- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 03-MAC Authentication Troubleshooting Guide | 113.95 KB |
Troubleshooting user access and authentication
MAC authentication issues
MAC authentication failures
Symptom
Failures or exceptions occur in MAC authentication for a user.
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· The user has come online through other authentication methods.
· MAC authentication is not enabled globally or on the interface.
· The authentication method configured on the device is not consistent with that on the RADIUS server.
· The authentication domain used by the MAC authentication user and related settings are not configured correctly.
· No response from the RADIUS server.
· The local authentication or RADIUS authentication request is rejected.
· Failed to deploy the authorization attributes.
· The user's MAC address has been set as a silent MAC address.
· The number of concurrent online MAC authentication users on the interface has reached the maximum.
Troubleshooting flow
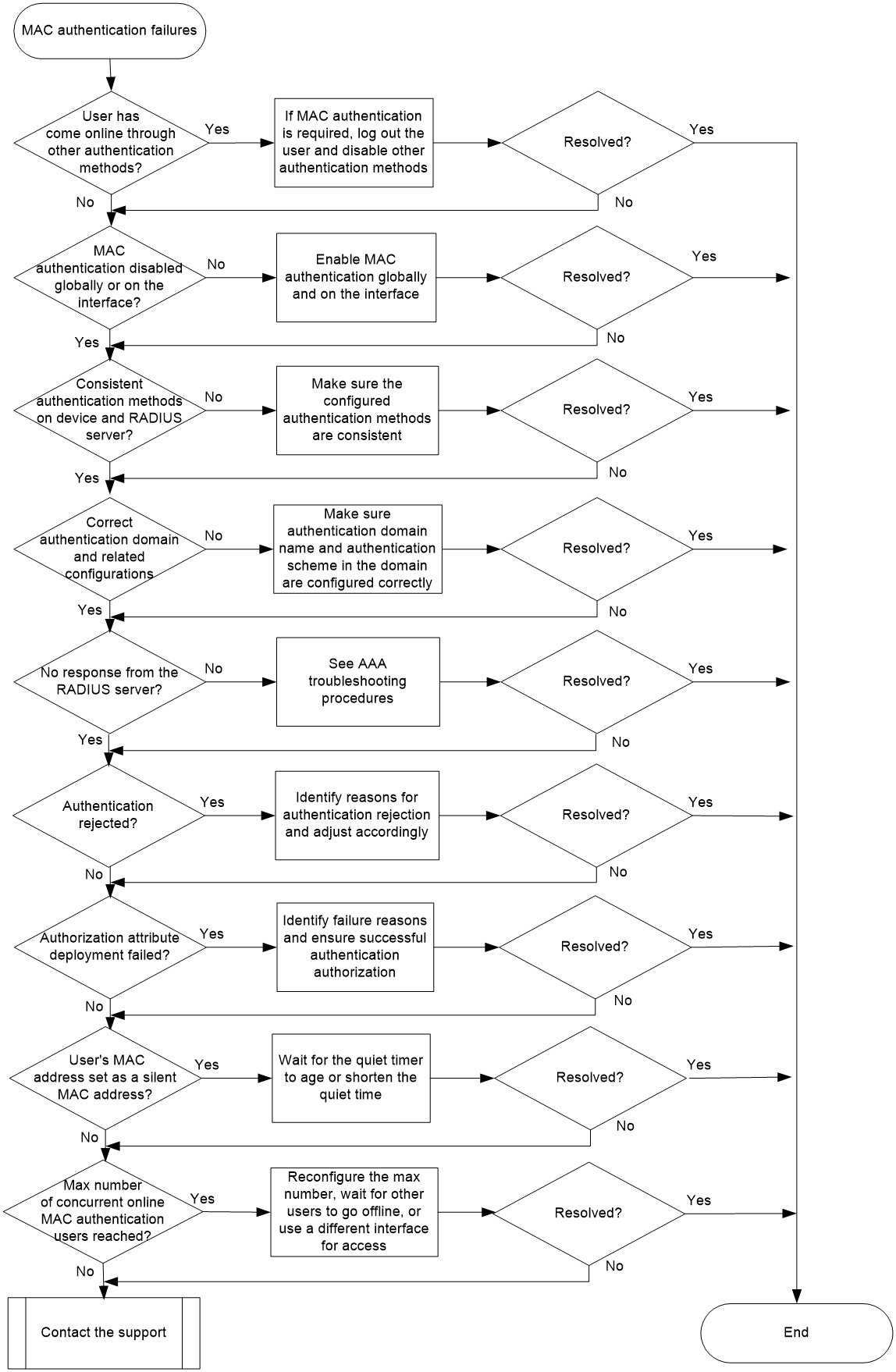
Figure 1 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 1 Flowchart for troubleshooting MAC authentication failures
Solution
|
CAUTION: · Do not enable the debugging commands when the device is operating normally. Enable the commands when you reproduce the issue after it has occurred. · Save the execution results of the following steps promptly, so that information can be quickly collected and provided if the issue persists. |
1. Check whether the user has come online through other authentication methods.
By default, the authentication order on a port is 802.1X authentication and then MAC authentication.
