- Table of Contents
-
- 04-Layer 3 Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-ARP Configuration
- 02-IP Addressing Configuration
- 03-DHCP Configuration
- 04-DHCPv6 Configuration
- 05-DNS Configuration
- 06-IPv6 DNS Configuration
- 07-NAT Configuration
- 08-Adjacency Table Configuration
- 09-Flow Classification Configuration
- 10-IPv6 Basics Configuration
- 11-IP Performance Optimization Configuration
- 12-IP Routing Basics
- 13-Static Routing Configuration
- 14-IPv6 Static Routing Configuration
- 15-GRE Configuration
- 16-RIP Configuration
- 17-RIPng Configuration
- 18-Policy-Based Routing Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 14-IPv6 Static Routing Configuration | 77.68 KB |
Configuring IPv6 static routing
Configuring IPv6 static routing
Displaying and maintaining IPv6 static routes
IPv6 static routing configuration example
Configuring IPv6 static routing
The term "router" in this document refers to both routers and routing-capable access controllers.
Overview
Static routes are manually configured. If a network's topology is simple, you only need to configure static routes for the network to work correctly.
Static routes cannot adapt to network topology changes. If a fault or a topological change occurs in the network, the network administrator has to modify the static routes manually.
IPv6 static routes work well in simple IPv6 network environments.
Configuring IPv6 static routing
Before you configure an IPv6 static route, complete the following tasks:
· Configure parameters for the related interfaces.
· Configure link layer attributes for the related interfaces.
· Enable IPv6 packet forwarding.
· Make sure that the neighboring nodes can reach each other.
To configure an IPv6 static route:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Configure an IPv6 static route. |
ipv6 route-static ipv6-address prefix-length { interface-type interface-number [ next-hop-address ] | next-hop-address } [ preference preference-value ] |
By default, no IPv6 static route is configured. |
|
3. Delete all IPv6 static routes, including the default route. |
delete ipv6 static-routes all |
Optional. The undo ipv6 route-static command deletes one IPv6 static route. |
Displaying and maintaining IPv6 static routes
|
Command |
Remarks |
|
|
Display IPv6 static route information. |
display ipv6 routing-table protocol static [ inactive | verbose ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view. |
IPv6 static routing configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 1, configure IPv6 static routes so that hosts, switches, and AC can reach each other.
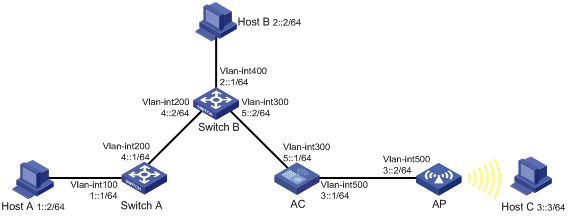
Configuration procedure
1. Configure the IPv6 addresses of all VLAN interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure AC basic functions. (For more information, see WLAN Configuration Guide.)
3. Configure IPv6 static routes:
# Configure the default IPv6 static route on Switch A.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] ipv6 route-static :: 0 4::2
# Configure two IPv6 static routes on Switch B.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] ipv6 route-static 1:: 64 4::1
[SwitchB] ipv6 route-static 3:: 64 5::1
# Configure the default IPv6 static route on AC.
<AC> system-view
[AC] ipv6 route-static :: 0 5::2
4. Configure the IPv6 addresses of all the hosts based upon the network diagram, and configure the default gateways of Host A, Host B, and Host C as 1::1, 2::1, and 3::1.
5. Verify the configuration:
# Display the IPv6 routing table on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display ipv6 routing-table
Routing Table :
Destinations : 5 Routes : 5
Destination : ::/128 Protocol : Static
NextHop : 4::2 Preference : 60
Interface : Vlan-interface200 Cost : 0
Destination : ::1/128 Protocol : Direct
NextHop : ::1 Preference : 0
Interface : InLoop0 Cost : 0
Destination : 1::/64 Protocol : Direct
NextHop : 1::1 Preference : 0
Interface : Vlan-interface100 Cost : 0
Destination : 1::1/128 Protocol : Direct
NextHop : ::1 Preference : 0
Interface : InLoop0 Cost : 0
Destination : FE80::/10 Protocol : Direct
NextHop : :: Preference : 0
Interface : NULL0 Cost : 0
# Verify the connectivity with the ping command.
[SwitchA] ping ipv6 3::1
PING 3::1 : 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
Reply from 3::1
bytes=56 Sequence=1 hop limit=254 time = 63 ms
Reply from 3::1
bytes=56 Sequence=2 hop limit=254 time = 62 ms
Reply from 3::1
bytes=56 Sequence=3 hop limit=254 time = 62 ms
Reply from 3::1
bytes=56 Sequence=4 hop limit=254 time = 63 ms
Reply from 3::1
bytes=56 Sequence=5 hop limit=254 time = 63 ms
--- 3::1 ping statistics ---
5 packet(s) transmitted
5 packet(s) received
0.00% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 62/62/63 ms
