- Table of Contents
-
- Fundamentals Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Feature Matrix
- 02-CLI Configuration
- 03-Controlling Login Users
- 04-File Management Configuration
- 05-FTP and TFTP Configuration
- 06-Device Management Configuration
- 07-Basic System Configuration
- 08-HTTP Configuration
- 09-Logging In to the AP Configuration
- 10-Index
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 08-HTTP Configuration | 113.58 KB |
Table of Contents
Logging In to the Device Through HTTP
Configuring the Port Number of the HTTP Service
Associating the HTTP Service with an ACL
Displaying and Maintaining HTTP
Associating the HTTPS Service with an SSL Server Policy
Associating the HTTPS Service with a Certificate Attribute Access Control Policy
Configuring the Port Number of the HTTPS Service
Associating the HTTPS Service with an ACL
Displaying and Maintaining HTTPS
l The models listed in this document are not applicable to all regions. Please consult your local sales office for the models applicable to your region.
l Support of the H3C WA series WLAN access points (APs) for features may vary by AP model. For more information, see Feature Matrix.
l The interface types and the number of interfaces vary by AP model.
l The term AP in this document refers to common APs, wireless bridges, and mesh APs.
This chapter includes these sections:
l Configuring the Port Number of the HTTP Service
l Associating the HTTP Service with an ACL
l Displaying and Maintaining HTTP
HTTP Overview
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is used for transferring web page information across the Internet. It is an application-level protocol in the TCP/IP protocol suite. The connection-oriented Transport Control Protocol (TCP) is adopted on the transport layer.
Currently, HTTP/1.0 is supported on the device.
How HTTP Works
The client/server mode is used for communication in HTTP. The client and the server exchange messages by following these procedures:
1) A TCP connection is created between the client and the server. Typically, the port number is 80.
2) The client sends a request to the server.
3) The server processes the request and sends back a response.
4) The TCP connection is closed.
Logging In to the Device Through HTTP
You can log in to the device by using the HTTP protocol with HTTP service enabled, accessing and controlling the device with Web-based network management.
To implement security management on the device, use the following methods to enhance the security of the device.
l Enable HTTP service only when necessary.
l Change the port number of the HTTP service as a port number not commonly used (for example 8080), thus reducing attacks from illegal users on the HTTP service.
l Associate the HTTP service with an ACL to let pass only the filtered clients.
Protocols and Standards
RFC 1945: Hypertext Transfer Protocol – HTTP/1.0
Enabling the HTTP Service
The device can act as the HTTP server and the users can access and control the device through the Web function only after the HTTP service is enabled.
Follow these steps to enable the HTTP service:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enable the HTTP service |
ip http enable |
Required The default setting varies with devices. |
Configuring the Port Number of the HTTP Service
Configuration of the port number of the HTTP service can reduce the attacks from illegal users on the HTTP service.
Follow these steps to configure the port number of the HTTP service:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Configure the port number of the HTTP service |
ip http port port-number |
Required By default, the port number of the HTTP service is 80. |
![]()
If you execute the ip http port command for multiple times, the last configured port number is used.
Associating the HTTP Service with an ACL
By associating the HTTP service with an ACL, only the clients that pass ACL filtering are allowed to access the device.
Follow these steps to associate the HTTP service with an ACL:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enters system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Associate the HTTP service with an ACL |
ip http acl acl-number |
Required The HTTP service is not associated with an ACL by default. |
![]()
l The HTTP service can be associated with a WLAN ACL (with the ACL numbers 100 to 199) and basic ACL (with the ACL numbers 2000 to 2999), and the two types of ACLs will not overwrite each other. However, ACLs of the same type will overwrite each other, or, in other words, if you execute the ip http acl command for multiple times to associate the HTTP with the same type of ACLs, the HTTP service is only associated with the last specified ACL.
l When the HTTP service is associated with a WLAN ACL, the HTTP service uses this ACL to filter wireless clients only, and does not filter wired clients with this ACL.
l For more information about ACLs, see ACL in the ACL and QoS Configuration Guide.
Displaying and Maintaining HTTP
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Display information about HTTP |
display ip http |
Available in any view |
HTTP Configuration Example
Network requirements
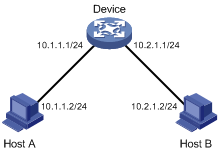
As shown in Figure 1-1, filter users logging in through Web interface according to the source IP addresses, enabling only users in the 10.1.1.0/24 segment to access and control the device through the Web interface.
Figure 1-1 HTTP network diagram
Configuration procedure
1) Configure the HTTP server Device.
# Create basic ACL 2000, allowing packets with the source IP address in 10.1.1.0/24.
<Device> system-view
[Device] acl number 2000
[Device-acl-basic-2000] rule permit source 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[Device-acl-basic-2000] quit
# Associate the HTTP service to ACL 2000.
[Device] ip http acl 2000
# Enable the HTTP service.
[Device] ip http enable
2) Verify the configuration.
l If you open the IE on Host A, and type http://10.1.1.1, you can open the Web login page of Device.
l If you open the IE on Host B, and type http://10.2.1.1, you cannot open the Web login page of Device.