Execute the display dot1x connection command to check whether the user has successfully passed 802.1X authentication and come online. If the user has come online, determine whether the user needs to come online again through MAC authentication. If MAC authentication is required, log out the user, disable 802.1X authentication, and then configure the user to perform MAC authentication.
2. Check whether MAC authentication is enabled globally or on the interface:
a. Execute the display mac-authentication command, if MAC authentication is not configured. is prompted, global MAC authentication is disabled. To enable it, execute the mac-authentication command in system view.
b. Execute the display mac-authentication command. If global MAC authentication configuration exists, but MAC authentication configuration on the user authentication interface does not exist, execute the mac-authentication command in the view of the user authentication interface.
3. Check whether the authentication method configured on the device is consistent with that on the RADIUS server.
The device supports using both CHAP and PAP authentication methods for MAC authentication.
Execute the dis mac-authentication command to check whether the authentication method used for MAC authentication displayed in the Authentication method field is consistent with that configured on the RADIUS server. If they are different, execute the mac-authentication authentication-method command to modify the configuration on the device.
4. Check whether the authentication domain and related configurations are configured correctly.
MAC authentication users accessing through the port will select the authentication domain in the following order: the authentication domain specified on the port, the authentication domain specified in system view, and then the default authentication domain of the system.
a. Execute the display mac-authentication command on the device to check whether a MAC authentication domain for user authentication is configured on the system and authentication interface.
<Sysname> display mac-authentication
Global MAC authentication parameters:
MAC authentication : Enabled
Authentication method : PAP
Authentication domain : Not configured, use default domain
…
Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/6 is link-up
MAC authentication : Enabled
Carry User-IP : Disabled
Authentication domain : Not configured
…
b. If an authentication domain used for MAC authentication users is configured on the authentication interface, execute the display domain command to check whether the authentication scheme in the authentication domain is configured correctly. If an authentication domain is not configured on the authentication interface, but is configured in system view, execute the display domain command to check whether the authentication scheme in the authentication domain is configured correctly.
c. If no authentication domain used for MAC authentication users is configured on both the authentication interface and system view, check the configuration of the default authentication domain.
d. If no default authentication domain exists and a domain to accommodate users assigned to nonexistent domains has been configured by the domain if-unknown command, check whether the authentication scheme in the domain is configured correctly.
e. If none of the authentication domains mentioned above exists on the device, the user cannot perform authentication.
5. Check whether the RADIUS server is responsive.
For more information, see troubleshooting RADIUS server unresponsiveness in AAA troubleshooting procedures.
6. Check whether the authentication request is rejected:
Execute the debugging mac-authetication event command to enable debugging for MAC authentication events.
¡ If the system prompts Local authentication request was rejected., it indicates that the local authentication request is rejected. The causes for local authentication rejection includes non-existent local user, incorrect user password, and incorrect service type.
¡ If the system prompts The RADIUS server rejected the authentication request., it indicates that the request is rejected by the RADIUS server. Common causes for server authentication rejection includes missing username on the server, inconsistent username formats, incorrect username password, and RADIUS server policy mismatch.
Execute the debugging radius error command on the device to enable debugging for RADIUS errors. You can also execute the test-aaa command to perform a RADIUS request test on the device. After identifying the issue, adjust the server, device, and client configurations accordingly.
7. Check whether authorization attributes failed to be deployed.
Execute the debugging mac-authentication event command to enable debugging for MAC address authentication events. If the device prompts Authorization failure.,, it indicates an authorization failure.
a. Check whether the authorization-fail-offline feature has been configured in system view using the authorization fail user offline command. If this feature is not configured, users can stay online after authorization failures by default. This indicates that the authentication failure is not caused by an authorization failure. Proceed with other steps.
b. Check whether the authorization attribute settings on the server are correct. Make sure the authorization attributes deployed by the server are correct.
c. Execute commands such as display acl or display vlan to check whether the corresponding authorization attributes exist on the device. If the attributes do not exist, create relevant authorization attributes on the device, and make sure that the user can obtain the authorization information.
