- Table of Contents
-
- 04-Policies
- 01-Security policy
- 02-Security policy redundancy analysis
- 03-Security policy hit analysis
- 04-Security policy optimization
- 05-Policy-based NAT
- 06-Interface NAT
- 07-AFT
- 08-QoS
- 09-Bandwidth management
- 10-Application audit
- 11-Application proxy
- 12-IP reputation
- 13-Domain reputation
- 14-Blacklist
- 15-Connection limit
- 16-Server connection detection
- 17-Access rate limit
- 18-DLP
- 19-Server load balancing
- 20-Outbound link load balancing
- 21-Inbound link load balancing
- 22-Transparent DNS proxy
- 23-NetShare control
- 24-Zero trust policy
- 25-Trusted application proxies
- 26-Trusted API proxies
- 27-NAT66
- 28-uRPF
- 29-Load balancing common configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 05-Policy-based NAT | 110.78 KB |
Policy-based NAT
This help contains the following topics:
¡ Configure a policy-based NAT44 rule
¡ Configure a policy-based NAT64 rule
¡ Configure a policy-based NAT66 rule
Introduction
Policy-based NAT supports the following types of rules, which are applicable to different scenarios:
· NAT44 rule—Used for NAT translation between IPv4 networks.
· NAT64 rule—Used for NAT translation between IPv4 networks and IPv6 networks.
· NAT66 rule—Used for NAT translation between IPv6 networks.
Policy-based NAT supports the following translation modes:
· Source address translation—Translates the source IP address and source port of the packets. The NO-PAT and PAT modes are supported. For more information about NO-PAT and PAT, see "NAT."
· Destination address translation—Translates the destination IP address and destination port of the packets. Policy-based NAT supports translating different destination IP addresses and destination ports of the matching packets to the same IP address and port.
