- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 05-Portal Troubleshooting Guide | 204.48 KB |
Troubleshooting user access and authentication
Portal issues
Portal authentication page pushing failures
Symptom
When a user accesses any webpage that is not the portal Web server page, or directly accesses the portal Web server page, no portal authentication page is pushed for the user.
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· The host, server, and device cannot reach one other.
· HTTP proxy has been enabled on the browser.
· The webpage address entered by the user contains a non-standard TCP port number (neither 80 nor 443).
· Exceptions occur on the intermediate network or DNS server.
· HTTPS redirect on the device is not working properly.
· HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) has been enabled on the HTTPS website the user accesses.
· The portal server cannot identify the escaped characters of special characters in the URL.
· Portal server configuration errors.
Troubleshooting flow
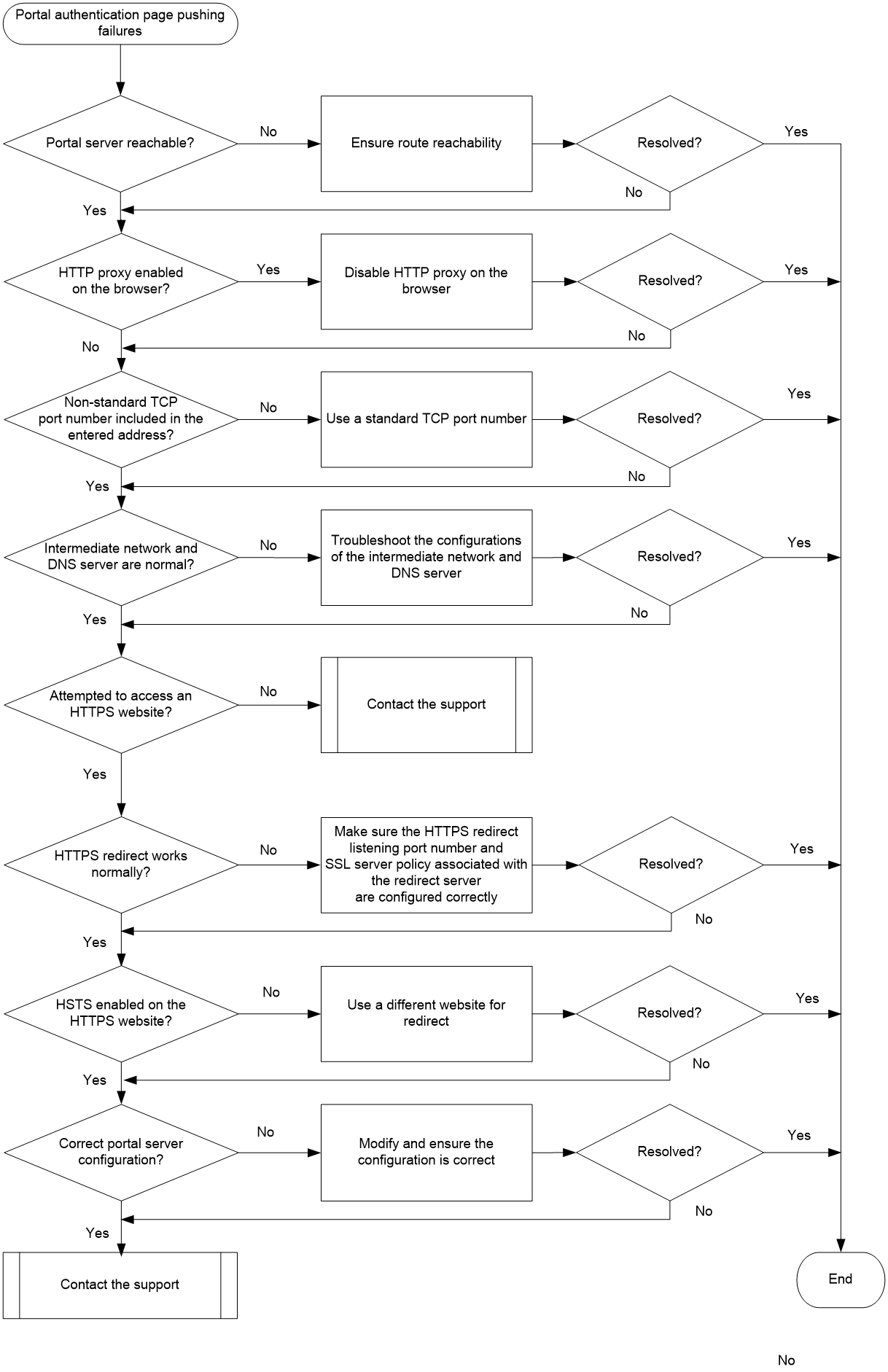
Figure 1 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 1 Flowchart for troubleshooting portal authentication page pushing failures
