- Table of Contents
-
- 07-IP Multicast Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Multicast overview
- 02-IGMP snooping configuration
- 03-PIM snooping configuration
- 04-Multicast VLAN configuration
- 05-Multicast routing and forwarding configuration
- 06-IGMP configuration
- 07-PIM configuration
- 08-MSDP configuration
- 09-Multicast VPN overview
- 10-MDT-based MVPN configuration
- 11-RSVP-TE-based MVPN configuration
- 12-mLDP-based MVPN configuration
- 13-BIER-based MVPN configuration
- 14-MVPN extranet configuration
- 15-MLD snooping configuration
- 16-IPv6 PIM snooping configuration
- 17-IPv6 multicast VLAN configuration
- 18-IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding configuration
- 19-MLD configuration
- 20-IPv6 PIM configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 13-BIER-based MVPN configuration | 2.70 MB |
Inclusive tunnel establishment
Selective tunnel establishment and tunnel switchover
MVPN extended community attributes
BIER-based MVPN tasks at a glance
Prerequisites for configuring BIER-based MVPN
Enabling IP multicast routing for a VPN instance
Configuring BGP MVPN route exchange
Configuring BGP IPv4 MVPN route exchange
Configuring BGP IPv6 MVPN route exchange
Configuring BGP extended communities
Allowing the device to add community attributes to C-multicast routes sent to BGP peers
Enabling compatibility for the extended communities of the IPv6 address type
Creating a BIER-based MVPN instance
Creating an MVPN IPv4 address family
Specifying the MVPN source interface
Enabling IPv6 underlay for MVPN
Configuring source IPv6 addresses for encapsulation
Configuring G-BIER multicast service prefix information
Specifying the multicast service source address of the G-BIER tunnel
Configuring the source address of the BIERv6 or MSR6 tunnel
Configuring inclusive tunnels and selective tunnels
Enabling inclusive tunnel creation
Enabling selective tunnel creation
Setting the tunnel holddown timer
Enabling inter-AS auto-discovery
Configuring multicast warm backup
Enabling multicast warm backup
Configuring the selection of the master IDF based on (S, G) entries
Display and maintenance commands for BIER-based MVPN
BIER-based MVPN configuration examples
Example: Configuring intra-AS BIER-based MVPN (G-BIER encapsulation)
Example: Configuring intra-AS BIER-based MVPN (BIERv6 encapsulation)
Example: Configuring intra-AS BIER-based MVPN (MSR6 encapsulation)
Example: Configuring intra-AS BIER-based MVPN (EVPN L3VPN over SRv6-based G-BIER encapsulation)
Example: Configuring BIER-based MVPN for the public instance (G-BIER encapsulation)
Example: Configuring BIER-based MVPN for the public instance (BIERv6 encapsulation)
Example: Configuring BIER-based MVPN for the public instance (MSR6 encapsulation)
Example: Configuring inter-AS option A BIER-based MVPN (G-BIER encapsulation)
Example: Configuring inter-AS option C BIER-based MVPN (G-BIER encapsulation)
Configuring BIER-based MVPN
BIER-based MVPN overview
Basic concepts
BIER domain and BIER sub-domain
All BFRs in a network are referred to as a BIER domain. A BIER domain can contain one or more sub-domains. Each sub-domain is identified by a sub-domain ID. All BFIRs and BFERs in a sub-domain are called BIER edge devices.
BFR ID
A BFR ID uniquely identifies a BIER edge device in a sub-domain. A transit BFR does not need to have a BFR ID.
BFR prefix
A BFR prefix is an IP address that uniquely identifies a BFR in a sub-domain. A BFR prefix must be routable in the sub-domain and can only be the IP address of a loopack interface.
Bit string
A bit string represents a set of BIER edge devices, with each bit corresponding to a BFR ID, starting from the rightmost position. The bit string length (BSL) refers to the number of bits in the bit string. A bit string with three bits can identify a maximum of three BIER edge devices. The BIER edge device with BFR ID is represented as 001.
Set identifier
When the number of BFR IDs is greater than the number of bits in the bit string, the bit string needs to be divided into sets identified by set identifiers (SI). For example, if the maximum BFR ID is 10 in a BIER sub-domain and the bit string length is 4, the bit string needs to be divided into three SIs (SI 0, SI 1, and SI 2). The maximum SI is (Maximum BFR ID–1)/BSL rounded down to the nearest integer.
Bit Index Routing Table
The Bit Index Routing Table (BIRT) is generated based on the BIER information ((sub-domain, BSL, and BFR ID) and routing informtion carried by IGP. The BIRT is used to guide the forwarding of BIER packets in a BIER sub-domain.
Forwarding Bit Mask
The Forwarding Bit Mask (F-BM) represents a set of edge nodes in a BIER sub-domain that are reachable through a BFR neighbor (BFR-NBR). The bit mask is obtained by taking the logical OR of the bit strings of all reachable edge nodes.
Bit Index Forwarding Table
The Bit Index Forwarding Table (BIFT) can guide the per-hop forwarding of multicast traffic in a BIER sub-domain.
The BIFT is used to map from the BFR ID of a BFER to the corresponding F-BM and BFR-NBR. Multiple BIFT can exist on a BFR. Each BIFT is identified by a combination of the BSL, SD, and SI).
Operating mechanism
The running mechanism of NG MVPN over G-BIER is as follows:
1. The multicast source-side PE first interacts with the receiver-side PE through BGP MVPN routes to identify which receiver-side PEs need to receive the multicast traffic.
2. The source-side PE and receiver-side PE exchange BIER information (BFR ID, Sub domain ID, BFR prefix) through the Intra-AS I-PMSI A-D Route, S-PMSI A-D Route, and Leaf A-D Route carried in BGP messages.
3. Multicast data is seamlessly transferred from the private to the public network when it travels from the CE to the PE through a compatible tunnel according to the PIM routing table. The source-side PE encapsulates the private network multicast data with a BIER header and sends it through the tunnel to the remote PE, which then restores it to a private network multicast message by stripping the label information.
4. When multicast traffic on the multicast source-side PE meets the conditions for selecting a switch-over tunnel, a selective tunnel is established. The private network multicast data encapsulating the BIER head is then transmitted through this selective tunnel.
BIER-based MVPN operation
BIER-based MVPN encapsulates multicast traffic in a private network and sends it to other nodes in the BIER sub domain.
The multicast source-side PE sends BGP MVPN routes to receiver-side PEs for establishing BIER tunnels. This process is similar to that of RSVP-TE-based MVPN and mLDP-based MVPN except that the Intra-AS I-PMSI A-D route, S-PMSI A-D route, and Leaf A-D route carry BIER information, including BFR ID, sub-domain ID, and BFR prefix. For more information about RSVP-TE-based MVPN and mLDP-based MVPN, see "Configuring RSVP-TE-based MVPN" and "Configuring mLDP-based MVPN."
After encapsulating the received private network multicast traffic with Bit String, the PE performs BIER forwarding for the traffic in the public network. For more information about BIER forwarding, see BIER Configuration Guide.
Similar to RSVP-TE-based MVPN and mLDP-based MVPN, in BIER-based MVPN mode, multicast packets of a VPN instance are seamlessly transmitted from a CE to the inclusive tunnel on the PE based on the PIM routing table. These packets are then transmitted to the remote PE through the inclusive tunnel. After receiving the packets, the remote PE decapsulates the packets to get the original private packets. The multicast source-side PE creates selective tunnels when multicast traffic that meets the tunnel switchover criterion arrives.
|
|
NOTE: BIER supports multiple encapsulation types. The operation of different encapsulation types are similar, with different BIER header formats. For more information, see BIER configuration in BIER Configuration Guide. |
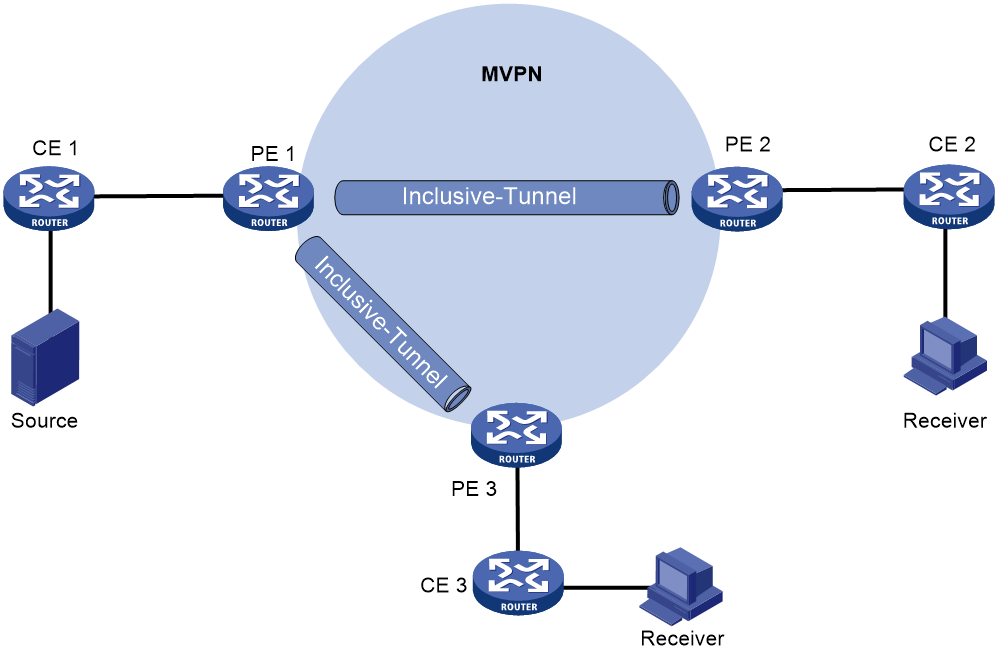
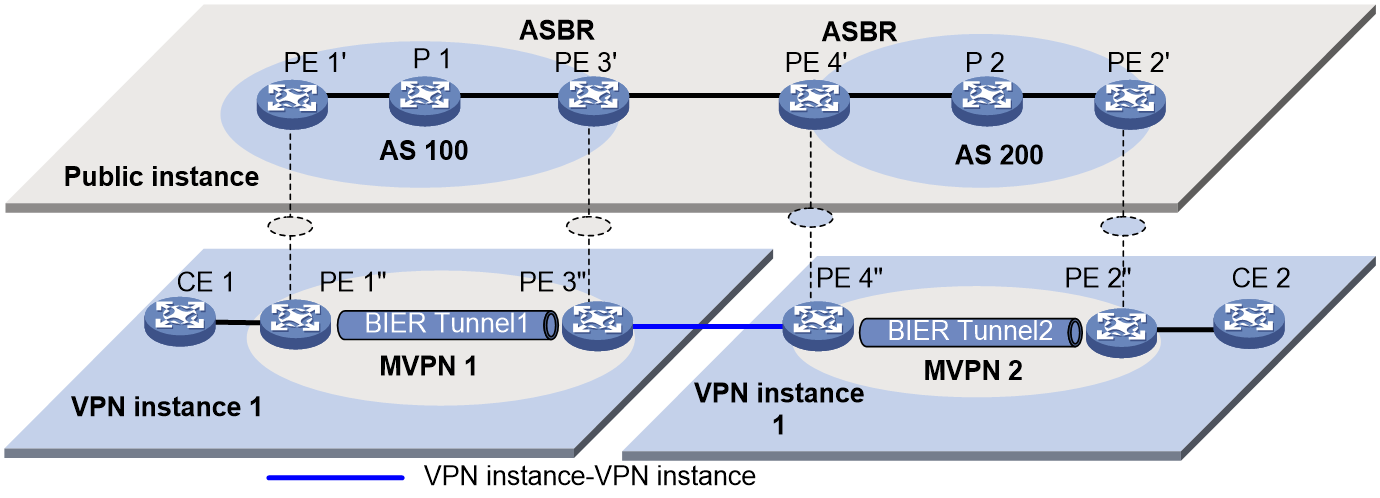
Inclusive tunnel establishment
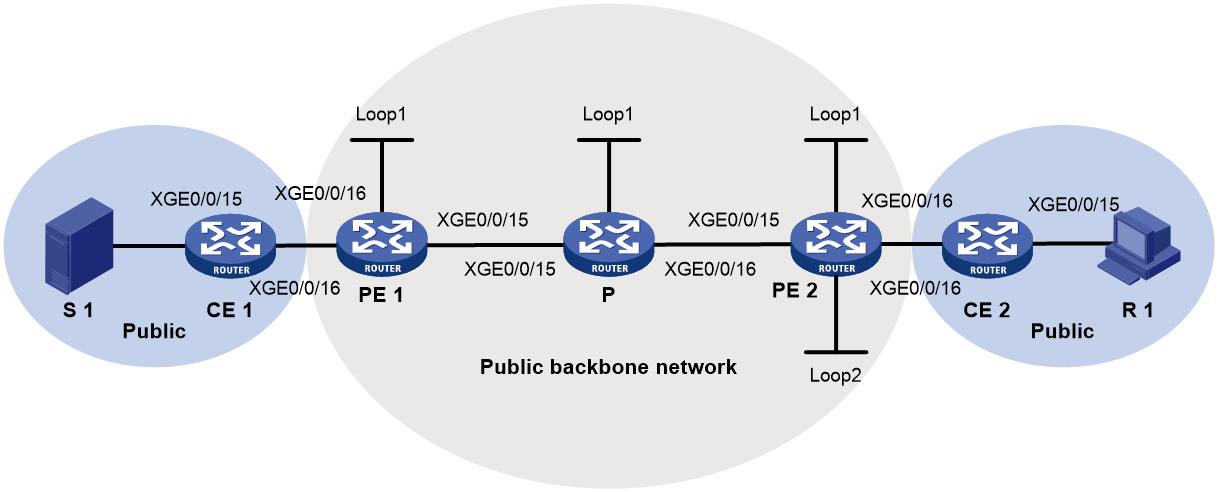
As shown in Figure 1, the private network runs PIM, and the public network uses BIER. The inclusive tunnels are established as follows:
1. PE 1 sends an Intra-AS I-PMSI A-D route to PE 2 and PE 3. The route contains the following information:
¡ Route Target—Controls route transmission and receiving. It is configured as the export target of PE 1.
¡ PMSI Tunnel attribute—Transmits tunnel information, where the value for the Tunnel Type field is the BIER tunnel, and the field contains BIER information including Sub domain ID, BFR ID, and BFR prefix for PE 1.
2. Upon receiving the Intra-AS I-PMSI A-D route, PE 2 and PE 3 identify whether the Route Target field matches the Import Target configured in the local VPN instance. If they match, the PEs accept the route and respond with a Leaf A-D route to PE 1. The route contains the following information:
¡ Route Target— Controls route transmission and receiving. It is configured as the export target of PE 2 or PE 3.
¡ PMSI Tunnel attribute—Transmits tunnel information, where the value for the Tunnel Type field is the BIER tunnel. This field contains information about the BFIRs and BFERs in the same sub domain as PE 1. The information is obtained by checking the BFR ID and BFR prefix configured in the local sub domain with an ID same as that in the Intra-AS I-PMSI A-D route sent by PE 1.
3. Upon receiving the Leaf A-D route, PE 1 identifies whether the Route Target field matches the Import Target configured in the local VPN instance. If they match, PE 1 accept the route and marks PE 2 and PE 3 as members of the MVPN. At the same time, PE 1 obtains the SI based on the BFR ID in the route and the value of the BSL in the BIER sub domain. Then PE 1 combines information about all leaf nodes and generates the bit string to establish an inclusive tunnel.
Figure 1 Inclusive tunnel establishment
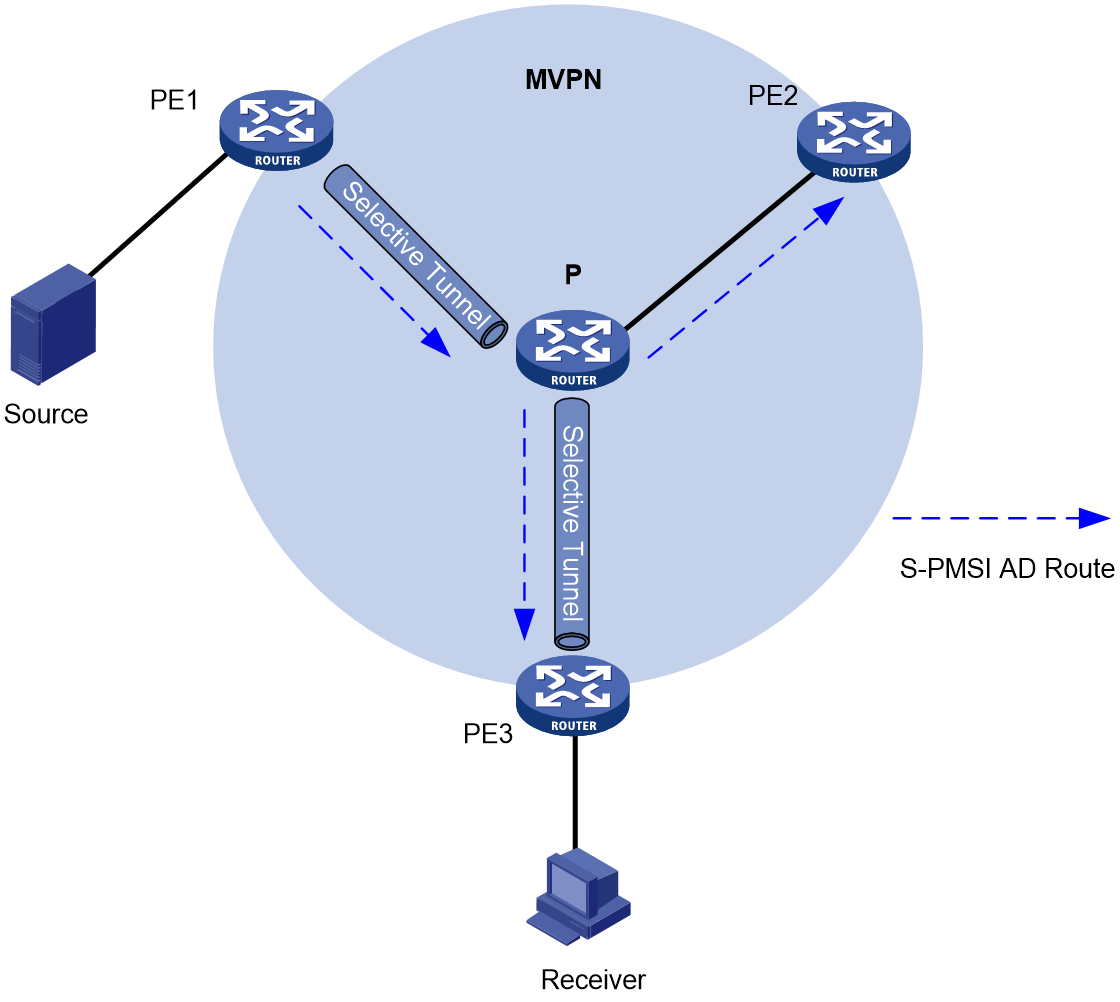
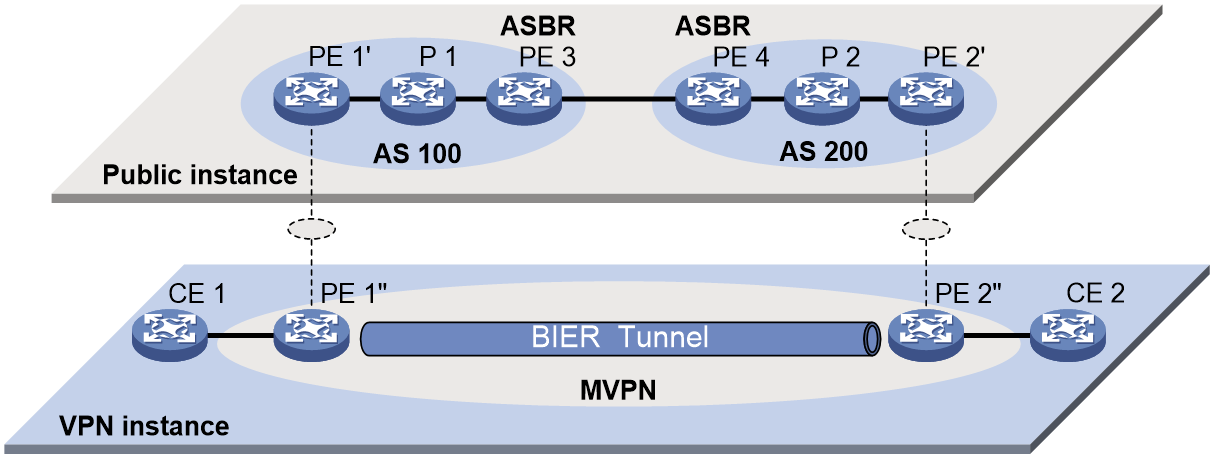
Selective tunnel establishment and tunnel switchover
BIER-based MVPN supports switchover from the inclusive tunnel to selective tunnels to off-load traffic for specific (S, G) entries from the inclusive tunnel. An MVPN can have multiple selective tunnels.
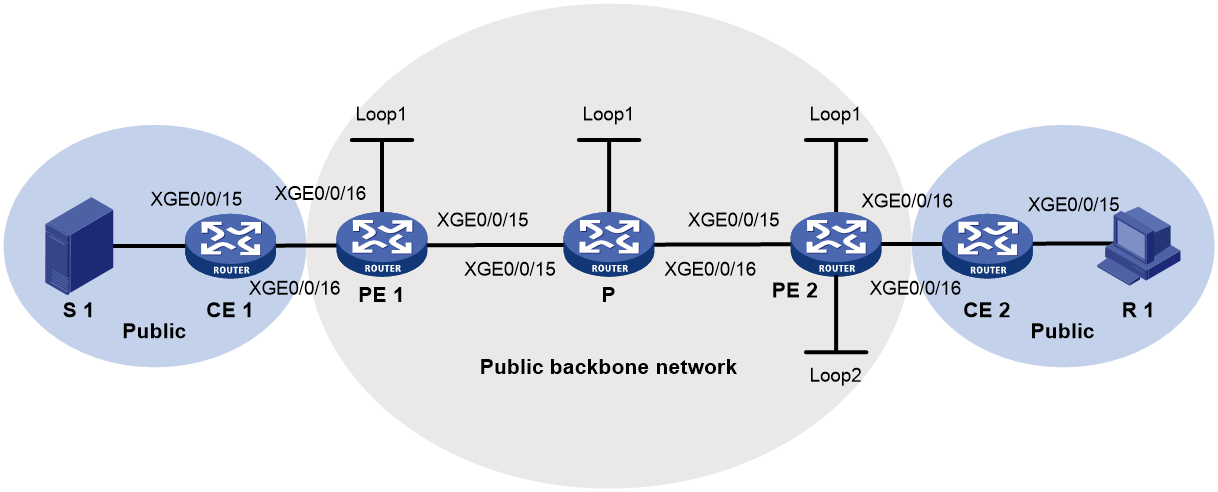
As shown in Figure 2, the process of selective tunnel creation and the tunnel switchover is as follows:
1. PE 1 sends an S-PMSI A-D route to PE 2 and PE 3. The route contains the following information:
¡ Route Target—Controls route transmission and receiving. It is configured as the export target of PE 1.
¡ PMSI Tunnel attribute—Transmits tunnel information, where the value for the Tunnel Type field is the BIER tunnel, and the field contains BIER information including Sub domain ID, BFR ID, and BFR prefix for PE 1.
2. Upon receiving the S-PMSI A-D route, PE 2 and PE 3 identify whether the Route Target field matches the Import Target configured in the local VPN instance. If they match, the PEs accept the route and if a downstream receiver exists, the two PEs respond with a Leaf A-D route to PE 1. The route contains the following information:
¡ Route Target— Controls route transmission and receiving. It is configured as the export target of PE 2 or PE 3.
¡ PMSI Tunnel attribute—Transmits tunnel information, where the value for the Tunnel Type field is the BIER tunnel. This field contains information about the BFIRs and BFERs in the same sub domain as PE 1. The information is obtained by checking the BFR ID and BFR prefix configured in the local sub domain with an ID the same as that in the S-PMSI A-D route sent by PE 1.
3. Upon receiving the Leaf A-D route, PE 1 identifies whether the Route Target field matches the Import Target configured in the local VPN instance. If they match, PE 1 accept the route and marks PE 2 and PE 3 as members of the MVPN. At the same time, PE 1 obtains the SI based on the BFR ID in the route and the value of the BSL in the BIER sub domain. Then PE 1 combines information about all leaf nodes and generates bit string for the (S, G) entry to establish a selective tunnel.
Figure 2 Selective tunnel establishment and tunnel switchover
Control plane
In the NG MVPN over BIER scenario, BIER is used to establish a carrying tunnel. Multicast private network traffic is encapsulated by BIER and sent across the public network to other nodes in the BIER sub-domain.
The control plane package of NG MVPN over BIER includes the following unique technical implementations:
· Receiver PE collects information.
In this scenario, the multicast source-side PE first recognizes which receiver-side PEs the multicast traffic needs to be transmitted to. Then, the source-side PE encapsulates the Bit String based on the received private network multicast traffic. In this, the gathering mechanism of each PE member within MVPN is similar to the process under RSVP-TE and mLDP modes in MVPN.
· Added a new BIER tunnel type attribute.
To support NG MVPN over BIER, RFC 8556 defines the information required when using BIER tunnels in BGP MVPN services, namely, a BIER-type PTA (PMSI Tunnel attribute). This BIER-type PTA is used when BIER tunnels are employed in BGP MVPN services. Originally, the MPLS Label field of the PTA was used to identify the upstream allocation tags of the MVPN instance. In the MVPN based on BIER tunnels, this field is no longer used. Instead, a new BGP attribute carrying the IPv6 source address (multicast service source address, src-dt4, or src-dt6) used to identify the MVPN instance is used. This attribute is referred to as the multicast service identifier (MSID). For BIERv6 or MSR6, This attribute is referred to as Prefix-SID. The value of the MPLS label field in the PTA is set to 0.
MSID attributes
In MVPN over G-BIER, the newly added BGP attricute MSID is used to identify the MVPN-instance. The multicast source address within MSID is carried by the multicast source-side PE in the class 1 route 'Intra-AS I-PMSI A-D route', and is announced to the recipient-side PE. The recipient-side PE records the corresponding relationship between this source address and the MVPN-instance. When the recipient-side PE receives a multicast packet encapsulated in G-BIER, it will use the multicast source address in the packet to find the corresponding MVPN-instance, find the corresponding entry in the multicast forwarding table of the MVPN instance, and forward the multicast packet.
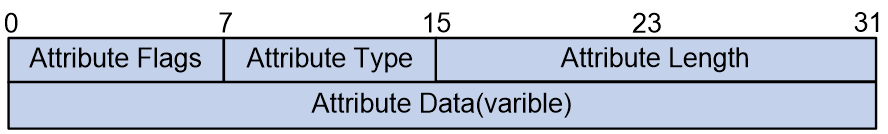
The BGP MSID attricutes and their content adhere to the format requirements defined by BGP attricutes, shown as Figure 3.
Figure 3 MSID Attribute Format
The meaning of each field in the MSID Attribute is as follows:
· Attribute Flags: 8 bits, identify (ID) attricutes.
· Attribute Type: 8bits, representing the category field of the attribute, named as MSID.
· Attribute Length: 16 bits, indicating the length of the attribute.
