- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 05-OSPFv3 Troubleshooting Guide | 84.11 KB |
Layer 3—IP Routing Troubleshooting Guide
Troubleshooting OSPFv3
OSPFv3 neighbor down
Symptom
· The OSPFv3 neighbor goes down.
· OSPF neighbor flapping occurs.
Common causes
The following are the common causes for this type of issue:
· The BFD session is down, which indicates that BFD detects a link failure.
· The remote device fails.
· CPU usage or memory usage is excessively high.
· Link failures occur.
· The OSPFv3 interface is not up.
· The IP addresses of the two ends are not on the same network.
· The OSPFv3 settings of the two ends do not match.
¡ Router ID conflict occurs.
¡ Area types of the two ends are not consistent.
¡ OSPFv3 authentication modes of the two ends are not consistent.
¡ The timer settings of the two ends are not consistent.
¡ The network types of the OSPFv3 interfaces at the two ends do not match.
Troubleshooting flow
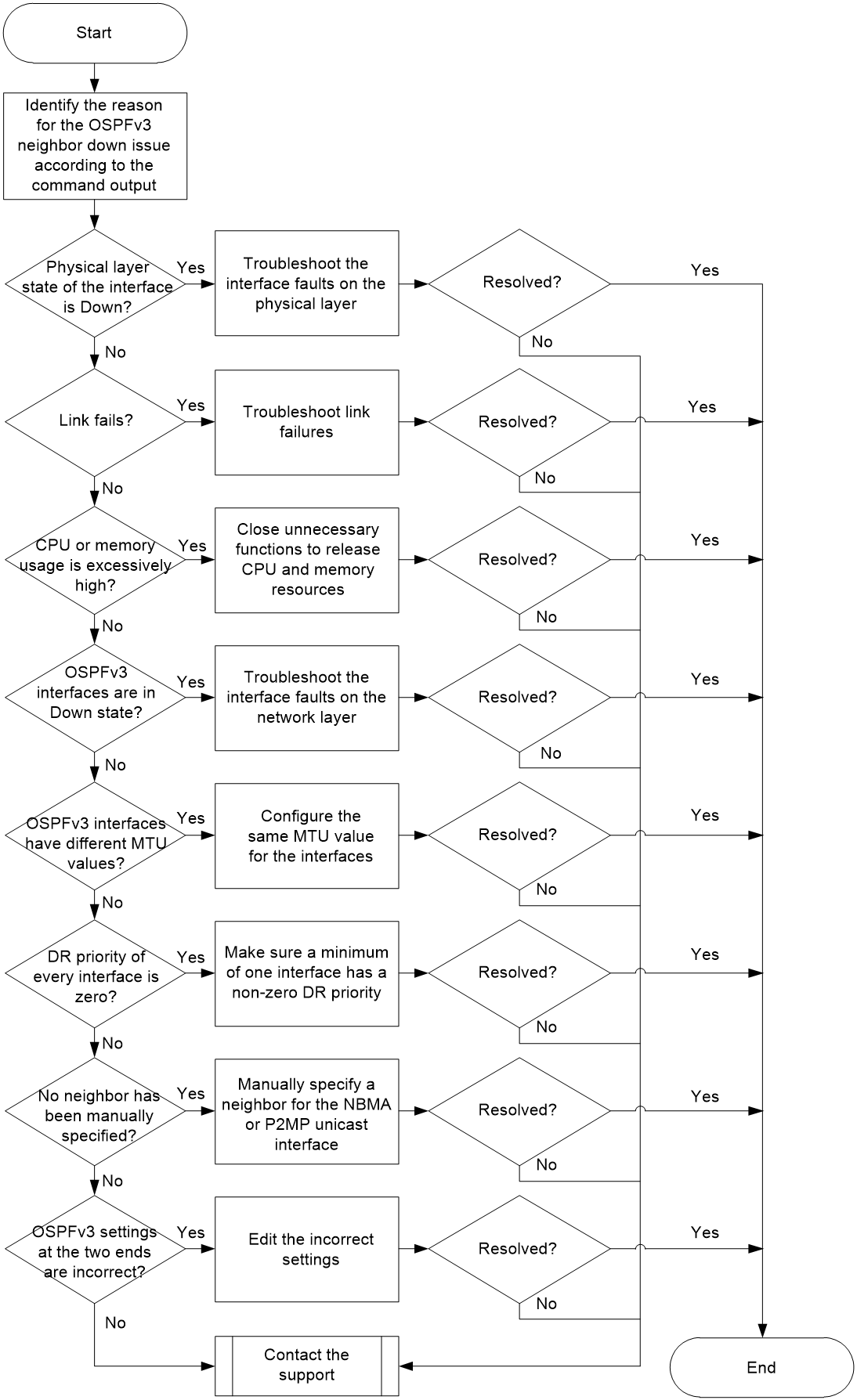
Figure 1 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 1 Flowchart for troubleshooting OSPFv3 neighbor down
Solution
1. Identify the reason for the OSPFv3 neighbor down issue through the CLI.
Execute the display ospfv3 event-log peer command. The Reason field in the command output represents the reasons for neighbor state changes. Common options include:
¡ DeadExpired
The device does not receive any Hello packet before the dead timer expires, and the OSPFv3 neighbor state becomes Down. In this case, proceed to step 2.
