- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-802.1X Troubleshooting Guide | 91.07 KB |
Troubleshooting user access and authentication
802.1X issues
802.1X user authentication failure
Symptom
A user fails 802.1X authentication or an exception occurs during 802.1X authentication.
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· 802.1X is not enabled globally or on the interface that the user accesses.
· The 802.1X client cannot correctly send or receive authentication packets.
· The authentication method configured on the device is inconsistent with that on the RADIUS server.
· Incorrect settings exist in the authentication domain used by the 802.1X user or other authentication-related settings have errors.
· The RADIUS server does not respond.
· The RADIUS server rejects the authentication request of the user.
· Authorization attribute assignment fails.
· The 802.1X user is in quiet state.
· The maximum number of online 802.1X users already reached.
Troubleshooting flow
Figure 1 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 1 Flowchart for troubleshooting 802.1X user authentication failure
Solution
|
IMPORTANT: · As a best practice, do not enable debugging when the device is running correctly. However, you can enable debugging when a fault occurs for troubleshooting purposes. · Save the results of the steps in this section in a timely manner, so that you can quickly collect and provide feedback if the fault cannot be resolved. |
1. Verify that 802.1X is enabled globally and on the interface that the user accesses.
Execute the display dot1x command on the device to identify whether 802.1X is enabled both globally and on the interface that the user accesses.
¡ If message 802.1X is not configured appears, 802.1X is not enabled globally. You can execute the dot1x command in system view to globally enable 802.1X.
¡ If the output from the display dot1x command has global configuration information but does not have interface-specific configuration information, 802.1X is not enabled on the interface. You can execute the dot1x command in interface view.
2. Verify that the 802.1X client can correctly send and receive authentication packets.
¡ Verify that the 802.1X client version is a version supported by both the device and the server.
¡ Verify that the link between the device and the 802.1X client is correctly connected.
¡ Capture packets to inspect whether the device can correctly exchange data packets with the client and analyze the captured packet file to locate and resolve the issue.
3. Verify that the authentication method is consistent on the device and the RADIUS server.
On the device, 802.1X supports EAP termination (PAP and CHAP authentication methods) and EAP relay (EAP authentication method). When you configure the authentication method, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
¡ Make sure the authentication method configured on the device and the RADIUS server is consistent and the client supports the authentication method.
¡ Local authentication only supports EAP termination.
Execute the display dot1x command on the device to check the current 802.1X authentication method.
<Sysname> display dot1x
Global 802.1X parameters:
802.1X authentication : Enabled
DR member configuration conflict : Unknown
EAP authentication : Enabled
...
If the authentication method is inconsistent with the server, you can execute the dot1x authentication-method command to change the authentication method.
4. Verify that the authentication domain and its related settings are correctly configured.
The device chooses an authentication domain for an 802.1X user in the following order: The mandatory 802.1X authentication domain specified on the interface that the user accesses -> The ISP domain specified in the username -> The default ISP domain in the system.
a. Execute the display dot1x command on the device to examine whether a mandatory 802.1X authentication domain has been specified on the interface that the user accesses.
<Sysname> display dot1x
...
Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/6 is link-up
802.1X authentication : Enabled
...
Multicast trigger : Enabled
Mandatory auth domain : Not configured
...
If a mandatory 802.1X authentication domain has been specified, execute the display domain command to verify that authentication methods are correctly configured in the mandatory 802.1X authentication domain.
b. If no mandatory 802.1X authentication domain has been specified, check the 802.1X username for a domain name. If the 802.1X username includes a domain name, verify that the domain name delimiter is also supported by the RADIUS server, and then locate the domain specified by the username and verify that the settings in the domain are correct.
c. If the 802.1X username does not include a domain name, check the configuration of the default authentication domain.
d. If the default authentication domain does not exist, identify whether the domain if-unknown command has been executed. If the command has been executed, verify that authentication methods are correctly configured in the domain specified by using the command.
e. If none of the above mentioned authentication domains on the device are available for the user, the user cannot complete the authentication.
5. Verify that the RADIUS server can respond to the device.
For more information about the troubleshooting procedure, see the issue of RADIUS server no response in “Troubleshooting AAA.”
6. Identify whether the offline reason is authentication rejection.
Execute the debugging dot1x event command to enable 802.1X authentication event debugging.
¡ If the system generates debugging message Local authentication request was rejected, the user is rejected by local authentication. Causes for local authentication rejection include nonexistence of local user account, incorrect username or password, and incorrect user service type.
¡ If the system generates debugging message The RADIUS server rejected the authentication request, the user is rejected by the RADIUS server. Many reasons can cause RADIUS server authentication rejection. The most common ones include absence of username on the server, incorrect username or password, and no matching RADIUS authorization policy. You can execute the debugging radius error command to enable RADIUS error debugging and check the debugging messages in the command output. In addition, execute the test-aaa command on the device to initiate a RADIUS request test. After you locate the issue, adjust the settings of the server, device, and client accordingly.