This chapter includes these sections:
l HTTPS Configuration Task List
l Associating the HTTPS Service with an SSL Server Policy
l Associating the HTTPS Service with a Certificate Attribute Access Control Policy
l Configuring the Port Number of the HTTPS Service
l Associating the HTTPS Service with an ACL
l Displaying and Maintaining HTTPS
HTTPS Overview
The Secure HTTP (HTTPS) refers to the HTTP protocol that supports the Security Socket Layer (SSL) protocol.
The SSL protocol of HTTPS enhances the security of the device in the following ways:
l Uses the SSL protocol to ensure the legal clients to access the device securely and prohibit the illegal clients;
l Encrypts the data exchanged between the HTTPS client and the device to ensure the data security and integrity, thus realizing the security management of the device;
l Defines certificate attribute-based access control policy for the device to control the access right of the client, in order to further avoid attacks from illegal clients.
![]()
l The total number of HTTP connections and HTTPS connections on a device cannot exceed ten.
l For more information about SSL, see SSL in the Security Configuration Guide.
HTTPS Configuration Task List
Complete these tasks to configure HTTPS:
|
Configuration task |
Remarks |
|
Required |
|
|
Required |
|
|
Associating the HTTPS Service with a Certificate Attribute Access Control Policy |
Optional |
|
Optional |
|
|
Optional |
Associating the HTTPS Service with an SSL Server Policy
Before enabling the HTTPS service, associate the HTTPS service with a created SSL server policy.
Follow these steps to associate the HTTPS service with an SSL server policy:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Associate the HTTPS service with an SSL server policy |
ip https ssl-server-policy policy-name |
Required Not associated by default |
![]()
l If the ip https ssl-server-policy command is executed repeatedly, the HTTPS service is only associated with the last specified SSL server policy.
l When the HTTPS service is disabled, the association between the HTTPS service and the SSL server is automatically removed. To enable it again, you need to re-associate the HTTPS service with an SSL server policy.
l When the HTTPS service is enabled, no modification of its associated SSL server policy takes effect.
Enabling the HTTPS Service
The device can act as the HTTPS server and users can access and control the device through the Web function only when the HTTPS service is enabled.
Follow these steps to enable the HTTPS service:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enable the HTTPS service |
ip https enable |
Required Disabled by default. |
![]()
l After the HTTPS service is enabled, you can use the display ip https command to view the state of the HTTPS service and verify the configuration.
l Enabling of the HTTPS service will trigger an SSL handshake negotiation process. During the process, if the local certificate of the device already exists, the SSL negotiation is successfully performed, and the HTTPS service can be started normally. If no local certificate exists, a certificate application process will be triggered by the SSL negotiation. Since the application process takes much time, the SSL negotiation may fail and the HTTPS service cannot be started normally. Therefore, the ip https enable command must be executed for multiple times to ensure normal startup of the HTTPS service.
Associating the HTTPS Service with a Certificate Attribute Access Control Policy
Associating the HTTPS service with a configured certificate access control policy helps control the access right of the client, thus providing the device with enhanced security.
Follow these steps to associate the HTTPS service with a certificate attribute access control policy:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Associate the HTTPS service with a certificate attribute access control policy |
ip https certificate access-control-policy policy-name |
Required Not associated by default. |
![]()
l If the ip https certificate access-control-policy command is executed repeatedly, the HTTPS server is only associated with the last specified certificate attribute access control policy.
l If the HTTPS service is associated with a certificate attribute access control policy, the client-verify enable command must be configured in the SSL server policy. Otherwise, the client cannot log onto the device.
l If the HTTPS service is associated with a certificate attribute access control policy, the latter must contain at least one permit rule. Otherwise, no HTTPS client can log onto the device.
l For the configuration of an SSL server policy, see PKI in the Security Configuration Guide.
Configuring the Port Number of the HTTPS Service
Configuration of the port number of the HTTPS service can reduce the attacks from illegal users on the HTTPS service.
Follow these steps to configure the port number of the HTTPS service:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Configure the port number of the HTTPS service |
ip https port port-number |
Optional By default, the port number of the HTTPS service is 443. |
![]()
If you execute the ip https port command for multiple times, the last configured port number is used.
Associating the HTTPS Service with an ACL
Associating the HTTPS service with an ACL can filter out requests from some clients to let pass only clients that pass the ACL filtering.