Solution
1. Verify that the route configuration on the client and portal server are correct.
After disabling the firewall on the client, use the ping command to check whether the portal server is reachable. If the server cannot be pinged, first check whether the route configurations on the client and the portal server are correct. Then proceed with the following steps:
¡ Check whether the return route from the portal server to the client is configured correctly.
¡ Whether multiple NICs are present on the client or the portal server.
If multiple NICs exist, some traffic between the client and the server might not pass through the network configured with portal authentication. Identify the NIC from which the user's Web access traffic is sent out. For example, if a Windows client is used, execute the route print command in the CMD window to view specific route information and identify the NIC.
Finally, use the ping command to test the connectivity for each pair of devices along the network path so as to locate the issue. First, ping the gateway from the client (for successful ping, you must disable authentication first), and then ping the server from the gateway.
2. Whether HTTP proxy has been enabled on the browser of the client.
If HTTP proxy has been enabled on the browser, users might be unable to access the portal authentication page. You must disable HTTP proxy. For example, open the Windows Internet Explorer browser, click Tools, select Internet Options > Connections > LAN Settings, and then clear the Use a proxy server for your LAN option in the Proxy server area.
3. Check whether the entered address includes a non-standard TCP port number.
Non-standard TCP port numbers refer to port numbers other than 80 or 443. If the webpage address entered by the user includes a non-standard TCP port number, the portal authentication page might be prevented from popping up. For example, http://10.1.1.1:18008. For HTTP addresses, use port 80. For HTTPS protocol addresses, use port 443.
4. Check whether exceptions have occurred on the intermediate network or DNS server:
a. Check whether the DNS server IP address is configured as a permitted address on the device.
b. Check the connectivity of the intermediate network and troubleshoot DNS server issues. On the gateway, collect traffic statistics on the downlink interface connecting the client and the uplink interface connecting the DNS server, or mirror and capture the client's packets accessing the DNS server. Confirm whether the gateway has sent out DNS requests, but has not received responses.
5. Check whether HTTPS redirect has been enabled:
a. Check whether the user is accessing an HTTPS website. If so, portal needs to redirect the user's HTTPS requests. Do not specify a TCP port number used by any other service. To display TCP port numbers that have been used by services, use the display tcp command.
b. Check whether the SSL server policy associated with the HTTPS redirect server exists. If not, complete the relevant configuration.
6. Check whether HSTS has been enabled on the HTTPS website.
With HSTS enabled, an HTTPS website requires browsers to access it using HTTPS and the certificate must be valid. When the device redirects the user's browser through HTTPS, the device uses a self-signed certificate (because it does not have the target website's certificate) to impersonate the target website and establish an SSL connection with the browser. If the browser detects the certificate as untrusted, HTTPS redirect will fail, preventing the portal authentication page from popping up. This issue is related to the specific HSTS protocol enforcement requirements set by the website, and cannot be resolved. In this case, try other websites as a best practice.
7. Check whether the portal server configuration is correct:
¡ Check whether an IP address group is configured on the portal server and whether the device is associated with an IP address group.
¡ Check whether the client IP address is within the range of the IP address group configured on the portal server.
8. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ Device configuration files, log information, and alarm messages.
¡ Screenshots of portal-related configurations on the server.
¡ Files containing the packets captured between the device and the server.
¡ Screenshots of the issue taken on the client's browser.
¡ Portal filtering rules for packet matching displayed after you execute the display portal rule command.
¡ If the issue persists, execute the debugging portal, debugging http-redirect all, or debugging ip packet command to collect debugging information.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
N/A
Portal authentication failures
Symptom
Failures or exceptions occur in portal authentication for a user.
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· The shared key configured in portal authentication server view on the device is inconsistent with that configured on the portal authentication server.
· The address of the portal authentication server configured in portal authentication server view on the device does not exist.