· Attribute Data: Variable length, representing the attribute data, expressed using a Sub-TLV with no fixed fields.
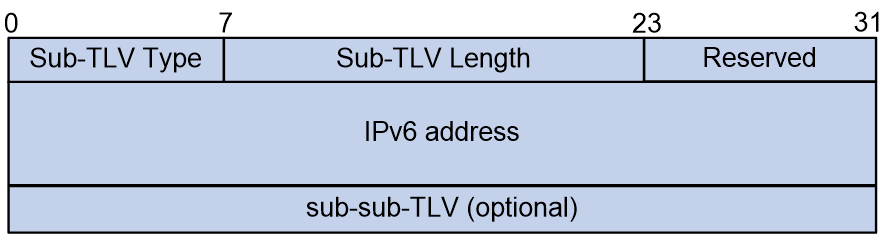
The Attribute Data is a Sub-TLV with no fixed fields, and its specific format is shown in Figure 4.
The meanings of each field in the Sub-TLV are as follows:
· Sub-TLV Type: 8 bits, indicating the type of the Sub-TLV.
· Sub-TLV Length: A 16-bit value representing the length of the Sub-TLV.
· Reserved: 8 bits, reserved field.
· IPv6 address: The source IPv6 address.
· sub-sub-TLV: Variable length, indicating the sub-sub-TLVs carried by this Sub-TLV, currently only supporting the Structure sub-sub-TLV.
The format of the Structure sub-sub-TLV is shown as in Figure 5.
Figure 5 Structure sub-sub-TLV format
The meanings of each field in the Structure sub-sub-TLV are as follows:
· sub-sub-TLV Type: 8 bits, the type of sub-sub-TLV, with a value of 1 indicating a Structure sub-sub-TLV.
· sub-sub-TLV Length: 16 bits, the length of the sub-sub-TLV, with a value of 5.
· Flags: 8 bits, a flag field for future expansion, currently required to be 0.
· Prefix Length: 8 bits, indicating the length of the prefix.
· The length of the multicast service ID, known as MSID Length, is 8 bits.
· Must Be Zero: 16bits, reserved field.
Prefix-SID attributes
In MVPN over BIERv6, the BGP attribute Prefix-SID is used to carry the IPv6 source address encapsulated by the BIERv6 tunnel. The multicast source-side PE advertises the tunnel source address to the receiver-side PE by carrying the Prefix-SID in Type 1 routes, Intra-AS I-PMSI A-D routes, and Type 3 routes, S-PMSI A-D routes. Upon receiving Type 1 and Type 3 routes, the receiver-side PE matches the Route Target attribute carried by the route with the local VPN instance or public network instance and records the relationship between the Prefix-SID and the VPN or public network instance. When the receiver-side PE receives a multicast packet encapsulated by BIERv6, it identifies the corresponding VPN or public network instance based on the BIERv6 tunnel source address in the packet, establishes multicast forwarding table entries in the corresponding MVPN instance, and forwards the multicast packet.
The BGP Prefix-SID attribute and its contents follow the format requirements defined by the RFC standard, as shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6 BGP Prefix-SID Format
The meanings of each field in the BGP Prefix-SID are as follows:
· TLV Type: This is the type of TLV. A value of 5 means that SRv6 carries a three-stratum service; a value of 6 means that SRv6 carries a two-stratum service.
· TLV Length: The length of the TLV.
· Reserved: Reserved field.
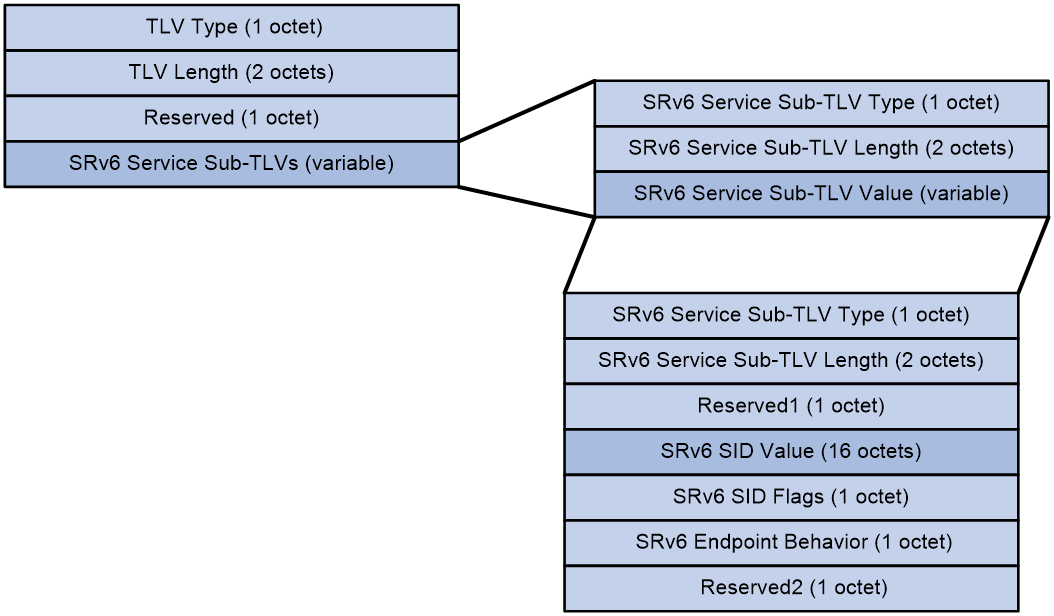
· SRv6 Service Sub-TLVs: The service information related to Prefix-SID, which is of variable length.
The SRv6 Service Sub-TLV package contains the following fields:
· Service Sub-TLV Type in SRv6: The type of Prefix-SID information is fixed at 1, indicating SRv6 SID Information Sub-TLV.
· SRv6 Service Sub-TLV Length: The length of the SRv6 Service Sub-TLV.
· SRv6 Service Sub-TLV Value: The value of the SRv6 Service Sub-TLV, which is variable in length.
When the type is SRv6 SID Information Sub-TLV, the SRv6 Service Sub-TLV includes the following fields:
· SRv6 Service Sub-TLV Type: The type of SRv6 Service Sub-TLV, with a fixed value of 1.
· SRv6 Service Sub-TLV Length: The length of the SRv6 SID Information Sub-TLV.
· Reserved1: A reserved field.
· SRv6 SID Value: The value of the Prefix-SID, representing the Src.DT4 SID and Src.DT6 SID for the BIERv6 tunnel source address, is carried by this field.
· SRv6 SID Flags: The flags for the Prefix-SID, with a fixed value of 0.}
· SRv6 Endpoint Behavior: The type of Prefix-SID. A value of 0x45 indicates a Src.DT4 SID, and 0x44 indicates a Src.DT6 SID.
· Reserved2: A reserved field.
MVPN extended community attributes
Introduction
MVPN's extended community attributes are primarily used for the advertisement and reception of C-multicast routes, including the following two types:
· The Source AS Extended Community attricute is used to identify the AS number where the multicast source is located, applicable in cross-domain scenarios.
· The VRF Route Import Extended Community attribute is used to identify the IP address of the multicast source-side PE and the VPN-instance where the multicast source is located.
The format of Source AS Extended Community and VRF Route Import Extended Community within the extended community attribute is depicted respectively in Figure 7 and Figure 8.
Figure 7 Format of the Source AS Extended Community
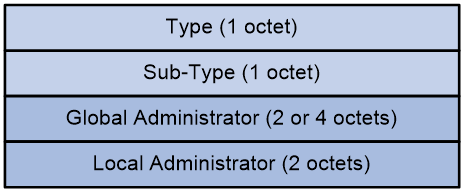
The Source AS Extended Community package includes the following fields:
· Type: The type of the extended community attribute, which can either be 0x00 (representing the extended community attribute of a 2-byte AS number type) OR 0x02 (representing the extended community attribute of a 4-byte AS number type).
· Sub-Type: The subtype of the extended community attribute, with a value of 0x09, indicating it is a Source AS Extended Community.
· Global Administrator: The AS number, where the multicast source is located, can be in either a 2-byte format or a 4-byte format.
· Local Administrator: Has a value of 0, currently without special meaning.
Figure 8 Format of the VRF Route Import Extended Community
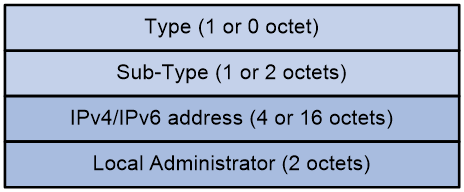
The VRF Route Import Extended Community includes the following fields:
· Type: The type of the extended community attribute, with a value of 0x01 (for IPv4 address type extended community attribute) or no value (for IPv6 address type extended community attribute).
· Sub-Type: The subtype of the extended community attribute, with a value of 0x0b (when it's an IPv4 address type extended community attribute) or 0x000b (when it's an IPv6 address type extended community attribute), indicating it is a VRF Route Import Extended Community.
· IPv4/IPv6 address: The IP address of the multicast source-side PE.
· Local Administrator: The VPN instance where the multicast source is located.
Operating mechanism
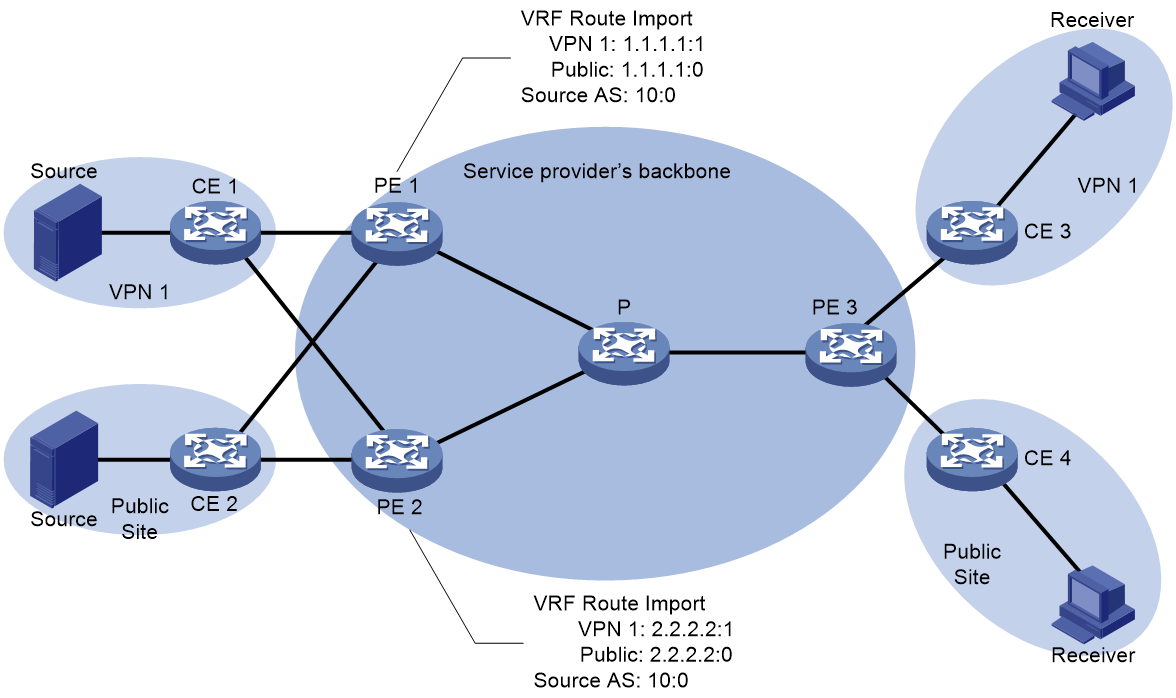
As shown in Figure 9, PE 1 and PE 2 are multicast source PEs, while PE 3 is a receiving-side PE. Both PE 1 and PE 2 are connected to VPN 1 and the public network instance sites. On PE 1, the VRF Route Import Extended Community value for VPN 1 is 1.1.1.1:1; for the public network instance on PE 1, the value is 1.1.1.1:0 (the Local Administrator value in the VRF Route Import Extended Community for the public network instance must be 0); the Source AS Extended Community value on PE 1 is 10:0. On PE 2, the VRF Route Import Extended Community value for VPN 1 is 2.2.2.2:1; for the public network instance on PE 2, the value is 2.2.2.2:0 (the Local Administrator value in the VRF Route Import Extended Community for the public network instance must be 0); the Source AS Extended Community value on PE 2 is 10:0.
Figure 9 MVPN extended community attributes working mechanism
After establishing BGP MVPN address family sessions with PE 3 respectively, both PE 1 and PE 2 will release unicast route information to the multicast source to PE 3. The multicast source unicast route information of VPN-instance is carried via BGP VPNv4 or VPNv6 routes. The public network instance's multicast source unicast route information is carried via BGP IPv4/IPv6 unicast routes OR BGP IPv4/IPv6 multicast routes. All BGP routes carrying the announced unicast route information to the multicast source will include Source AS Extended Community and VRF Route Import Extended Community.
Upon receiving the BGP routes of unicast routing information to multicast sources announced by PE 3, PE 3 will prefer the BGP routes, then store the Source AS Extended Community and VRF Route Import Extended Community carried by the routes for later construction of the C-multicast route. It is assumed in this instance that PE 3 has preferred the BGP route of the unicast routing information to the multicast source of VPN 1 announced by PE 1, and the BGP route of the unicast routing information to a multicast source of a public network instance announced by PE 2.
The construction process of C-multicast routing for VPN-instance VPN 1 and public network instance is as follows:
· When PE 3 receives a multicast join message from CE 3, it constructs a C-multicast route, and then transmits it to PE 1 and PE 2. The Source AS field of this route is the AS number in the received Source AS Extended Community. The Route Target attricutes carried by the route is the VRF Route Import Extended Community of the preferred BGP route, which is 1.1.1.1:1.
¡ Upon receiving the C-multicast routing, PE 1 compares the IP address carried in the RT attricutes of the C-multicast routing and discovers it is 1.1.1.1, which is the local source interface address. So, PE 1 accepts the C-multicast routing. Then, PE 1 determines the C-multicast routing belongs to VPN-instance VPN 1 based on the Local Administrator in the RT attricutes and adds the C-multicast routing to the multicast routing table of VPN 1.
¡ Upon receiving the C-multicast route, PE 2 compares the IP address carried in the RT attribute of the C-multicast route, identifies it as 1.1.1.1, which is not the local source interface address, and discards the C-multicast route.
When the multicast source in VPN 1 sends multicast packets subsequently, as only PE 1 has formed the multicast entry, the multicast packets will be encapsulated by BIER at PE 1 and transmitted through the BIER public network tunnel to PE 3. After decapsulation at PE 3, they are forwarded to CE 3.
· When PE 3 receives a multicast join message from CE 4, it constructs a C-multicast route and then sends it to PE 1 and PE 2. The Source AS field of this route is the AS number from the received Source AS Extended Community, and the Route Target attricutes it carries are the VRF Route Import Extended Community of the preferred BGP route, which is 2.2.2.2:0.
¡ Upon receiving the C-multicast route, PE 2 compares the IP address in the RT attribute of the route, recognizes it as 2.2.2.2, which is the local source interface address, and accepts the C-multicast route. Then, PE 2 uses the Local Administrator in the RT attribute to determine that the C-multicast route belongs to the public network instance and adds the route to the multicast routing table of the public network instance.
¡ Upon receiving the C-multicast route, PE 1 compares the IP address carried in the RT attricutes of the C-multicast route and finds out that it is 2.2.2.2, not the local source interface address, thus discards the C-multicast route.
When the multicast source in the public network instance subsequently transmits multicast packets, since only PE 2 forms the multicast entry, the multicast packets will be encapsulated in BIER at PE 2, and then transmitted to PE 3 through the BIER public network tunnel. After decapsulation on PE 3, the packets are forwarded to CE 4.
Inter-AS BIER-based MVPN
In an inter-AS VPN networking scenario, VPN sites are located in multiple ASs. These sites must be interconnected. Inter-AS VPN provides the following solutions:
· VRF-to-VRF connections between ASBRs—This solution is also called inter-AS option A.
· EBGP redistribution of labeled VPN-IPv4 routes between ASBRs—ASBRs advertise VPN-IPv4 routes to each other through MP-EBGP. This solution is also called inter-AS option B.
· Multihop EBGP redistribution of labeled VPN-IPv4 routes between PE devices—PEs advertise VPN-IPv4 routes to each other through MP-EBGP. This solution is also called inter-AS option C.
For more information about the three inter-AS VPN solutions, see MPLS L3VPN configuration in MPLS Configuration Guide.
Inter-AS option A BIER-based MVPN
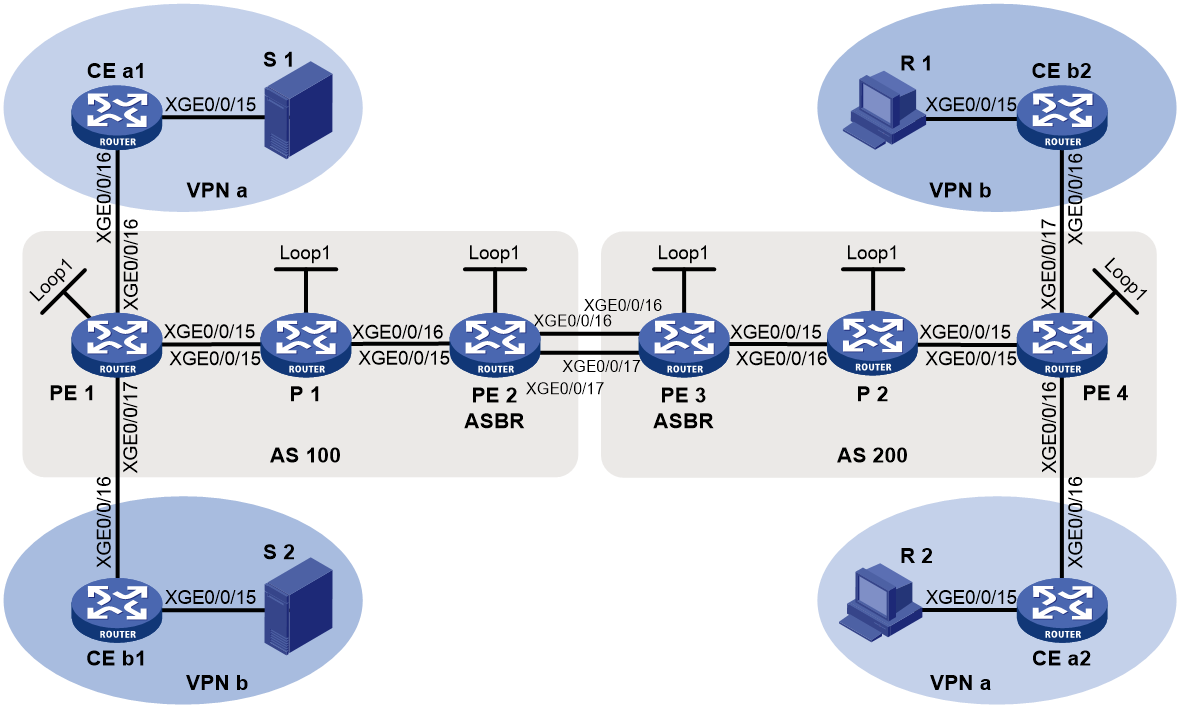
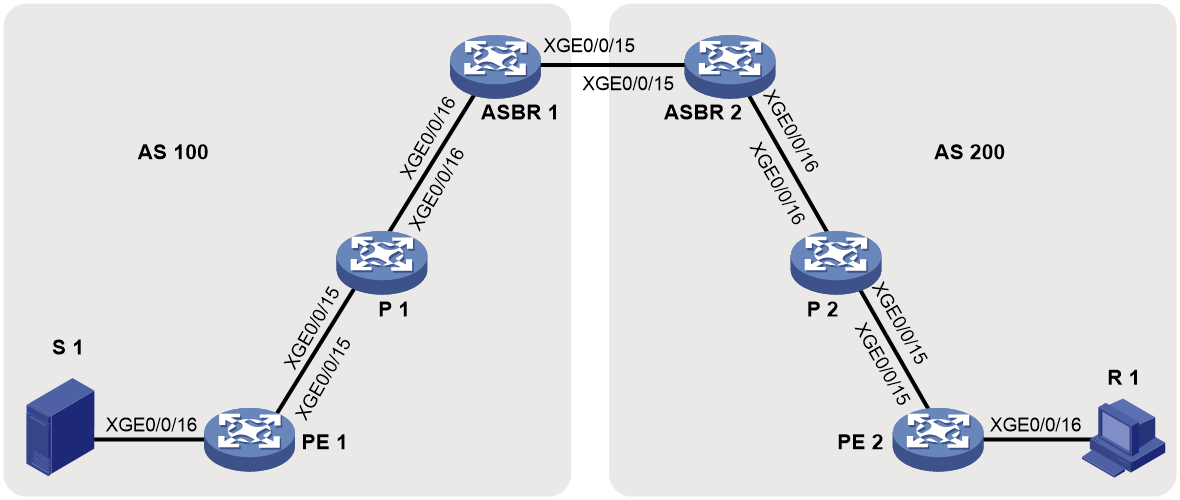
As shown in Figure 10:
· A VPN instance spans AS 100 and AS 200.
· PE 3 and PE 4 are ASBRs for AS 100 and AS 200, respectively.
· PE 3 and PE 4 are interconnected through their respective VPN instance and treat each other as a CE.
Figure 10 Inter-AS option A BIER-based MVPN
To implement inter-AS option A mLDP-based MVPN, a separate MVPN must be created in each AS. Multicast data of the VPN instance is transmitted across the ASs through the separate MVPNs in each AS.
Multicast packets of the VPN instance are delivered as follows:
1. CE 1 forwards a multicast packet of VPN instance 1 to PE 1.
2. PE 1 encapsulates the multicast packet into an MPLS packet and forwards it to PE 3 through BIER tunnel 1.
3. PE 3 considers PE 4 as a CE of MVPN 1, so PE 3 decapsulates the MPLS packet and forwards the multicast packet to PE 4.
4. PE 4 considers PE 2 as a CE of MVPN 2, so PE 4 encapsulates the multicast packet into an MPLS packet and then forwards the packet to PE 2 through BIER tunnel 2.
5. PE 2 decapsulates the MPLS packet and then forwards the multicast packet to CE 2.
In inter-AS option A, PEs in different ASs cannot advertise Source Active A-D routes to each other. Therefore, you must configure MSDP or Anycast-RP between RPs to allow Source Active A-D routes to be advertised across ASs.
Inter-AS option C BIER-based MVPN
Only G-BIER and MSR6 support Inter-AS option C BIER-based MVPN.
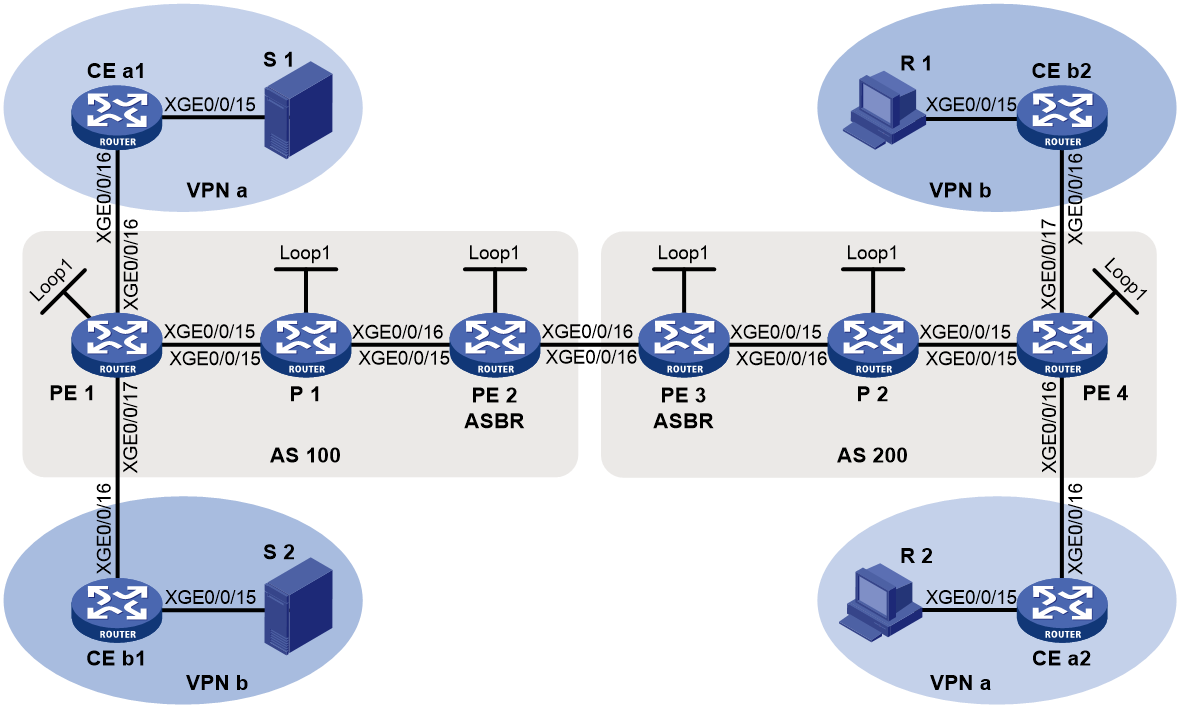
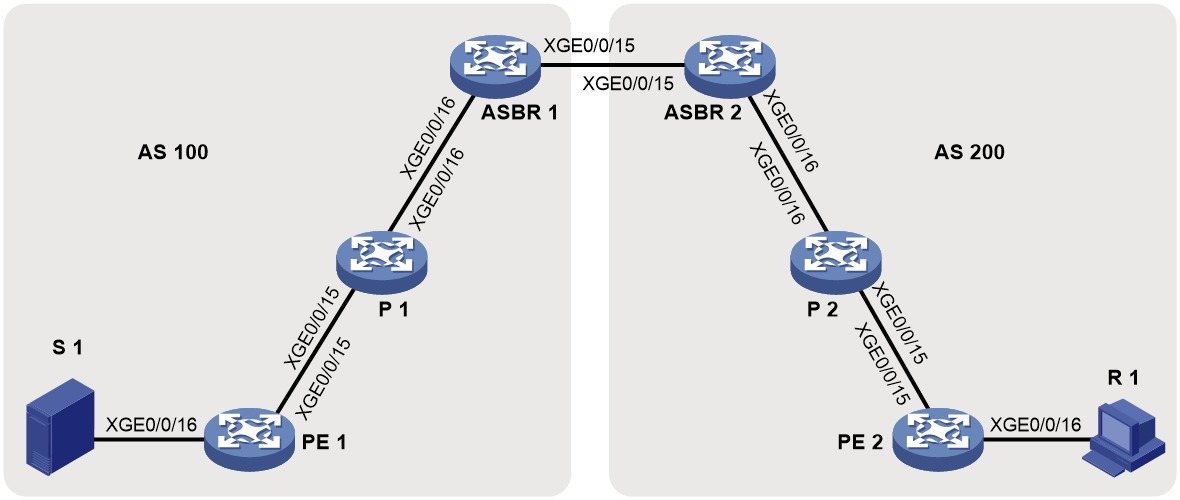
As shown in Figure 11:
· A VPN instance spans AS 100 and AS 200.
· PE 3 and PE 4 are the ASBRs for AS 100 and AS 200, respectively.
· PE 3 and PE 4 are interconnected through MP-EBGP and treat each other as a P device.
