- Table of Contents
-
- 09-Network Management Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-System Maintenance and Debugging Configuration
- 02-NQA Configuration
- 03-NTP Configuration
- 04-IPC Configuration
- 05-SNMP Configuration
- 06-RMON Configuration
- 07-Mirroring Configuration
- 08-Information Center Configuration
- 09-sFlow Configuration
- 10-Flow Log Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 09-sFlow Configuration | 86.67 KB |
Configuring the sFlow agent and sFlow collector information
Enabling sFlow in AP group view
Displaying and maintaining sFlow
Troubleshooting sFlow configuration
The remote sFlow collector cannot receive sFlow packets
Configuring sFlow
Sampled Flow (sFlow) is a traffic monitoring technology used to collect and analyze traffic statistics.
As shown in Figure 1, the sFlow system involves an sFlow agent embedded in a device and a remote sFlow collector. The sFlow agent collects interface counter information and packet content information and encapsulates the sampled information in sFlow packets. When the sFlow packet buffer is full, or the aging timer of sFlow packets expires, the sFlow agent sends the sFlow packets in UDP datagrams to the specified sFlow collector. The sFlow collector analyzes the information and displays the results.
sFlow provides the following sampling mechanisms:
· Flow sampling—Obtains packet content information.
· Counter sampling—Obtains interface counter information.
Figure 1 sFlow system
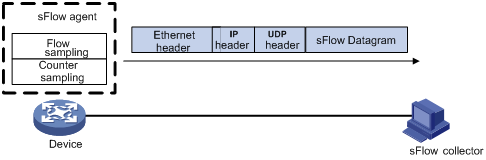
sFlow has the following advantages:
· Supports traffic monitoring on Gigabit and higher-speed networks.
· Provides good scalability to allow one sFlow collector to monitor multiple sFlow agents.
· Saves money by embedding the sFlow agent in a device, instead of using a dedicated sFlow agent device.
The device supports only the sFlow agent function.
sFlow configuration task list
|
Task |
Remarks |
|
Required. |
|
|
Perform at least one of the tasks. |
|
Configuring the sFlow agent and sFlow collector information
|
Command |
Remarks |
|
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Configure an IP address for the sFlow agent. |
sflow agent { ip ip-address | ipv6 ipv6-address } |
Optional. Not specified by default. The device periodically checks whether the sFlow agent has an IP address. If the sFlow agent has no IP address configured, the device automatically selects an interface IP address for the sFlow agent but does not save the IP address. NOTE: · H3C recommends that you configure an IP address manually for the sFlow agent. · Only one IP address can be specified for the sFlow agent on the device. |
|
3. Configure the sFlow collector information. |
sflow collector collector-id { { ip ip-address | ipv6 ipv6-address } | datagram-size size | description text | port port-number | time-out seconds } * |
By default, the device presets a certain number of sFlow collectors. Use the display sflow command to display the parameters of the preset sFlow collectors. You can configure up to 10 sFlow collectors. |
|
4. Specify the sFlow version. |
sflow version { 4 | 5 } |
Optional. The default depends on the device model. |
|
5. Specify the source IP address of sFlow packets. |
sflow source { ip ip-address | ipv6 ipv6-address } * |
Optional. Not specified by default. |
Configuring flow sampling
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter Ethernet interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Set the flow sampling mode. |
sflow sampling-mode { determine | random } |
Optional. The default setting is random. |
|
4. Specify the number of packets out of which flow sampling samples a packet on the interface. |
sflow sampling-rate interval |
By default, flow sampling samples a packet out of 2000 packets. |
|
5. Set the maximum number of bytes of a packet (starting from the packet header) that flow sampling can copy. |
sflow flow max-header length |
Optional. The default setting is 128 bytes. H3C recommends that you use the default value. |
|
6. Specify the sFlow collector for flow sampling. |
sflow flow collector collector-id |
No collector is specified for flow sampling by default. |
Configuring counter sampling
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Set the interval for counter sampling. |
sflow counter interval seconds |
Counter sampling is disabled by default. |
|
4. Specify the sFlow collector for counter sampling. |
sflow counter collector collector-id |
No collector is specified for counter sampling by default. |
Enabling sFlow
The flow sampling configuration can take effect only when sFlow is enabled.