8. Check whether the user's MAC address has been set as a silent MAC address.
Execute the display mac-authentication command to view the information displayed in the Silent MAC users field. If the user's MAC address is a silent MAC address, wait for the quiet timer to age before performing MAC authentication again. You can reconfigure the quiet timer using the mac-authentication timer quiet command.
9. Check whether the number of concurrent online MAC authentication users on the interface has reached the maximum:
a. Execute the display mac-authentication command to view information on the authentication interface. View the maximum number of concurrent online users allowed on the interface displayed in the Max online users field and the number of current online users displayed in the Current online users field. Compare the two numbers to determine whether the number of concurrent online MAC authentication users on the interface has reached the maximum.
b. If the maximum number of concurrent online users has been reached, execute the mac-authentication max-user command to increase the maximum number of concurrent MAC authentication users on the interface.
c. If the number of maximum number of concurrent MAC authentication users cannot be increased, wait for other users to go offline or use a different port for user access.
10. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
¡ Log information collected after you execute the mac-authentication access-user log enable command.
¡ Debugging information collected after you execute the debugging mac-authentication all and debugging radius all commands.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
· MACA_ENABLE_NOT_EFFECTIVE
· MACA_LOGIN_FAILURE
MAC authentication user disconnections
Symptom
A MAC authentication user is disconnected unexpectedly after passing authentication and coming online.
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· The user has come online using 802.1X authentication.
· MAC authentication-related configurations on the device have changed.
· Real-time accounting of MAC authentication user's traffic has failed.
· The user failed MAC reauthentication.
· The server forces the user offline.
· The user goes offline after offline detection is enabled.
· The user session has timed out.
Troubleshooting flow
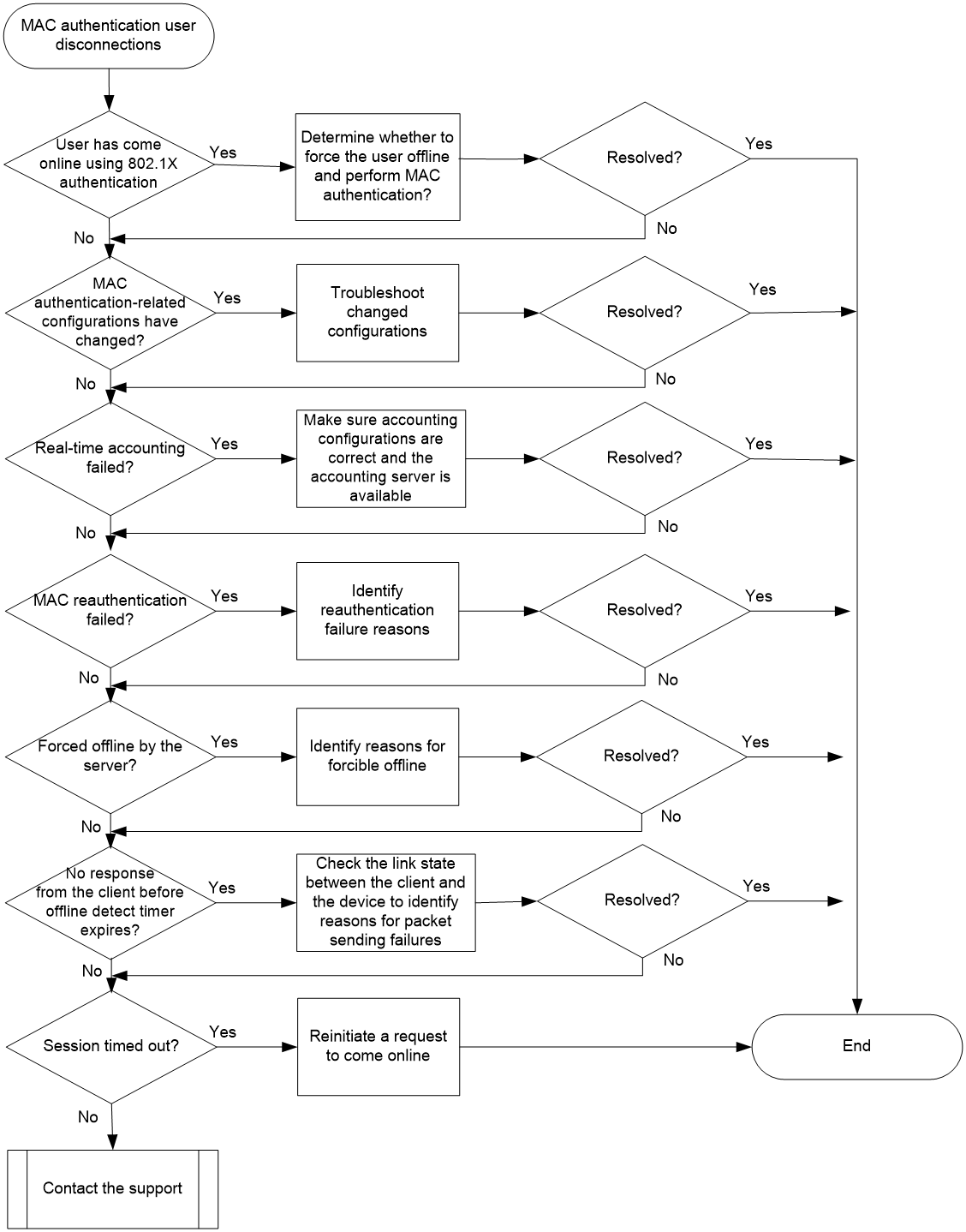
Figure 2 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 2 Flowchart for troubleshooting MAC authentication user disconnections
Solution
|
CAUTION: · Do not enable the debugging commands when the device is operating normally. Enable the commands when you reproduce the issue after it has occurred. · Save the execution results of the following steps promptly, so that information can be quickly collected and provided if the issue persists. |
1. Check whether disconnection occurs because the user has come online after passing 802.1X authentication.
By default, the authentication order on a port is 802.1X authentication and then MAC authentication.
If the user first passes MAC authentication, Web authentication is terminated immediately, but 802.1X authentication will proceed. If the user also passes 802.1X authentication, the 802.1X authentication information will overwrite the MAC authentication information of the user.
Execute the display dot1x connection command to check whether the user has successfully passed 802.1X authentication and come online. If the user has come online, determine whether the user needs to come online again through MAC authentication. If MAC authentication is required, log off the user, disable 802.1X authentication, and then configure the user to perform MAC authentication.