· PEs in different ASs establish a multihop MP-EBGP session to advertise VPN-IPv4 routes to each other.
Figure 11 Inter-AS option C BIER-based MVPN
To implement inter-AS option C mLDP-based MVPN, only one MVPN needs to be created cross all ASs. Multicast data is transmitted across the ASs through this MVPN.
Multicast packets of the VPN instance are delivered as follows:
1. Upon receiving a multicast packet of a multicast group in the VPN instance, CE 1 advertises the RP information for this group to PE 1 as follows:
¡ If the RP is PE 1, CE 1 directly sends a register message to PE 1 to advertise the RP information.
¡ If the RP is CE 1 or CE 2, CE 1 advertises the RP information to PE 1 through MSDP or Anycast-RP depending on the actual configuration.
2. PE 1 sends a source-active A-D route to PE 2 through BGP.
3. PE 2 sends a C-multicast route to join the multicast group if it has a receiver attached. The C-multicast route will be advertised to PE 1 through BGP.
4. PE 1 encapsulates the multicast packet into an MPLS packet and then sends the packet to PE 2 through the BIER tunnel.
5. PE 2 decapsulates the MPLS packet and then sends the multicast packet to CE 2.
Protocols and standards
· RFC 8279, Multicast Using Bit Index Explicit Replication (BIER)
· RFC 8296, Encapsulation for Bit Index Explicit Replication (BIER) in MPLS and Non-MPLS Networks
· RFC 8401, Bit Index Explicit Replication (BIER) Support via IS-IS
· RFC 8444, OSPFv2 Extensions for Bit Index Explicit Replication (BIER)
· RFC 8556, Multicast VPN Using Bit Index Explicit Replication
· RFC9272, Underlay Path Calculation Algorithm and Constraints for Bit Index Explicit Replication (BIER)
· draft-xie-bier-ipv6-encapsulation
· draft-cheng-msr6-design-consideration
BIER-based MVPN tasks at a glance
To configure BIER-based MVPN, perform the following tasks on PEs:
1. Enabling IP multicast routing for a VPN instance
2. Configuring BGP MVPN route exchange
¡ Configuring BGP IPv4 MVPN route exchange
¡ Configuring BGP IPv6 MVPN route exchange
3. Configuring BGP extended communities
¡ Allowing the device to add community attributes to C-multicast routes sent to BGP peers
¡ Enabling compatibility for the extended communities of the IPv6 address type
4. Creating a BIER-based MVPN instance
5. Creating an MVPN IPv4 address family
6. Specifying the MVPN source interface
7. Enabling IPv6 underlay for MVPN
8. Configuring source IPv6 addresses for encapsulation
¡ Configuring G-BIER multicast service prefix information
¡ Specifying the multicast service source address
¡ Configuring the source address of the BIERv6 or MSR6 tunnel
9. Configuring inclusive tunnels and selective tunnels
¡ Enabling inclusive tunnel creation
¡ (Optional.) Enabling selective tunnel creation
¡ (Optional.) Setting the tunnel holddown timer
10. (Optional.) Enabling inter-AS auto-discovery
11. (Optional.) Configuring BIER FRR
12. (Optional.) Configuring multicast warm backup
¡ Enabling multicast warm backup
13. (Optional.) Configuring the selection of the master IDF based on (S, G) entries
Prerequisites for configuring BIER-based MVPN
Before you configure BIER-based MVPN, complete the following tasks:
· Configure a unicast routing protocol on the public network.
· Configure MPLS LDP or SRv6 on the public network.
· Configure BIER on the public network.
· Configure BGP to enable PEs to mutually establish neighbor relationship.
Enabling IP multicast routing for a VPN instance
Restrictions and guidelines
For a multi-VPN instance scenario, you must configure different route targets for each VPN instance.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a VPN instance and enter its view.
ip vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
For more information about this command, see MPLS L3VPN commands in MPLS Command Reference.
3. Configure an RD for the VPN instance.
route-distinguisher route-distinguisher
For more information about this command, see MPLS L3VPN commands in MPLS Command Reference.
4. Configure route targets for the VPN instance.
vpn-target vpn-target&<1-8> [ both | export-extcommunity | import-extcommunity ]
For more information about this command, see MPLS L3VPN commands in MPLS Command Reference.
5. Return to system view.
quit
6. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
7. Associate the interface with the VPN instance.
ip binding vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
By default, an interface is associated with no VPN instance and belongs to the public network.
For more information about this command, see MPLS L3VPN commands in MPLS Command Reference.
8. Return to system view.
quit
9. Enable IP multicast routing for the VPN instance and enter MRIB view of the VPN instance.
IPv4:
multicast routing vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
By default, IP multicast routing is disabled for a VPN instance.
For more information about the commands, see multicast routing and forwarding commands in IP Multicast Command Reference.
Configuring BGP MVPN route exchange
Configuring BGP IPv4 MVPN route exchange
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter BGP instance view.
bgp as-number [ instance instance-name ]
3. Specify a BGP MVPN peer and its AS number.
peer ipv6-address as-number as-number
4. Enter BGP IPv4 MVPN address family view.
address-family ipv4 mvpn
5. Enable BGP to exchange IPv4 unicast routing information with BGP peers.
peer ipv6-address enable
By default, BGP cannot exchange IPv4 unicast routing information with BGP peers.
For more information about this command, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
6. (Optional.) Specify the maximum number of routes that a router can receive from a peer or peer group.
peer { group-name | ipv4-address [ mask-length ] } route-limit prefix-number [ { alert-only | discard | reconnect reconnect-time } | percentage-value ] *
By default, the number of routes that a router can receive from a peer or peer group is not limited.
7. (Optional.) Configure the BGP Additional Paths feature.
a. Configure the BGP Additional Paths capabilities.
peer { group-name | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] } additional-paths { receive | send } *
By default, no BGP Additional Paths capabilities are configured
b. Set the maximum number of Add-Path optimal routes that can be advertised to a peer or peer group.
peer { group-name | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] } advertise additional-paths best number
By default, a maximum number of one Add-Path optimal route can be advertised to a peer or peer group.
c. Set the maximum number of Add-Path optimal routes that can be advertised to all peers.
additional-paths select-best best-number
By default, a maximum number of one Add-Path optimal route can be advertised to all peers.
For more information about the commands in this step, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
8. (Optional.) Advertise the COMMUNITY or Large Community attribute to a peer or peer group.
¡ Advertise the COMMUNITY attribute to a peer or peer group.
peer { group-name | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] } advertise-community
By default, the COMMUNITY attribute advertisement to a peer or peer group is disabled.
¡ Advertise the Large Community attribute to a peer or peer group.
peer { group-name | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] } advertise-large-community
By default, the Large Community attribute advertisement to a peer or peer group is disabled.
For more information about the commands in this step, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
9. (Optional.) Disable route target filtering of received BGP IPv4 MVPN routes.
undo policy vpn-target
By default, a PE device filters route targets for received BGP IPv4 MVPN routes.
10. (Optional.) Set the optimal route selection delay timer.
route-select delay delay-value
By default, the optimal route selection delay timer is 0 seconds, which means optimal route selection is not delayed.
For more information about this command, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
11. Prefer routes learned from the specified peer or peer group during optimal route selection.
peer { group-name | ipv4-address [ mask-length ] | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] } high-priority
By default, BGP does not prefer routes learned from any peer or peer groups during optimal route selection.
For more information about this command, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
Configuring BGP IPv6 MVPN route exchange
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter BGP instance view.
bgp as-number [ instance instance-name ]
3. Specify a BGP MVPN peer and its AS number.
peer ipv6-address as-number as-number
4. Enter BGP IPv6 MVPN address family view.
address-family ipv6 mvpn
5. Enable BGP to exchange IPv6 unicast routing information with dynamic BGP peers.
peer ipv6-address enable
By default, BGP cannot exchange IPv6 unicast routing information with dynamic BGP peers.
For more information about this command, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
6. (Optional.) Specify the maximum number of routes that a router can receive from a peer or peer group.
peer { group-name | ipv4-address [ mask-length ] } route-limit prefix-number [ { alert-only | discard | reconnect reconnect-time } | percentage-value ] *
By default, the number of routes that a router can receive from a peer or peer group is not limited.
7. (Optional.) Configure the BGP Additional Paths feature.
a. Configure the BGP Additional Paths capabilities.
peer { group-name | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] } additional-paths { receive | send } *
By default, no BGP Additional Paths capabilities are configured
b. Set the maximum number of Add-Path optimal routes that can be advertised to a peer or peer group.
peer { group-name | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] } advertise additional-paths best number
By default, a maximum number of one Add-Path optimal route can be advertised to a peer or peer group.
c. Set the maximum number of Add-Path optimal routes that can be advertised to all peers.
additional-paths select-best best-number
By default, a maximum number of one Add-Path optimal route can be advertised to all peers.
For more information about the commands in this step, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
8. (Optional.) Advertise the COMMUNITY or Large Community attribute to a peer or peer group.
¡ Advertise the COMMUNITY attribute to a peer or peer group.
peer { group-name | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] } advertise-community
By default, the COMMUNITY attribute advertisement to a peer or peer group is disabled.
¡ Advertise the Large Community attribute to a peer or peer group.
peer { group-name | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] } advertise-large-community
By default, the Large Community attribute advertisement to a peer or peer group is disabled.
For more information about the commands in this step, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
9. (Optional.) Disable route target filtering of received BGP IPv6 MVPN routes.
undo policy vpn-target
By default, a PE device filters route targets for received BGP IPv6 MVPN routes.
10. (Optional.) Set the optimal route selection delay timer.
route-select delay delay-value
By default, the optimal route selection delay timer is 0 seconds, which means optimal route selection is not delayed.
For more information about this command, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
11. Prefer routes learned from the specified peer or peer group during optimal route selection.
peer { group-name | ipv4-address [ mask-length ] | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] } high-priority
By default, BGP does not prefer routes learned from any peer or peer groups during optimal route selection.
For more information about this command, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
Configuring BGP extended communities
Allowing the device to add community attributes to C-multicast routes sent to BGP peers
About this task
Perform this task to add the following attributes to routes sent to BGP peers:
· Source AS Extended Community—Carries the number of AS where the MVPN source resides. The format of this attribute is 32-bit AS number:0, for example, 100:0.
· VRF Route Import Extended Community—Carries the source address and the VPN instance to which the BGP route belongs. The format of the attribute is 32-bit or 128-bit source address:VPN instance index, for example, 192.168.122.15:1.
· IDF Negotiation Community—If both peers in a BGP session receive routes carrying this attribute from each other, they will negotiate and elect the master IDF and standby IDF. The value of this attribute is 0x0000ffff. This attribute can be added to routes only if you enable multicast warm backup by using the warm-root-standby command. If multicast warm backup is not enabled, only the Source AS Extended Community and VRF Route Import Extended Community attributes are added to routes.
In a multicast VPN, the multicast source-side PE will distribute locally generated Source AS Extended Community, VRF Route Import Extended Community, and IDF Negotiation Community attributes through routes from private network CEs to other PEs for the establishment of multicast entries and master IDF election. However, when an MVPN belongs to a public network instance and both the PE and CE are in the public network, the multicast source-side PE cannot automatically determine which routes need to carry those attributes.
You can perform this task to specify the CEs in the public network for which the three attributes are added.
Restrictions and guidelines
· If the multicast source and multicast receivers are in the public network and IPv6 underlay is enabled for MVPN, perform this task in BGP IPv6 unicast address family view or BGP IPv6 multicast address family view. If IPv6 underlay is disabled for MVPN, perform this task in BGP IPv4 unicast address family view or BGP IPv4 multicast address family view.
· If the multicast source and multicast receivers are in a private network, perform this task in BGP VPNv4 address family view, BGP VPNv6 address family view, or BGP EVPN address family view.
· Perform this task in BGP IPv4 unicast address family view has the same effect as performing this task in BGP IPv4 multicast address family view. Perform this task in BGP IPv6 unicast address family view has the same effect as performing this task in BGP IPv6 multicast address family view.
· Perform this task in BGP IPv4 unicast address family view has the same effect as performing this task in BGP IPv6 unicast address family view.
· Before you perform this task in BGP IPv4 unicast address family view, BGP IPv4 multicast address family view, BGP VPNv4 address family view, you must establish BGP IPv4 MVPN peer relationship.
· Before you perform this task in BGP IPv6 unicast address family view, BGP IPv6 multicast address family view, BGP VPNv6 address family view, you must establish BGP IPv6 MVPN peer relationship.
· After you execute the mvpn-advertise-rt-import command in the following views, the VPN instance index in advertised BGP routes is 0:
¡ BGP IPv4 unicast address family view.
¡ BGP IPv4 multicast address family view.
¡ BGP IPv6 unicast address family view.
¡ BGP IPv6 multicast address family view.
If the source command is used to specify the MVPN source interface, the source address is the IP address of the MVPN source interface. If the source command is not used, the source address is the router ID of the BGP instance to which the device belongs.
The VPN instance and source IP address identify the device that generates a route.
· If a route from a BGP peer contains the three attributes, the device will not add or modify them.
· After you execute the undo peer mvpn-rt-import command, the device no longer adds the three attributes to received routes and deletes the attributes that have been added to routes.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter BGP instance view.
bgp as-number [ instance instance-name ]
3. Enter one of the following views:
¡ Enter BGP VPNv4 address family view.
address-family vpnv4
¡ Enter BGP VPNv6 address family view.
address-family vpnv6
¡ Enter BGP EVPN address family view.
address-family l2vpn evpn
¡ Enter BGP IPv4 unicast address family view.
address-family ipv4 [ unicast ]
¡ Enter BGP IPv4 multicast address family view.
address-family ipv4 multicast
¡ Enter BGP IPv6 unicast address family view.
address-family ipv6 [ unicast ]
¡ Enter BGP IPv6 multicast address family view.
address-family ipv6 multicast
4. Allow the device to add the Source AS Extended Community, VRF Route Import Extended Community, and IDF Negotiation Community attributes to routes sent to BGP peers.
mvpn-advertise-rt-import
By default, the device is disabled from adding the three attributes to routes sent to BGP peers.
5. (Optional.) Allow the device to add the Source AS Extended Community, VRF Route Import Extended Community, and IDF Negotiation Community attributes to routes received from BGP peers.
mvpn-advertise-rt-import
By default, the device is disabled from adding the three attributes to routes received from BGP peers.
This command is available only in BGP IPv4 unicast address family view, BGP IPv4 multicast address family view, BGP IPv6 unicast address family view, and BGP IPv6 multicast address family view.
Enabling compatibility for the extended communities of the IPv6 address type
About this task
According to IANA, the values of the VRF Route Import and Route Target extended communities of the IPv6 address type are 0x000b and 0x0002, respectively. H3C devices carry the two extended communities in BGP routes with the values as specified by IANA. Some vendors define the VRF Route Import and Route Target extended communities as 0x010b and 0x0102, respectively. H3C devices cannot interoperate with devices from such vendors.
This feature enables the device to modify the values of the VRF Route Import and Route Target extended communities in sent BGP routes to 0x010b and 0x0102, respectively. This feature can also modifies the values of the VRF Route Import and Route Target extended communities in received BGP routes to 0x000b and 0x0002, respectively.
Restrictions and guidelines
For this feature to take effect, you must execute the ipv6 underlay enable command. The device can send the extended communities of the IPv6 address type only after you execute the ipv6 underlay enable command.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter BGP instance view.
bgp as-number [ instance instance-name ]
3. Enter one of the following views:
¡ Enter BGP VPNv4 address family view.
address-family vpnv4
¡ Enter BGP VPNv6 address family view.
address-family vpnv6
¡ Enter BGP IPv4 unicast address family view.
address-family ipv4 [ unicast ]
¡ Enter BGP IPv4 multicast address family view.
address-family ipv4 multicast
¡ Enter BGP IPv6 unicast address family view.
address-family ipv6 [ unicast ]
¡ Enter BGP IPv6 multicast address family view.
address-family ipv6 multicast
¡ Enter BGP IPv4 MVPN address family view.
address-family ipv4 mvpn
¡ Enter BGP IPv6 MVPN address family view.
address-family ipv6 mvpn
4. Enable compatibility for the extended communities of the IPv6 address type.
peer { group-name | ipv4-address [ mask-length ] | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] } mvpn-ipv6-rt-compatible
By default, compatibility for the extended communities of the IPv6 address type is disabled.
Creating a BIER-based MVPN instance
About this task
You can create one or more BIER-based MVPN instances on a PE device to provide services for VPN instances or the public network instance.
The public network instance can be considered as a special VPN instance. The public network instance allows a PE to forward Layer 3 multicast traffic of the public network through a BIER tunnel.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a BIER-based MVPN instance and enter its view.
¡ Create an MVPN for a VPN instance and enter MVPN view.
multicast-vpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name mode bier
¡ Create an MVPN for the public network instance and enter MVPN view.
multicast-vpn public-instance mode bier
Creating an MVPN IPv4 address family
Restrictions and guidelines
Configurations in MVPN IPv4 address family view apply only to IPv4 multicast.
Configurations in MVPN IPv6 address family view apply only to IPv6 multicast.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter MVPN view.
multicast-vpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name mode bier
3. Create an MVPN address family and enter its view.
IPv4:
address-family ipv4
IPv6:
address-family ipv6
Specifying the MVPN source interface
About this task
MVPN source interface information is transmitted between the multicast source PE and the receiver PE through Type 1 Intra-AS I-PMSI A-D Routes and Type 4 Leaf A-D Routes in BGP messages to identify the local node.
Restrictions and guidelines
For an MVPN that transmits both IPv4 and IPv6 multicast packets, you must specify the same MVPN source interface in MVPN IPv4 and IPv6 address family views.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter MVPN view.
multicast-vpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name mode bier
3. Enter MVPN address family view.
IPv4:
address-family ipv4
IPv6:
address-family ipv6
4. Specify the MVPN source interface.
source interface-type interface-number
By default, no MVPN source interface is specified.
Enabling IPv6 underlay for MVPN
About this task
By default, the originating router's IP address in a BGP MVPN route and the router ID in the VRF Route Import extended community are both IPv4 addresses. If the two addresses in a BGP MVPN route from another vendor's device are IPv6 addresses, BGP MVPN route exchange will fail. This function enables the device to carry the IPv6 address of the MVPN source interface in the two fields and to identify and accept BGP MVPN routes with IPv6 addresses.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter MVPN address family view.
IPv4:
address-family ipv4
IPv6:
address-family ipv6
3. Enable IPv6 underlay for MVPN.
ipv6 underlay enable
By default, IPv6 underlay is disabled for MVPN.
Configuring source IPv6 addresses for encapsulation
Configuring G-BIER multicast service prefix information
About this task
In a BIER-based MVPN, you must configure a multicast service prefix for each multicast source-side PE. The PEs calculate a multicast service source address for identifying different MVPN instances based on the prefix address and length, multicast service ID (configured with the tunnel-source command) and the ID length. A PE uses this source address as the IPv6 source address when encapsulating multicast packets in BIER. This source address keeps unchanged when multicast packets are transmitted on the public network.
Restrictions and guidelines
Make sure the multicast service prefix addresses are different for different PEs and are different from the IPv6 addresses on the device. After the configuration, execute the display multicast-service-prefix configuration command to identify whether the multicast service prefixes are deployed successfully.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure multicast service prefix information.
multicast-service-prefix prefix-name ipv6-prefix ipv6-address prefix-length service-id-length id-length
By default, no multicast service prefix information is configured.
Specifying the multicast service source address of the G-BIER tunnel
About this task
With this multicast service source address configured, a multicast source-side PE uses this address as the source IPv6 address for BIER encapsulation. This source address keeps unchanged when multicast packets are transmitted on the public network.
The multicast service source address is calculated based on the prefix address and length, and multicast service ID and ID length, which are configured by using the multicast-service-prefix command.
Restrictions and guidelines
To bind a multicast service source address to only one MVPN instance, you can configure only one multicast service address in one MVPN address family view.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter MVPN view.
multicast-vpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name mode bier
3. Enter MVPN address family view.
IPv4:
address-family ipv4
IPv6:
address-family ipv6
4. Specify the multicast service source address.
tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix prefix-name service-id id-number service-id-length id-length
By default, no multicast service source address is specified.
Configuring the source address of the BIERv6 or MSR6 tunnel
About this task
A multicast source-side PE uses the source address of the BIERv6 or MSR6 tunnel as the source IPv6 address for BIERv6 or MSR6 encapsulation. This source address keeps unchanged when multicast packets are transmitted on the public network.
A multicast source-side PE can carry an SID (the source address of the BIERv6 or MSR6 tunnel) in a type-1 route (Intra-AS I-PMSI A-D route) or type-3 route (S-PMSI A-D route). After a multicast receiver-side PE receives a type-1 or type-3 route, it matches a VPN instance or the public network instance according to the route target attribute in the route. Then, it records the mapping between the SID and the VPN instance or the public network instance. After a multicast receiver-side PE receives a BIERv6- or MSR6-encapsulated multicast packet, it finds the VPN instance or the public network instance corresponding to the source address of the BIERv6 or MSR6 tunnel. Then, it creates a multicast forwarding entry in the MVPN corresponding to the VPN instance or the public network instance, and forwards the packet.
Restrictions and guidelines
For the sid ipv6-address option to take effect, you must configure the static length (the static static-length option) for the specified locator.
For the specified multicast service source address to take effect, it must be in the range of the static start SRv6 SID to the static end SRv6 SID of the locator. To view the static start SRv6 SID and the static end SRv6 SID, see the Static SID start and Static SID end fields, respectively, in the display segment-routing ipv6 locator command output. For more information about the display segment-routing ipv6 locator command, see SRv6 commands in Segment Routing Command Reference.
To bind a BIERv6 or MSR6 tunnel source address to only one MVPN instance, you must configure only one BIERv6 or MSR6 tunnel source address in the same MVPN address family view.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter MVPN view.
multicast-vpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name mode bier
3. Enter MVPN address family view.
IPv4:
address-family ipv4
IPv6:
address-family ipv6
4. Specify the source address of the BIERv6 or MSR6 tunnel.
IPv4 multicast VPN:
src-dt4 locator locator-name sid ipv6-address
By default, no BIERv6 or MSR6 tunnel source address is specified in an IPv4 multicast VPN.
This command is supported only in MVPN IPv4 address family view.
IPv6 multicast VPN:
src-dt6 locator locator-name sid ipv6-address
By default, no BIERv6 or MSR6 tunnel source address is specified in an IPv6 multicast VPN.
This command is supported only in MVPN IPv6 address family view.
5. Execute the quit command twice to return to system view.
quit
quit
6. Enter BGP instance view.
bgp as-number [ instance instance-name ]
7. Enter BGP IPv4 MVPN or BGP IPv6 MVPN address family view.
¡ Enter BGP IPv4 MVPN address family view.
address-family ipv4 mvpn
¡ Enter BGP IPv6 MVPN address family view.
address-family ipv6 mvpn
8. Enable the device to send routes with SIDs to an IPv6 peer or peer group.
peer { group-name | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] } prefix-sid
By default, the device cannot send routes with SIDs to IPv6 peers.
This command is not needed for an MSR6 tunnel.
Configuring inclusive tunnels and selective tunnels
Enabling inclusive tunnel creation
Restrictions and guidelines
Once created, the inclusive tunnel always exists no matter whether multicast traffic is present or not.
Only one inclusive tunnel can be established between two PEs in an MVPN.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter MVPN view.
multicast-vpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name mode bier
3. Enter MVPN address family view.
IPv4:
address-family ipv4
IPv6:
address-family ipv6
4. Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation.
inclusive-tunnel dynamic [ sub-domain sub-domain-id ] [ bsl bsl-value ]
By default, dynamic inclusive tunnel creation is disabled.
Enabling selective tunnel creation
About this task
Multicast traffic that matches the tunnel switchover criterion is switched over to selective tunnels from the inclusive tunnel after selective tunnel are created.
Restrictions and guidelines
Selective tunnels are created only after the multicast traffic is transmitted over the inclusive tunnel.
Multicast packets for multiple (S, G) entries can share the same selective tunnel.
Multiple selective tunnels can be created between two PEs in an MVPN. These selective tunnels are independent from one another.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter MVPN view.
multicast-vpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name mode bier
3. Enter MVPN address family view.
IPv4:
address-family ipv4
IPv6:
address-family ipv6
4. Enable dynamic selective tunnel creation.
MVPN IPv4 address family:
selective-tunnel dynamic [ acl { ipv4-acl-number | name ipv4-acl-name } ] [ threshold threshold-value ] [ sub-domain sub-domain-id ] [ bsl bsl-value ] [ tunnel-limit number ]
MVPN IPv6 address family:
selective-tunnel dynamic [ acl { ipv6-acl-number | name ipv6-acl-name } ] [ threshold threshold-value ] [ sub-domain sub-domain-id ] [ bsl bsl-value ] [ tunnel-limit number ]
By default, dynamic selective tunnel creation is disabled.
Setting the tunnel holddown timer
About this task
To avoid multicast data loss during tunnel switchover, set the holddown timer for multicast traffic to switch back from selective tunnels to the inclusive tunnel.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter MVPN view.
multicast-vpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name mode bier
3. Enter MVPN address family view.
IPv4:
address-family ipv4
IPv6:
address-family ipv6
4. Set the tunnel holddown timer.
selective-tunnel holddown holddown-time
By default, the holddown timer is 60 seconds for multicast traffic to switch back from selective tunnels to the inclusive tunnel.
Enabling inter-AS auto-discovery
About this task
This feature inhibits the device from carrying the NO_EXPORT attribute in intra-AS A-D routes and S-PMSI A-D routes sent to BGP. Use this feature on the multicast source-side PE in an inter-AS MVPN scenario so that these routes can be discovered on the devices out of the local AS.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter MVPN view.
multicast-vpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name mode bier
3. Enter MVPN address family view.
IPv4:
address-family ipv4
IPv6:
address-family ipv6
4. Enable inter-AS auto-discovery.
auto-discovery inter-as
By default, inter-AS auto-discovery is disabled.
Configuring BIER FRR
About this task
When the source-side PE fails, multicast services will be interrupted. Multicast services will be restored only after the unicast routes converge. However, the long convergence time of unicast routes cannot meet the real-time requirements of multicast services. FRR can solve this problem.
A multicast source is connected to the public network through PE1 and PE 2. Two BIER tunnels are established with PE 1 and PE 2 as the roots and the receiver-side PE as the leaf. In normal cases, the multicast data traffic is transmitted over both BIER tunnels. The receiver-side PE accept the multicast data traffic from the primary BIER tunnel drops multicast data traffic from the backup tunnel. With FRR enabled, the receiver-side PE saves the primary and backup interfaces for the same (S, G) entry and detects the multicast data traffic on them. If the multicast data traffic is not received on the primary interface, it indicates that the primary tunnels fails. The receiver-side PE accepts the multicast data traffic from the backup tunnel. This improves the convergence speed and reliability of multicast services.
Restrictions and guidelines
If the multicast source and multicast receivers are in the public network, perform this task in BGP address family view. If the multicast source and multicast receivers are in a private network, perform this task in MVPN address family view.
Configuring FRR in MVPN address family view
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter MVPN view.
multicast-vpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name mode bier
3. Enter MVPN address family view.
IPv4:
address-family ipv4
IPv6:
address-family ipv6
4. Enable MVPN FRR.
c-multicast frr [ acl-number | name acl-name ]
By default, MVPN FRR is disabled.