· Source and destination address translation—Translates the source IP address, source port, destination IP address, and destination port of the packets. The source address translation supports NO-PAT and PAT modes. The destination address translation supports translating different destination IP addresses and destination ports of the matching packets to the same IP address and port.
Configure policy-based NAT
NAT can be performed in the inbound or outbound direction.
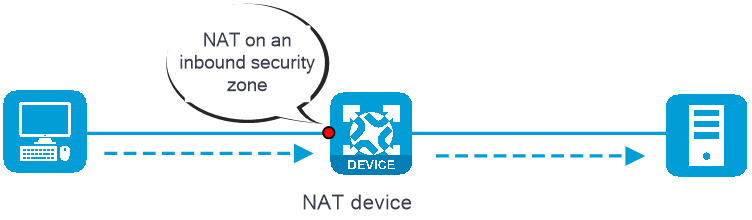
· Inbound NAT—Performs address translation for packets received in a security zone, as shown in Figure 1.
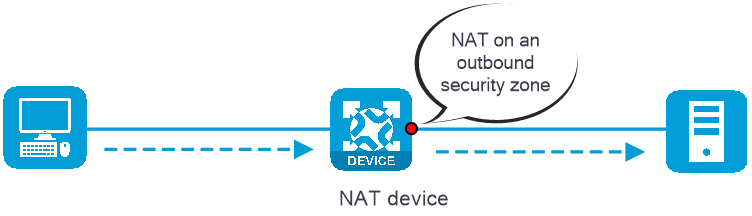
· Outbound NAT—Performs address translation for packets sent out of a security zone, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 1 NAT on an inbound security zone
Figure 2 NAT on an outbound security zone
Configuration flowchart
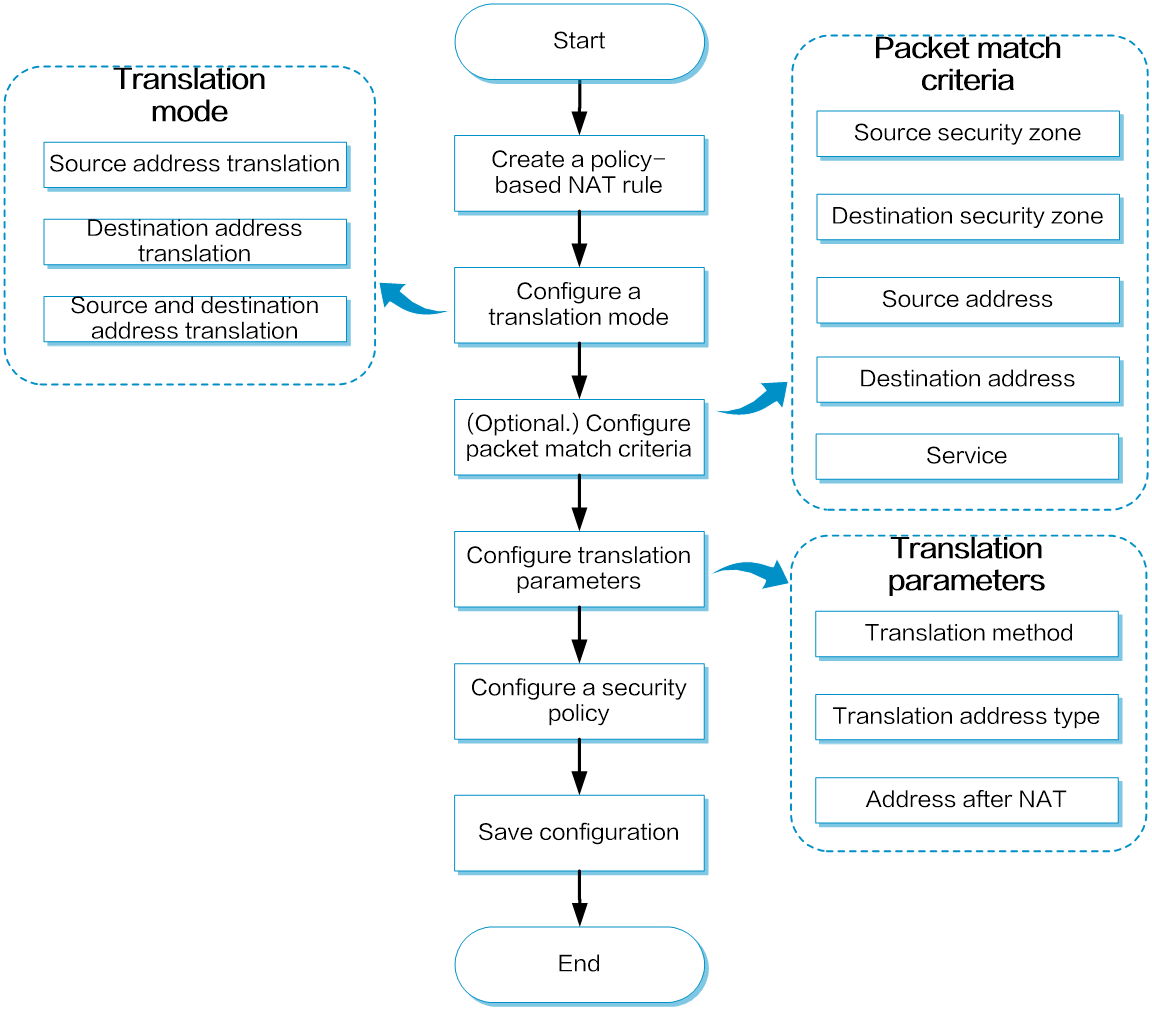
Policy-based NAT supports packet match criteria including security zone, address object group, and service object group. Policy-based NAT supports source address translation, destination address translation, and source and destination address translation. Figure 3 shows the configuration flowchart.
Figure 3 Policy-based NAT configuration flowchart
Configure a policy-based NAT44 rule
Procedure
1. (Optional.) Create a security zone. (Details not shown.)
2. (Optional.) Create an address object group. (Details not shown.)
3. (Optional.) Create a service object group. (Details not shown.)
4. (Optional.) Create a NAT address group.
a. Click the Objects tab.
b. In the navigation pane, select Object Groups > NAT Address Groups.
c. Click Create.
d. Create a NAT address group.
e. Click OK.
5. Create a policy-based NAT44 rule.
a. Click the Policies tab.
b. In the navigation pane, select Policy-Based NAT.
c. Click Create.
d. Create a policy-based NAT rule, and select the rule type as NAT44.
e. Click OK.