2. Check whether MAC authentication-related configurations on the device have changed:
a. Execute the display mac-authentication command to check whether the configurations (such as feature enabling and authentication method) related to MAC authentication on the device have changed.
b. Execute the display domain command to check whether the configurations (such as authorization attributes) in the user authentication domain have changed.
3. Check whether real-time accounting failed.
Execute the debugging mac-authentication event command to enable debugging for MAC authentication events. If the system prompts Real-time accounting failure., it indicates that real-time charging accounting failed. Check the link state between the device and the accounting server, and whether the related accounting configurations on the device and the accounting server have changed.
4. Check whether disconnection occurs because of a reauthentication failure:
a. Execute the display mac-authentication command and view the information displayed in the Periodic reauth field to check whether MAC reauthentication is enabled on the authentication interface.
b. Execute the mac-authentication access-user log enable logoff command to enable logging for MAC authentication user logoffs.
c. Identify the reasons for the reauthentication failure as described in "MAC authentication failures."
5. Check whether the RADIUS server forced the user offline.
Execute the debugging mac-authentication event command to enable debugging for MAC authentication events. If the system prompts The RADIUS server forcibly logged out the user., it indicates that the server forced the user offline. Please contact the server administrator to identify the reasons for forcible logoff by the server.
6. Check whether no user packet is received before the offline detect timer expires:
a. Execute the display mac-authentication command and view the information displayed in the Offline detection field on the authentication interface to check whether the offline detection has been enabled.
b. Execute the debugging mac-authentication event command to enable debugging for MAC authentication events. If the system prompts Offline detect timer expired., it indicates that no packet was received from the online MAC authentication user on the interface before the offline detect timer expires. The device disconnected the user connection, causing the user to go offline.
c. Check the link state between the user client and the device to identify the reasons for packet sending failures.
7. Check whether the user session has timed out:
a. Execute the debugging radius packet command to enable RADIUS packet debugging. Verify that the Session-Timeout attribute is carried in the responses from the server.
b. Execute the debugging mac-authentication event command to enable debugging for MAC authentication events. If the system prompts User session timed out., it indicates that the user goes offline because of user session timeout.
c. Disconnections caused by user session timeouts are normal. Users can reinitiate a request to come online.
8. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
¡ Log information collected after you execute the mac-authentication access-user log enable command.
¡ Debugging information collected after you execute the debugging mac-authentication all and debugging radius all commands.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
MACA_LOGOFF