Configuring FRR in BGP address family view
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter BGP instance view.
bgp as-number [ instance instance-name ]
3. Enter BGP multicast address family view.
IPv4:
address-family ipv4 multicast
IPv6:
address-family ipv6 multicast
4. Enable public network FRR.
pic
By default, public network FRR is disabled.
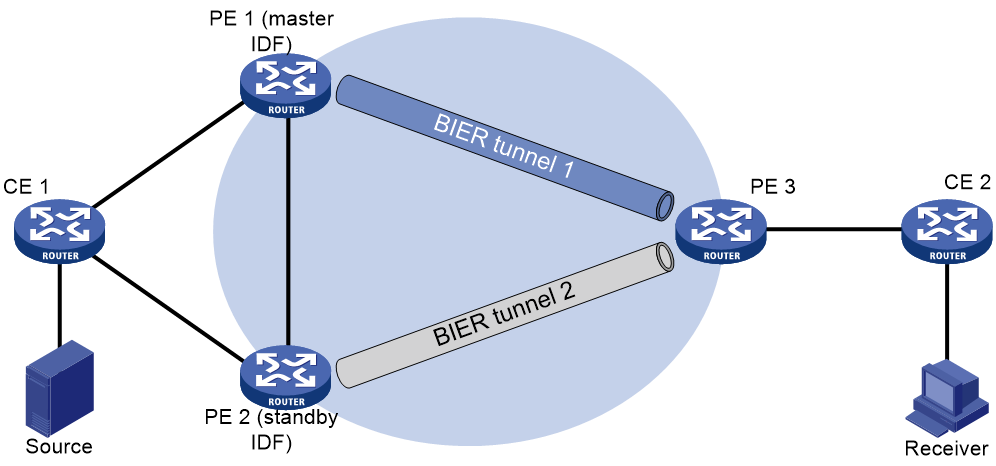
Configuring multicast warm backup
Enabling multicast warm backup
About this task
In multicast VPN, services will be interrupted when the multicast source-side PE becomes faulty. Multicast services can only resume after unicast route convergence, which takes too long to meet real-time service requirements.
Deploying two multicast source-side PEs in the network and enabling multicast warm backup on both PEs and corresponding receiver-side PEs can resolve the problem.
As shown in Figure 12, the multicast source is accessed through two PEs (PE 1 and PE 2) to the public network. The receiver-side PE sends multicast join requests to both PE 1 and PE 2, forming two BIER tunnels with PE 1 and PE 2 as roots and the receiver-side PE (PE 3) as the leaf.
At any given time, only one multicast source-side PE is responsible for sending multicast traffic to the receiver-side PE. When the link is normal, the multicast source-side PE responsible for sending multicast traffic to the receiver-side is called the master ingress designated forwarder (IDF), and the other multicast source-side PE is the standby IDF. When the master IDF fails, the standby IDF takes over to send multicast traffic to the receiver-side PE.
Restrictions and guidelines
· Only BIER-based MVPN supports this feature.
· Multicast warm backup and multicast FRR are mutually exclusive and cannot be both configured for the same MVPN.
· Multicast warm backup and multicast load splitting are mutually exclusive and cannot be both configured for the same MVPN. For more information about multicast load splitting, see the load-splitting command in IP Multicast Command Reference.
· Due to the periodic detection of traffic, multicast warm backup is suitable for only scenarios involving continuous, high-speed forwarding of multicast traffic. Otherwise, the lack of detected traffic might prevent the standby IDF from taking over the forwarding of traffic from the master IDF.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter MVPN view.
multicast-vpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name mode bier
3. Enter MVPN address family view.
IPv4:
address-family ipv4
IPv6:
address-family ipv6
4. Enable multicast warm backup.
warm-root-standby [ acl-number | name acl-name ]
By default, multicast warm backup is disabled.
Configuring the selection of the master IDF based on (S, G) entries
About this task
A multicast source is accessed through two PEs (PE 1 and PE 2) to the public network. The receiver-side PE sends multicast join requests to both PE 1 and PE 2, forming two BIER tunnels with PE 1 and PE 2 as roots and the receiver-side PE (PE 3) as the leaf.
The following master IDF selection rules are supported:
· MVPN instance-based—Selects the root of the BIER tunnel with a lower source IP address as the master IDF.
· (S, G) entry-based—Uses a specific hash function to calculate a hash value based on the BIER tunnel source address, the multicast source address S, and the multicast group address G and selects the root of the BIER tunnel with a smaller hash value as the master IDF.
Restrictions and guidelines
· Before performing this task, use the warm-root-standby command to enable multicast warm backup.
· Multicast warm backup and multicast FRR are mutually exclusive and cannot be both configured for the same MVPN.
· You can use the following commands to specify a source IP address for a BIER tunnel:
¡ To specify a source IP address source address of a G-BIER tunnel, use the tunnel-source command.
¡ To specify a source IP address for a BIERv6 or MSR6 tunnel in IPv4 multicast VPN, use the src-dt4 locator command.
¡ To specify a source IP address for a BIERv6 or MSR6 tunnel in IPv6 multicast VPN, use the src-dt6 locator command.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure the selection of the master IDF based on (S, G) entries.
multicast-vpn idf-selection source-group
By default, the master IDF is selected based on MVPN instances.
Display and maintenance commands for BIER-based MVPN
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
|
Display BGP MVPN peer group information. |
display bgp [ instance instance-name ] group ipv4 mvpn [ group-name group-name ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] group ipv6 mvpn [ group-name group-name ] |
|
|
Display information about BGP MVPN peers or peer groups. |
display bgp [ instance instance-name ] peer ipv4 mvpn [ ip-address mask-length | { ip-address | group-name group-name } log-info | [ ip-address ] verbose ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] peer ipv6 mvpn [ ip-address mask-length | { ip-address | group-name group-name } log-info | [ ip-address ] verbose ] |
|
|
Display information about BGP IPv4 MVPN routes. |
display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv4 mvpn [ { public | route-distinguisher route-distinguisher } [ route-type { intra-as I inter-as | s-pmsi | leaf | source-active | shared-tree | source-tree } ] [ mvpn-prefix ] | statistics ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv4 mvpn [ public | route-distinguisher route-distinguisher ] [ mvpn-prefix [ advertise-info ] ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv4 mvpn [ route-type { intra-as I inter-as | s-pmsi | leaf | source-active | shared-tree | source-tree } [ statistics ] ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv4 mvpn peer ip-address { advertised-routes | received-routes } [ mvpn-prefix [ verbose ] | statistics ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv4 mvpn { as-path-acl { as-path-acl-number | as-path-acl-name } | as-path-regular-expression regular-expression } display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv4 mvpn { public | route-distinguisher route-distinguisher } route-type { inter-as | intra-as | leaf | s-pmsi | shared-tree | source-active | source-tree } time-range min-time max-time |
|
|
Display information about BGP IPv6 MVPN routes. |
display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv6 mvpn [ { public | route-distinguisher route-distinguisher } [ route-type { inter-as |intra-as | leaf | s-pmsi | shared-tree | source-active | source-tree } ] [ mvpn-prefix ] | statistics ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv6 mvpn [ public | route-distinguisher route-distinguisher ] [ mvpn-prefix [ advertise-info ] ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv6 mvpn [ route-type { inter-as |intra-as | leaf | s-pmsi | shared-tree | source-active | source-tree } [ statistics ] ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv6 mvpn peer { ipv4-address | ipv6-address } { advertised-routes | received-routes } [ mvpn-prefix [ verbose ] | statistics ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv6 mvpn { as-path-acl { as-path-acl-number | as-path-acl-name } | as-path-regular-expression regular-expression } display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv6 mvpn { public | route-distinguisher route-distinguisher } route-type { inter-as | intra-as | leaf | s-pmsi | shared-tree | source-active | source-tree } time-range min-time max-time |
|
|
Display the contents of the Source AS and VRF Route Import extended community attributes added to BGP routes. |
display bgp [ instance instance-name ] { ipv4 | ipv6 } route-target mvpn |
|
|
Display information about C-multicast A-D routes. |
display multicast-vpn { vpn-instance vpn-instance-name| public-instance } [ ipv6 ] c-multicast routing-table [ group-address [ mask { mask-length | mask } ] | source-address [ mask { mask-length | mask } ] | outgoing-interface { exclude | include | match } interface-type interface-number ] |
|
|
Display BIER tunnel neighbor information for MVPN. |
display multicast-vpn { vpn-instance vpn-instance-name | public-instance } neighbor [ interface tunnel number ] |
|
|
Display information about the inclusive tunnel for a VPN instance. |
display multicast-vpn { vpn-instance vpn-instance-name | public-instance } [ ipv6 ] inclusive-tunnel { local | remote } |
|
|
Display information about selective tunnels for a VPN instance. |
display multicast-vpn { vpn-instance vpn-instance-name | public-instance } [ ipv6 ] selective-tunnel { local [ interface interface-type interface-number ] | remote } |
|
|
Display multicast service prefix configuration. |
display multicast-service-prefix configuration |
|
|
Display BIERv6 tunnel source addresses. |
display multicast-src-dt configuration [ locator locator-name ] |
|
|
Reset BGP sessions for BGP IPv4 MVPN address family. |
reset bgp [ instance instance-name ] { as-number | ipv4-address [ mask-length ] | all | external | group group-name | internal } ipv4 mvpn reset bgp [ instance instance-name ] ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] ipv4 mvpn |
|
|
Reset BGP sessions for BGP IPv6 MVPN address family. |
reset bgp [ instance instance-name ] { as-number | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] | all | external | group group-name | internal } ipv6 mvpn reset bgp [ instance instance-name ] ipv4-address [ mask-length ] ipv6 mvpn |
|
For more information about the display bgp group, display bgp peer, display bgp update-group, and reset bgp commands, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
BIER-based MVPN configuration examples
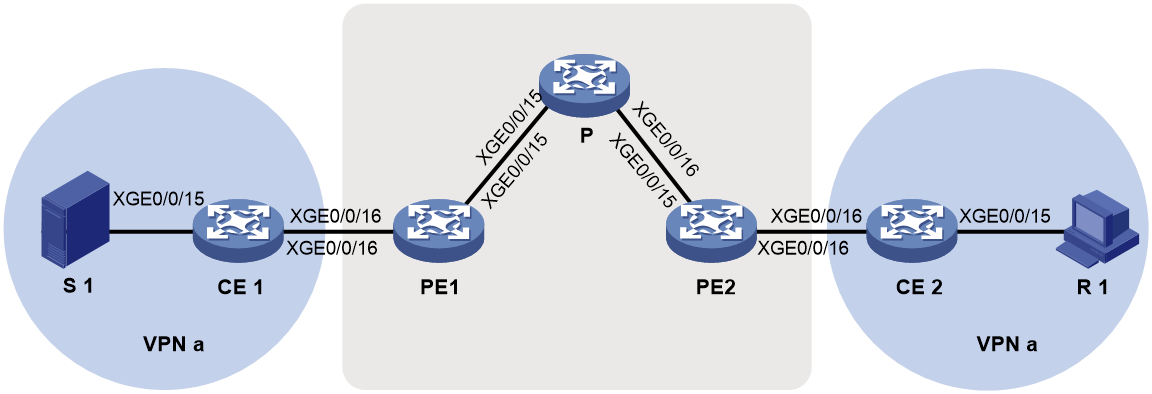
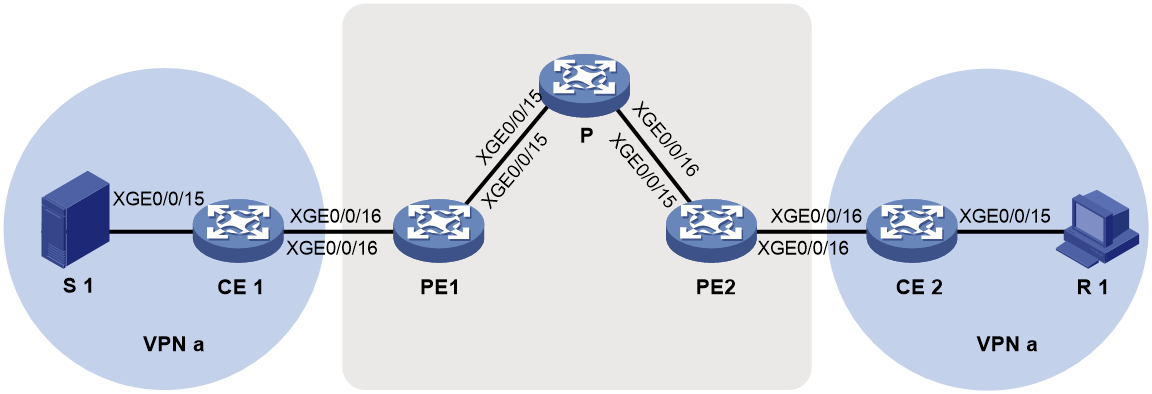
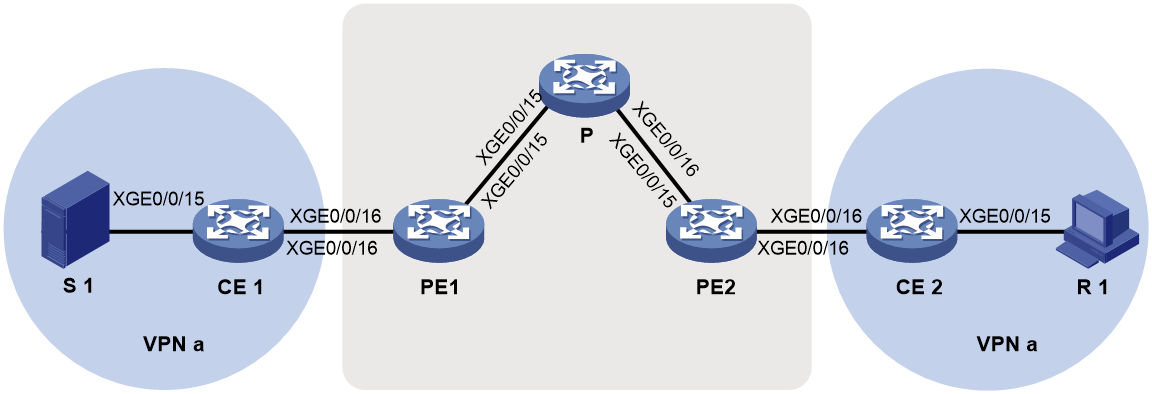
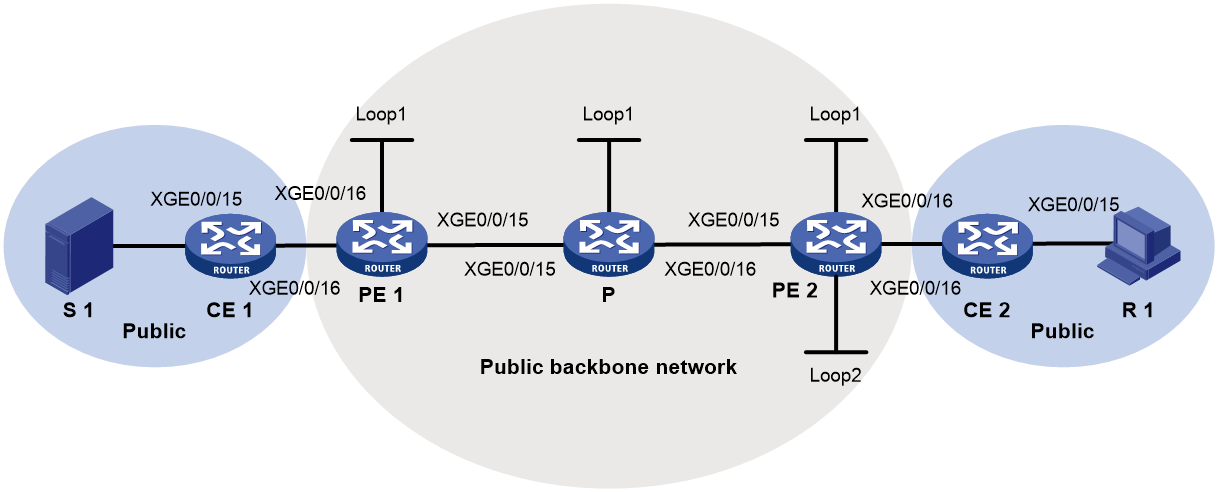
Example: Configuring intra-AS BIER-based MVPN (G-BIER encapsulation)
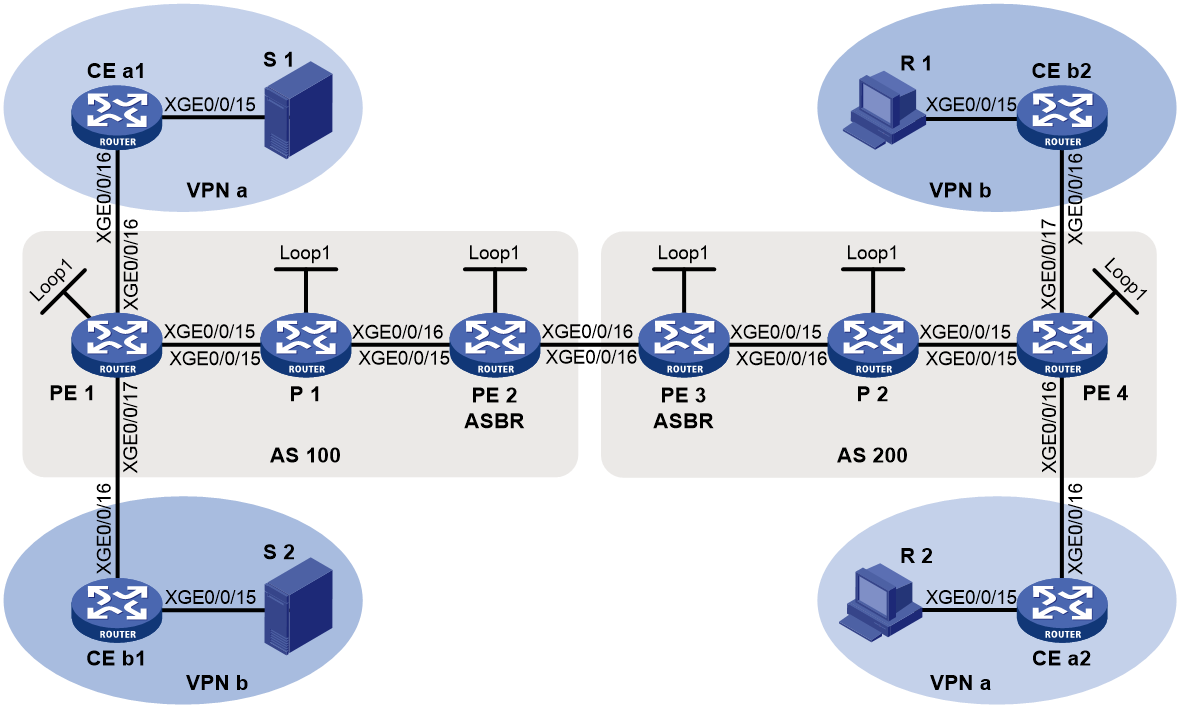
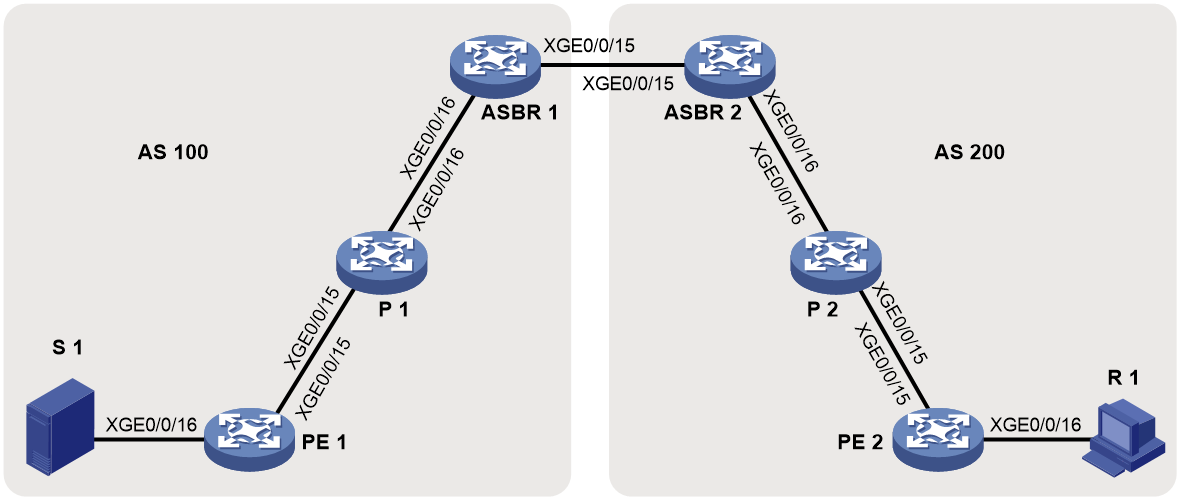
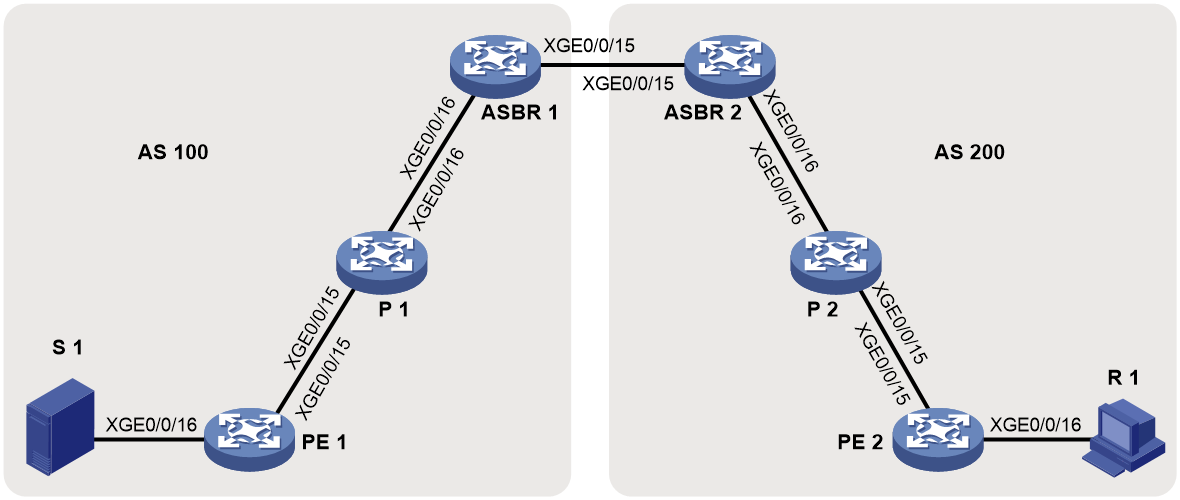
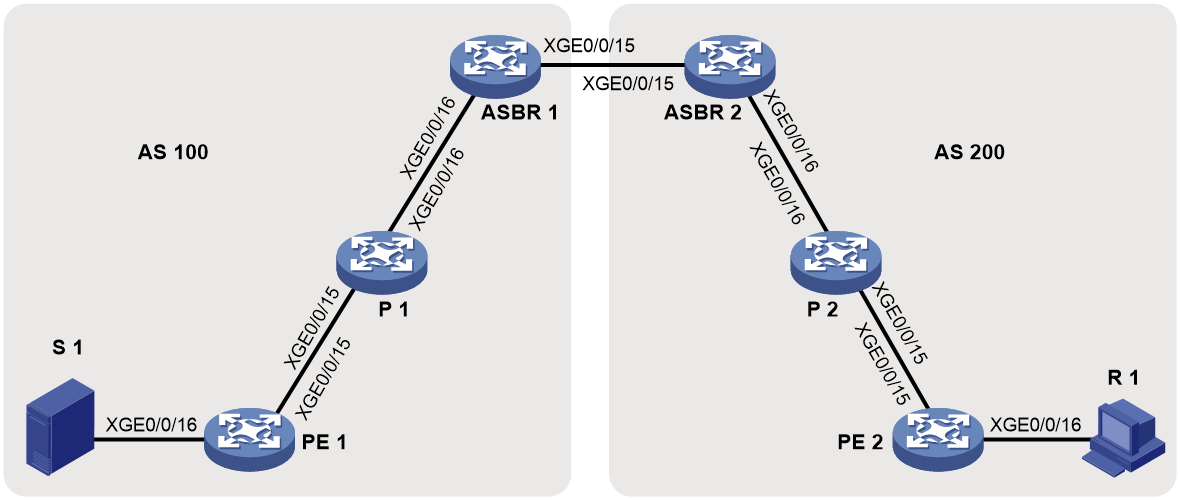
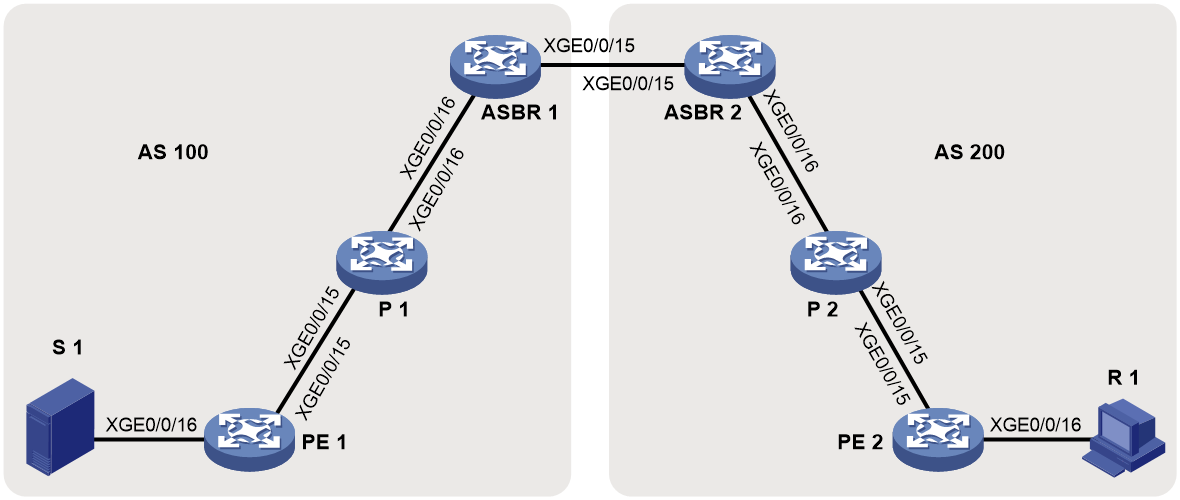
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 13, configure intra-AS BIER-based MVPN with the G-BIER encapsulation to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
· In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and BIER |
· Configure IS-IS on the public network, and configure RIP between the PEs and the CEs. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and PE 2 on their respective Loopback 1. · Configure BIER on the public network: sub-domain 0, BSL 128, and max-SI 32. · Configure the BFR prefix of PE 1, PE 2 and P as the IPv6 addresses for their respective Loopback 1, and configure the multicast policy reserved address for each device. |
|
IP multicast routing |
· Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1 and PE 2. · Enable IP multicast routing on CE 1 and CE 2. |
|
IGMP |
· Enable IGMPv2 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE 2. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on PE 1 and PE 2. · Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on CE 1 and CE 2. · Configure Loopback 2 of PE 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a to provide services for all multicast groups. |
|
MSDP |
When the RP is configured on a CE, the CE uses an MSDP peer to receive type-5 routes from PEs. · Enable MSDP on CE a2, and specify Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 as the local MSDP connection interface. · Enable MSDP on PE 2 for VPN instance a, and specify Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 as the local MSDP connection interface. |
Table 1 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
10.110.7.2/24 |
R 1 |
— |
10.110.9.2/24 |
|
P |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:6::2/64 |
CE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.110.7.1/24 |
|
P |
XGE0/0/16 |
9000:7::2/64 |
CE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.2.2/24 |
|
P |
Loop1 |
2.2.2.2/32 2222::2222/128 |
CE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.110.9.1/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:6::1/64 |
CE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.4.2/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.2.1/24 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:7::1/64 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.1/32 1111::1111/128 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.4.1/24 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop2 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.2/32 1112::1112/128 |
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1111::1111 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Assign PE 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 1, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[PE1] bier
[PE1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5001::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5001::1
# Configure a multicast service prefix.
[PE1] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1234:1:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Configure SRv6.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1111::1111
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:2:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 12
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:6::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.2.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 2, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 2
[PE1-LoopBack2] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-LoopBack2] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[PE1-LoopBack2] pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack2] quit
# Configure Loopback 2 as a C-BSR and a C-RP in VPN instance a.
[PE1] pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim-a] c-bsr 3.3.3.3
[PE1-pim-a] c-rp 3.3.3.3
[PE1-pim-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 1112::1112 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 1112::1112 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1112::1112 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1112::1112 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1112::1112 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route rip 2
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] bier enable
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Configure RIP.