· The portal packets are invalid.
· The authentication domain used by the portal user is configured incorrectly.
· The shared key configured in RADIUS scheme view on the device is inconsistent with that configured on the RADIUS server.
· Failed to obtain the physical information of the user.
· The RADIUS server has denied the authentication.
· The RADIUS server is unresponsive.
· Failed to deploy the authorization ACL or user profile.
Troubleshooting flow
Figure 2 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 2 Flowchart for troubleshooting portal authentication failures
Solution
1. Check whether shared key configured in portal authentication server view on the device is inconsistent with that configured on the portal authentication server.
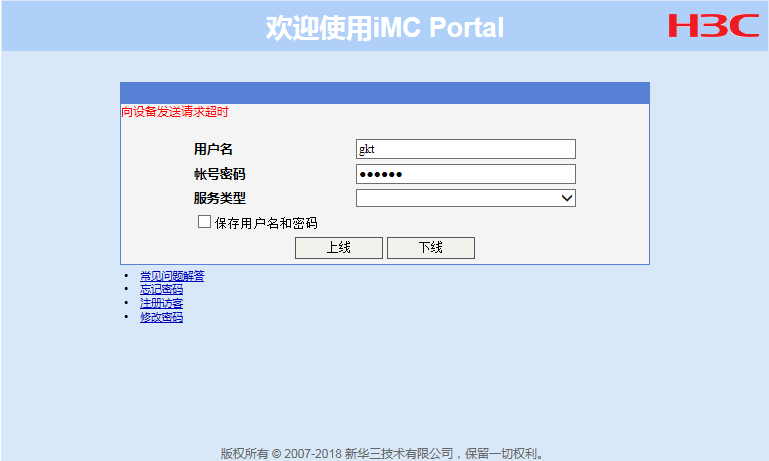
As shown in Figure 3, if the IMC server is used, enter the username and password and then click Log In, check whether a message indicating the request to the device timed out is prompted. If so, this indicates that the shared key configured in portal authentication server view on the device might be inconsistent with that configured on the server.
Figure 3 Error message on the portal login page (1)
You can troubleshoot using the following methods:
¡ Execute the debugging portal error command on the device to enable portal error debugging. If the following information is displayed on the device, it indicates that the shared key configured on the device is inconsistent with that configured on the portal server.
*Jul 28 17:51:20:774 2021 Sysname PORTAL/7/ERROR: -MDC=1; Packet validity check failed due to invalid key.
¡ Execute the display portal auth-error-record command to check whether the following information is displayed in the Auth error reason field of the command output: Packet validity check failed due to invalid authenticator.
If the shared keys are inconsistent, modify the shared key configured in portal authentication server view on the device or on the portal authentication server to ensure consistency.
2. Check whether the address of the portal authentication server configured in portal authentication server view on the device exists.
When the device receives an authentication packet sent by the portal server, it validates whether the source IP address of the packet is in the list of portal authentication server addresses configured on the device. If not, the device considers the authentication packet to be invalid and drops it.
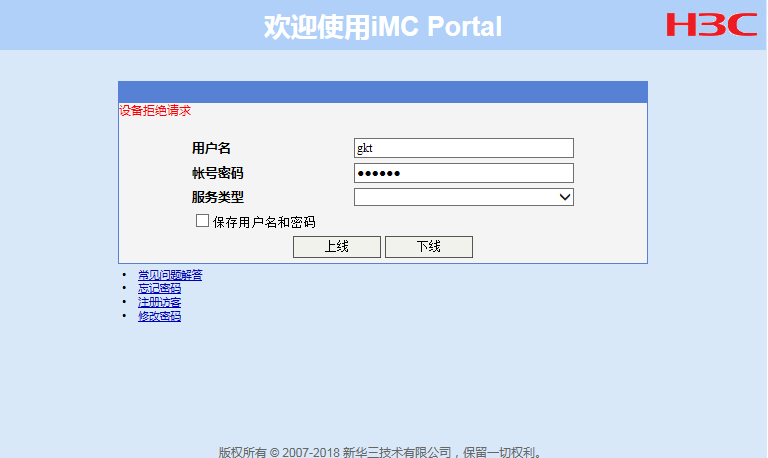
As shown in Figure 4, if the IMC server is used, enter the username and password and then click Log In, check whether a message indicating the request to the device timed out is prompted. If so, this indicates that the authentication server address configured in portal server view on the device might not exist.