Enabling sFlow in radio view
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter AP template view. |
wlan ap ap-name [ model model-name [ id ap-id ] ] |
The model name of the AP must be provided when you create an AP template. |
|
3. Enter radio view. |
radio radio-number [ type { dot11a | dot11an | dot11b | dot11g | dot11gn | dot11ac } ] |
Support for radio types varies by the AP. |
|
4. Enable sFlow on the AP. |
sflow enable |
Optional. By default, sFlow is enabled on an AP. |
Enabling sFlow in AP group view
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Create an AP group and enter AP group view. |
wlan ap-group group-name |
By default, an AP group named default_group exists. All APs are in this AP group. |
|
3. Enable sFlow on the specified radio of the AP group. |
· 5 GHz radio: · 2.4 GHz radio: |
Optional. By default, sFlow is enabled in an AP group. |
Displaying and maintaining sFlow
|
Task |
Command |
Remarks |
|
Display sFlow configuration information (centralized devices). |
display sflow [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Display sFlow configuration information (distributed devices–centralized IRF devices–in standalone mode). |
display sflow [ slot slot-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
|
Display sFlow configuration information (distributed devices–in IRF mode). |
display sflow [ chassis chassis-number slot slot-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
sFlow configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 2, perform the following tasks:
· Enable flow sampling and counter sampling on Ethernet 1/1 of the device to monitor traffic on the port.
· Configure the device to send sampled information to the sFlow collector through Ethernet 1/3.

Configuration procedure
1. Configure the sFlow agent and sFlow collector information:
# Configure the IP address of Ethernet 1/3 on the device as 3.3.3.1/16.
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface ethernet 1/3
[Device-Ethernet1/3] ip address 3.3.3.1 16
[Device-Ethernet1/3] quit
# Configure the IP address for the sFlow agent.
[Device] sflow agent ip 3.3.3.1
# Configure parameters for an sFlow collector: specify sFlow collector ID 2, IP address 3.3.3.2, the default port number, and description of netserver for the sFlow collector.
[Device] sflow collector 2 ip 3.3.3.2 description netserver
2. Configure counter sampling:
# Set the counter sampling interval to 120 seconds.
[Device] interface ethernet 1/1
[Device-Ethernet1/1] sflow counter interval 120
# Specify sFlow collector 2 for counter sampling.
[Device-Ethernet1/1] sflow counter collector 2
3. Configure flow sampling:
# Set the flow sampling mode and the sampling interval.
[Device-Ethernet1/1] sflow sampling-mode random
[Device-Ethernet1/1] sflow sampling-rate 4000
# Specify sFlow collector 2 for flow sampling.
[Device-Ethernet1/1] sflow flow collector 2
# Display the sFlow configuration and operation information.
[Device-Ethernet1/1] display sflow
sFlow Version: 5
sFlow Global Information:
Agent IP:3.3.3.1(CLI)
Collector Information:
ID IP Port Aging Size Description
1 6343 0 1400
2 3.3.3.2 6543 N/A 1400 netserver
3 6343 0 1400
4 6343 0 1400
5 6343 0 1400
6 6343 0 1400
7 6343 0 1400
8 6343 0 1400
9 6343 0 1400
10 6343 0 1400
sFlow Port Information:
Interface CID Interval(s) FID MaxHLen Rate Mode Status
Eth1/1 2 120 2 128 4000 Random Active
The output shows that Ethernet 1/1 enabled with sFlow is active, the counter sampling interval is 120 seconds, and the packet sampling interval is 4000.
Troubleshooting sFlow configuration
The remote sFlow collector cannot receive sFlow packets
Symptom
The remote sFlow collector cannot receive sFlow packets.
Analysis
The possible reasons include:
· The sFlow collector is not specified.
· sFlow is not configured on the interface.
· The IP address of the sFlow collector specified on the sFlow agent is different from that of the remote sFlow collector.
· No IP address is configured for the Layer 3 interface on the device.
· An IP address is configured for the Layer 3 interface on the device. However, the UDP packets that have the IP address as the source cannot reach the sFlow collector.
· The physical link between the device and the sFlow collector fails.
Solution
To resolve the problem:
1. Use the display sflow command to verify that sFlow is correctly configured.
2. Verify that a correct IP address is configured for the device to communicate with the sFlow collector.
3. Verify that the physical link between the device and the sFlow collector is up.