[PE1] rip 2 vpn-instance a
[PE1-rip-2] undo summary
[PE1-rip-2] version 2
[PE1-rip-2] network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
[PE1-rip-2] network 10.110.2.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-rip-2] import-route bgp
[PE1-rip-2] quit
2. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 1.1.1.2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.2 32
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1112::1112 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
# Assign PE 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 2, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[PE2] bier
[PE2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 2
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5002::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5002::1
# Configure SRv6.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1112::1112
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 2:2:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure a multicast service prefix.
[PE2] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1234:2:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 12
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:7::1 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.4.1 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1111::1111 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route rip 2
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] bier enable
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Configure RIP.
[PE2] rip 2 vpn-instance a
[PE2-rip-2] undo summary
[PE2-rip-2] version 2
[PE2-rip-2] network 10.110.4.0 0.0.0.255
[PE2-rip-2] import-route bgp
[PE2-rip-2] quit
3. Configure P:
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
<P> system-view
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] is-level level-1
[P-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1 and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P] interface loopback 1
[P-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.2 32
[P-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2222::2222 128
[P-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-LoopBack1] quit
# Assign P to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 4, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[P] bier
[P-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 4
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5004::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5004::1
# Configure SRv6.
[P] segment-routing ipv6
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2222::2222
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 4:2:: 96 static 8
[P-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:6::2 128
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 9000:7::2 64
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] bier enable
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
4. Configure CE 1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CE1> system-view
[CE1] multicast routing
[CE1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.110.7.1 24
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.2.2 24
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure RIP.
[CE1] rip 2
[CE1-rip-2] undo summary
[CE1-rip-2] version 2
[CE1-rip-2] network 10.110.2.0 0.0.0.255
[CE1-rip-2] network 10.110.7.0 0.0.0.255
[CE1-rip-2] quit
5. Configure CE 2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CE2> system-view
[CE2] multicast routing
[CE2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IGMP on the interface.
[CE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.110.9.1 24
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.4.2 24
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure RIP.
[CE2] rip 2
[CE2-rip-2] undo summary
[CE2-rip-2] version 2
[CE2-rip-2] network 10.110.4.0 0.0.0.255
[CE2-rip-2] network 10.110.9.0 0.0.0.255
[CE2-rip-2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif0
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x30
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Multicast service prefix:
Prefix length ID length ID offset MS Flags
64 10 0 0
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 1112::1112
Uptime: 00:10:05 Originating router: 1.1.1.2
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnel in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif1
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x10
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Multicast service prefix:
Prefix length ID length ID offset MS Flags
64 10 0 0
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 1112::1112
Uptime: 00:00:23 Originating router: 1.1.1.2
# Display C-multicast A-D route information for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a c-multicast routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(10.110.7.2, 225.0.0.1)
CreateTime: 00:02:20
Tunnel Information: BIERVOif1
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 2.
[PE2] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel remote
Total 1 inclusive tunnel
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 1112::1112
Uptime: -- Originating router: 1.1.1.2
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 2.
[PE2] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel remote
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 1112::1112
Uptime: -- Originating router: 1.1.1.2
Example: Configuring intra-AS BIER-based MVPN (BIERv6 encapsulation)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 14, configure intra-AS BIER-based MVPN with the BIERv6 encapsulation to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
· In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and BIER |
· Configure IS-IS on the public network, and configure RIP between the PEs and the CEs. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and PE 2 on their respective Loopback 1. · Configure BIER on the public network: sub-domain 0, BSL 128, and max-SI 32. · Configure the BFR prefix of PE 1, PE 2, and P as the IPv6 addresses for their respective Loopback 1, and configure the End.BIER SID for each device. |
|
IP multicast routing |
· Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1 and PE 2. · Enable IP multicast routing on CE 1 and CE 2. |
|
IGMP |
· Enable IGMPv2 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE 2. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on PE 1 and PE 2. · Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on CE 1 and CE 2. · Configure Loopback 2 of PE 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a to provide services for all multicast groups. |
Table 2 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
10.110.7.2/24 |
R 1 |
— |
10.110.9.2/24 |
|
P |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:6::2/64 |
CE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.110.7.1/24 |
|
P |
XGE0/0/16 |
9000:7::2/64 |
CE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.2.2/24 |
|
P |
Loop1 |
2.2.2.2/32 2222::2222/128 |
CE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.110.9.1/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:6::1/64 |
CE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.4.2/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.2.1/24 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:7::1/64 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.1/32 1111::1111/128 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.4.1/24 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop2 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.2/32 1112::1112/128 |
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1111::1111 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1111::1111
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:2:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 1, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[PE1] bier
[PE1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the BIERv6 encapsulation.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type bierv6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:2::1 as the End.BIER SID.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-bier locator aaa sid 1:2::1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bier] quit
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator a sid 1:2::2
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:6::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.2.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 10.110.2.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 2, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 2
[PE1-LoopBack2] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-LoopBack2] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[PE1-LoopBack2] pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack2] quit
# Configure Loopback 2 as a C-BSR and a C-RP in VPN instance a.
[PE1] pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim-a] c-bsr 3.3.3.3
[PE1-pim-a] c-rp 3.3.3.3
[PE1-pim-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 1112::1112 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 1112::1112 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1112::1112 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1112::1112 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1112::1112 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1112::1112 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route rip 2
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] bier enable
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Configure RIP.
[PE1] rip 2 vpn-instance a
[PE1-rip-2] undo summary
[PE1-rip-2] version 2
[PE1-rip-2] network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
[PE1-rip-2] network 10.110.2.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-rip-2] import-route bgp
[PE1-rip-2] quit
2. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 1.1.1.2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.2 32
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1112::1112 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1112::1112
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 2:2:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 2, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[PE2] bier
[PE2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 2
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the BIERv6 encapsulation.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type bierv6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 2:2::1 as the End.BIER SID.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-bier locator aaa sid 2:2::1
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bier] quit
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 2:2::2
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:7::1 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.4.1 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1111::1111 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1111::1111 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route rip 2
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] bier enable
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Configure RIP.
[PE2] rip 2 vpn-instance a
[PE2-rip-2] undo summary
[PE2-rip-2] version 2
[PE2-rip-2] network 10.110.4.0 0.0.0.255
[PE2-rip-2] import-route bgp
[PE2-rip-2] quit
3. Configure P:
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
<P> system-view
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] is-level level-1
[P-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1 and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P] interface loopback 1
[P-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.2 32
[P-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2222::2222 128
[P-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[P] segment-routing ipv6
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2222::2222
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 4:2:: 96 static 8
[P-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign P to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 4, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[P] bier
[P-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 4
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the BIERv6 encapsulation.
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type bierv6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 4:2::1 as the End.BIER SID.
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-bier locator aaa sid 4:2::1
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[P-bier] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:6::2 64
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 9000:7::2 64
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] bier enable
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
4. Configure CE 1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CE1> system-view
[CE1] multicast routing
[CE1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.110.7.1 24
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.2.2 24
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure RIP.
[CE1] rip 2
[CE1-rip-2] undo summary
[CE1-rip-2] version 2
[CE1-rip-2] network 10.110.2.0 0.0.0.255
[CE1-rip-2] network 10.110.7.0 0.0.0.255
[CE1-rip-2] quit
5. Configure CE 2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CE2> system-view
[CE2] multicast routing
[CE2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IGMP on the interface.
[CE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.110.9.1 24
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.4.2 24
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure RIP.
[CE2] rip 2
[CE2-rip-2] undo summary
[CE2-rip-2] version 2
[CE2-rip-2] network 10.110.4.0 0.0.0.255
[CE2-rip-2] network 10.110.9.0 0.0.0.255
[CE2-rip-2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif0
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x30
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 1112::1112
Uptime: 00:10:05 Originating router: 1.1.1.2
2: BFR-ID: 3 BFR prefix: 1113::1113
Uptime: 00:09:50 Originating router: 1.1.1.3
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnel in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif1
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x10
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 1112::1112
Uptime: 00:00:23 Originating router: 1.1.1.2
# Display C-multicast A-D route information for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a c-multicast routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(10.110.7.2, 225.0.0.1)
CreateTime: 00:02:20
Tunnel Information: BIERVOif1
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 2.
[PE2] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel remote
Total 1 inclusive tunnel
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 1112::1112
Uptime: -- Originating router: 1.1.1.2
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 2.
[PE2] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel remote
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 1112::1112
Uptime: -- Originating router: 1.1.1.2
Example: Configuring intra-AS BIER-based MVPN (MSR6 encapsulation)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 15, configure intra-AS BIER-based MVPN with the MSR6 encapsulation to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
· In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and BIER |
· Configure IS-IS on the public network, and configure RIP between the PEs and the CEs. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and PE 2 on their respective Loopback 1. · Configure BIER on the public network: sub-domain 0, BSL 128, and max-SI 32. · Configure the BFR prefix of PE 1, PE 2, and P as the IPv6 addresses for their respective Loopback 1, and configure the End.RGB SID for each device. |
|
IP multicast routing |
· Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1 and PE 2. · Enable IP multicast routing on CE 1 and CE 2. |
|
IGMP |
· Enable IGMPv2 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE 2. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on PE 1 and PE 2. · Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on CE 1 and CE 2. · Configure Loopback 2 of PE 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a to provide services for all multicast groups. |
Table 3 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
10.110.7.2/24 |
R 1 |
— |
10.110.9.2/24 |
|
P |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:6::2/64 |
CE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.110.7.1/24 |
|
P |
XGE0/0/16 |
9000:7::2/64 |
CE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.2.2/24 |
|
P |
Loop1 |
2.2.2.2/32 2222::2222/128 |
CE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.110.9.1/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:6::1/64 |
CE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.4.2/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.2.1/24 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:7::1/64 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.1/32 1111::1111/128 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.4.1/24 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop2 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.2/32 1112::1112/128 |
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1111::1111 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1111::1111
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:2:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 1, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[PE1] bier
[PE1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:2::1
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 1:2::2
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:6::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.2.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 2, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 2
[PE1-LoopBack2] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-LoopBack2] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[PE1-LoopBack2] pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack2] quit
# Configure Loopback 2 as a C-BSR and a C-RP in VPN instance a.
[PE1] pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim-a] c-bsr 3.3.3.3
[PE1-pim-a] c-rp 3.3.3.3
[PE1-pim-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 1112::1112 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 1112::1112 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1112::1112 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1112::1112 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1112::1112 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route rip 2
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] bier enable
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Configure RIP.
[PE1] rip 2 vpn-instance a
[PE1-rip-2] undo summary
[PE1-rip-2] version 2
[PE1-rip-2] network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
[PE1-rip-2] network 10.110.2.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-rip-2] import-route bgp
[PE1-rip-2] quit
2. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 1.1.1.2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.2 32
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1112::1112 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1112::1112
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 2:2:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 2, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[PE2] bier
[PE2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 2
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 2:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 2:2::1
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 2:2::2
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:7::1 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.4.1 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1111::1111 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route rip 2
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] bier enable
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Configure RIP.
[PE2] rip 2 vpn-instance a
[PE2-rip-2] undo summary
[PE2-rip-2] version 2
[PE2-rip-2] network 10.110.4.0 0.0.0.255
[PE2-rip-2] import-route bgp
[PE2-rip-2] quit
3. Configure P:
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
<P> system-view
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] is-level level-1
[P-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1 and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P] interface loopback 1
[P-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.2 32
[P-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2222::2222 128
[P-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[P] segment-routing ipv6
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2222::2222
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 4:2:: 96 static 8
[P-segment-routing-ipv6 locator-aaa] quit
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign P to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 4, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[P] bier
[P-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 4
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 4:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 4:2::1
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:6::2 128
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 9000:7::2 64
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] bier enable
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
4. Configure CE 1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CE1> system-view
[CE1] multicast routing
[CE1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.110.7.1 24
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.2.2 24
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure RIP.
[CE1] rip 2
[CE1-rip-2] undo summary
[CE1-rip-2] version 2
[CE1-rip-2] network 10.110.2.0 0.0.0.255
[CE1-rip-2] network 10.110.7.0 0.0.0.255
[CE1-rip-2] quit
5. Configure CE 2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CE2> system-view
[CE2] multicast routing
[CE2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IGMP on the interface.
[CE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.110.9.1 24
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.4.2 24
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure RIP.
[CE2] rip 2
[CE2-rip-2] undo summary
[CE2-rip-2] version 2
[CE2-rip-2] network 10.110.4.0 0.0.0.255
[CE2-rip-2] network 10.110.9.0 0.0.0.255
[CE2-rip-2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif0
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x30
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 1112::1112
Uptime: 00:10:05 Originating router: 1.1.1.2
2: BFR-ID: 3 BFR prefix: 1113::1113
Uptime: 00:09:50 Originating router: 1.1.1.3
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnel in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif1
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x10
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 1112::1112
Uptime: 00:00:23 Originating router: 1.1.1.2
# Display C-multicast A-D route information for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a c-multicast routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(10.110.7.2, 225.0.0.1)
CreateTime: 00:02:20
Tunnel Information: BIERVOif1
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 2.
[PE2] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel remote
Total 1 inclusive tunnel
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 1112::1112
Uptime: -- Originating router: 1.1.1.2
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 2.
[PE2] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel remote
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 1112::1112
Uptime: -- Originating router: 1.1.1.2
Example: Configuring intra-AS BIER-based MVPN (EVPN L3VPN over SRv6-based G-BIER encapsulation)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 13, configure intra-AS BIER-based MVPN with the G-BIER encapsulation to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
· In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and BIER |
· Configure IS-IS on the public network, and configure RIP between the PEs and the CEs. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and PE 2 on their respective Loopback 1. · Configure BIER on the public network: sub-domain 0, BSL 128, and max-SI 32. · Configure the BFR prefix of PE 1, PE 2 and P as the IPv6 addresses for their respective Loopback 1, and configure the multicast policy reserved address for each device. |
|
IP multicast routing |
· Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1 and PE 2. · Enable IP multicast routing on CE 1 and CE 2. |
|
IGMP |
· Enable IGMPv2 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE 2. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on PE 1 and PE 2. · Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on CE 1 and CE 2. · Configure Loopback 2 of PE 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a to provide services for all multicast groups. |
|
MSDP |
When the RP is configured on a CE, the CE uses an MSDP peer to receive type-5 routes from PEs. · Enable MSDP on CE a2, and specify Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 as the local MSDP connection interface. · Enable MSDP on PE 2 for VPN instance a, and specify Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 as the local MSDP connection interface. |
Figure 16 Network diagram
Table 4 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
10.110.7.2/24 |
R 1 |
— |
10.110.9.2/24 |
|
P |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:6::2/64 |
CE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.110.7.1/24 |
|
P |
XGE0/0/16 |
9000:7::2/64 |
CE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.2.2/24 |
|
P |
Loop1 |
2.2.2.2/32 2222::2222/128 |
CE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.110.9.1/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:6::1/64 |
CE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.4.2/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.2.1/24 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:7::1/64 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.1/32 1111::1111/128 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.4.1/24 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop2 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.2/32 1112::1112/128 |
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1111::1111 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Assign PE 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 1, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[PE1] bier
[PE1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5001::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5001::1
# Configure a multicast service prefix.
[PE1] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1234:1:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Configure SRv6.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1111::1111
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:2:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 12
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:6::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.2.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 2, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 2
[PE1-LoopBack2] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-LoopBack2] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[PE1-LoopBack2] pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack2] quit
# Configure Loopback 2 as a C-BSR and a C-RP in VPN instance a.
[PE1] pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim-a] c-bsr 3.3.3.3
[PE1-pim-a] c-rp 3.3.3.3
[PE1-pim-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 1112::1112 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 1112::1112 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1112::1112 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1112::1112 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1112::1112 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE1-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route rip 2
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa evpn
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] bier enable
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Configure RIP.
[PE1] rip 2 vpn-instance a
[PE1-rip-2] undo summary
[PE1-rip-2] version 2
[PE1-rip-2] network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
[PE1-rip-2] network 10.110.2.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-rip-2] import-route bgp
[PE1-rip-2] quit
2. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 1.1.1.2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.2 32
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1112::1112 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
# Assign PE 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 2, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[PE2] bier
[PE2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 2
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5002::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5002::1
# Configure SRv6.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1112::1112
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 2:2:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure a multicast service prefix.
[PE2] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1234:2:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 12
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:7::1 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.4.1 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family l2vpn evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] peer 1111::1111 advertise encap-type srv6
[PE2-bgp-default-evpn] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route rip 2
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa evpn
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] bier enable
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Configure RIP.
[PE2] rip 2 vpn-instance a
[PE2-rip-2] undo summary
[PE2-rip-2] version 2
[PE2-rip-2] network 10.110.4.0 0.0.0.255
[PE2-rip-2] import-route bgp
[PE2-rip-2] quit
3. Configure P:
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
<P> system-view
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] is-level level-1
[P-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1 and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P] interface loopback 1
[P-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.2 32
[P-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2222::2222 128
[P-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-LoopBack1] quit
# Assign P to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 4, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[P] bier
[P-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 4
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5004::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5004::1
# Configure SRv6.
[P] segment-routing ipv6
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2222::2222
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 4:2:: 96 static 8
[P-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:6::2 128
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 9000:7::2 64
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] bier enable
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
4. Configure CE 1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CE1> system-view
[CE1] multicast routing
[CE1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.110.7.1 24
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.2.2 24
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure RIP.
[CE1] rip 2
[CE1-rip-2] undo summary
[CE1-rip-2] version 2
[CE1-rip-2] network 10.110.2.0 0.0.0.255
[CE1-rip-2] network 10.110.7.0 0.0.0.255
[CE1-rip-2] quit
5. Configure CE 2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CE2> system-view
[CE2] multicast routing
[CE2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IGMP on the interface.
[CE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.110.9.1 24
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.4.2 24
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure RIP.
[CE2] rip 2
[CE2-rip-2] undo summary
[CE2-rip-2] version 2
[CE2-rip-2] network 10.110.4.0 0.0.0.255
[CE2-rip-2] network 10.110.9.0 0.0.0.255
[CE2-rip-2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif0
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x30
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Multicast service prefix:
Prefix length ID length ID offset MS Flags
64 10 0 0
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 1112::1112
Uptime: 00:10:05 Originating router: 1.1.1.2
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnel in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif1
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x10
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Multicast service prefix:
Prefix length ID length ID offset MS Flags
64 10 0 0
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 1112::1112
Uptime: 00:00:23 Originating router: 1.1.1.2
# Display C-multicast A-D route information for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a c-multicast routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(10.110.7.2, 225.0.0.1)
CreateTime: 00:02:20
Tunnel Information: BIERVOif1
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 2.
[PE2] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel remote
Total 1 inclusive tunnel
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 1112::1112
Uptime: -- Originating router: 1.1.1.2
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 2.
[PE2] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel remote
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 1112::1112
Uptime: -- Originating router: 1.1.1.2
Example: Configuring BIER-based MVPN for the public instance (G-BIER encapsulation)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 17, configure BIER-based MVPN for the public instance to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
In the public instance, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. |
|
Instances to which PE interfaces belong |
All interfaces belong to the public instance. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and BIER |
· Configure IS-IS on the public network, and configure RIP between the PEs and the CEs. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and PE 2 by using Loopback 1. · Configure BIER on the public network. |
|
IP multicast routing |
· Enable IP multicast routing for the public instance on PE 1 and PE 2. · Enable IP multicast routing on CE 1 and CE 2. |
|
IGMP |
· Enable IGMPv2 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE 2. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on PE 1 and Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on PE 2. · Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on CE 1 and CE 2. · Configure Loopback 2 of PE 2 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for the public instance to provide services for all multicast groups. |
Table 5 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
10.110.7.2/24 |
R 1 |
— |
10.110.1.2/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:6::1/64 |
P |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:6::2/64 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.2.1/24 |
P |
XGE0/0/17 |
9000:8::2/64 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.1/32 1111::1111/128 |
P |
Loop1 |
2.2.2.2/32 2222::2222/128 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:8::1/64 |
CE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.110.7.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.5.1/24 |
CE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.2.2/24 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.3/32 1113::1113/128 |
CE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.110.10.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop2 |
33.33.33.33/32 |
CE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.5.2/24 |
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1111::1111 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1111::1111
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:2:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 1, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[PE1] bier
[PE1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5001::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5001::1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bier] quit
# Configure a multicast service prefix.
[PE1] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1234:1:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Create the public instance, and configure route targets for the public instance.
[PE1] ip public-instance
[PE1-public-instance] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-public-instance] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-public-instance] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for the public instance.
[PE1] multicast routing
[PE1-mrib] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for the public instance.
[PE1] multicast-vpn public-instance mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for the public instance.
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for the public instance.
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for the public instance.
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 12
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on the public network, and enable IS-IS on it.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:6::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15 isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 on the public network, and enable PIM-SM on it.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 10.110.2.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 1113::1113 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 1113::1113 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1113::1113 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1113::1113 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1113::1113 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1113::1113 advertise-ext-community
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route rip 2
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] bier enable
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Configure RIP.
[PE1] rip 2
[PE1-rip-2] undo summary
[PE1-rip-2] version 2
[PE1-rip-2] network 10.110.2.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-rip-2] import-route bgp allow-ibgp
[PE1-rip-2] quit
2. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 1.1.1.3
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.3 32
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1113::1113 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1113::1113
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator bbb ipv6-prefix 2:2:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-bbb] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 3, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1..
[PE2] bier
[PE2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 3
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5003::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5003::1
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bier] quit
# Configure a multicast service prefix.
[PE2] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1232:3:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Create the public instance, and configure route targets for the public instance.
[PE2] ip public-instance
[PE2-public-instance] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-public-instance] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-public-instance] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for the public instance.
[PE2] multicast routing
[PE2-mrib] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for the public instance.
[PE2] multicast-vpn public-instance mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for the public instance.
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for the public instance.
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for the public instance.
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 12
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] quit
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on the public network, and enable IS-IS on it.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:8::1 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 on the public network, and enable PIM-SM on it.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.5.1 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 2, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 2
[PE2-LoopBack2] ip address 33.33.33.33 32
[PE2-LoopBack2] pim sm
[PE2-LoopBack2] quit
# Configure Loopback 2 as a C-BSR and a C-RP of the public network.
[PE2] pim
[PE2-pim] c-bsr 33.33.33.33
[PE2-pim] c-rp 33.33.33.33
[PE2-pim] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] segment-routing ipv6 locator bbb
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] 1111::1111 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1111::1111 advertise-ext-community
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route rip 2
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator bbb to the IS-IS process.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] bier enable
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator bbb
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Configure RIP.
[PE2] rip 2
[PE2-rip-2] undo summary
[PE2-rip-2] version 2
[PE2-rip-2] network 10.110.5.0 0.0.0.255
[PE2-rip-2] network 33.33.33.33 0.0.0.0
[PE2-rip-2] import-route bgp allow-ibgp
[PE2-rip-2] quit
3. Configure P:
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
<P> system-view
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] is-level level-1
[P-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator a
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P] interface loopback 1
[P-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.2 32
[P-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2222::2222 128
[P-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-LoopBack1] quit
# Assign P to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 4, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[P] bier
[P-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 4
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5004::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5004::1
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on the public network, and enable IS-IS on it.
[P] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:6::2 64
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 on the public network, and enable IS-IS on it.
[P] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 9000:8::2 64
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Enable BIER for IS-IS process 1.
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] bier enable
[P-isis-1] quit
4. Configure CE 1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CE1> system-view
[CE1] multicast routing
[CE1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on the public network, and enable PIM-SM on it.
[CE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.110.7.1 24
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 on the public network, and enable PIM-SM on it.
[CE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 10.110.2.2 24
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Configure RIP.
[CE1] rip 2
[CE1-rip-2] undo summary
[CE1-rip-2] version 2
[CE1-rip-2] network 10.110.2.0 0.0.0.255
[CE1-rip-2] network 10.110.7.0 0.0.0.255
[CE1-rip-2] quit
5. Configure CE 2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CE2> system-view
[CE2] multicast routing
[CE2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on the public network, and enable IGMP on it.
[CE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.110.10.1 24
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 on the public network, and enable PIM-SM on it.
[CE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 10.110.5.2 24
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Configure RIP.
[CE2] rip 2
[CE2-rip-2] undo summary
[CE2-rip-2] version 2
[CE2-rip-2] network 10.110.5.0 0.0.0.255
[CE2-rip-2] network 10.110.10.0 0.0.0.255
[CE2-rip-2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for the public instance on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn public-instance inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif0
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x30
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Multicast service prefix:
Prefix length ID length ID offset MS Flags
64 10 0 0
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 3 BFR prefix: 1113::1113
Uptime: 00:09:50 Originating router: 1.1.1.3
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for the public instance on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn public-instance selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnel in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif1
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x10
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Multicast service prefix:
Prefix length ID length ID offset MS Flags
64 10 0 0
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 3 BFR prefix: 1113::1113
Uptime: 00:00:23 Originating router: 1.1.1.3
# Display C-multicast A-D route information for the public instance on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a c-multicast routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(10.110.7.2, 225.0.0.1)
CreateTime: 00:02:20
Tunnel Information: BIERVOif1
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for the public instance on PE 2.