Figure 4 Error message on the portal login page (2)
You can troubleshoot using the following method:
¡ Execute the debugging portal error command on the device to enable portal error debugging. If the following information is displayed on the device, it indicates that the IP address of the portal authentication server configured on the device is incorrect.
*Jul 28 19:15:10:665 2021 Sysname PORTAL/7/ERROR: -MDC=1;Packet source unknown. Server IP:192.168.161.188, VRF Index:0.
¡ Execute the display portal auth-error-record command to check whether the following information is displayed in the Auth error reason field of the command output: Packet source unknown. Server IP:X.X.X.X, VRF index:0.
If the address is incorrect, execute the ip command to modify the portal server's IP address in portal authentication sever view on the device.
3. Check whether the portal packets are invalid.
Upon receiving a portal packet sent by the portal server, the device performs a validity check on the packet. If the packet length is incorrect, or errors exist on the packet checksum, the packet will be considered as invalid and dropped.
You can check whether the portal packet is invalid using the following methods:
¡ Execute the display portal packet statistics command to check whether invalid packets exist and whether the number of invalid packets is increasing. If invalid packets exist, execute the debugging portal error command on the device to enable portal error debugging for troubleshooting.
¡ Execute the display portal auth-error-record command to check whether the following information is displayed in the Auth error reason field of the command output: Packet type invalid or Packet validity check failed because packet length and version don't match.
If the portal packets are invalid, identify the reason for invalidity and make modifications accordingly.
4. Check the authentication domain configuration used by the portal user:
The device selects the authentication domain for a portal user in this order:
a. ISP domain specified for the interface.
b. ISP domain carried in the username.
c. System default ISP domain.
If the chosen domain does not exist on the device, the device searches for the ISP domain configured to accommodate users assigned to nonexistent domains. If no such ISP domain is configured, user authentication fails.
Execute the display portal command to check whether an authentication domain is used on the authentication interface.
¡ If an authentication domain is used, check whether the authentication domain exists on the device, and whether the authentication, authorization, and accounting configurations in the domain are configured correctly.
¡ If no authentication domain is used, check whether the domain included in the username exists. If the domain does not exist, check whether the default authentication domain exists and whether the configuration in the default authentication domain is correct.
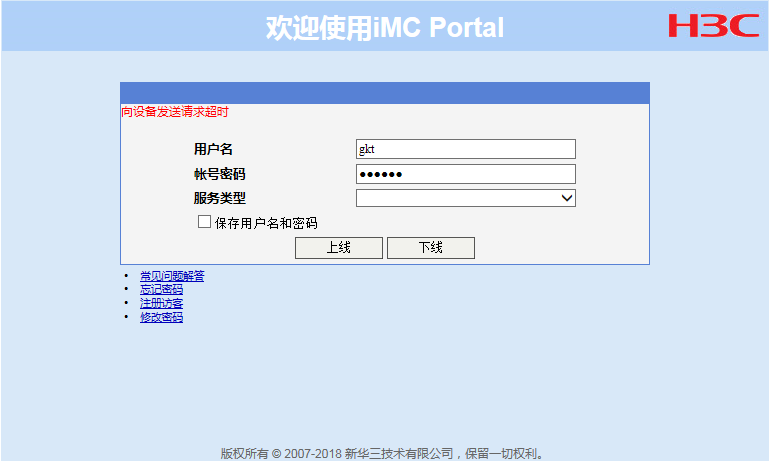
As shown in Figure 5, if the IMC server is used, enter the username and password and then click Log In, check whether a message indicating request rejection is prompted. If so, this indicates that the authentication domain configuration on the device might be incorrect.
Figure 5 Error message on the portal login page (3)
You can troubleshoot using the following method:
¡ Execute the debugging portal error command on the device to enable portal error debugging. If the following information is displayed on the device, it indicates that the authentication domain is configured incorrectly on the device and further troubleshooting is required.
*Jul 28 19:49:12:725 2021 Sysname PORTAL/7/ERROR: -MDC=1; User-SM [21.0.0.21]: AAA processed authentication request and returned error.
¡ Execute the display portal auth-error-record command to check whether the following information is displayed in the Auth error reason field of the command output: AAA authentication failed or AAA returned an error.