7. Verify that authorization attributes are assigned successfully to the user.
a. Execute the debugging dot1x event command to enable 802.1X authentication event debugging. If the system generates message Authorization failure, the authorization has failed.
b. Verify that the authorization attributes, for example, the authorization ACL and VLAN, on the server are configured correctly, to ensure that the server assigns accurate authorization attributes to the user.
c. Execute the display acl and display vlan commands to verify that the corresponding authorization attributes exist on the device. If an authorization attribute does not exist, you must create it on the device to ensure that the user can obtain the authorization information.
8. Examine whether the 802.1X user is in quiet state.
Execute the display dot1x command on the device and check the Quiet timer and Quiet period fields and the Auth state field in the Online 802.1X users area. If the quiet timer is enabled and the value for the Auth state is Unauthenticated for the 802.1X user, the 802.1X user is in quiet state.
The device cannot process any 802.1X authentication requests for the quiet 802.1X user until the quiet timer expires. You can wait until the quiet timer expires or execute the dot1x timer quiet-period command to shorten the quiet period. When the quiet timer expires, initiate 802.1X authentication for the user and verify that the user can pass 802.1X authentication.
9. Identify whether the number of online 802.1X users has reached the maximum value.
a. Execute the display dot1x interface command on the device to check the information on the interface that the user accesses. The Max online users field displays the maximum number of online users supported on the interface and the Online 802.1X users field displays the current number of online users on the interface. Compare the values for these two fields to determine whether the number of online 802.1X users has reached the maximum value.
b. If the number of online 802.1X users on the interface has reached the maximum value, you can execute the dot1x max-user command to increase the maximum number of online 802.1X users allowed on the interface.
c. If the number of online 802.1X users on the interface cannot be increased, you can wait for other users to go offline or connect the user to another interface.
10. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
¡ The debugging messages collected by executing the debugging dot1x all and debugging radius all commands.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
· DOT1X_CONFIG_NOTSUPPORT
· DOT1X_LOGIN_FAILURE
· DOT1X_MACBINDING_EXIST
802.1X user logoff
Symptom
An 802.1X user goes offline unexpectedly after it passes authentication successfully to come online.
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· Settings related to 802.1X authentication have changes on the device.
· The user fails online user handshake.
· Real-time accounting fails for the user.
· 802.1X reauthentication fails.
· The server forces the user to go offline.
· The user goes offline after offline detection is enabled.
· The session of the user times out.
Troubleshooting flow
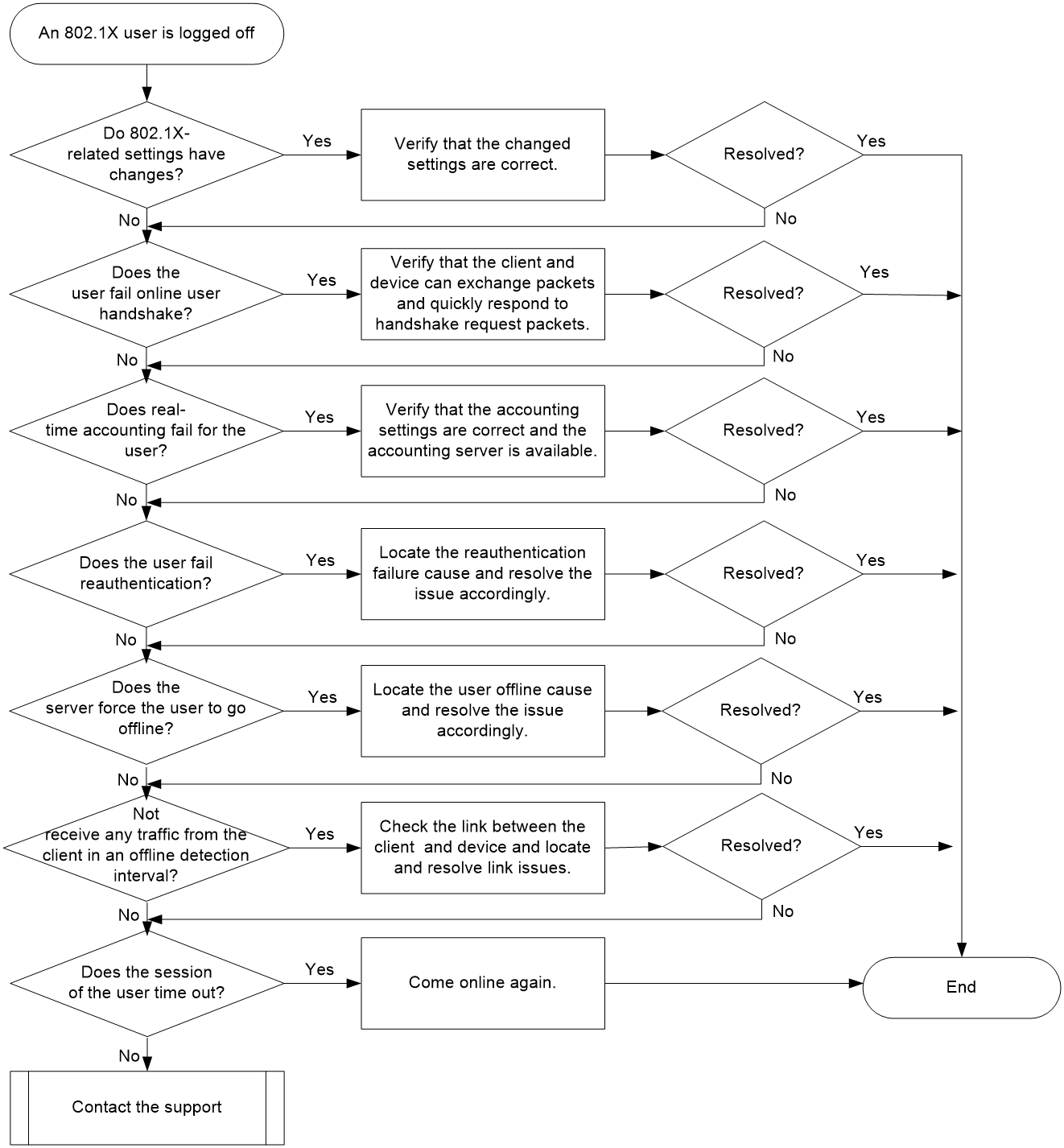
Figure 2 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 2 Flowchart for troubleshooting 802.1X user logoff
Solution
|
IMPORTANT: · As a best practice, do not enable debugging when the device is running correctly. However, you can enable debugging when a fault occurs for troubleshooting purposes. · Save the results of the steps in this section in a timely manner, so that you can quickly collect and provide feedback if the fault cannot be resolved. |
1. Identify whether settings related to 802.1X authentication have changes on the device and verify that the changed settings are correct.
a. Execute the display dot1x command to examine whether the 802.1X authentication settings on the device have changes, and verify that the changed settings are correct.