[PE3] display multicast-vpn public-instance inclusive-tunnel remote
Total 1 inclusive tunnel
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 3 BFR prefix: 1113::1113
Uptime: -- Originating router: 1.1.1.3
Example: Configuring BIER-based MVPN for the public instance (BIERv6 encapsulation)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 18, configure BIER-based MVPN for the public instance to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
In the public instance, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. |
|
Instances to which PE interfaces belong |
All interfaces belong to the public instance. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and BIER |
· Configure IS-IS on the public network, and configure RIP between the PEs and the CEs. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and PE 2 by using Loopback 1. · Configure BIER on the public network: sub-domain 0, BSL 128, and max-SI 32. · Configure the BFR prefix of PE 1, PE 2 and P as the IPv6 addresses for their respective Loopback 1, and configure the End.BIER SID for each device. |
|
IP multicast routing |
· Enable IP multicast routing for the public instance on PE 1 and PE 2. · Enable IP multicast routing on CE 1 and CE 2. |
|
IGMP |
· Enable IGMPv2 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE 2. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on PE 1 and Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on PE 2. · Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on CE 1 and CE 2. · Configure Loopback 2 of PE 2 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for the public instance to provide services for all multicast groups. |
Table 6 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
10.110.7.2/24 |
R 1 |
— |
10.110.1.2/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:6::1/64 |
P |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:6::2/64 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.2.1/24 |
P |
XGE0/0/17 |
9000:8::2/64 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.1/32 1111::1111/128 |
P |
Loop1 |
2.2.2.2/32 2222::2222/128 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:8::1/64 |
CE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.110.7.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.5.1/24 |
CE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.2.2/24 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.3/32 1113::1113/128 |
CE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.110.10.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop2 |
33.33.33.33/32 |
CE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.5.2/24 |
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1111::1111 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1111::1111
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:1:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 1, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[PE1] bier
[PE1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the BIERv6 encapsulation.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type bierv6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:1::1 as the End.BIER SID.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-bier locator aaa sid 1:1::1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bier] quit
# Create the public instance, and configure route targets for the public instance.
[PE1] ip public-instance
[PE1-public-instance] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-public-instance] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-public-instance] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for the public instance.
[PE1] multicast routing
[PE1-mrib] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for the public instance.
[PE1] multicast-vpn public-instance mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for the public instance.
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for the public instance.
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for the public instance.
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 1:1::2
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] bier enable
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on the public network, and enable IS-IS on it.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:6::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15 isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 on the public network, and enable PIM-SM on it.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.2.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 1113::1113 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 1113::1113 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1113::1113 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1113::1113 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1113::1113 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1113::1113 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1113::1113 advertise-ext-community
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route rip 2
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Configure RIP.
[PE1] rip 2
[PE1-rip-2] undo summary
[PE1-rip-2] version 2
[PE1-rip-2] network 10.110.2.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-rip-2] import-route bgp allow-ibgp
[PE1-rip-2] quit
2. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 1.1.1.3
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.3 32
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1113::1113 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1113::1113
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 2:2:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 3, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1..
[PE2] bier
[PE2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 3
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the BIERv6 encapsulation.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type bierv6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 2:2::1 as the End.BIER SID.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-bier locator aaa sid 2:2::1
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bier] quit
# Create the public instance, and configure route targets for the public instance.
[PE2] ip public-instance
[PE2-public-instance] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-public-instance] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-public-instance] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for the public instance.
[PE2] multicast routing
[PE2-mrib] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for the public instance.
[PE2] multicast-vpn public-instance mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for the public instance.
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for the public instance.
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for the public instance.
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 2:2::2
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] quit
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] bier enable
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on the public network, and enable IS-IS on it.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:8::1 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 on the public network, and enable PIM-SM on it.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.5.1 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 2, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 2
[PE2-LoopBack2] ip address 33.33.33.33 32
[PE2-LoopBack2] pim sm
[PE2-LoopBack2] quit
# Configure Loopback 2 as a C-BSR and a C-RP of the public network.
[PE2] pim
[PE2-pim] c-bsr 33.33.33.33
[PE2-pim] c-rp 33.33.33.33
[PE2-pim] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1111::1111 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1111::1111 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1111::1111 advertise-ext-community
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route rip 2
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Configure RIP.
[PE2] rip 2
[PE2-rip-2] undo summary
[PE2-rip-2] version 2
[PE2-rip-2] network 10.110.5.0 0.0.0.255
[PE2-rip-2] network 33.33.33.0 0.0.0.0
[PE2-rip-2] import-route bgp allow-ibgp
[PE2-rip-2] quit
3. Configure P:
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
<P> system-view
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] is-level level-1
[P-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator a
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P] interface loopback 1
[P-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.2 32
[P-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2222::2222 128
[P-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[P] segment-routing ipv6
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2222::2222
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] locator a ipv6-prefix 4:1:: 64 static 32
[P-segment-routing-ipv6 locator-a] quit
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign P to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 4, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[P] bier
[P-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 4
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the BIERv6 encapsulation.
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type bierv6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 4:1::1 as the End.BIER SID.
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-bier locator a sid 4:1::1
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[P-bier] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] bier enable
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator a
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on the public network, and enable IS-IS on it.
[P] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:6::2 64
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 on the public network, and enable IS-IS on it.
[P] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 9000:8::2 64
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
4. Configure CE 1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CE1> system-view
[CE1] multicast routing
[CE1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on the public network, and enable PIM-SM on it.
[CE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.110.7.1 24
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 on the public network, and enable PIM-SM on it.
[CE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.2.2 24
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure RIP.
[CE1] rip 2
[CE1-rip-2] undo summary
[CE1-rip-2] version 2
[CE1-rip-2] network 10.110.2.0 0.0.0.255
[CE1-rip-2] network 10.110.7.0 0.0.0.255
[CE1-rip-2] quit
5. Configure CE 2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CE2> system-view
[CE2] multicast routing
[CE2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on the public network, and enable IGMP on it.
[CE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.110.10.1 24
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 on the public network, and enable PIM-SM on it.
[CE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.5.2 24
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure RIP.
[CE2] rip 2
[CE2-rip-2] undo summary
[CE2-rip-2] version 2
[CE2-rip-2] network 10.110.5.0 0.0.0.255
[CE2-rip-2] network 10.110.10.0 0.0.0.255
[CE2-rip-2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for the public instance on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn public-instance inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif0
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x30
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 3 BFR prefix: 1113::1113
Uptime: 00:09:50 Originating router: 1.1.1.3
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for the public instance on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn public-instance selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnel in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif1
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x10
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 3 BFR prefix: 1113::1113
Uptime: 00:00:23 Originating router: 1.1.1.3
# Display C-multicast A-D route information for the public instance on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a c-multicast routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(10.110.7.2, 225.0.0.1)
CreateTime: 00:02:20
Tunnel Information: BIERVOif1
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for the public instance on PE 2.
[PE3] display multicast-vpn public-instance inclusive-tunnel remote
Total 1 inclusive tunnel
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 3 BFR prefix: 1113::1113
Uptime: -- Originating router: 1.1.1.3
Example: Configuring BIER-based MVPN for the public instance (MSR6 encapsulation)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 19, configure BIER-based MVPN for the public instance to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
In the public instance, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. |
|
Instances to which PE interfaces belong |
All interfaces belong to the public instance. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and BIER |
· Configure IS-IS on the public network, and configure RIP between the PEs and the CEs. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and PE 2 by using Loopback 1. · Configure BIER on the public network: sub-domain 0, BSL 128, and max-SI 32. · Configure the BFR prefix of PE 1, PE 2 and P as the IPv6 addresses for their respective Loopback 1, and configure the End.RGB SID for each device. |
|
IP multicast routing |
· Enable IP multicast routing for the public instance on PE 1 and PE 2. · Enable IP multicast routing on CE 1 and CE 2. |
|
IGMP |
· Enable IGMPv2 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE 2. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on PE 1 and Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on PE 2. · Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on CE 1 and CE 2. · Configure Loopback 2 of PE 2 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for the public instance to provide services for all multicast groups. |
Table 7 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
10.110.7.2/24 |
R 1 |
— |
10.110.1.2/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:6::1/64 |
P |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:6::2/64 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.2.1/24 |
P |
XGE0/0/17 |
9000:8::2/64 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.1/32 1111::1111/128 |
P |
Loop1 |
2.2.2.2/32 2222::2222/128 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
9000:8::1/64 |
CE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.110.7.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.5.1/24 |
CE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.2.2/24 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.3/32 1113::1113/128 |
CE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.110.10.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop2 |
33.33.33.33/32 |
CE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.5.2/24 |
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1111::1111 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1111::1111
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:1:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 1, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[PE1] bier
[PE1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:1::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:1::1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bier] quit
# Create the public instance, and configure route targets for the public instance.
[PE1] ip public-instance
[PE1-public-instance] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-public-instance] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-public-instance] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for the public instance.
[PE1] multicast routing
[PE1-mrib] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for the public instance.
[PE1] multicast-vpn public-instance mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for the public instance.
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for the public instance.
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for the public instance.
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] src-dt4 locator a sid 1:1::2
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-public-instance] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] bier enable
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on the public network, and enable IS-IS on it.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:6::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15 isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 on the public network, and enable PIM-SM on it.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.2.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 1113::1113 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 1113::1113 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1113::1113 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1113::1113 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1113::1113 advertise-ext-community
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1113::1113 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] segment-routing ipv6 locator a
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route rip 2
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Configure RIP.
[PE1] rip 2
[PE1-rip-2] undo summary
[PE1-rip-2] version 2
[PE1-rip-2] network 10.110.2.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-rip-2] import-route bgp allow-ibgp
[PE1-rip-2] quit
2. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 1.1.1.3
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.3 32
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1113::1113 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1113::1113
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 3:1:: 64 static 32
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 2, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1..
[PE2] bier
[PE2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 2
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 3:1::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 3:1::1
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bier] quit
# Create the public instance, and configure route targets for the public instance.
[PE2] ip public-instance
[PE2-public-instance] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-public-instance] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-public-instance] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for the public instance.
[PE2] multicast routing
[PE2-mrib] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for the public instance.
[PE2] multicast-vpn public-instance mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for the public instance.
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for the public instance.
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation, enable dynamic selective tunnel creation, and specify 3:1::2 as the MSR6 tunnel source address for locator a.
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4]inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4]selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4]src-dt4 locator a sid 3:1::2
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance-ipv4] quit
[PE2-mvpn-public-instance] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] bier enable
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on the public network, and enable IS-IS on it.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:8::1 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 on the public network, and enable PIM-SM on it.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.5.1 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 2, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 2
[PE2-LoopBack2] ip address 33.33.33.33 32
[PE2-LoopBack2] pim sm
[PE2-LoopBack2] quit
# Configure Loopback 2 as a C-BSR and a C-RP of the public network.
[PE2] pim
[PE2-pim] c-bsr 33.33.33.33
[PE2-pim] c-rp 33.33.33.33
[PE2-pim] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1111::1111 advertise-ext-community
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1111::1111 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] segment-routing ipv6 locator a
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route rip 2
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] quit
# Configure RIP.
[PE2] rip 2
[PE2-rip-2] undo summary
[PE2-rip-2] version 2
[PE2-rip-2] network 10.110.5.0 0.0.0.255
[PE2-rip-2] network 33.33.33.33 0.0.0.0
[PE2-rip-2] import-route bgp allow-ibgp
[PE2-rip-2] quit
3. Configure P:
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
<P> system-view
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] is-level level-1
[P-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator a
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P] interface loopback 1
[P-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.2 32
[P-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2222::2222 128
[P-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[P] segment-routing ipv6
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2222::2222
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 4:1:: 64 static 32
[P-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[P-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign P to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 4, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[P] bier
[P-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 4
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 4:1::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 4:1::1
[P-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[P-bier] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[P] isis 1
[P-isis-1] bier enable
[P-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P-isis-1] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on the public network, and enable IS-IS on it.
[P] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 9000:6::2 64
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 on the public network, and enable IS-IS on it.
[P] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 9000:8::2 64
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
4. Configure CE 1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CE1> system-view
[CE1] multicast routing
[CE1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on the public network, and enable PIM-SM on it.
[CE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.110.7.1 24
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 on the public network, and enable PIM-SM on it.
[CE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.2.2 24
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure RIP.
[CE1] rip 2
[CE1-rip-2] undo summary
[CE1-rip-2] version 2
[CE1-rip-2] network 10.110.2.0 0.0.0.255
[CE1-rip-2] network 10.110.7.0 0.0.0.255
[CE1-rip-2] quit
5. Configure CE 2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CE2> system-view
[CE2] multicast routing
[CE2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 on the public network, and enable IGMP on it.
[CE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.110.10.1 24
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 on the public network, and enable PIM-SM on it.
[CE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.5.2 24
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure RIP.
[CE2] rip 2
[CE2-rip-2] undo summary
[CE2-rip-2] version 2
[CE2-rip-2] network 10.110.5.0 0.0.0.255
[CE2-rip-2] network 10.110.10.0 0.0.0.255
[CE2-rip-2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for the public instance on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn public-instance inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif0
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x30
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 3 BFR prefix: 1113::1113
Uptime: 00:09:50 Originating router: 1.1.1.3
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for the public instance on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn public-instance selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnel in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif1
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x10
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 3 BFR prefix: 1113::1113
Uptime: 00:00:23 Originating router: 1.1.1.3
# Display C-multicast A-D route information for the public instance on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn public-instance c-multicast routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(10.110.7.2, 225.0.0.1)
CreateTime: 00:02:20
Tunnel Information: BIERVOif1
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for the public instance on PE 2.
[PE2] display multicast-vpn public-instance inclusive-tunnel remote
Total 1 inclusive tunnel
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 3 BFR prefix: 1113::1113
Uptime: -- Originating router: 1.1.1.3
Example: Configuring inter-AS option A BIER-based MVPN (G-BIER encapsulation)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 20, configure inter-AS option A BIER-based MVPN to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
· In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 2 is a receiver. · In VPN instance b, S 2 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. · PIM-SM is used in VPN instance a. · PIM-SSM is used in VPN instance b. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 belongs to VPN instance b. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 belongs to VPN instance b. · PE 3: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 and Loopback 2 belong to VPN instance b. · PE 4: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belong to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 belongs to VPN instance b. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and BIER |
· Configure IS-IS in AS 100 and AS 200, and configure OSPF between the PEs and the CEs. · Establish IBGP peer connections between PE 1 and PE 2, and between PE 3 and PE 4 on their respective Loopback 1. Establish EBGP peer connections between PE 2 and PE 3 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16. · Establish BGP IPv4 MVPN peer connections between PE 1 and PE 2, and between PE 3 and PE 4 on their respective Loopback 1. · Configure BIER in AS 100 and AS 200. · Emable BIER on P 1 and P 2. |
|
IP multicast routing |
· Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1 and PE 4. · Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b on PE 1 and PE 4. · Enable IP multicast routing on CE a1, CE a2, CE b1, and CE b2. |
|
IGMP |
· Enable IGMPv2 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE a2. · Enable IGMPv3 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE b2. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on all private interfaces on PE 1 and PE 4. · Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on CE a1, CE a2, CE b1, and CE b2. · Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 of PE 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a in AS 100 to provide services for all multicast groups. · Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 of PE 4 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance b in AS 200 to provide services for all multicast groups. |
Table 8 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
12.1.1.100/24 |
R 1 |
— |
12.4.1.100/24 |
|
S 2 |
— |
12.2.1.100/24 |
R 2 |
— |
12.3.1.100/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.1.1.1/24 1011::1/80 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.4.1.1/24 1041::1/80 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.1.1.1/24 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.3.1.2/24 |
|
PE 1 |
- |
|
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10.6.1.2/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/17 |
11.2.1.1/24 |
PE 3 |
Loop1 |
3.3.3.3/32 3333::3333/128 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.1/32 1111::1111/128 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.5.1.2/24 1051::2/80 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.2.1.2/24 1021::2/80 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.3.1.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.3.1.1/24 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/17 |
11.4.1.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10.6.1.1/24 |
PE 4 |
- |
|
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
2.2.2.2/32 2222::2222/128 |
PE 4 |
Loop1 |
4.4.4.4/24 4444::4444/128 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.1.1.2/24 1011::2/80 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.5.1.1/24 1051::1/80 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.2.1.1/24 1021::1/80 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.4.1.2/24 1041::2/80 |
|
P 1 |
Loop1 |
5.5.5.5/32 5555::5555/128 |
P 2 |
Loop1 |
6.6.6.6/32 6666::6666/128 |
|
CE a1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.1.1.1/24 |
CE b1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.2.1.1/24 |
|
CE a1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.1.1.2/24 |
CE b1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.2.1.2/24 |
|
CE a2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.3.1.1/24 |
CE b2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.4.1.1/24 |
|
CE a2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.3.1.2/24 |
CE b2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.4.1.2/24 |
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1111::1111 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BIER.
[PE1] bier
[PE1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5001::1
# Configure SRv6.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1111::1111
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:2:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure a multicast service prefix.
[PE1] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1234:1:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 1
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Create a VPN instance named b, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance b
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] route-distinguisher 200:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing in VPN instance b.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance b
[PE1-mrib-b] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance b.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance b mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance b.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance b.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance b.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 2
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 1011::1 80
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.1.1.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance b, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip binding vpn-instance b
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 11.2.1.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 as a C-BSR and a C-RP of VPN instance a.
[PE1] pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim-a] c-bsr 11.1.1.1
[PE1-pim-a] c-rp 11.1.1.1
[PE1-pim-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2222::2222 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2222::2222 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 2222::2222 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2222::2222 enable
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2222::2222 next-hop-local
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2222::2222 prefix-sid
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route ospf 2
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance b
[PE1-bgp-default-b] address-family ipv4
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route ospf 3
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-b] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] bier enable
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[PE1] ospf 2 vpn-instance a
[PE1-ospf-2] import-route bgp
[PE1-ospf-2] area 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE1-ospf-2] quit
[PE1] ospf 3 vpn-instance b
[PE1-ospf-3] import-route bgp
[PE1-ospf-3] area 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE1-ospf-3] quit
2. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 2.2.2.2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.2 32
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2222::2222 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BIER.
[PE2] bier
[PE2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 2
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5002::1
# Configure SRv6.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2222::2222
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 2:2:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure a multicast service prefix.
[PE2] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1234:2:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 1
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Create a VPN instance named b, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance b
[PE2-vpn-instance-b] route-distinguisher 200:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b.
[PE2] multicast routing vpn-instance b
[PE2-mrib-b] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance b.
[PE2] multicast-vpn vpn-instance b mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance b.
[PE2-mvpn-b] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance b.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance b.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 2
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] quit
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 1021::2 80
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.3.1.1 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance b, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip binding vpn-instance b
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 10.6.1.1 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1111::1111 next-hop-local
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1111::1111 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-bgp-default-a] peer 10.3.1.2 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] peer 10.3.1.2 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance b
[PE2-bgp-default-b] peer 10.6.1.2 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default-b] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-b] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-b] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-b] peer 10.6.1.2 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-b] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-b] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] bier enable
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
3. Configure PE 3:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE3> system-view
[PE3] router id 3.3.3.3
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE3] isis 1
[PE3-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE3-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE3-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00
[PE3-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE3-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE3] interface loopback 1
[PE3-LoopBack1] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[PE3-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 3333::3333 128
[PE3-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE3-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BIER.
[PE3] bier
[PE3-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 3
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5003::1
# Configure SRv6.
[PE3] segment-routing ipv6
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3333::3333
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 3:2:: 96 static 8
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure a multicast service prefix.
[PE3] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1234:3:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE3] ip vpn-instance a
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 300:1
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a.
[PE3] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE3-mrib-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE3] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE3-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance a.
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 1
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Create a VPN instance named b, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE3] ip vpn-instance b
[PE3-vpn-instance-b] route-distinguisher 400:1
[PE3-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity
[PE3-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity
[PE3-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b.
[PE3] multicast routing vpn-instance b
[PE3-mrib-b] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance b.
[PE3] multicast-vpn vpn-instance b mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance b.
[PE3-mvpn-b] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance b.
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance b.
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 2
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] quit
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 1041::1 80
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.3.1.2 24
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance b, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip binding vpn-instance b
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 10.6.1.2 24
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE3] bgp 200
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 4444::4444 as-number 200
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 4444::4444 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 4444::4444 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4444::4444 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4444::4444 next-hop-local
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4444::4444 prefix-sid
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE3-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE3-bgp-default-a] peer 10.3.1.1 as-number 100
[PE3-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] peer 10.3.1.1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE3-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE3-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance b
[PE3-bgp-default-b] peer 10.6.1.1 as-number 100
[PE3-bgp-default-b] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-b] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-b] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route direct
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-b] peer 10.6.1.1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-b] quit
[PE3-bgp-default-b] quit
[PE3–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE3] isis 1
[PE3-isis-1] bier enable
[PE3-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE3-isis-1] quit
4. Configure PE 4:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE4> system-view
[PE4] router id 4.4.4.4
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE4] isis 1
[PE4-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE4-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE4-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[PE4-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE4-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE4-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE4] interface loopback 1
[PE4-LoopBack1] ip address 4.4.4.4 32
[PE4-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 4444::4444 128
[PE4-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE4-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BIER.
[PE4] bier
[PE4-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 4
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5004::1
# Configure SRv6.
[PE4] segment-routing ipv6
[PE4-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 4444::4444
[PE4-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 4:2:: 96 static 8
[PE4-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE4-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure a multicast service prefix.
[PE4] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1234:4:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE4] ip vpn-instance a
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 300:1
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a.
[PE4] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE4-mrib-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE4] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 1
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Create a VPN instance named b, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE4] ip vpn-instance b
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] route-distinguisher 400:1
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b.
[PE4] multicast routing vpn-instance b
[PE4-mrib-b] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance b.
[PE4] multicast-vpn vpn-instance b mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance b.
[PE4-mvpn-b] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance b.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance b.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 2
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] quit
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 1051::2 80
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.3.1.1 24
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance b, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip binding vpn-instance b
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 11.4.1.1 24
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 as a C-BSR and a C-RP of VPN instance a.
[PE4] pim vpn-instance a
[PE4-pim-a] c-bsr 11.1.1.1
[PE4-pim-a] c-rp 11.1.1.1
[PE4-pim-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE4] bgp 200
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 3333::3333 as-number 200
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 3333::3333 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE4-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 3333::3333 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 3333::3333 enable
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 3333::3333 next-hop-local
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2222::2222 prefix-sid
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE4-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route ospf 2
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE4-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance b
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE4-bgp-default-b] address-family ipv4
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route ospf 3
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route direct
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] quit
[PE4-bgp-default-b] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE4] isis 1
[PE4-isis-1] bier enable
[PE4-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE4-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE4-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE4-isis-1] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[PE4] ospf 2 vpn-instance a
[PE4-ospf-2] import-route bgp
[PE4-ospf-2] area 0.0.0.0
[PE4-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE4-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE4-ospf-2] quit
[PE4] ospf 3 vpn-instance b
[PE4-ospf-3] import-route bgp
[PE4-ospf-3] area 0.0.0.0
[PE4-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE4-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE4-ospf-3] quit
5. Configure P 1:
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] is-level level-1
[P1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0005.00
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface loopback 1
[P1-LoopBack1] ip address 5.5.5.5 32
[P1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 5555::5555 128
[P1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BIER.
[P1] bier
[P1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 5
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5005::1
# Configure SRv6.
[P1] segment-routing ipv6
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 5555::5555
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 5:2:: 96 static 8
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 1011::2 80
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 1021::1 80
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] bier enable
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
6. Configure P 2:
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P2] isis 1
[P2-isis-1] is-level level-1
[P2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0006.00
[P2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface loopback 1
[P2-LoopBack1] ip address 6.6.6.6 32
[P2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 6666::6666 128
[P2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BIER.
[P2] bier
[P2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 6
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5006::1
# Configure SRv6.
[P2] segment-routing ipv6
[P2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 6666::6666
[P2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 6:2:: 96 static 8
[P2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[P2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 1051::1 80
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 1041::2 80
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1 and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface loopback 1
[P2-LoopBack1] ip address 6.6.6.6 32
[P2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 6666::6666 128
[P2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-LoopBack1] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[P2] isis 1
[P2-isis-1] bier enable
[P2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P2-isis-1] quit
7. Configure CE a1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEa1> system-view
[CEa1] multicast routing
[CEa1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.1.1.1 24
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.1.1.2 24
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEa1] ospf 1
[CEa1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEa1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
8. Configure CE b1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEb1> system-view
[CEb1] multicast routing
[CEb1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.2.1.1 24
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.2.1.2 24
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEb1] ospf 1
[CEb1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEb1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEb1-ospf-1] quit
9. Configure CE a2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEa2> system-view
[CEa2] multicast routing
[CEa2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IGMP on the interface.
[CEa2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.3.1.1 24
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.3.1.2 24
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEa2] ospf 1
[CEa2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEa2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEa2-ospf-1] quit
10. Configure CE b2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEb2> system-view
[CEb2] multicast routing
[CEb2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IGMP on the interface.
[CEb2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.4.1.1 24
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp version 3
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.4.1.2 24
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEb2] ospf 1
[CEb2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEb2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEb2-ospf-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif0
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x10
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Multicast service prefix:
Prefix length ID length ID offset MS Flags
64 10 0 0
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 2222::2222
Uptime: 00:01:00 Originating router: 2.2.2.2
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnels in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif2
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x10
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Multicast service prefix:
Prefix length ID length ID offset MS Flags
64 10 0 0
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 2222::2222
Uptime: 00:10:01 Originating router: 2.2.2.2
# Display C-multicast A-D route information for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a c-multicast routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(12.1.1.100, 225.0.0.1)
CreateTime: 02:54:43
Tunnel Information: BIERVOif1
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 2.
[PE2] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel remote
Total 1 inclusive tunnel
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 2222::2222
Uptime: -- Originating router: 2.2.2.2
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 2.
[PE2] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel remote
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 2 BFR prefix: 2222::2222
Uptime: -- Originating router: 2.2.2.2
# Display information about the PIM routing table for VPN instance a on PE 2.
[PE2] display pim vpn-instance a routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entries; 1 (S, G) entries
(12.1.1.100, 225.0.0.1)
RP: 11.1.1.1
Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT ACT SRC-ACT SC
UpTime: 00:56:25
Upstream interface: BIERVIif0(1.1.1.1)
Upstream neighbor: 1.1.1.1
RPF prime neighbor: 1.1.1.1
Downstream interface information:
Total number of downstream interfaces: 1
1: Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
Protocol: pim-sm, UpTime: 00:56:25, Expires: 00:03:17
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 3.
[PE3] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif0
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 3333::3333>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x10
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 3
BFR prefix: 3333::3333
Multicast service prefix:
Prefix length ID length ID offset MS Flags
64 10 0 0
Root: 3.3.3.3 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: 00:01:00 Originating router: 4.4.4.4
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 3.
