- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 02-Equal-Cost Route Troubleshooting Guide | 60.05 KB |
Troubleshooting Layer 3 IP routing issues
Equal-cost route issues
Some next hops of equal-cost routes do not participate in load sharing or the load sharing is uneven
Symptom
· Traffic is not distributed to one or multiple next hops of equal-cost routes. When you use the display counters rate outbound interface command to observe the packet transmission rate of related interfaces, you can find that the transmission rate is 0 on one or multiple output interfaces of the equal-cost routes.
· Traffic is load shared unevenly. When you use the display counters rate outbound interface command to observe the packet transmission rate of related interfaces, you can find that one or multiple output interfaces of the equal-cost routes have a noticeably lower transmission rate.
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· The number of next hops exceeds the maximum number of next hops supported by the device.
· The routes with the output interface have not been configured or properly issued.
· The physical link state and the data link layer state of the output interface are not up.
· The IP address of the output interface and that of the next hop interface are not in the same network segment.
· The device does not have an ARP or ND entry for the next hop.
· The load sharing mode is inappropriate.
· The hardware resources are insufficient.
· The last hop traversed by the traffic is configured with load sharing.
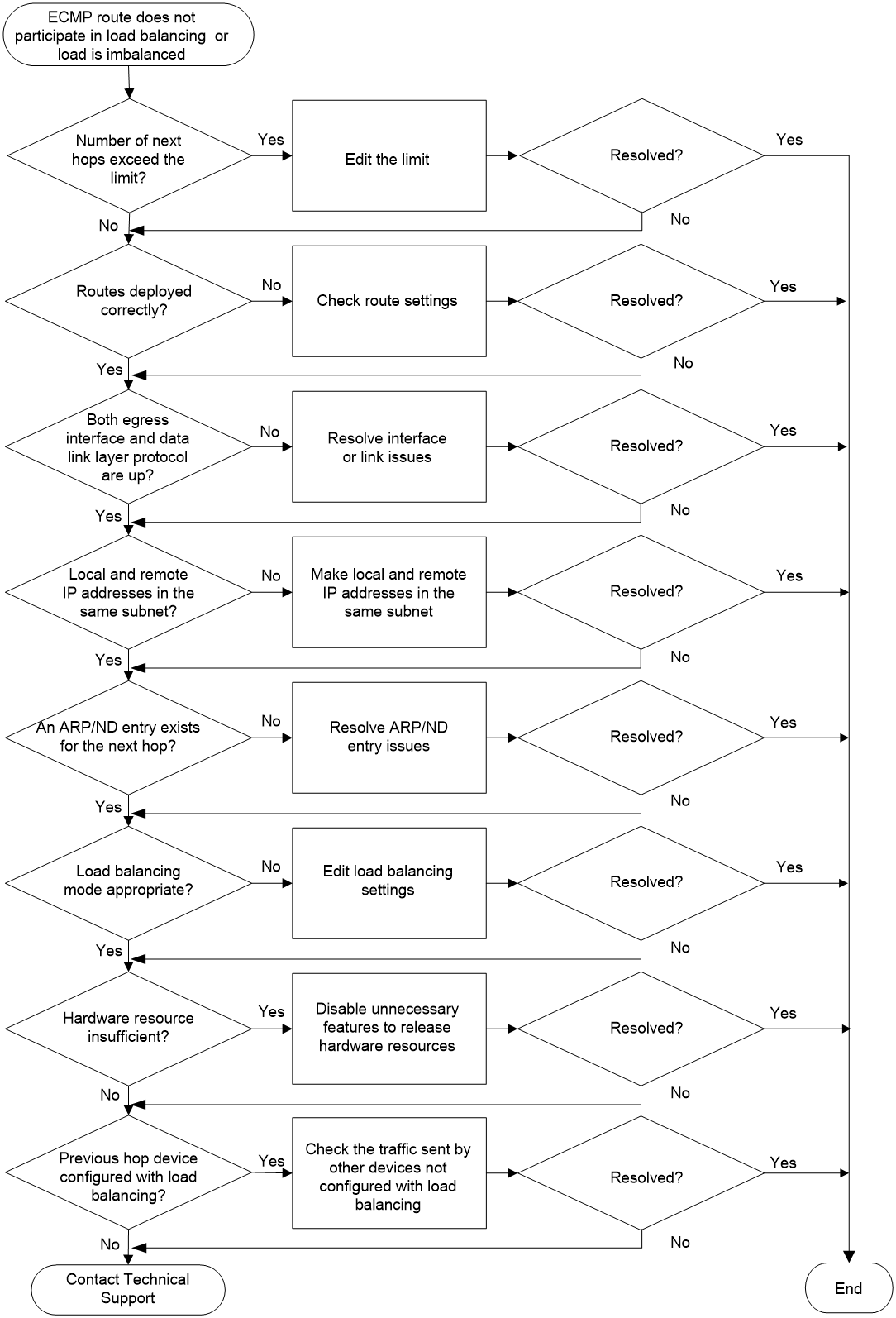
Troubleshooting flow
Figure 1 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 1 Flowchart for troubleshooting equal-cost route issues
Solution
a. To view the maximum number of IPv4 equal-cost routes supported by the system, execute the display max-ecmp-num command. To view the maximum number of IPv6 equal-cost routes supported by the system, execute the display ipv6 max-ecmp-num command.