If the authentication domain is configured incorrectly, execute the related command to configure a correct authentication domain used by the portal user.
5. Check whether the shared key configured in RADIUS scheme view on the device is consistent with that configured on the RADIUS server.
As shown in Figure 6, if the IMC server is used, enter the username and password and then click Log In, check whether a message indicating the request to the device timed out is prompted. If so, this indicates that the shared key configured in RADIUS scheme view is inconsistent with that configured on the server.
Figure 6 Error message on the portal login page (4)
Execute the debugging portal error command on the device to enable portal error debugging. If the following information is displayed on the device, it indicates that the shared key configured in RADIUS scheme view is inconsistent with that configured on the server.
*Jul 28 19:49:12:725 2021 Sysname RADIUS/7/ERROR: -MDC=1; The response packet has an invalid Response Authenticator value.
When the device initiates an authentication request to the RADIUS server, the server first validates the shared key used in the request. If the validation fails, the server notifies the device of the failure. If the shared key configuration is incorrect, make sure the shared key configured in the RADIUS scheme view is consistent with that configured on the server.
6. Check whether the device failed to obtain physical information about the user.
During the user's onboarding process, portal searches for the user's physical information, and identifies information such as the interface through which the user accesses based on the corresponding physical information. If the search for physical information fails, the user will fail to come online.
You can troubleshoot using the following method:
¡ Execute the debugging portal event command on the device to enable portal event debugging. If the following information is displayed on the device, it indicates that the device failed to obtain physical information about the user.
*Jul 28 19:49:12:725 2021 Sysname PORTAL/7/ERROR: -MDC=1; User-SM [21.0.0.21]: Failed to find physical info for ack_info.
¡ Execute the display portal auth-error-record or display portal auth-fail-record command to check whether the following information is displayed in the Auth error reason field of the command output: Failed to obtain user physical information or Failed to get physical information.
After you confirm that obtaining the user's physical information failed, check whether an entry for the authentication user exists on the device. If no entry exists, go to the next step.
7. Check whether the RADIUS server has rejected the authentication:
a. Many reasons might cause the RADIUS server to reject the authentication of a user. Most common ones include incorrect username or password, or failure in matching the RADIUS server's authorization policy. To resolve these issues, first check the authentication logs on the server, or enable RADIUS error debugging on the device by using the debugging radius error command to view the relevant debugging information. After identifying the root causes, adjust the configurations on the server, client, or device accordingly.
b. Execute the display portal auth-fail-record command to identify the portal authentication failure reason for the user displayed in the Auth error reason field of the command output.
8. Check whether the RADIUS server is unresponsive.
You can troubleshoot using the following methods:
¡ Execute the display radius scheme command and view the server's state displayed in the State field. If the state is Blocked, it indicates the server is unavailable.
¡ Check whether the device prints the following log:
RADIUS/4/RADIUS_AUTH_SERVER_DOWN: -MDC=1; RADIUS authentication server was
blocked: server IP=192.168.161.188, port=1812, VPN instance=public.
¡ Execute the debugging radius event command on the device to enable debugging for RADIUS events. If the following information is printed on the device, it indicates that the RADIUS server is unresponsive.
*Jul 28 19:49:12:725 2021 Sysname RADIUS/7/evnet: -MDC=1; Reached the maximum retries.
After confirming that the RADIUS server is unresponsive, proceed with the following steps:
a. Check whether the device's IP address has been added on the server.
- If not, add the device's IP address on the server. If yes, make sure the added device IP address is consistent with the source IP address of the authentication request. By default, the source IP address of RADIUS packets sent to the RADIUS server is the IP address of the outgoing interface for these packets.
- If yes, make sure the device IP address added on the server is the source IP address of the authentication request.
b. View packets on both the device and the server, and check whether exceptions has occurred in the intermediate links. For example, a firewall in the intermediate network might not allow RADIUS (default authentication port 1812) packets to pass through. If a large number of users cannot be authenticated and RADIUS server down records appear in the logs on the device, there is a high probability that exceptions has occurred on the server or the intermediate network, and further check is required.