[PE3] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnel in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif1
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 3333::3333>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x10
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 3
BFR prefix: 3333::3333
Multicast service prefix:
Prefix length ID length ID offset MS Flags
64 10 0 0
Root: 3.3.3.3 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: 00:10:01 Originating router: 4.4.4.4
# Display C-multicast A-D route information for VPN instance a on PE 3.
[PE3] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a c-multicast routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(12.1.1.100, 225.0.0.1)
CreateTime: 02:54:43
Tunnel Information: BIERVOif1
# Display information about the PIM routing table for VPN instance a on PE 3.
[PE3] display pim vpn-instance a routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entries; 1 (S, G) entries
(12.1.1.100, 225.0.0.1)
RP: 11.1.1.1
Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT ACT RC
UpTime: 00:54:22
Upstream interface: Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
Upstream neighbor: 10.3.1.1
RPF prime neighbor: 10.3.1.1
Downstream interface information:
Total number of downstream interfaces: 1
1: BIERVOif1
Protocol: MD, UpTime: 00:54:18, Expires: -
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance b on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b inclusive-tunnel remote
Total 1 inclusive tunnel
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 3
BFR prefix: 3333::3333
Root: 3.3.3.3
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: -- Originating router: 4.4.4.4
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel remote
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 3
BFR prefix: 3333::3333
Root: 3.3.3.3
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: -- Originating router: 4.4.4.4
Example: Configuring inter-AS option C BIER-based MVPN (G-BIER encapsulation)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 21, configure inter-AS option C BIER-based MVPN to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
· In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 2 is a receiver. · In VPN instance b, S 2 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. · PIM-SM is used in VPN instance a. · PIM-SSM is used in VPN instance b. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 belongs to VPN instance b. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 3: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 4: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belong to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 belongs to VPN instance b. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and BIER |
· Configure OSPF in AS 100 and AS 200, and configure OSPF between the PEs and the CEs. · Establish BGP peer connections between the following devices on their respective Loopback 1: PE 1 and PE 2, PE 2 and PE 3, PE 3 and PE 4, PE 4 and PE 1. Establish EBGP peer connections between PE 2 and PE 3 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16. · Configure BIER in AS 100 and AS 200. · Emable BIER on P 1 and P 2. |
|
IP multicast routing |
· Enable IP multicast routing on PE 1, PE 2 and PE 4. · Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1 and PE 4. · Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b on PE 1 and PE 4. · Enable IP multicast routing on CE a1, CE a2, CE b1, and CE b2. |
|
IGMP |
· Enable IGMPv2 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE a2. · Enable IGMPv3 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE b2. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on all private interfaces on PE 1 and PE 4. · Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on CE a1, CE a2, CE b1, and CE b2. · Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 of PE 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance ato provide services for all multicast groups. |
Table 9 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
12.1.1.100/24 |
R 1 |
— |
12.4.1.100/24 |
|
S 2 |
— |
12.2.1.100/24 |
R 2 |
— |
12.3.1.100/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
1011::1/80 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/15 |
1041::1/80 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.1.1.1/24 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/16 |
1031::2/80 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/17 |
11.2.1.1/24 |
PE 3 |
Loop1 |
3.3.3.3/32 3333::3333/128 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.1/32 1111::1111/128 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/15 |
1051::2/80 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
1021::2/80 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.3.1.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
1031::1/80 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/17 |
11.4.1.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
2.2.2.2/32 2222::2222/128 |
PE 4 |
Loop1 |
4.4.4.4/32 4444::4444/128 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
1011::2/80 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
1051::1/80 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
1021::1/80 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
1041::2/80 |
|
P 1 |
Loop1 |
5.5.5.5/32 5555::5555/128 |
P 2 |
Loop1 |
6.6.6.6/32 6666::6666/128 |
|
CE a1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.1.1.1/24 |
CE b1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.2.1.1/24 |
|
CE a1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.1.1.2/24 |
CE b1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.2.1.2/24 |
|
CE a2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.3.1.1/24 |
CE b2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.4.1.1/24 |
|
CE a2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.3.1.2/24 |
CE b2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.4.1.2/24 |
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1111::1111 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BIER.
[PE1] bier
[PE1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5001::1
# Configure SRv6.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1111::1111
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:2:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure a multicast service prefix.
[PE1] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1234:1:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 1
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Create a VPN instance named b, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance b
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] route-distinguisher 200:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing in VPN instance b.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance b
[PE1-mrib-b] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance b.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance b mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance b.
[PE1-mvpn-b] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance b.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance b.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 2
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 1011::1 80
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.1.1.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance b, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip binding vpn-instance b
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 11.2.1.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a.
[PE1] pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim-a] c-bsr 11.1.1.1
[PE1-pim-a] c-rp 11.1.1.1
[PE1-pim-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2222::2222 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2222::2222 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4444::4444 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4444::4444 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4444::4444 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE1–bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] bier bfr-prefix proxy
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2222::2222 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 4444::4444 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4444::4444 enable
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4444::4444 prefix-sid
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route ospf 2
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance b
[PE1-bgp-default-b] address-family ipv4
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route ospf 3
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-b] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] bier enable
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[PE1] ospf 2 vpn-instance a
[PE1-ospf-2] import-route bgp
[PE1-ospf-2] area 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE1-ospf-2] quit
[PE1] ospf 3 vpn-instance b
[PE1-ospf-3] import-route bgp
[PE1-ospf-3] area 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE1-ospf-3] quit
2. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 2.2.2.2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.2 32
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2222::2222 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BIER.
[PE2] bier
[PE2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 2
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5002::1
# Configure SRv6.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2222::2222
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 2:2:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 1021::2 80
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 1031::1 80
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1031::2 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-bier isisv6 1
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1111::1111 next-hop-local
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1031::2 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1031::2 capability bier
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] bier enable
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] import-bier bgp4+
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
3. Configure PE 3:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE3> system-view
[PE3] router id 3.3.3.3
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE3] isis 1
[PE3-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE3-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE3-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00
[PE3-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE3-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE3] interface loopback 1
[PE3-LoopBack1] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[PE3-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 3333::3333 128
[PE3-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE3-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BIER.
[PE3] bier
[PE3-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 3
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5003::1
# Configure SRv6.
[PE3] segment-routing ipv6
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3333::3333
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 3:2:: 96 static 8
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 1041::1 80
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an Iv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 1031::2 80
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE3] bgp 200
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 4444::4444 as-number 200
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 4444::4444 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 1031::1 as-number 100
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6] import-bier isisv6 1
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4444::4444 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4444::4444 next-hop-local
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1031::1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1031::1 capability bier
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE3–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE3] isis 1
[PE3-isis-1] bier enable
[PE3-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] import-bier bgp4+
# Redistribute IPv6 BGP routes into IS-IS.
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] import-route bgp4+ level-1
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE3-isis-1] quit
4. Configure PE 4:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE4> system-view
[PE4] router id 4.4.4.4
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE4] isis 1
[PE4-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE4-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE4-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[PE4-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE4-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE4-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE4] interface loopback 1
[PE4-LoopBack1] ip address 4.4.4.4 32
[PE4-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 4444::4444 128
[PE4-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE4-LoopBack1] quit
# Assign PE 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 1, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[PE4] bier
[PE4-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 4
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5004::1
# Configure SRv6.
[PE4] segment-routing ipv6
[PE4-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 4444::4444
[PE4-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 4:2:: 96 static 8
[PE4-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE4-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Configure a multicast service prefix.
[PE4] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1234:4:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE4] ip vpn-instance a
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 300:1
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a.
[PE4] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE4-mrib-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE4] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 1
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Create a VPN instance named b, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE4] ip vpn-instance b
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] route-distinguisher 400:1
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b.
[PE4] multicast routing vpn-instance b
[PE4-mrib-b] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance b.
[PE4] multicast-vpn vpn-instance b mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance b.
[PE4-mvpn-b] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance b.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance b.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 2
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] quit
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 1051::2 80
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.3.1.1 24
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance b, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip binding vpn-instance b
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 11.4.1.1 24
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE4] bgp 200
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 3333::3333 as-number 200
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 3333::3333 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 as-number 100
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE4-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3333::3333 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE4–bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE4–bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1111::1111 prefix-sid
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE4-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route ospf 2
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE4-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance b
[PE4-bgp-default-b] address-family ipv4
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route ospf 3
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route direct
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] quit
[PE4-bgp-default-b] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE4] isis 1
[PE4-isis-1] bier enable
[PE4-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE4-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE4-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE4-isis-1] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[PE4] ospf 2 vpn-instance a
[PE4-ospf-2] import-route bgp 200
[PE4-ospf-2] area 0.0.0.0
[PE4-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE4-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE4-ospf-2] quit
[PE4] ospf 3 vpn-instance b
[PE4-ospf-3] import-route bgp 200
[PE4-ospf-3] area 0.0.0.0
[PE4-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE4-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE4-ospf-3] quit
5. Configure P 1:
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] is-level level-1
[P1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0005.00
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface loopback 1
[P1-LoopBack1] ip address 5.5.5.5 32
[P1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 5555::5555 128
[P1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BIER.
[P1] bier
[P1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 5
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5005::1
# Configure SRv6.
[P1] segment-routing ipv6
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 5555::5555
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 5:2:: 96 static 8
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 1011::2 80
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 1021::1 80
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] bier enable
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
6. Configure P 2:
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P2] isis 1
[P2-isis-1] is-level level-1
[P2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0006.00
[P2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface loopback 1
[P2-LoopBack1] ip address 6.6.6.6 32
[P2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 6666::6666 128
[P2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BIER.
[P2] bier
[P2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 6
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5006::1
# Configure SRv6.
[P2] segment-routing ipv6
[P2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 6666::6666
[P2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 6:2:: 96 static 8
[P2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[P2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 1051::1 80
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 1041::2 80
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[P2] isis 1
[P2-isis-1] bier enable
[P2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P2-isis-1] quit
7. Configure CE a1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEa1> system-view
[CEa1] multicast routing
[CEa1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.1.1.1 24
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.1.1.2 24
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEa1] ospf 1
[CEa1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEa1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEa1-ospf-1] quit
8. Configure CE b1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEb1> system-view
[CEb1] multicast routing
[CEb1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.2.1.1 24
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.2.1.2 24
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEb1] ospf 1
[CEb1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEb1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEb1-ospf-1] quit
9. Configure CE a2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEa2> system-view
[CEa2] multicast routing
[CEa2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IGMP on the interface.
[CEa2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.3.1.1 24
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.3.1.2 24
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEa2] ospf 1
[CEa2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEa2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEa2-ospf-1] quit
10. Configure CE b2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEb2> system-view
[CEb2] multicast routing
[CEb2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IGMPv3 on the interface.
[CEb2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.4.1.1 24
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp version 3
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.4.1.2 24
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEb2] ospf 1
[CEb2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEb2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEb2-ospf-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif0
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x10
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Multicast service prefix:
Prefix length ID length ID offset MS Flags
64 10 0 0
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: 00:01:00 Originating router: 4.4.4.4
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnels in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif2
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x10
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Multicast service prefix:
Prefix length ID length ID offset MS Flags
64 10 0 0
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: 00:10:01 Originating router: 4.4.4.4
# Display C-multicast A-D route information for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a c-multicast routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(12.1.1.100, 225.0.0.1)
CreateTime: 02:54:43
Tunnel Information: BIERVOif2
# Display information about the PIM-SM routing entries for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display pim vpn-instance a routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entries; 1 (S, G) entries
(12.1.1.100, 225.0.0.1)
RP: 11.1.1.1 (local)
Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT 2MSDP ACT RC SRC-ACT 2MVPN
UpTime: 00:00:43
Upstream interface: Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
Upstream neighbor: 11.1.1.2
RPF prime neighbor: 11.1.1.2
Downstream interface information:
Total number of downstream interfaces: 1
1: BIERVOif2
Protocol: MD, UpTime: 00:00:30, Expires: -
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance b on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif3
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x10
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Multicast service prefix:
Prefix length ID length ID offset MS Flags
64 10 0 0
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: 00:01:00 Originating router: 4.4.4.4
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance b on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnels in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif4
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x10
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Multicast service prefix:
Prefix length ID length ID offset MS Flags
64 10 0 0
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: 00:10:01 Originating router: 4.4.4.4
# Display information about the PIM-SSM routing entries for VPN instance b on PE 1.
[PE1] display pim vpn-instance b routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entries; 1 (S, G) entries
(12.2.1.100, 232.0.0.0)
Protocol: pim-ssm, Flag: RC
UpTime: 00:26:06
Upstream interface: Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17
Upstream neighbor: 11.2.1.2
RPF prime neighbor: 11.2.1.2
Downstream interface information:
Total number of downstream interfaces: 1
1: BIERVOif4
Protocol: MD, UpTime: 00:25:56, Expires: -
# Display cross-AS BFR information on PE 2.
[PE2] display bier inter-as bfr-info sub-domain 0
Sub-domain 0
BFR prefix: 3333::3333
BFR-ID: 3
AS number: 200
Protocol: BGP
Sub protocol: EBGP
BFR ID range: 4,6
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel remote
Total 1 inclusive tunnel
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: -- Originating router: 4.4.4.4
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel remote
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: -- Originating router: 4.4.4.4
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance b on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b inclusive-tunnel remote
Total 1 inclusive tunnel
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: -- Originating router: 4.4.4.4
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance b on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b selective-tunnel remote
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: -- Originating router: 4.4.4.4
Example: Configuring static cross-AS BIER in inter-AS option C BIER-based MVPN (BIERv6 encapsulation)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 22, configure static cross-AS BIER in inter-AS option C BIER-based MVPN to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
· In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 2 is a receiver. · In VPN instance b, S 2 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. · PIM-SM is used in VPN instance a. · PIM-SSM is used in VPN instance b. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 belongs to VPN instance b. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 3: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 4: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belong to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 belongs to VPN instance b. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and BIER |
· Configure OSPF in AS 100 and AS 200, and configure OSPF between the PEs and the CEs. · Establish BGP peer connections between the following devices on their respective Loopback 1: PE 1 and PE 2, PE 2 and PE 3, PE 3 and PE 4, PE 4 and PE 1. Establish EBGP peer connections between PE 2 and PE 3 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16. · Configure BIER in AS 100 and AS 200. · Emable BIER on P 1 and P 2. |
|
IP multicast routing |
· Enable IP multicast routing on PE 1, PE 2 and PE 4. · Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1 and PE 4. · Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b on PE 1 and PE 4. · Enable IP multicast routing on CE a1, CE a2, CE b1, and CE b2. |
|
IGMP |
· Enable IGMPv2 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE a2. · Enable IGMPv3 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE b2. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on all private interfaces on PE 1 and PE 4. · Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on CE a1, CE a2, CE b1, and CE b2. · Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 of PE 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance ato provide services for all multicast groups. |
Table 10 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
12.1.1.100/24 |
R 1 |
— |
12.4.1.100/24 |
|
S 2 |
— |
12.2.1.100/24 |
R 2 |
— |
12.3.1.100/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
1011::1/80 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/15 |
1041::1/80 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.1.1.1/24 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/16 |
1031::2/80 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/17 |
11.2.1.1/24 |
PE 3 |
Loop1 |
3.3.3.3/32 3333::3333/128 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.1/32 1111::1111/128 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/15 |
1051::2/80 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
1021::2/80 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.3.1.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
1031::1/80 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/17 |
11.4.1.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
2.2.2.2/32 2222::2222/128 |
PE 4 |
Loop1 |
4.4.4.4/32 4444::4444/128 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
1011::2/80 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
1051::1/80 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
1021::1/80 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
1041::2/80 |
|
P 1 |
Loop1 |
5.5.5.5/32 5555::5555/128 |
P 2 |
Loop1 |
6.6.6.6/32 6666::6666/128 |
|
CE a1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.1.1.1/24 |
CE b1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.2.1.1/24 |
|
CE a1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.1.1.2/24 |
CE b1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.2.1.2/24 |
|
CE a2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.3.1.1/24 |
CE b2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.4.1.1/24 |
|
CE a2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.3.1.2/24 |
CE b2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.4.1.2/24 |
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1111::1111 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1111::1111
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:2:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 1, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[PE1] bier
[PE1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the BIERv6 encapsulation.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type bierv6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:2::1 as the End.BIER SID.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-bier locator aaa sid 1:2::1
# Configure static cross-AS BIER.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-neighbor end-bier 3:2::1 bfr-id 3 to 4
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-neighbor end-bier 3:2::1 bfr-id 6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bier] quit
# Configure a multicast service prefix.
[PE1] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1234:1:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 1:2::2
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Create a VPN instance named b, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance b
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] route-distinguisher 200:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing in VPN instance b.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance b
[PE1-mrib-b] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance b.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance b mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance b.
[PE1-mvpn-b] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance b.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance b.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 1:2::3
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 1011::1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.1.1.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance b, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip binding vpn-instance b
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 11.2.1.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a.
[PE1] pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim-a] c-bsr 11.1.1.1
[PE1-pim-a] c-rp 11.1.1.1
[PE1-pim-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2222::2222 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2222::2222 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4444::4444 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4444::4444 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4444::4444 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE1–bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] bier bfr-prefix proxy
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2222::2222 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 4444::4444 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 4444::4444 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4444::4444 enable
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4444::4444 prefix-sid
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route ospf 2
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance b
[PE1-bgp-default-b] address-family ipv4
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route ospf 3
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-b] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] bier enable
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[PE1] ospf 2 vpn-instance a
[PE1-ospf-2] import-route bgp
[PE1-ospf-2] area 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE1-ospf-2] quit
[PE1] ospf 3 vpn-instance b
[PE1-ospf-3] import-route bgp
[PE1-ospf-3] area 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE1-ospf-3] quit
[PE1] commit
2. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 2.2.2.2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.2 32
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 2222::2222 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2222::2222
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 2:2:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 2, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[PE2] bier
[PE2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 2
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the BIERv6 encapsulation.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type bierv6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 2:2::1 as the End.BIER SID.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-bier locator aaa sid 2:2::1
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bier] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 1021::2 80
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 1031::1 80
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1031::2 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-bier isisv6 1
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1111::1111 next-hop-local
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1031::2 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1031::2 capability bier
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] bier enable
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
# Redistribute IPv6 BGP routes into IS-IS.
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] import-bier bgp4+ level-1
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
3. Configure PE 3:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE3> system-view
[PE3] router id 3.3.3.3
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE3] isis 1
[PE3-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE3-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE3-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00
[PE3-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE3-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE3] interface loopback 1
[PE3-LoopBack1] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[PE3-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 3333::3333 128
[PE3-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE3-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE3] segment-routing ipv6
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3333::3333
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 3:2:: 96 static 8
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 3 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 3, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[PE3] bier
[PE3-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 3
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the BIERv6 encapsulation.
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type bierv6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 3:2::1 as the End.BIER SID.
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-bier locator aaa sid 3:2::1
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[PE3-bier] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 1041::1 80
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an Iv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 1031::2 80
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE3] bgp 200
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 4444::4444 as-number 200
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 4444::4444 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 1031::1 as-number 100
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6] import-bier isisv6 1
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4444::4444 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4444::4444 next-hop-local
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1031::1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1031::1 capability bier
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE3–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE3] isis 1
[PE3-isis-1] bier enable
[PE3-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] import-bier bgp4+
# Redistribute IPv6 BGP routes into IS-IS.
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] import-route bgp4+ level-1
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE3-isis-1] quit
4. Configure PE 4:
# Configure a global router ID, and enable IP multicast routing.
<PE4> system-view
[PE4] router id 4.4.4.4
[PE4] multicast routing
[PE4] quit
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE4] isis 1
[PE4-isis-1] is-level level-1
[PE4-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE4-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[PE4-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE4-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE4-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE4] interface loopback 1
[PE4-LoopBack1] ip address 4.4.4.4 32
[PE4-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 4444::4444 128
[PE4-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE4-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE4] segment-routing ipv6
[PE4-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 4444::4444
[PE4-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 4:2:: 96 static 8
[PE4-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[PE4-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 4, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 1.
[PE4] bier
[PE4-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 4
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
# Configure BIER with the BIERv6 encapsulation.
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type bierv6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 4:2::1 as the End.BIER SID.
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-bier locator aaa sid 4:2::1
# Configure static cross-AS BIER.
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-neighbor end-bier 2:2::1 bfr-id 1 to 2
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-neighbor end-bier 2:2::1 bfr-id 5
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[PE4-bier] quit
# Configure a multicast service prefix.
[PE4] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1234:4:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE4] ip vpn-instance a
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 300:1
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a.
[PE4] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE4-mrib-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE4] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 4:2::2
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Create a VPN instance named b, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE4] ip vpn-instance b
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] route-distinguisher 400:1
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b.
[PE4] multicast routing vpn-instance b
[PE4-mrib-b] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance b.
[PE4] multicast-vpn vpn-instance b mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance b.
[PE4-mvpn-b] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance b.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance b.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 4:2::3
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] quit
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 1051::2 80
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.3.1.1 24
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance b, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip binding vpn-instance b
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 11.4.1.1 24
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE4] bgp 200
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 3333::3333 as-number 200
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 3333::3333 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 as-number 100
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 1111::1111 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE4-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3333::3333 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE4–bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE4–bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1111::1111 prefix-sid
[PE4–bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1111::1111 enable
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1111::1111 prefix-sid
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE4-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route ospf 2
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE4-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance b
[PE4-bgp-default-b] address-family ipv4
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route ospf 3
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route direct
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] quit
[PE4-bgp-default-b] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE4] isis 1
[PE4-isis-1] bier enable
[PE4-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE4-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE4-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE4-isis-1] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[PE4] ospf 2 vpn-instance a
[PE4-ospf-2] import-route bgp
[PE4-ospf-2] area 0.0.0.0
[PE4-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE4-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE4-ospf-2] quit
[PE4] ospf 3 vpn-instance b
[PE4-ospf-3] import-route bgp
[PE4-ospf-3] area 0.0.0.0
[PE4-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE4-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE4-ospf-3] quit
5. Configure P 1:
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] is-level level-1
[P1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0005.00
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface loopback 1
[P1-LoopBack1] ip address 5.5.5.5 32
[P1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 5555::5555 128
[P1-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BIER.
[P1] bier
[P1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 5
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type bierv6 bsl 128 max-si 32
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-bier locator aaa sid 5:2::1
# Configure SRv6.
[P1] segment-routing ipv6
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 5555::5555
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 5:2:: 96 static 8
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 1011::2 80
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 1021::1 80
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] bier enable
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
6. Configure P 2:
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P2] isis 1
[P2-isis-1] is-level level-1
[P2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0006.00
[P2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 1, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface loopback 1
[P2-LoopBack1] ip address 6.6.6.6 32
[P2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 6666::6666 128
[P2-LoopBack1] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BIER.
[P2] bier
[P2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 6
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack1
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type bierv6 bsl 128 max-si 32
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-bier locator aaa sid 6:2::1
# Configure SRv6.
[P2] segment-routing ipv6
[P2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 6666::6666
[P2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 6:2:: 96 static 8
[P2-segment-routing-ipv6-locator-aaa] quit
[P2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 1051::1 80
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 1041::2 80
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[P2] isis 1
[P2-isis-1] bier enable
[P2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P2-isis-1] quit
7. Configure CE a1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEa1> system-view
[CEa1] multicast routing
[CEa1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.1.1.1 24
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.1.1.2 24
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEa1] ospf 1
[CEa1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEa1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEa1-ospf-1] quit
[CEa1] commit
8. Configure CE b1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEb1> system-view
[CEb1] multicast routing
[CEb1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.2.1.1 24
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.2.1.2 24
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEb1] ospf 1
[CEb1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEb1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEb1-ospf-1] quit
[CEb1] commit
9. Configure CE a2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEa2> system-view
[CEa2] multicast routing
[CEa2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IGMP on the interface.
[CEa2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.3.1.1 24
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.3.1.2 24
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEa2] ospf 1
[CEa2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEa2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEa2-ospf-1] quit
[CEa2] commit
10. Configure CE b2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEb2> system-view
[CEb2] multicast routing
[CEb2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IGMPv3 on the interface.
[CEb2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.4.1.1 24
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp version 3
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.4.1.2 24
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEb2] ospf 1
[CEb2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEb2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEb2-ospf-1] quit
[CEb2] commit
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif0
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x10
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: 00:01:00 Originating router: 4.4.4.4
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnels in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif2
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x10
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: 00:10:01 Originating router: 4.4.4.4
# Display C-multicast A-D route information for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a c-multicast routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(12.1.1.100, 225.0.0.1)
CreateTime: 02:54:43
Tunnel Information: BIERVOif2
# Display information about the PIM-SM routing entries for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display pim vpn-instance a routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entries; 1 (S, G) entries
(12.1.1.100, 225.0.0.1)
RP: 11.1.1.1 (local)
Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT 2MSDP ACT RC SRC-ACT 2MVPN
UpTime: 00:00:43
Upstream interface: Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
Upstream neighbor: 11.1.1.2
RPF prime neighbor: 11.1.1.2
Downstream interface information:
Total number of downstream interfaces: 1
1: BIERVOif2
Protocol: MD, UpTime: 00:00:30, Expires: -
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance b on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif3
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x10
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: 00:01:00 Originating router: 4.4.4.4
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance b on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnels in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel interface: BIERVOif4
Tunnel identifier: BIER <0x0, 0x1, 1111::1111>
Tunnel state: Up
Flags: 0x10
Sub-domain ID/BSL: 0/128
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: 00:10:01 Originating router: 4.4.4.4
# Display information about the PIM-SSM routing entries for VPN instance b on PE 1.
[PE1] display pim vpn-instance b routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entries; 1 (S, G) entries
(12.2.1.100, 232.0.0.0)
Protocol: pim-ssm, Flag: RC
UpTime: 00:26:06
Upstream interface: Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17
Upstream neighbor: 11.2.1.2
RPF prime neighbor: 11.2.1.2
Downstream interface information:
Total number of downstream interfaces: 1
1: BIERVOif4
Protocol: MD, UpTime: 00:25:56, Expires: -
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel remote
Total 1 inclusive tunnel
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: -- Originating router: 4.4.4.4
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel remote
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: -- Originating router: 4.4.4.4
# Display information about the BIER inclusive tunnel for VPN instance b on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b inclusive-tunnel remote
Total 1 inclusive tunnel
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: -- Originating router: 4.4.4.4
# Display information about BIER selective tunnels for VPN instance b on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b selective-tunnel remote
Tunnel type: BIER
Tunnel state: --
Flags: 0x0
Sub-domain ID: 0
BFR-ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1111::1111
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: BFR-ID: 4 BFR prefix: 4444::4444
Uptime: -- Originating router: 4.4.4.4
Example: Configuring warm backup and local protection for intra-AS BIER-based MVPN (MSR6 encapsulation)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 23, configure warm backup and local protection for intra-AS BIER-based MVPN with the MSR6 encapsulation to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Functions |
· Warm backup on source-side PEs: When the master IDF fails, the standby IDF takes over to send multicast traffic to the receiver-side PE. · Local protection on the public network: When an intermediate node or the master path fails, the traffic will be quickly switched over to the standby path before unicast routes are converged on other devices. |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/18, and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/18 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. · PE 3: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. · PE 4: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and BIER |
· Configure IS-IS on the public network, and establish EBGP peer connections between the PEs and the CEs. · Establish IBGP peer connections between PE 1, PE 2, PE 3, and PE 4 on their respective Loopback 0. · Configure BIER on the public network: sub-domain 0, BSL 128, and max-SI 32. · Configure the BFR prefixes of PE 1, PE 2, P 1, P 2, P 3, P 4, PE 3, and PE 4 as the IPv6 addresses for their respective Loopback 0, and configure the End.RGB SID for each device. |
|
IP multicast routing |
· Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1, PE 2, PE 3, and PE 4. · Enable IP multicast routing on CE 1 and CE 2. |
|
IGMP |
Enable IGMPv3 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 of PE 3 and PE 4. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on all private interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on PE 1, PE 2, PE 3, and PE 4. · Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on CE 1, and CE 2. · Configure Loopback 1 of PE 1 and PE 2 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a to provide services for all multicast groups. |
Table 11 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
7.12.1.10/24 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10:7::4/64 |
|
R 2 |
— |
7.13.1.10/24 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10:8::4/64 |
|
CE 1 |
Vlan-int100 |
7.12.1.11/24 7:12:1::11/64 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10:10::4/64 |
|
CE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.2.0.11/24 10:2::11/64 |
P 2 |
Loop0 |
4.4.4.4/32 4::4/128 |
|
CE 1 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10.3.0.11/24 10:3::11/64 |
P 3 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10:9::5/64 |
|
CE 2 |
Vlan-int100 |
7.12.1.12/24 7:12:1::12/64 |
P 3 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10:11::5/64 |
|
CE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.2.0.22/24 10:2::22/64 |
P 3 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10:12::5/64 |
|
CE 2 |
XGE0/0/18 |
10.4.0.22/24 10:4::22/64 |
P 3 |
Loop0 |
5.5.5.5/32 5::5/128 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.3.0.1/24 10:3::1/64 |
P 4 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10:10::6/64 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10:5::1/64 |
P 4 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10:11::6/64 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/18 |
10:6::1/64 |
P 4 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10:13::6/64 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop0 |
1.1.1.1/32 1::1/128 |
P 4 |
Loop0 |
6.6.6.6/32 6::6/128 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1.2.3.4/32 1:2:3::4/128 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10:12::7/64 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/18 |
10.4.0.2/24 10:4::2/64 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.14.0.7/24 10:14::7/64 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10:5::2/64 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/16 |
7.13.1.11/24 7:13:1::11/64 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10:7::2/64 |
PE 3 |
Loop0 |
7.7.7.7/32 7::7/128 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop0 |
2.2.2.2/32 2::2/128 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.6.2/24 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
1.2.3.3/32 1:2:3::3/128 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10:13::8/64 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10:6::3/64 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.14.0.8/24 10:14::8/64 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10:8::3/64 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/16 |
7.13.1.12/24 7:13:1::12/64 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10:9::3/64 |
PE 4 |
Loop0 |
8.8.8.8/32 8::8/128 |
|
P 1 |
Loop0 |
3.3.3.3/32 3::3/128 |
|
|
|
Procedure
1. Configure CE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<CE1> system-view
[CE1] router id 11.11.11.11
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing.