Table 1 Configuration items for policy-based NAT44 rules
|
Item |
Description |
||
|
Rule name |
Enter the name of a policy-based NAT44 rule. Chinese characters are supported. |
||
|
Rule description |
Enter the description of the policy-based NAT44 rule. |
||
|
Translation mode |
Translation mode: · Source address translation—Translates the source IP address and source port of packets. · Destination address translation—Translates the destination IP address and destination port of packets. · Source and destination address translation—Translates the source IP address, source port, destination IP address, and destination port of packets. |
||
|
Original packets |
Src zone |
Select source security zones for packet match. |
|
|
Dst zone |
Select destination security zones for packet match. |
||
|
Source IP |
Select a source IP address, IP subnet, or address object group for packet match. |
||
|
Destination IP |
Select a destination IP address, IP subnet, or address object group for packet match. If the translation mode is destination address translation or source and destination address translation, this field must be specified. |
||
|
Service |
Select a service object group for packet match. |
||
|
Source address translation |
Translation method |
Select a source address translation method: · Dynamic IP+port—Uses the PAT method to translate both the source IP addresses and source ports of packets. · Dynamic IP—Uses the NO-PAT method to translate only the source IP addresses of packets. · Static IP—Translates the source IP addresses of packets to a fixed IP address. · No translation—This rule and rules with lower priority than this rule are not used for source address translation. |
|
|
Address |
Select a NAT address type for source address translation: · Address object group—Uses IP addresses in an address object group for source address translation. · NAT address group—Uses IP addresses in a NAT address group for source address translation. · IP address—Uses a fixed IP address for source address translation. · Network address—Uses IP addresses on a network for source address translation. · Easy IP—Uses the outgoing interface IP address of the device for source address translation. |
||
|
Source IP after NAT |
Select a NAT address for source address translation. |
||
|
Allow reverse NAT |
Enable reverse address translation. Reverse address translation uses existing NO-PAT entries to translate the destination address for connections actively initiated from the external network to the internal network. This option is available only when the translation mode is set to Dynamic IP. |
||
|
User original port preferentially |
Preferentially use the original port for PAT. When the original port has been allocated, another port is used. This option is available only when the translation mode is set to Dynamic IP+port. |
||
|
Destination address translation |
Translation method |
Select a destination address translation method: · Static IP—Translates the destination IP addresses of packets to a fixed IP address. · Address object group—Translates the destination IP addresses of packets to addresses in an address object group. · No translation—This rule and rules with lower priority than this rule are not used for source address translation. |
|
|
Destination IP after NAT |
Set the destination IP address after translation. |
||
|
Port after NAT |
Set the destination port after translation. |
||
|
Enable this rule |
Enable this policy-based NAT44 rule. |
||
|
Counting |
Enable the counting of times that the policy-based NAT44 rule is matched. |
||
Configure a policy-based NAT64 rule
Procedure
1. (Optional.) Create a security zone. (Details not shown.)
2. (Optional.) Create an address object group. (Details not shown.)
3. (Optional.) Create a service object group. (Details not shown.)
4. Create a policy-based NAT64 rule.
a. Click the Policies tab.
b. In the navigation pane, select Policy-Based NAT.
c. Click Create.
d. Create a policy-based NAT rule, and select the rule type as NAT64.
e. Click OK.
Table 2 Configuration items for policy-based NAT64 rules
|
Item |
Description |
||
|
Rule name |
Enter the name of a policy-based NAT64 rule. Chinese characters are supported. |
||
|
Rule description |
Enter the description of the policy-based NAT64 rule. |
||
|
Translation mode |
Translation mode: · V4toV6—Translates the source IP address and destination IP address of packets when an IPv4 host first initiates a connection to the IPv6 network. · V6toV4—Translates the source IP address and destination IP address of packets when an IPv6 host first initiates a connection to the IPv4 network. |
||
|
Original packets |
Src zone |
Select source security zones for packet match. |
|
|
Source IP |
Select a source IP address, IP subnet, or address object group for packet match. |
||
|
Destination IP |
Select a destination IP address, IP subnet, or address object group for packet match. |
||
|
Service |
Select a service object group for packet match. |
||
|
Source address translation |
Translation method |
Select a source address translation method: · Dynamic IP+port—Uses the PAT method to translate both the source IP addresses and source ports of packets. · Dynamic IP—Uses the NO-PAT method to translate only the source IP addresses of packets. · Static IP—Translates the source IP addresses of packets to a fixed IP address. · Prefix translation—Uses IPv6 prefixes to translate the source IP addresses of packets. |
|
|
Source IP after NAT |
Select a NAT address for source address translation. This option is available only when the translation method is Dynamic IP+port, Dynamic IP, or Static IP. |
||
|
Prefix translation |
Select a prefix translation type: · General prefix—Uses the general prefix for source address translation. · IVI prefix—Uses the IVI prefix for source address translation. · NAT64 prefix—Uses the NAT64 prefix for source address translation. This option is available only when the translation method is Prefix translation. |
||
|
IPv6 prefix |
Configure the IPv6 address prefix for the prefix translation method. This option is available only when the prefix translation type is General prefix or NAT64 prefix. |
||
|
Prefix length |
Configure the IPv6 prefix length. This option is available only when the prefix translation type is General prefix or NAT64 prefix. |
||
|
Destination address translation |
Translation method |
Select a destination address translation method: · Prefix translation—Uses the IPv6 prefixes for destination address translation. · NAT server mapping—Translates the destination IP addresses and destination port numbers of packets to a fixed destination IP address and destination port number. · Static translation—Translates the destination IP addresses of packets to a fixed IP address. |
|
|
Prefix translation |
Select a prefix translation type: · General prefix—Uses the general prefix for source address translation. · IVI prefix—Uses the IVI prefix for source address translation. · NAT64 prefix—Uses the NAT64 prefix for source address translation. This option is available only when the translation method is Prefix translation. |
||
|
IPv6 prefix |
Configure the IPv6 address prefix for the prefix translation method. This option is available only when the prefix translation type is General prefix or IVI prefix. |
||
|
Prefix length |
Configure the IPv6 prefix length. This option is available only when the prefix translation type is General prefix or IVI prefix. |
||
|
Destination IP after NAT |
Set the destination IP address after translation. |
||
|
Port after NAT |
Set the destination port after translation. This option is available only when the translation method is NAT server mapping. |
||
|
Enable this rule |
Enable this policy-based NAT64 rule. |
||
|
Counting |
Enable the counting of times that the policy-based NAT64 rule is matched. |
||
Configure a policy-based NAT66 rule
Procedure
1. (Optional.) Create a security zone. (Details not shown.)
