- Table of Contents
-
- 13-Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-System maintenance and debugging configuration
- 02-NQA configuration
- 03-NTP configuration
- 04-SNMP configuration
- 05-RMON configuration
- 06-Event MIB configuration
- 07-NETCONF configuration
- 08-EAA configuration
- 09-Process monitoring and maintenance configuration
- 10-Sampler configuration
- 11-Mirroring configuration
- 12-NetStream configuration
- 13-IPv6 NetStream configuration
- 14-Information center configuration
- 15-Flow log configuration
- 16-GOLD configuration
- 17-Packet capture configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 11-Mirroring configuration | 123.79 KB |
Contents
Local port mirroring implementation
Feature and hardware compatibility
Local port mirroring configuration task list
Creating a local mirroring group
Configuring source ports for the local mirroring group
Configuration restrictions and guidelines
Configuring source ports in system view
Configuring source ports in interface view
Configuring the monitor port for the local mirroring group
Configuration restrictions and guidelines
Configuring the monitor port in system view
Configuring the monitor port in interface view
Displaying and maintaining port mirroring
Port mirroring configuration examples
Local port mirroring configuration example
Feature and hardware compatibility
Flow mirroring configuration task list
Configuring a traffic behavior
Applying a QoS policy to an interface
Configuring port mirroring
Overview
Port mirroring copies the packets passing through a port to a port that connects to a data monitoring device for packet analysis.
Terminology
The following terms are used in port mirroring configuration.
Mirroring source
The mirroring sources can be one or more monitored ports called source ports.
Packets passing through mirroring sources are copied to a port connecting to a data monitoring device for packet analysis. The copies are called mirrored packets.
Source device
The device where the mirroring sources reside is called a source device.
Mirroring destination
The mirroring destination connects to a data monitoring device and is the destination port (also known as the monitor port) of mirrored packets. Mirrored packets are sent out of the monitor port to the data monitoring device.
A monitor port might receive multiple copies of a packet when it monitors multiple mirroring sources. For example, two copies of a packet are received on Port 1 when the following conditions exist:
· Port 1 is monitoring bidirectional traffic of Port 2 and Port 3 on the same device.
· The packet travels from Port 2 to Port 3.
Destination device
The device where the monitor port resides is called the destination device.
Mirroring direction
The mirroring direction specifies the direction of the traffic that is copied on a mirroring source.
· Inbound—Copies packets received.
· Outbound—Copies packets sent.
· Bidirectional—Copies packets received and sent.
Mirroring group
Port mirroring is implemented through local mirroring groups. A mirroring group must contain one or more mirroring ports and one monitor port.
Local port mirroring implementation
In local port mirroring, the following conditions exist:
· The source device is directly connected to a data monitoring device.
· The source device acts as the destination device to forward mirrored packets to the data monitoring device.
A local mirroring group is a mirroring group that contains the mirroring sources and the mirroring destination on the same device.
|
|
NOTE: Whether a local mirroring group supports mirroring across cards or interface modules depends on the device model. |
Figure 1 Local port mirroring implementation
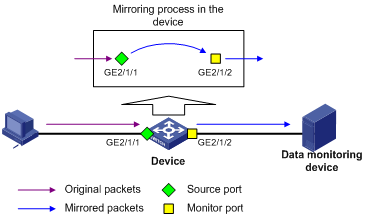
As shown in Figure 1, the source port GigabitEthernet 2/1/1 and the monitor port GigabitEthernet 2/1/2 reside on the same device. Packets received on GigabitEthernet 2/1/1 are copied to GigabitEthernet 2/1/2. GigabitEthernet 2/1/2 then forwards the packets to the data monitoring device for analysis.
Feature and hardware compatibility
The port mirroring feature is not available on FIP-600 switches.
Local port mirroring configuration task list
|
Tasks at a glance |
|
1. (Required.) Creating a local mirroring group |
|
2. (Required.) Configuring source ports for the local mirroring group |
|
3. (Required.) Configuring the monitor port for the local mirroring group |
Creating a local mirroring group
|
Command |
Remarks |
|
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Create a local mirroring group. |
mirroring-group group-id local |
By default, no local mirroring groups exist. |
Configuring source ports for the local mirroring group
To configure source ports for a local mirroring group, use one of the following methods:
· Assign a list of source ports to the mirroring group in system view.