¡ BFDDown
The BFD session goes down, causing the OSPFv3 neighbor state to become Down. In this case, proceed to step 2.
¡ 1-Way
The neighbor’s OSPFv3 state becomes Down. It sends 1-way Hello packets to the local device, causing the OSPFv3 state becomes Init on the local device. In this case, troubleshoot faults on the neighbor.
¡ IntPhyChange
The interface goes down or its MTU changes, tearing down the neighbor relationship. In this case, execute the display interface [ interface-type [ interface-number | interface-number.subnumber ] ] command to view the running state and related information about the interface, and troubleshoot the interface faults. For other situations, proceed to step 11.
2. Identify whether the physical layer state of the interface is UP.
Execute the display interface [ interface-type [ interface-number | interface-number.subnumber ] ] command to identify whether the physical layer state of the OSPFv3 interface is UP.
¡ If the physical layer state of the interface is DOWN, the interface has failed. First resolve this issue.
¡ If the physical layer state of the interface is UP, proceed to step 3.
3. Identify whether the link fails.
Execute the ping command to identify whether the link fails. If the link operates correctly, proceed to step 4.
4. Identify whether the CPU usage is excessively high.
Execute the display cpu-usage command to examine the CPU usage. If the CPU usage of the device's MPU and interface module is excessively high, OSPFv3 packets might fail to receive or send protocol packets correctly, causing neighbor flapping. To resolve this issue, close unnecessary functions. If the CPU usage is not high, proceed to step 5.
5. Identify whether the memory usage exceeds the memory usage threshold.
Execute the display memory-threshold command. If the Current free-memory state field in the output, which represents the current memory usage of the system, displays Minor, Severe, or Critical, it indicates that the remaining free memory is relatively low. In this case, the device might be unable to send or receive OSPFv3 packets, or might process OSPFv3 packets slowly. To resolve this issue, close unnecessary functions. If the Current free-memory state field displays Normal, proceed to step 6.
6. Identify whether each OSPFv3 interface is in a normal state.
Execute the display ospfv3 interface command to identify whether the OSPFv3 interface is in a normal state.
¡ If the OSPFv3 interface is in Down state, identify whether OSPFv3 is enabled on the interface. If OSPFv3 is enabled, troubleshoot the interface issue on the network layer.
¡ If the OSPFv3 interface is in a normal state, including DR, BDR, DROther, and P-2-P, proceed to step 7.
7. Identify whether the OSPFv3 interfaces have the same MTU value.
If the ospfv3 mtu-ignore command is not executed for the interfaces, the interfaces must have the same MTU value. If they have different MTU values, OSPFv3 neighbor relationships cannot be established. Execute the display interface [ interface-type [ interface-number | interface-number.subnumber ] ] command to view the MTU information of each interface.
¡ If the interfaces have different MTU values, execute the mtu size command in interface view to configure the same MTU value for the interfaces.
¡ If the interfaces have the same MTU value, proceed to step 8.
8. Identify whether the DR priority of each interface is not zero.
On a broadcast or NBMA network, to elect a DR correctly, make sure that a minimum of one OSPFv3 interface has a non-zero DR priority. If all OSPFv3 interfaces have the DR priority of zero, the neighbor states at both ends can only become 2-Way. Execute the display ospfv3 interface command to view OSPFv3 interface information. The Priority field in the command output displays the DR priority of the interface.
If one or multiple interfaces have non-zero DR priorities, proceed to step 9.
9. Identify whether a neighbor has been manually specified for the NBMA or P2MP unicast interface.
When the network type of an interface is NBMA or P2MP unicast, you must use the ospfv3 peer command to specify a neighbor by its link-local address. Execute the display this command in interface view. If the network type of the interface is NBMA or P2MP unicast, execute the ospfv3 peer command to manually specify a neighbor by its link-local address.
If a neighbor has been manually specified for the NBMA or P2MP unicast interface, proceed to step 10.
10. Identify whether the OSPFv3 settings at the two ends are incorrect.
a. Execute the display ospfv3 command to view the OSPFv3 router IDs of the two ends. If the two ends are configured with the same router ID, edit the configuration to avoid the conflict. If the two ends are configured with different router IDs, proceed to the next step.
b. Execute the display ospfv3 interface command to view the area IDs of the two ends. If the two ends are configured with different area IDs, edit the configuration to ensure consistency. If the two ends are configured with the same area ID, proceed to the next step.
c. Execute the display ospfv3 interface command to view the network types of interfaces at the two ends. If the two interfaces are configured with different network types, edit the configuration to ensure consistency. If PTP is specified for one end and broadcast for the other, the neighbor relationship can enter Full state, but routing information cannot be calculated.