9. Check whether the authorization ACL or user profile failed to be deployed.
With portal strict checking enabled, if the authorized ACL or user profile does not exist on the device or the device fails to be deployed, the device will force the portal user offline.
a. Execute the display portal command and view the Strict checking field to check whether strict checking is enabled on the device. Then determine whether you need to enable strict checking. If it is not required, disable it directly. If it is required, go to step b.
b. Execute the display acl or display user-profile command on the device to check whether the ACL or user profile authorized by the AAA server does not exist. If the ACL or user profile does not exist, determine whether authorization by the server is required. If yes, add the corresponding ACL or user profile configurations on the device.
10. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
¡ Information collected after you execute the display portal auth-error-record or display portal auth-fail-record command.
¡ Screenshots of portal-related configurations on the portal server.
¡ Files containing the packets captured between the device and the AAA server.
¡ Screenshots of the issue taken on the client's browser.
¡ Debugging information collected after you enable the debugging portal command.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
RADIUS/4/RADIUS_AUTH_SERVER_DOWN
Portal authentication user disconnections
A portal user is disconnected after coming online for a period of time.
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· The user session has timed out.
· User idle cut.
· Accounting update failures.
· User traffic reaches the threshold.
· The server forces the user offline.
· The user failed the online detection.
· The interface where the user accesses is down.
Troubleshooting flow
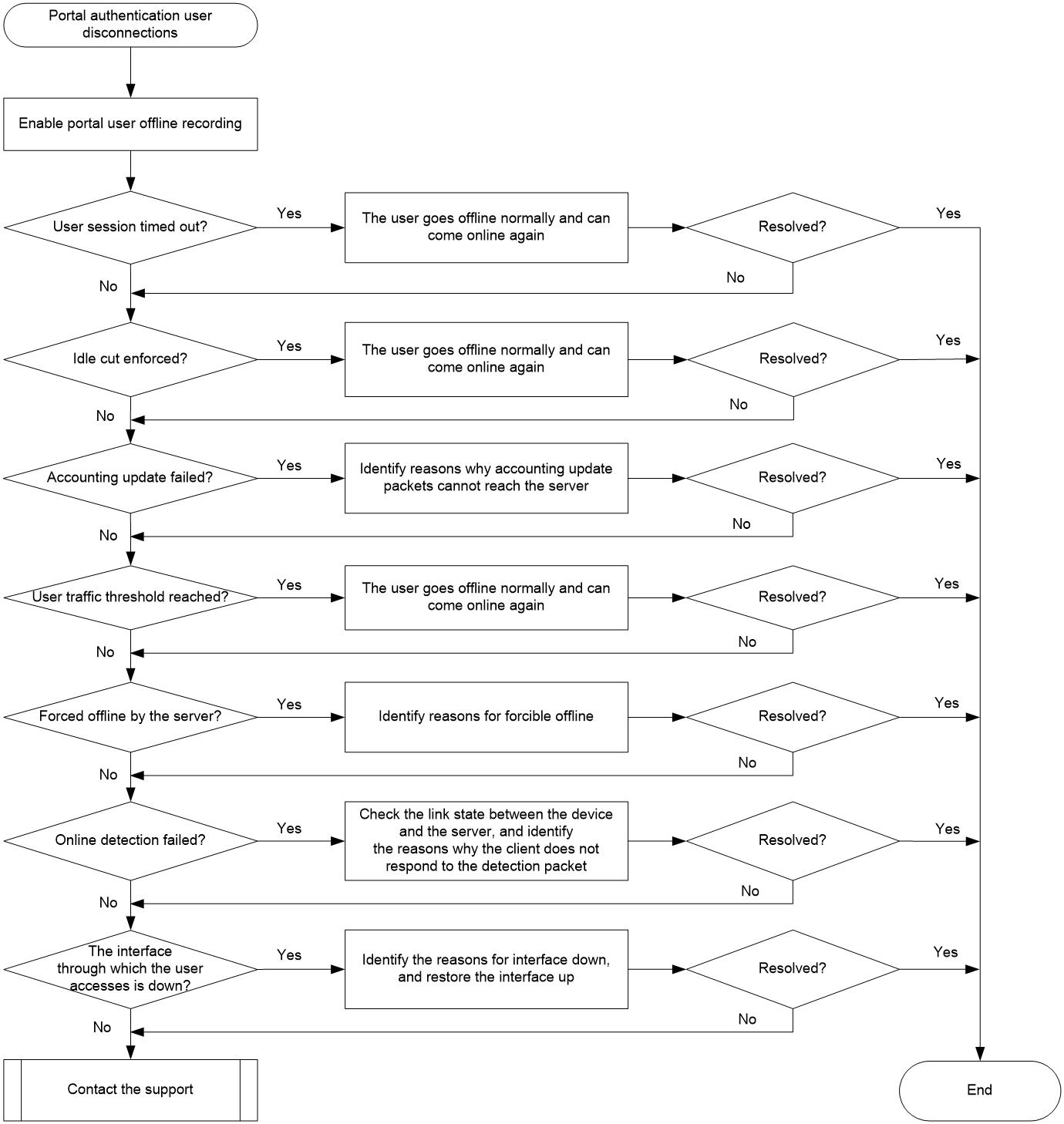
Figure 7 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 7 Flow chart for troubleshooting portal authentication user disconnections