· Assign a port to the mirroring group as a source port in interface view.
To assign multiple ports to the mirroring group as source ports in interface view, repeat the operation.
Configuration restrictions and guidelines
When you configure source ports for a local mirroring group, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· The member port of a Layer 3 aggregate interface cannot be configured as a source port for a mirroring group.
· A mirroring group can contain multiple source ports.
· A port can act as a source port for only one mirroring group.
· A source port cannot be configured as a monitor port.
Configuring source ports in system view
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Configure source ports for a local mirroring group. |
mirroring-group group-id mirroring-port interface-list { both | inbound | outbound } |
By default, no source port is configured for a local mirroring group. |
Configuring source ports in interface view
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
· Enter interface view: · Enter CPOS interface view: |
N/A |
|
3. Configure the port as a source port for a local mirroring group. |
mirroring-group group-id mirroring-port { both | inbound | outbound } |
By default, a port does not act as a source port for any local mirroring groups. |
Configuring the monitor port for the local mirroring group
To configure the monitor port for a mirroring group, use one of the following methods:
· Configure the monitor port for the mirroring group in system view.
· Assign a port to the mirroring group as the monitor port in interface view.
Configuration restrictions and guidelines
When you configure the monitor port for a local mirroring group, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· Use a monitor port only for port mirroring, so the data monitoring device receives only the mirrored traffic.
· A mirroring group can contain only one monitor port.
Configuring the monitor port in system view
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Configure the monitor port for a local mirroring group. |
mirroring-group group-id monitor-port interface-type interface-number |
By default, no monitor port is configured for a local mirroring group. |
Configuring the monitor port in interface view
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure the port as the monitor port for a mirroring group. |
mirroring-group group-id monitor-port |
By default, a port does not act as the monitor port for any local mirroring groups. |
Displaying and maintaining port mirroring
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display mirroring group information. |
display mirroring-group { group-id | all | local } |
Port mirroring configuration examples
Local port mirroring configuration example
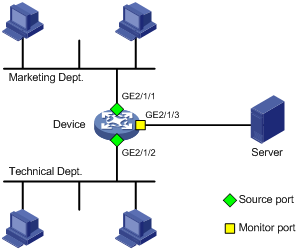
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 2, configure local port mirroring in source port mode to enable the server to monitor the bidirectional traffic of the two departments.
Configuration procedure
# Create local mirroring group 1.
<Device> system-view
[Device] mirroring-group 1 local
# Configure GigabitEthernet 2/1/1 and GigabitEthernet 2/1/2 as source ports for local mirroring group 1.
[Device] mirroring-group 1 mirroring-port gigabitethernet 2/1/1 gigabitethernet 2/1/2 both
# Configure GigabitEthernet 2/1/3 as the monitor port for local mirroring group 1.
[Device] mirroring-group 1 monitor-port gigabitethernet 2/1/3
# Disable the spanning tree feature on the monitor port (GigabitEthernet 2/1/3).
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/3
[Device-GigabitEthernet2/1/3] undo stp enable
[Device-GigabitEthernet2/1/3] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify the mirroring group configuration.
[Device] display mirroring-group all
Mirroring group 1:
Type: Local
Status: Active
Mirroring port:
GigabitEthernet2/1/1 Both
GigabitEthernet2/1/2 Both
Monitor port: GigabitEthernet2/1/3
Configuring flow mirroring
Flow mirroring copies packets matching a class to a destination for packet analyzing and monitoring. It is implemented through QoS policies.
To configure flow mirroring, perform the following tasks:
· Define traffic classes and configure match criteria to classify packets to be mirrored. Flow mirroring allows you to flexibly classify packets to be analyzed by defining match criteria.
· Configure traffic behaviors to mirror the matching packets to interfaces that connect to data monitoring devices.
The matching packets are copied to the specified interfaces and then sent to the data monitoring devices for analysis.
For more information about QoS policies, traffic classes, and traffic behaviors, see ACL and QoS Configuration Guide.
Feature and hardware compatibility
The flow mirroring feature is not available on FIP-600 switches.