2. (Optional.) Create an address object group. (Details not shown.)
3. (Optional.) Create a service object group. (Details not shown.)
4. Create a policy-based NAT66 rule.
a. Click the Policies tab.
b. In the navigation pane, select Policy-Based NAT.
c. Click Create.
d. Create a policy-based NAT rule, and select the rule type as NAT66.
e. Click OK.
Table 3 Configuration items for policy-based NAT66 rules
|
Item |
Description |
||
|
Rule name |
Enter the name of a policy-based NAT66 rule. Chinese characters are supported. |
||
|
Rule description |
Enter the description of the policy-based NAT66 rule. |
||
|
Translation mode |
Translation mode: · Source address translation—Translates the source IP address and source port of packets. · Destination address translation—Translates the destination IP address and destination port of packets. · Source and destination address translation—Translates the source IP address, source port, destination IP address, and destination port of packets. |
||
|
Original packets |
Src zone |
Select source security zones for packet match. |
|
|
Dst zone |
Select destination security zones for packet match. |
||
|
Source IP |
Select a source IP address, IP subnet, or address object group for packet match. |
||
|
Destination IP |
Select a destination IP address, IP subnet, or address object group for packet match. If the translation mode is destination address translation or source and destination address translation, this field must be specified. |
||
|
Service |
Select a service object group for packet match. |
||
|
Source address translation |
Translation method |
Select a source address translation method: · Dynamic IP+port—Uses the PAT method to translate both the source IP addresses and source ports of packets. · Dynamic IP—Uses the NO-PAT method to translate only the source IP addresses of packets. · Static IP—Translates the source IP addresses of packets to a fixed IP address · NPTV6—Uses the NPTV6 method to translate the prefixes in the source IPv6 addresses of packets to the configured prefix. To use this method, you must configure packet match rules for original packets. · No translation—This rule and rules with lower priority than this rule are not used for source address translation. |
|
|
Source IP after NAT |
Select a NAT address for source address translation. |
||
|
IPv6 prefix |
Configure the IPv6 address prefix for the prefix translation method. This option is available only when the prefix translation method is NPTV6. |
||
|
Prefix length |
Configure the IPv6 prefix length. This option is available only when the prefix translation method is NPTV6. |
||
|
Destination address translation |
Translation method |
Select a destination address translation method: · Translation—Translates the destination IP addresses of packets to a fixed IP address. · NPTV6—Uses the NPTV6 method to translate the prefixes in the destination IPv6 addresses of packets to the configured prefix. · No translation—This rule and rules with lower priority than this rule are not used for destination address translation. |
|
|
Destination IP after NAT |
Set the destination IP address after translation. |
||
|
Port after NAT |
Set the destination port after translation. |
||
|
IPv6 prefix |
Configure the IPv6 address prefix for the prefix translation method. This option is available only when the translation method is NPTV6. |
||
|
Prefix length |
Configure the IPv6 prefix length. This option is available only when the translation method is NPTV6. |
||
|
Enable this rule |
Enable this policy-based NAT66 rule. |
||
|
Counting |
Enable the counting of times that the policy-based NAT66 rule is matched. |
||
Restrictions and guidelines
· By default, the NAT rules in policy-based NAT are sorted in descending order of their configuration order. You can rearrange NAT rules to change their priorities. A rule has a higher priority than rules listed after it.
· A NAT address group cannot be used by both PAT and NO-PAT modes.
· If a packet matches both a policy-based NAT rule and an interface NAT rule, the packet is translated as follows:
¡ For source and destination address translation method:
- If the translation methods of the policy-based NAT rule and the interface NAT rule are the same, the device translates the packet by using the policy-based NAT rule.
- If the translation methods of the policy-based NAT rule and the interface NAT rule are different, the device translates the packet by using the two rules.
¡ If the translation method of the policy-based NAT rule is bidirectional, the device translates the packet by using the policy-based NAT rule, and the interface NAT rule does not take effect.
· When you add address ranges to a NAT address group, make sure address ranges do not overlap.
· The address object group used by a NAT rule cannot contain a host name or address object group.
· If you select Automatically generate security policy when creating or copying a NAT rule, the device generates a security policy based on the original packet information you configured. If you modify the original packet information, you must click Refresh to reflect the modification in the generated security policy.