Follow these steps to associate the HTTPS service with an ACL:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Associate the HTTPS service with an ACL |
ip https acl acl-number |
Required Not associated by default. |
![]()
l The HTTPS service can be associated with a WLAN ACL (with the ACL numbers 100 to 199) and basic ACL (with the ACL numbers 2000 to 2999), and the two types of ACLs will not overwrite each other. However, ACLs of the same type will overwrite each other, that is, if you execute the ip https acl command for multiple times to associate the HTTPS service with the same type of ACLs, the HTTPS service is only associated with the last specified ACL.
l When the HTTPS service is associated with a WLAN ACL, the HTTPS service uses this ACL to filter wireless clients only, and does not filter wired clients with this ACL.
l For more information about ACLs, see ACL in the ACL and QoS Configuration Guide.
Displaying and Maintaining HTTPS
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Display information about HTTPS |
display ip https |
Available in any view |
HTTPS Configuration Example
Network requirements
Users can access and control the device through logging in to the Web page. To prevent unauthorized users from accessing and controlling the device and enhance the device management security, the device requires the users log in to the Web page through HTTPS and authenticates the users using SSL, and ensures that the transmitted data will not be spoofed and tampered.
To meet the requirements, perform the following configurations:
l Configure Device as the HTTPS server and apply a certificate for Device.
l Apply a certificate for the HTTPS client Host for Device to authenticate it.
The name of the CA (Certificate Authority) that issues certificate to Device is new-ca.
![]()
l In this configuration example, Windows Server serves as CA and you need to install Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) component.
l Before the following configurations, ensure that there is an available route between Device, Host and CA.
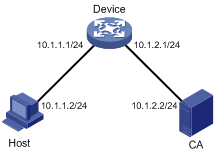
Figure 2-1 Network diagram for HTTPS configuration
Configuration procedure
1) Configure the HTTPS server Device.
# Configure PKI entity en, and specify its common name as http-server1, and FQDN as ssl.security.com.
<Device> system-view
[Device] pki entity en
[Device-pki-entity-en] common-name http-server1
[Device-pki-entity-en] fqdn ssl.security.com
[Device-pki-entity-en] quit
# Configure PKI domain 1, specify the trusted CA as new-ca, the URL of the server for certificate request as http://10.1.2.2/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll, the authority for certificate request as RA, and the entity name as en.
[Device] pki domain 1
[Device-pki-domain-1] ca identifier new-ca
[Device-pki-domain-1] certificate request url http://10.1.2.2/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll
[Device-pki-domain-1] certificate request from ra
[Device-pki-domain-1] certificate request entity en
[Device-pki-domain-1] quit
# Generate a local RSA key pair.
[Device] public-key local create rsa
# Retrieve a CA certificate.
[Device] pki retrieval-certificate ca domain 1
# Request a local certificate for Device.
[Device] pki request-certificate domain 1
# Configure an SSL server policy myssl, specify PKI domain 1 for it, and enable the SSL server to perform certificate-based authentication of the client.
[Device] ssl server-policy myssl
[Device-ssl-server-policy-myssl] pki-domain 1
[Device-ssl-server-policy-myssl] client-verify enable
[Device-ssl-server-policy-myssl] quit
# Configure certificate attribute group mygroup1, and configure the attribute rules, specifying that the Distinguished Name (DN) in the issuer name includes new-ca.
[Device] pki certificate attribute-group mygroup1
[Device-pki-cert-attribute-group-mygroup1] attribute 1 issuer-name dn ctn new-ca
[Device-pki-cert-attribute-group-mygroup1] quit
# Create certificate access control policy myacp and create a control rule, specifying that a certificate is considered valid when it matches the attribute rule in certificate attribute group mygroup.
[Device] pki certificate access-control-policy myacp
[Device-pki-cert-acp-myacp] rule 1 permit mygroup1
[Device-pki-cert-acp-myacp] quit
# Associate the HTTPS service with the SSL server policy myssl.
[Device] ip https ssl-server-policy myssl
# Associate the HTTPS service with certificate attribute access control policy myacp, ensuring that only HTTPS clients retrieving a certificate from new-ca can access the HTTPS server.
[Device] ip https certificate access-control-policy myacp
# Enable the HTTPS service.
[Device] ip https enable
# Create a local user usera, set the password to 123, and service type to telnet.
[Device] local-user usera
[Device-luser-usera] password simple 123
[Device-luser-usera] service-type telnet
2) Configure the HTTPS client Host
Open the IE on Host, type http://10.1.2.2/certsrv, and request a certificate for Host as prompted.
3) Verify the configuration
Open the IE explorer on Host, enter https://10.1.1.1, select the certificate issued by new-ca for Host, and then you can log in to Device. On the login page, type username usera, and password 123, and then you can enter the Web configuration page of Device to access and control it.
![]()
l The URL of the HTTPS server starts with https://, and that of the HTTP server starts with http://.
l For more information about PKI commands, see PKI in the Security Command Reference.
l For more information about the public-key local create rsa command, see Public Key in the Security Command Reference.
l For more information about SSL commands, see SSL in the Security Command Reference.