b. To view the number of IPv4 equal-cost routes destined for a specific address, execute the display ip routing-table ip-address longer-match command with the destination address specified. To view the number of IPv6 equal-cost routes destined for a specific address, execute the display ipv6 routing-table ipv6-address longer-match command with the destination address specified. In the command output, all routes with the same destination but different next hops are equal-cost routes. The number of those equal-cost routes equals Summary count minus count A. The Summary count argument represents the value of the Summary count field in the command output. The count A argument represents the number of routes whose mask length is different from that of the destination address.
- If the number of equal-cost routes with the same destination reaches the upper limit, the excess equal-cost routes will not be flushed to the routing table. To edit the next hop of an equal-cost route in the routing table, delete the equal-cost route, and then configure a new equal-cost route.
- If the number of equal-cost routes with the same destination is lower the upper limit, proceed to step 2.
2. Identify whether the equal-cost routes have been correctly flushed to the routing table.
Execute one of the following commands as needed to view the routes with the related destination:
¡ display ip routing-table [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] ip-address [ mask-length | mask ] [ longer-match ] verbose
¡ display ipv6 routing-table [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] [ longer-match ] [ verbose ]
If the routing table does not contain the equal-cost route with the desired next hop and output interface, check for route configuration errors. If the route configuration is correct, proceed to step 3.
Execute the display interface [ interface-type [ interface-number | interface-number.subnumber ] ] or display ipv6 interface [ interface-type [ interface-number ] ] [ brief ] command to view states of the output interface.
¡ If the interface is not up at the physical layer or data link layer, resolve the interface or link failure.
¡ If the physical link state and the data link layer state of the output interface are up, proceed to step 4.
Execute the display interface brief or display ipv6 interface brief command on both the local device and the next hop device to view IP addresses of the interfaces that connect the two devices.
¡ If IP addresses of the two interfaces are not in the same network segment, execute the ip address/ipv6 address command in interface view for either of the interfaces to adjust its IP address. This operation ensures that IP addresses of the two interfaces are in the same network segment.
¡ If IP addresses of the two interfaces are not in the same network segment, proceed to step 5.
5. Identify whether an ARP or ND entry for the related next hop exists on the device.
To view ARP entries, execute the display arp command. To view ND entries, execute the display ipv6 neighbors command. If the device does not have an ARP or ND entry for the next hop, resolve this issue first. If the device has an ARP or ND entry for the next hop, proceed to step 6.
6. Identify whether the load sharing mode is appropriate.
Execute the display ip load-sharing mode command to view the current load sharing mode used by the device. If the load sharing mode is per-flow, the device selects the same next hop for packets with the same load sharing factors (such as source address, destination address, and source port). An inappropriate load sharing mode leads to uneven load sharing. An appropriate load sharing mode ensures that the device can evenly divide the traffic into a reasonable amount of data flows. The number of data flows should not be less than that of the next hops of equal-cost routes.
¡ If the load sharing mode is inappropriate, determine the load sharing factors based on the packets to be load shared, and then execute the ip load-sharing mode command to adjust the load sharing mode. For example, if the packets with the same destination address carry different source IP addresses, IP protocol numbers, and destination port numbers, you can add these fields into the ip load-sharing mode command. If the issue persists after the load sharing mode is fully adjusted, proceed to step 7.
¡ If the load sharing mode is appropriate, proceed to step 7.
7. Check for hardware resource insufficiency.
If the device is a switch or router that has hardware forwarding chips, you need to identify whether the hardware resources are insufficient.
¡ To view the IPv4 FIB entries that failed to be issued to the driver, use the display system internal fib prefix [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name] entry-status f command.
¡ To view the IPv6 FIB entries that failed to be issued to the driver, use the display system internal ipv6 fib prefix [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] entry-status f command.
The device is suffering from hardware resource insufficiency as long as the command output displays FIB entry information. To resolve this issue, disable unnecessary features to lower the hardware resource usage. If the issue persists, proceed to step 8.
8. Identify whether the last hop traversed by the traffic is configured with load sharing.
A device configured with load sharing might forward traffic to the local device. In this situation, affected by the load sharing algorithm, the traffic might be unevenly distributed when the local device transmits the traffic to nexthop devices. This is a normal phenomenon and no action is required. You need to identify whether the traffic from devices that are not configured with load sharing is unevenly distributed by the local device. If such an issue exists, proceed to step 9.
9. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
N/A