Flow mirroring configuration task list
|
Tasks at a glance |
|
(Required.) Configuring match criteria |
|
(Required.) Configuring a traffic behavior |
|
(Required.) Configuring a QoS policy |
|
(Required.) Applying a QoS policy to an interface |
For more information about the following commands except the mirror-to command, see ACL and QoS Command Reference.
Configuring match criteria
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Create a class and enter class view. |
traffic classifier tcl-name [ operator { and | or } ] |
By default, no traffic classes exist. |
|
3. Configure match criteria. |
if-match [ not ] match-criteria |
By default, no match criterion is configured in a traffic class. |
Configuring a traffic behavior
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Create a traffic behavior and enter traffic behavior view. |
traffic behavior behavior-name |
By default, no traffic behaviors exist. |
|
3. Configure a mirroring action to mirror traffic to an interface. |
mirror-to interface interface-type interface-number |
By default, no mirroring action is configured for a traffic behavior. |
|
4. (Optional.) Display traffic behavior configuration. |
display traffic behavior |
Available in any view. |
Configuring a QoS policy
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Create a QoS policy and enter QoS policy view. |
qos policy policy-name |
By default, no QoS policies exist. |
|
3. Associate a class with a traffic behavior in the QoS policy. |
classifier tcl-name behavior behavior-name |
By default, no traffic behavior is associated with a class. |
|
4. (Optional.) Display QoS policy configuration. |
display qos policy |
Available in any view. |
Applying a QoS policy to an interface
By applying a QoS policy to an interface, you can mirror the traffic in the specified direction of the interface. A policy can be applied to multiple interfaces. In one direction (inbound or outbound) of an interface, only one policy can be applied.
To apply a QoS policy to an interface:
|
Step |
Command |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
|
3. Apply a policy to the interface. |
qos apply policy policy-name { inbound | outbound } |
Flow mirroring configuration example
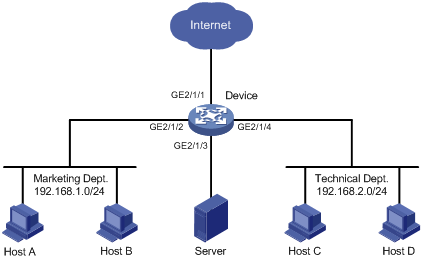
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 3, configure flow mirroring so that the server can monitor the following traffic:
· All traffic that the Technical Department sends to access the Internet.
· IP traffic that the Technical Department sends to the Marketing Department during working hours (8:00 to 18:00) on weekdays.
Configuration procedure
# Create a working hour range work, in which working hours are from 8:00 to 18:00 on weekdays.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] time-range work 8:00 to 18:00 working-day
# Create IPv4 advanced ACL 3000 to allow packets from the Technical Department to access the Internet and to the Marketing Department during working hours.
[DeviceA] acl advanced 3000
[DeviceA-acl-ipv4-adv-3000] rule permit tcp source 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 destination-port eq www
[DeviceA-acl-ipv4-adv-3000] rule permit ip source 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 destination 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 time-range work
[DeviceA-acl-ipv4-adv-3000] quit
# Create traffic class tech_c, and configure the match criterion as ACL 3000.
[DeviceA] traffic classifier tech_c
[DeviceA-classifier-tech_c] if-match acl 3000
[DeviceA-classifier-tech_c] quit
# Create traffic behavior tech_b, configure the action of mirroring traffic to port GigabitEthernet 2/1/3.
[DeviceA] traffic behavior tech_b
[DeviceA-behavior-tech_b] mirror-to interface gigabitethernet 2/1/3
[DeviceA-behavior-tech_b] quit
# Create QoS policy tech_p, and associate traffic class tech_c with traffic behavior tech_b in the QoS policy.
[DeviceA] qos policy tech_p
[DeviceA-qospolicy-tech_p] classifier tech_c behavior tech_b
[DeviceA-qospolicy-tech_p] quit
# Apply QoS policy tech_p to the incoming packets of GigabitEthernet 2/1/4.
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 2/1/4
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet2/1/4] qos apply policy tech_p inbound
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet2/1/4] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the server can monitor the following traffic:
· All traffic sent by the Technical Department to access the Internet.
· IP traffic that the Technical Department sends to the Marketing Department during working hours on weekdays.
(Details not shown.)