b. Execute the display domain command to examine whether settings in the authentication domain used by the user have changes, and verify that the changed settings are correct.
2. Identify whether the user fails online user handshake and troubleshoot the cause of the failure.
a. Execute the display dot1x command to check the Handshake field to identify whether 802.1X online user handshake is enabled on the interface that the user accesses.
b. Execute the debugging dot1x event command to enable 802.1X authentication event debugging. If the system generates debugging message Handshake interaction failure, the user has failed online user handshake. You can capture packets to identify whether the device and the client can correctly send and receive EAP data packets and analyze the captured packet file to locate and resolve the issue.
3. Examine whether real-time accounting fails for the user and troubleshoot the cause of the failure.
Execute the debugging dot1x event command to enable 802.1X authentication event debugging. If the system generates debugging message Real-time accounting failure, real-time accounting has failed for the user. In this case, check the link between the device and the accounting server for connectivity issues, and identify whether settings related to accounting have changes on the device and the accounting server. Verify that the changed settings are correct.
4. Identify whether the user is logged off due to a reauthentication failure and troubleshoot the cause of the failure.
a. Execute the display dot1x command to check the Periodic reauth field for the enabling status of 802.1X periodic reauthentication on the interface that the user accesses.
b. To troubleshoot the cause of the reauthentication failure, use the method in "802.1X user authentication failure."
5. Identify whether the user is logged off by the RADIUS server if RADIUS remote authentication is used.
Execute the debugging dot1x event command to enable 802.1X authentication event debugging. If the system generates debugging message The RADIUS server forcibly logged out the user, the user is logged off by the RADIUS server. You can contact the server administrator to identify the reason for the logoff.
6. Identify whether the user is logged off because the device has not received any traffic from the user before the offline detection timer expires, and troubleshoot the issue.
a. Execute the debugging dot1x event command to enable 802.1X authentication event debugging. If the system generates debugging message Offline detect timer expired, it indicates that the device has not received any traffic from the user on the interface within the offline detection interval. As a result, the device cuts off the user's connection, causing the user to go offline.
b. Check the link between the client and the device for connectivity issues to troubleshoot the reason why the client did not send any packets.
7. Examine whether the session of the user has timed out.
a. Identify whether the session timeout time has been configured for the 802.1X user.
- If RADIUS remote authentication is used, execute the debugging radius packet command to enable RADIUS packet debugging and check the debugging messages to identify whether the response packets sent from the server contain the Session-Timeout attribute.
- If local authentication is used, execute the display local-user command to check for the existence of the Session-timeout field in the command output.
b. Execute the debugging dot1x event command to enable 802.1X authentication event debugging. If the system generates debugging message User session timed out, the user goes offline due to session timeout.
c. It is normal for a user to go offline due to session timeout, and the user can come online again.
8. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
¡ The debugging messages collected by executing the debugging dot1x all and debugging radius all commands.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
· DOT1X_LOGOFF
· DOT1X_LOGOFF_ABNORMAL