Solution
1. Execute the portal logout-record enable command to enable portal user offline recording.
2. Check whether the user session has timed out.
If the AAA server has deployed the session timeout time (single online duration) to the portal user, once the user's online duration exceeds the timeout time, the device logs out the user.
Use the following methods to check whether the portal user goes offline because of session timeout:
¡ View the user offline records on the AAA server.
¡ Execute the display portal logout-record command to view the user logout reason.
<Sysname> display portal logout-record all
Total logout records: 1
User name : gkt
User MAC : 0800-2700-94ad
Interface : Vlan-interface100
User IP address : 21.0.0.20
AP : N/A
SSID : N/A
User login time : 2021-07-29 11:05:58
User logout time : 2021-07-29 11:05:58
Logout reason : Session timeout
¡ Execute the debugging portal error command on the device to enable portal error debugging. If the following information is displayed on the device, it indicates that the portal user is logged out because of user session timeout.
*Jul 28 17:51:20:774 2021 Sysname PORTAL/7/ERROR: -MDC=1; Session timer timed out and the user will be logged off.
The user logout triggered by session timeout is a normal logout. The user can come online again.
3. Check whether the user goes offline because of user idle cut.
With the idle cut feature configured, if the device or the AAA server has authorized an idle timeout period for the user, the device periodically checks the user's traffic after the user comes online. If the user's traffic generated within the specified idle timeout period is less than the specified data volume, the user will be forced offline.
You can use the following methods to check whether the portal user goes offline because of idle cut:
¡ View the user logout records on the AAA server.
¡ Execute the display portal logout-record command to view the user offline records.
<Sysname> display portal logout-record all
Total logout records: 1
User name : gkt
User MAC : 0800-2700-94ad
Interface : Vlan-interface100
User IP address : 21.0.0.20
AP : N/A
SSID : N/A
User login time : 2021-07-29 11:05:58
User logout time : 2021-07-29 11:05:58
Logout reason : Idle timeout
¡ Execute the debugging portal error command on the device to enable portal error debugging. If the following information is displayed on the device, it indicates that the portal user goes offline because of idle cut timer timeout.
*Jul 28 17:51:20:774 2021 Sysname PORTAL/7/ERROR: -MDC=1; Idle-cut timer timed out and the user will be logged off.
The logout triggered by idle timeout is a normal logout. The user can come online again.
4. Check whether accounting update failures.
When a remote portal authentication user comes online, the device periodically sends accounting-update packets to the AAA server. If the link between the device and the AAA server is disconnected or the server fails, the device fails to send accounting-update packets. When the maximum number of retransmissions is reached, transmission of accounting-update packets fails and the accounting update failure policy has been configured on the device, the user will be triggered to go offline. The accounting update failure policy is configured by using the accounting update-fail offline command.
You can use the following methods to check whether the user goes offline because of accounting update failures:
¡ Execute the display portal logout-record command to view the user offline records.
<Sysname> display portal logout-record all
Total logout records: 1
User name : gkt
User MAC : 0800-2700-94ad
Interface : Vlan-interface100
User IP address : 21.0.0.20
AP : N/A
SSID : N/A
User login time : 2021-07-29 11:05:58
User logout time : 2021-07-29 11:05:58
Logout reason : Accounting update failure
¡ Execute the display interface command to check whether the port on the device connected to the AAA server has any changes, or whether the AAA server has any exception records. Or, execute the display radius scheme command to check whether Block is displayed in the State field (indicating the state of the server). If yes, the reason for the user logout might be accounting update failures.
