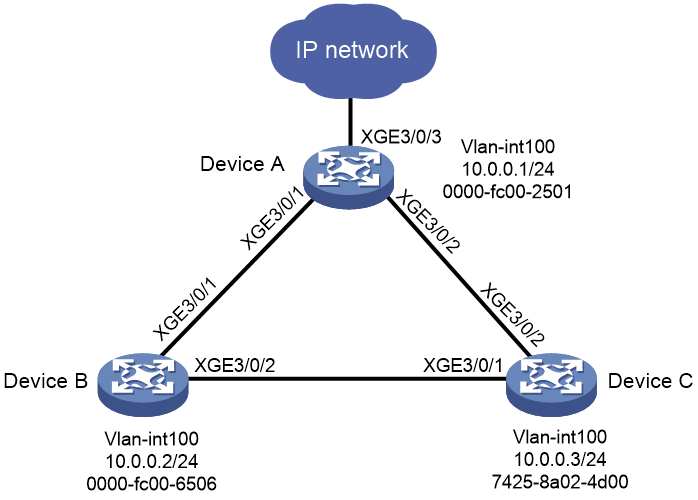
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, Devices A, B, and C form a loop because of cable misconnection, and spanning tree protocols are not enabled on the devices. As a result, MAC addresses are frequently moves among Devices A, B, and C. To deal with loop-triggered MAC flapping, perform the following tasks:
· Display MAC address move records to locate the Layer 2 loop.
· Configure MAC address move suppression on Device A to eliminate the Layer 2 loop.
Analysis
To meet the network requirements, you must perform the following tasks:
· For Devices A, B, and C to communicate with each other, assign all inter-connected ports to VLAN 100.
· Configure MAC address move suppression on one or more ports of Device A.
· To monitor the port status change of Device A, enable the log monitoring of the current terminal feature.
· For loop detection, create VLAN-interface 100 and assign an IP address to the interface on each device.
· To display MAC address move records, ping Device B from Device A.
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
|
Hardware |
Software version |
|
S12500G-AF |
Release 8053P05 and later |
|
S12500CR |
Release 8053P05 and later |
|
S10500X-G |
Release 7753P05 and later |
|
S7500X-G |
Release 7753P05 and later |
Procedures
Configuring Device A
# Enable the monitoring of logs on the current terminal.
<DeviceA> terminal monitor
<DeviceA> terminal debugging
# Create VLAN 100.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] vlan 100
[DeviceA-vlan100] quit
# Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 and Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 as trunk ports, and assign the ports to VLAN 100.
[DeviceA] interface range ten-gigabitethernet 3/0/1 ten-gigabitethernet 3/0/2
[DeviceA-if-range] port link-type trunk
[DeviceA-if-range] port trunk permit vlan 100
[DeviceA-if-range] quit
# Set the suppression interval to 300 seconds. A suppressed port will automatically come up after 300 seconds.
[DeviceA] mac-address notification mac-move suppression interval 300
# Set the suppression threshold to 0. A port will be shut down when the system detects a MAC address move on the port within a MAC move detection interval (1 minute by default).
[DeviceA] mac-address notification mac-move suppression threshold 0
# Enable MAC address move suppression on Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/0/1.
[DeviceA] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/0/1
[DeviceA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] mac-address notification mac-move suppression
[DeviceA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 100, and assign an IP address to the interface.
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface100] ip address 10.0.0.1 24
[DeviceA-Vlan-interface100] quit
Configuring Device B and Device C
1. Configure Device B:
# Create VLAN 100.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] vlan 100
[DeviceB-vlan100] quit
# Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 and Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 as trunk ports, and assign the ports to VLAN 100.
[DeviceB] interface range ten-gigabitethernet 3/0/1 ten-gigabitethernet 3/0/2
[DeviceB-if-range] port link-type trunk
[DeviceB-if-range] port trunk permit vlan 100
[DeviceB-if-range] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 100, and assign an IP address to the interface.
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 100
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface100] ip address 10.0.0.2 24
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface100] quit
2. Configure Device C in the same way Device B was configured. (Details not shown.)
Verifying the configuration
# Ping Device B from Device A. (Details not shown.)
# Verify that Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 on Device A is shut down.
[DeviceA] %Dec 11 09:51:06:309 2016 DeviceA IFNET/3/PHY_UPDOWN: -MDC=1; Physical state on the Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/1 changed to down.
%Dec 11 09:51:06:323 2016 DeviceA IFNET/5/LINK_UPDOWN: -MDC=1; Line protocol state on
the interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/1 changed to down.
# Verify that Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 is shut down because a MAC address move is detected.
[DeviceA] display interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/0/1
Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/1
Current state: mac-address moving down
Line protocol state: DOWN
...
# Verify that Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 comes up automatically after 300 seconds.
[DeviceA] %Dec 11 09:56:07:002 2016 DeviceA IFNET/3/PHY_UPDOWN: -MDC=1; Physical state on the Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/1 changed to up.
%Dec 11 09:56:07:004 2016 DeviceA IFNET/5/LINK_UPDOWN: -MDC=1; Line protocol state on
the interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/1 changed to up.
# Verify that the MAC address of Device B's VLAN-interface 100 moves between Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 and Ten-GigabitEthernet 3/0/2. You can manually shut down either port to eliminate the loop.
[DeviceA] display mac-address mac-move
MAC address VLAN Current port Source port Last time Times
0000-fc00-6506 100 XGE3/0/2 XGE3/0/1 2014-12-11 09:29:48 3
0000-fc00-6506 100 XGE3/0/1 XGE3/0/2 2014-12-11 09:51:03 4
--- 2 MAC address moving records found ---
Configuration files
· Device A:
#
sysname DeviceA
#
mac-address notification mac-move suppression interval 300
mac-address notification mac-move suppression threshold 0
#
vlan 1
#
vlan 100
#
interface Vlan-interface100
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 100
mac-address notification mac-move suppression
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 100
#
· Device B:
#
sysname DeviceB
#
vlan 1
#
vlan 100
#
interface Vlan-interface100
ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 100
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 100
#
· Device C:
#
sysname DeviceC
#
vlan 1
#
vlan 100
#
interface Vlan-interface100
ip address 10.0.0.3 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 100
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port link-type trunk
port trunk permit vlan 1 100
#