If the two ends are configured with the same network type, proceed to the next step.
d. Execute the display ospfv3 statistics error command every 10 seconds for 5 minutes to view OSPFv3 error statistics. Pay attention to the following fields:
- Authentication failure field. If the value of this field keeps increasing, it indicates that the two OSPFv3 neighbors are configured with different authentication modes. To resolve this issue, edit the authentication mode setting to make sure the two devices have the same authentication mode.
- HELLO: Hello-time mismatch field. If the value of this field keeps increasing, it indicates that the two OSPFv3 interfaces are configured with different hello intervals. To resolve this issue, edit the hello interval setting to make sure the OSPFv3 interfaces have the same hello interval value.
- HELLO: Dead-time mismatch field. If the value of this field keeps increasing, it indicates that the two OSPFv3 interfaces are configured with different dead intervals. To resolve this issue, edit the dead interval setting to make sure the OSPFv3 interfaces have the same dead interval value.
- HELLO: Ebit option mismatch field. If the value of this field keeps increasing, it indicates that OSPFv3 areas to which the two neighbors belong are of different types. (For example, one end is in a normal area and the other end is in a stub area.) To resolve this issue, edit the OSPFv3 area setting to make sure the two ends have the same area type.
If the issue persists, proceed to step 11.
11. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
Module name: OSPFV3-MIB
· ospfv3VirtIfStateChange (1.3.6.1.2.1.191.0.1)
· ospfv3NbrStateChange (1.3.6.1.2.1.191.0.2)
· ospfv3VirtNbrStateChange (1.3.6.1.2.1.191.0.3)
Log messages
· OSPFV3/6/OSPFV3_LAST_NBR_DOWN
· OSPFV3/5/OSPFV3_NBR_CHG
OSPFv3 neighbor unable to enter Full state
Symptom
The OSPFv3 neighbor state machine involves neighbor states of Down, Init, 2-way, ExStart, Exchange, Loading, and Full. Among them, the stable states are Down, 2-way, and Full.
· Down—OSPFv3 is not enabled.
· 2-way—The neighbor relationship between DR Others.
· Full—The local device and the neighbor are fully adjacent.
In networks using OSPFv3 for route calculation and forwarding, only 2-way and Full are normal neighbor states. If the neighbor state is neither 2-way nor Full, it indicates an abnormal neighbor relationship.
Common causes
The following are the common causes for this type of issue:
· OSPFv3 packets are dropped due to link failures.
· The DR priority configuration for the interfaces is not appropriate.
· The two ends are configured with different MTU values.
Troubleshooting flow
Figure 2 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 2 Flowchart for troubleshooting OSPFv3 neighbor unable to enter Full state
Solution
1. Execute the display ospfv3 peer command to view OSPFv3 neighbor information, and perform different tasks based on the neighbor state.
¡ If no neighbor information exists:
Identify whether a Router ID is configured for the OSPFv3 process. If no Router ID is configured, the OSPFv3 process cannot operate. If a Router ID is configured, it indicates that the OSPFv3 neighbor goes down or neighbor flapping occurs. See "OSPFv3 neighbor down" to troubleshoot the issue.
¡ If the neighbor state remains Init:
It indicates that the remote device cannot receive Hello packets from the local end. In this case, identify whether the link or the remote device fails.
¡ If the neighbor state remains 2-Way:
Execute the display ospfv3 interface verbose command to identify whether the DR priority for OSPFv3 interface of the device is zero.
If the DR priority of the OSPFv3 interface is zero, no action is required.
If the DR priority of the OSPFv3 interface is not zero, proceed to step 2.
¡ If the neighbor state remains ExStart:
It indicates that the device is performing DD negotiation but cannot perform DD synchronization. The following are the common causes for this type of issue:
- The interface cannot send and receive oversized packets correctly.
Execute the ping -s packet-size neighbor-address command multiple times and set 1500 or greater value for the packet-size argument to view the numbers of transmitted and received packets. If the remote end cannot be pinged, resolve the link issue first.
- The two ends are configured with different MTU values.
If the OSPFv3 interface is not configured to ignore MTU check by using the ospfv3 mtu-ignore command, identify whether the two ends are configured with the same MTU value. If they are configured with different MTU values, edit the MTU setting to make sure they have the same MTU value.
If the issue persists, proceed to step 2.
¡ If the neighbor state remains Exchange:
It indicates that the device is performing DD packet exchange. Troubleshoot this issue in the same way as when the neighbor state remains ExStart.
If the issue persists, proceed to step 2.
¡ If the neighbor state remains Loading:
Execute the reset ospfv3 [ process-id ] process command to restart the OSPFv3 process.
If the issue persists, proceed to step 2.
2. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
N/A