¡ Execute the debugging portal error command on the device to enable portal error debugging. If the following information is displayed on the device, it indicates that the portal user goes offline because of accounting update failures.
*Jul 28 17:51:20:774 2021 Sysname PORTAL/7/ERROR: -MDC=1; Processed accounting-update failed and user logout.
If you confirm that the user goes offline because of accounting update failures, check the link state between the device and the server, and check whether the relevant accounting configurations on the device and the AAA server have changed.
5. Check whether the user's traffic has reached the threshold.
When a user comes online, if the AAA server deploys a traffic threshold, the device will force the user offline once the user's traffic exceeds the deployed threshold.
You can use the following methods to check whether the user goes offline because traffic threshold reaching:
¡ Check the user offline records on the AAA server.
¡ Execute the display portal logout-record command to view the user offline records.
<Sysname> display portal logout-record all
Total logout records: 1
User name : gkt
User MAC : 0800-2700-94ad
Interface : Vlan-interface100
User IP address : 21.0.0.20
AP : N/A
SSID : N/A
User login time : 2021-07-29 11:05:58
User logout time : 2021-07-29 11:05:58
Logout reason : User traffic reached threshold
The user logout triggered by traffic threshold reaching is a normal logout. The user can come online again.
6. Check whether the AAA server actively kicks the user offline.
After RADIUS session-control feature is enabled on the device (using the radius session-control enable command), the device immediately forces a user offline upon reception of a disconnection request from the AAA server. If the feature is enabled, you can use the following methods to check whether the user is forced offline by the AAA server:
¡ View the user offline records on the AAA server.
¡ Execute the display portal logout-record command to view the user offline records.
<Sysname> display portal logout-record all
Total logout records: 1
User name : gkt
User MAC : 0800-2700-94ad
Interface : Vlan-interface100
User IP address : 21.0.0.20
AP : N/A
SSID : N/A
User login time : 2021-07-29 11:05:58
User logout time : 2021-07-29 11:05:58
Logout reason : Force logout by RADIUS server
For more information about the reasons for the forcible user logout, contact the server administrator.
7. Check whether the user goes offline because of online detection failures.
If the portal user online detection feature is enabled on the device (using the portal user-detect command), the device periodically sends detection packets to the user client. If the device has not received a response from the client after the specified maximum number of attempts, it will force the user offline.
Check whether the portal user online detection feature is enabled on the device. If the feature is enabled, you can use the following methods to check whether the user goes offline because of user online detection failures:
¡ View the user offline records on the AAA server.
¡ Execute the display portal logout-record command to view the user offline records.
<Sysname> display portal logout-record all
Total logout records: 1
User name : gkt
User MAC : 0800-2700-94ad
Interface : Vlan-interface100
User IP address : 21.0.0.20
AP : N/A
SSID : N/A
User login time : 2021-07-29 11:05:58
User logout time : 2021-07-29 11:05:58
Logout reason : User detection failure
After you confirm that the user goes offline because of user online detection failures, check the link state between the client and the device, and identify the reasons why the client does not respond to the detection packet.
8. Check whether the interface through which the portal user accesses is down.
If the interface used by the portal user goes down for a period of time, the device forces all portal users accessing through this interface offline.
You can confirm use the following methods to check whether the user has gone offline because of interface down:
¡ View the user logout records on the AAA server.
¡ Execute the display interface command to check whether the state of the interface changed. If the interface's state changed and the change time is close to the time when the user went offline, the reason for the user logout might be interface down.
¡ Execute the display portal logout-record command to view the user logout records
<Sysname> display portal logout-record all
Total logout records: 1
User name : gkt
User MAC : 0800-2700-94ad
Interface : Vlan-interface100
User IP address : 21.0.0.20
AP : N/A
SSID : N/A
User login time : 2021-07-29 11:05:58
User logout time : 2021-07-29 11:05:58
Logout reason : Interface down
If you confirm that the user goes offline because of the interface down, identify the reasons for interface down, such as loosely connected network cable.
9. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
¡ Screenshots of portal-related configurations on the portal server.
¡ User logout records on the AAA server.
¡ Files containing the packets captured between the device and the AAA server.
¡ Screenshots of the issue taken on the client's browser.
¡ Debugging information collected after you enable the debugging portal command.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
N/A