[CE1] multicast routing
[CE1-mrib] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing.
[CE1] ipv6 multicast routing
[CE1-mrib6] quit
# Create VLAN 100, and assign Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 to it.
[CE1] vlan 100
[CE1-vlan100] port ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CE1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to VLAN-interface 100, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE1] interface vlan-interface 100
[CE1-Vlan-interface100] ip address 7.12.1.11 24
[CE1-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 address 7:12:1::11 64
[CE1-Vlan-interface100] pim sm
[CE1-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 pim sm
[CE1-Vlan-interface100] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.2.0.11 24
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 10:2::11 64
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ospf cost 1000
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ospfv3 cost 1000
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] port link-mode route
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 10.3.0.11 24
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 address 10:3::11 64
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Configure BGP.
[CE1] bgp 65022
[CE1-bgp-default] peer 10.2.0.22 as-number 65022
[CE1-bgp-default] peer 10.3.0.1 as-number 100
[CE1-bgp-default] peer 10:2::22 as-number 65022
[CE1-bgp-default] peer 10:3::1 as-number 100
[CE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.2.0.22 enable
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.3.0.1 enable
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] address-family ipv6 unicast
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 10:2::22 enable
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 10:3::1 enable
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[CE1-bgp-default] quit
2. Configure CE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<CE2> system-view
[CE2] router id 22.22.22.22
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing.
[CE2] multicast routing
[CE2-mrib] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing.
[CE2] ipv6 multicast routing
[CE2-mrib6] quit
# Create VLAN 100, and assign Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 to it.
[CE2] vlan 100
[CE2-vlan100] port ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CE2] quit
# Assign IP addresses to VLAN-interface 100, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE2] interface vlan-interface 100
[CE2-Vlan-interface100] ip address 7.12.1.12 24
[CE2-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 address 7:12:1::12 64
[CE2-Vlan-interface100] pim sm
[CE2-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 pim sm
[CE2-Vlan-interface100] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.2.0.22 24
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 10:2::22 64
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ospf cost 1000
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ospfv3 cost 1000
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/18, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] port link-mode route
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] ip address
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] pim sm
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] ipv6 pim sm
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] ipv6 address 10:4::22 64
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] quit
# Configure BGP.
[CE2] bgp 65022
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 10.2.0.11 as-number 65022
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 10.4.0.2 as-number 100
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 10:2::11 as-number 65022
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 10:4::2 as-number 100
[CE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.2.0.11 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.4.0.2 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] address-family ipv6 unicast
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 10:2::11 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 10:4::2 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[CE2-bgp-default] quit
3. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 0
[PE1-LoopBack0] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:2:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 1, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE1] bier
[PE1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:2::5 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:2::5
# Configure detecting the reachability of the primary next hop through BFD session of echo packets.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] primary-path-detect bfd echo
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bier] quit
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 1:2::34
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] warm-root-standby
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] src-dt6 locator aaa sid 1:2::35
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] warm-root-standby
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.3.0.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 10:3::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis cost 1200
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 address 10:5::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/18 and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] isis cost 100
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] ipv6 address 10:6::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] quit
# Associate Loopback 1 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.2.3.4 32
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1:2:3::4 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure Loopback 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP.
[PE1] pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim-a] c-bsr 1.2.3.4
[PE1-pim-a] c-rp 1.2.3.4
[PE1-pim-a] quit
[PE1] ipv6 pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim6-a] c-bsr 1:2:3::4
[PE1-pim6-a] c-rp 1:2:3::4
[PE1-pim6-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 7::7 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 7::7 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 8::8 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 8::8 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 2::2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 7::7 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 8::8 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 2::2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 7::7 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 8::8 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] pic
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2::2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2::2 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2::2 advertise-community
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 7::7 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 7::7 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 8::8 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 8::8 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] pic
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 2::2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 2::2 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 2::2 advertise-community
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 7::7 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 7::7 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 8::8 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 8::8 prefix-sid
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] peer 10.3.0.11 as-number 65022
[PE1-bgp-default-a] peer 10:3::11 as-number 65022
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] pic
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] peer 10.3.0.11 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] pic
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] peer 10:3::11 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER fast reroute for the IS-IS process.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] bier enable
[PE1-isis-1] bier fast-reroute enable
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute lfa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute ti-lfa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
4. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 2.2.2.2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 0
[PE2-LoopBack0] ip address 2.2.2.2 32
[PE2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[PE2-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2::2
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:3:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 2, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE2] bier
[PE2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 2
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:3::5 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:3::5
# Configure detecting the reachability of the primary next hop through BFD session of echo packets.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] primary-path-detect bfd echo
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bier] quit
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:2
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE2] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 1:3::34
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] warm-root-standby
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] src-dt6 locator aaa sid 1:3::35
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] warm-root-standby
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/18 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] ip address 10.4.0.2 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] ipv6 address 10:4::2 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] ipv6 pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis cost 1200
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 10:5::2 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis cost 100
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 address 10:7::2 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Associate Loopback 1 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 1.2.3.3 32
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1:2:3::3 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] pim sm
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 pim sm
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure Loopback 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP.
[PE2] pim vpn-instance a
[PE2-pim-a] c-bsr 1.2.3.3
[PE2-pim-a] c-rp 1.2.3.3
[PE2-pim-a] quit
[PE2] ipv6 pim vpn-instance a
[PE2-pim6-a] c-bsr 1:2:3::3
[PE2-pim6-a] c-rp 1:2:3::3
[PE2-pim6-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 2.2.2.2
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 7::7 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 7::7 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 8::8 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 8::8 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 7::7 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 8::8 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 7::7 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 8::8 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] pic
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 advertise-community
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 7::7 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 7::7 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 8::8 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 8::8 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] pic
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 advertise-community
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 7::7 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 7::7 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 8::8 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 8::8 prefix-sid
[PE2–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-bgp-default-a] peer 10.4.0.22 as-number 65022
[PE2-bgp-default-a] peer 10:4::22 as-number 65022
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] pic
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] peer 10.4.0.22 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] pic
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] peer 10:4::22 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER fast reroute for the IS-IS process.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] bier enable
[PE2-isis-1] bier fast-reroute enable
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute lfa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute ti-lfa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
5. Configure P 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P1> system-view
[P1] router id 3.3.3.3
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface loopback 1
[P1-LoopBack0] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[P1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 3::3 128
[P1-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[P1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[P1] segment-routing ipv6
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3::3
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:4:: 96 static 8
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign P 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 3, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[P1] bier
[P1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 3
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:4::5 as the End.RGB SID.
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:4::5
# Configure detecting the reachability of the primary next hop through BFD session of echo packets.
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] primary-path-detect bfd echo
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[P1-bier] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis cost 100
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 address 10:6::3 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis cost 1300
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 10:8::3 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis cost 100
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 10:9::3 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Enable BIER fast reroute for the IS-IS process.
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] bier enable
[P1-isis-1] bier fast-reroute enable
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute lfa
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute ti-lfa
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
6. Configure P 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P2> system-view
[P2] router id 4.4.4.4
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P2] isis 1
[P2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[P2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface loopback 0
[P2-LoopBack0] ip address 4.4.4.4 32
[P2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 4::4 128
[P2-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[P2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[P2] segment-routing ipv6
[P2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 4::4
[P2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:5:: 96 static 8
[P2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign P 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 4, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[P2] bier
[P2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 4
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:5::5 as the End.RGB SID.
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:5::5
# Configure detecting the reachability of the primary next hop through BFD session of echo packets.
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] primary-path-detect bfd echo
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[P2-bier] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis cost 100
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 address 10:7::4 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis cost 1300
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 10:8::4 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis cost 100
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 10:10::4 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Enable BIER fast reroute for the IS-IS process.
[P2] isis 1
[P2-isis-1] bier enable
[P2-isis-1] bier fast-reroute enable
[P2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute lfa
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute ti-lfa
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P2-isis-1] quit
7. Configure P 3:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P3> system-view
[P3] router id 5.5.5.5
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P3] isis 1
[P3-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P3-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P3-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0005.00
[P3-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P3-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P3-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[P3] interface loopback 0
[P3-LoopBack0] ip address 5.5.5.5 32
[P3-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 5::5 128
[P3-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[P3-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P3-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[P3] segment-routing ipv6
[P3-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 5::5
[P3-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:6:: 96 static 8
[P3-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign P 3 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 5, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[P3] bier
[P3-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 5
[P3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[P3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:6::5 as the End.RGB SID.
[P3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:6::5
# Configure detecting the reachability of the primary next hop through BFD session of echo packets.
[P3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] primary-path-detect bfd echo
[P3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[P3-bier] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis cost 100
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 10:9::5 64
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis cost 1400
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 10:11::5 64
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] port link-mode route
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis cost 100
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 address 10:12::5 64
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Enable BIER fast reroute for the IS-IS process.
[P3] isis 1
[P3-isis-1] bier enable
[P3-isis-1] bier fast-reroute enable
[P3-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P3-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P3-isis-1-ipv6]fast-reroute lfa
[P3-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute ti-lfa
[P3-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P3-isis-1] quit
8. Configure P 4:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P4> system-view
[P4] router id 6.6.6.6
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P4] isis 1
[P4-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P4-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P4-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0006.00
[P4-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P4-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P4-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[P4] interface loopback 0
[P4-LoopBack0] ip address 6.6.6.6 32
[P4-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 6::6 128
[P4-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[P4-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P4-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[P4] segment-routing ipv6
[P4-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 6::6
[P4-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:7:: 96 static 8
[P4-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign P 4 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 6, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[P4] bier
[P4-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 6
[P4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[P4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:7::5 as the End.RGB SID.
[P4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:7::5
# Configure detecting the reachability of the primary next hop through BFD session of echo packets.
[P4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] primary-path-detect bfd echo
[P4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[P4-bier] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis cost 100
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 10:10::6 64
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis cost 1400
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 10:11::6 64
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] port link-mode route
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis cost 100
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 address 10:13::6 64
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Enable BIER fast reroute for the IS-IS process.
[P4] isis 1
[P4-isis-1] bier enable
[P4-isis-1] bier fast-reroute enable
[P4-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P4-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P4-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute lfa
[P4-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute ti-lfa
[P4-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P4-isis-1] quit
9. Configure PE 3:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE3> system-view
[PE3] router id 7.7.7.7
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE3] isis 1
[PE3-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE3-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE3-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0007.00
[PE3-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE3-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE3] interface loopback 0
[PE3-LoopBack0] ip address 7.7.7.7 32
[PE3-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 7::7 128
[PE3-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[PE3-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE3-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE3] segment-routing ipv6
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 7::7
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:8:: 96 static 8
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 3 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 7, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE3] bier
[PE3-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 7
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:8::5 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:8::5
# Configure detecting the reachability of the primary next hop through BFD session of echo packets.
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] primary-path-detect bfd echo
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[PE3-bier] quit
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE3] ip vpn-instance a
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:7
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE3] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE3-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE3] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE3-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE3] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE3-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 1:8::34
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv4] warm-root-standby
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE3-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv6] src-dt6 locator aaa sid 1:8::35
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv6] warm-root-standby
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM, IGMP, and MLD on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 7.13.1.11 24
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 7:13:1::11 64
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] igmp enable
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] igmp version 3
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mld enable
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] port link-mode route
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis cost 100
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 address 10:12::7 64
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis cost 1500
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 10:14::7 64
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE3] bgp 100
[PE3-bgp-default] router-id 7.7.7.7
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 8::8 as-number 100
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 8::8 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 2::2 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 8::8 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 2::2 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 8::8 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] pic
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2::2 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2::2 prefix-sid
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 8::8 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 8::8 prefix-sid
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv6] pic
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 2::2 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 2::2 prefix-sid
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 8::8 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 8::8 prefix-sid
[PE3–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE3-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] pic
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE3-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6-a] pic
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE3-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE3–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER fast reroute for the IS-IS process.
[PE3] isis 1
[PE3-isis-1] bier enable
[PE3-isis-1] bier fast-reroute enable
[PE3-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute lfa
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute ti-lfa
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE3-isis-1] quit
10. Configure PE 4:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE4> system-view
[PE4] router id 8.8.8.8
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE4] isis 1
[PE4-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE4-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE4-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0008.00
[PE4-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE4-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE4-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE4] interface loopback 0
[PE4-LoopBack0] ip address 8.8.8.8 32
[PE4-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 8::8 128
[PE4-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[PE4-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE4-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE4] segment-routing ipv6
[PE4-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 8::8
[PE4-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:9:: 96 static 8
[PE4-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 4 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 8, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE4] bier
[PE4-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 8
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:9::5 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:9::5
# Configure detecting the reachability of the primary next hop through BFD session of echo packets.
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] primary-path-detect bfd echo
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] quit
[PE4-bier] quit
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE4] ip vpn-instance a
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:8
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE4] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE4-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE4] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE4-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE4] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 1:9::34
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv4] warm-root-standby
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv6] src-dt6 locator aaa sid 1:9::35
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv6] warm-root-standby
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
[PE4-mvpn-a] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM, IGMP, and MLD on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 7.13.1.12 24
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 7:13:1::12 64
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] igmp enable
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] igmp version 3
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mld enable
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] port link-mode route
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis cost 100
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 address 10:13::8 64
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis cost 1500
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 10:14::8 64
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE4] bgp 100
[PE4-bgp-default] flush suboptimal-route
[PE4-bgp-default] router-id 8.8.8.8
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 7::7 as-number 100
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 7::7 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE4-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 2::2 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 7::7 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE4-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 2::2 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 7::7 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE4-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv4] pic
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2::2 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2::2 prefix-sid
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 7::7 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 7::7 prefix-sid
[PE4-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv6] pic
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 2::2 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 2::2 prefix-sid
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 7::7 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 7::7 prefix-sid
[PE4–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE4-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] pic
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE4-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6-a] pic
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE4-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER fast reroute for the IS-IS process.
[PE4] isis 1
[PE4-isis-1] bier enable
[PE4-isis-1] bier fast-reroute enable
[PE4-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE4-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE4-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute lfa
[PE4-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute ti-lfa
[PE4-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE4-isis-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display PIM routing entries for VPN instance a on PE 1 and PE 2.
[PE1] display pim vpn-instance a routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entries; 1 (S, G) entries
(7.12.1.10, 225.0.0.1)
RP: 1.2.3.4 (local)
Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT 2MSDP ACT RC SRC-ACT 2MVPN SC IDF-MN
UpTime: 00:00:16
Upstream interface: Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
Upstream neighbor: 10.3.0.11
RPF prime neighbor: 10.3.0.11
Downstream interface information:
Total number of downstream interfaces: 1
1: BIERVOif3
Protocol: MD, UpTime: 00:00:06, Expires: -
[PE2] display pim vpn-instance a routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entries; 1 (S, G) entries
(7.12.1.10, 225.0.0.1)
RP: 1.2.3.4
Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT ACT RC SRC-ACT IDF-BU
UpTime: 00:00:37
Upstream interface: Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18
Upstream neighbor: 10.4.0.22
RPF prime neighbor: 10.4.0.22
Downstream interface information:
Total number of downstream interfaces: 1
1: BIERVOif3 (Inactive)
Protocol: MD, UpTime: 00:00:27, Expires: -
# Display the BIER information of BFR prefixes for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display bier routing-table
Sub-domain 0
Total BFERs: 8
BFR ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1::1(Local)
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: N/A
BFR ID: 2
BFR prefix: 2::2
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 2
BFR prefix: 2::2
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/17 FE80::280E:94FF:FE96:F0A Invalid
BFR prefix: 4::4
NBRFlag: B
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/18 FE80::280E:9DFF:FE8C:100B 2147483653
BFR ID: 3
BFR prefix: 3::3
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 2
BFR prefix: 3::3
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/18 FE80::280E:9DFF:FE8C:100B Invalid
BFR prefix: 4::4
NBRFlag: B
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/17 FE80::280E:94FF:FE96:F0A 2147483654
BFR ID: 4
BFR prefix: 4::4
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 2
BFR prefix: 2::2
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/17 FE80::280E:94FF:FE96:F0A Invalid
BFR prefix: 4::4
NBRFlag: B
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/18 FE80::280E:9DFF:FE8C:100B Invalid
BFR ID: 5
BFR prefix: 5::5
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 2
BFR prefix: 3::3
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/18 FE80::7C75:17FF:FE29:508 Invalid
BFR prefix: 6::6
NBRFlag: B
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/17 FE80::7C74:E8FF:FEAC:407 2147483654
BFR ID: 6
BFR prefix: 6::6
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 2
BFR prefix: 2::2
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/17 FE80::7C74:E8FF:FEAC:407 Invalid
BFR prefix: 6::6
NBRFlag: B
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/18 FE80::7C75:17FF:FE29:508 Invalid
BFR ID: 7
BFR prefix: 7::7
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 2
BFR prefix: 3::3
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/18 FE80::280E:9DFF:FE8C:100B Invalid
BFR prefix: 8::8
NBRFlag: B
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/17 FE80::280E:94FF:FE96:F0A 2147483652
BFR ID: 8
BFR prefix: 8::8
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 2
BFR prefix: 2::2
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/17 FE80::280E:94FF:FE96:F0A Invalid
BFR prefix: 8::8
NBRFlag: B
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/18 FE80::280E:9DFF:FE8C:100B Invalid
Example: Configuring warm backup and local protection for inter-AS BIER-based MVPN (MSR6 encapsulation)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 24, configure warm backup and local protection for inter-AS BIER-based MVPN with the MSR6 encapsulation to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Functions |
· Warm backup on source-side PEs: When the master IDF fails, the standby IDF takes over to send multicast traffic to the receiver-side PE. · Local protection on the public network: When an intermediate node or the master path fails, the traffic will be quickly switched over to the standby path before unicast routes are converged on other devices. |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/18, and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/18 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. · PE 3: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. · PE 4: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and BIER |
· Configure IS-IS in AS 100 and AS 200 on the public network, establish EBGP peer connections between P 1 and P 3, and establish EBGP peer connections between P 2 and P 4. · Establish BGP peer connections on PE 1 with PE 2, PE 3, and PE 4 on their respective Loopback 0. · Establish BGP peer connections on PE 2 with PE 1, PE 3, and PE 4 on their respective Loopback 0. · Establish BGP peer connections on PE 3 with PE 1, PE 2, and PE 4 on their respective Loopback 0. · Establish BGP peer connections on PE 4 with PE 1, PE 2, and PE 3 on their respective Loopback 0. · Configure BIER on the public network: sub-domain 0, BSL 128, and max-SI 32. · Configure the BFR prefixes of PE 1, PE 2, P 1, P 2, P 3, P 4, PE 3, and PE 4 as the IPv6 addresses for their respective Loopback 0, and configure the End.RGB SID for each device. |
|
IP multicast routing |
· Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1, PE 2, PE 3, and PE 4. · Enable IP multicast routing on CE 1 and CE 2. |
|
IGMP |
Enable IGMPv2 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 of PE 3 and PE 4. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on all private interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on PE 1, PE 2, PE 3, and PE 4. · Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on CE 1, and CE 2. · Configure Loopback 1 of PE 1 and PE 2 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a to provide services for all multicast groups. |
Table 12 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
7.12.1.10/24 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10:7::4/64 |
|
R 2 |
— |
7.13.1.10/24 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10:8::4/64 |
|
CE 1 |
Vlan-int100 |
7.12.1.11/24 7:12:1::11/64 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10:10::4/64 |
|
CE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.2.0.11/24 10:2::11/64 |
P 2 |
Loop0 |
4.4.4.4/32 4::4/128 |
|
CE 1 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10.3.0.11/24 10:3::11/64 |
P 3 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10:9::5/64 |
|
CE 2 |
Vlan-int100 |
7.12.1.12/24 7:12:1::12/64 |
P 3 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10:11::5/64 |
|
CE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.2.0.22/24 10:2::22/64 |
P 3 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10:12::5/64 |
|
CE 2 |
XGE0/0/18 |
10.4.0.22/24 10:4::22/64 |
P 3 |
Loop0 |
5.5.5.5/32 5::5/128 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.3.0.1/24 10:3::1/64 |
P 4 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10:10::6/64 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10:5::1/64 |
P 4 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10:11::6/64 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/18 |
10:6::1/64 |
P 4 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10:13::6/64 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop0 |
1.1.1.1/32 1::1/128 |
P 4 |
Loop0 |
6.6.6.6/32 6::6/128 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1.2.3.4/32 1:2:3::4/128 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10:12::7/64 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/18 |
10.4.0.2/24 10:4::2/64 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.14.0.7/24 10:14::7/64 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10:5::2/64 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/16 |
7.13.1.11/24 7:13:1::11/64 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10:7::2/64 |
PE 3 |
Loop0 |
7.7.7.7/32 7::7/128 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop0 |
2.2.2.2/32 2::2/128 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.6.2/24 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
1.2.3.3/32 1:2:3::3/128 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10:13::8/64 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10:6::3/64 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.14.0.8/24 10:14::8/64 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10:8::3/64 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/16 |
7.13.1.12/24 7:13:1::12/64 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10:9::3/64 |
PE 4 |
Loop0 |
8.8.8.8/32 8::8/128 |
|
P 1 |
Loop0 |
3.3.3.3/32 3::3/128 |
|
|
|
Procedure
1. Configure CE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<CE1> system-view
[CE1] router id 11.11.11.11
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing.
[CE1] multicast routing
[CE1-mrib] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing.
[CE1] ipv6 multicast routing
[CE1-mrib6] quit
# Create VLAN 100, and assign Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 to it.
[CE1] vlan 100
[CE1-vlan100] port ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CE1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to VLAN-interface 100, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE1] interface vlan-interface 100
[CE1-Vlan-interface100] ip address 7.12.1.11 24
[CE1-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 address 7:12:1::11 64
[CE1-Vlan-interface100] pim sm
[CE1-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 pim sm
[CE1-Vlan-interface100] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.2.0.11 24
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ospf cost 1000
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ospfv3 cost 1000
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 10:2::11 64
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] port link-mode route
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 10.3.0.11 24
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 pim sm
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 address 10:3::11 64
[CE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Configure BGP.
[CE1] bgp 65022
[CE1-bgp-default] peer 10.2.0.22 as-number 65022
[CE1-bgp-default] peer 10.3.0.1 as-number 100
[CE1-bgp-default] peer 10:2::22 as-number 65022
[CE1-bgp-default] peer 10:3::1 as-number 100
[CE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.2.0.22 enable
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.3.0.1 enable
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv4] address-family ipv6 unicast
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 10:2::22 enable
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 10:3::1 enable
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[CE1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[CE1-bgp-default] quit
2. Configure CE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<CE2> system-view
[CE2] router id 22.22.22.22
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing.
[CE2] multicast routing
[CE2-mrib] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing.
[CE2] ipv6 multicast routing
[CE2-mrib6] quit
# Create VLAN 100, and assign Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 to it.
[CE2] vlan 100
[CE2-vlan100] port ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CE2] quit
# Assign IP addresses to VLAN-interface 100, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE2] interface vlan-interface 100
[CE2-Vlan-interface100] ip address 7.12.1.12 24
[CE2-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 address 7:12:1::12 64
[CE2-Vlan-interface100] pim sm
[CE2-Vlan-interface100] ipv6 pim sm
[CE2-Vlan-interface100] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.2.0.22 24
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ospf cost 1000
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ospfv3 cost 1000
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 10:2::22 64
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/18, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] port link-mode route
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] ip address 10.4.0.22 24
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] pim sm
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] ipv6 pim sm
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] ipv6 address 10:4::22 64
[CE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] quit
# Configure BGP.
[CE2] bgp 65022
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 10.2.0.11 as-number 65022
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 10.4.0.2 as-number 100
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 10:2::11 as-number 65022
[CE2-bgp-default] peer 10:4::2 as-number 100
[CE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.2.0.11 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.4.0.2 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route direct
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv4] address-family ipv6 unicast
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 10:2::11 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 10:4::2 enable
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[CE2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[CE2-bgp-default] quit
3. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 0
[PE1-LoopBack0] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:2:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 1, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE1] bier
[PE1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:2::5 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:2::5
# Configure detecting the reachability of the primary next hop through BFD session of echo packets.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] primary-path-detect bfd echo
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 1:2::34
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] warm-root-standby
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] src-dt6 locator aaa sid 1:2::35
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] warm-root-standby
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.3.0.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 10:3::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis cost 1200
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 address 10:5::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/18 and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] isis cost 100
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] ipv6 address 10:6::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] quit
# Associate Loopback 1 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.2.3.4 32
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1:2:3::4 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure Loopback 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP.
[PE1] pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim-a] c-bsr 1.2.3.4
[PE1-pim-a] c-rp 1.2.3.4
[PE1-pim-a] quit
[PE1] ipv6 pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim6-a] c-bsr 1:2:3::4
[PE1-pim6-a] c-rp 1:2:3::4
[PE1-pim6-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4::4 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4::4 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 7::7 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 7::7 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 7::7 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 8::8 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 8::8 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 8::8 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 2::2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 7::7 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 8::8 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 2::2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 7::7 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 8::8 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] pic
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2::2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2::2 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2::2 advertise-community
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 7::7 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 7::7 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 8::8 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 8::8 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4::4 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] pic
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 2::2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 2::2 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 2::2 advertise-community
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 7::7 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 7::7 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 8::8 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 8::8 prefix-sid
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] peer 10.3.0.11 as-number 65022
[PE1-bgp-default-a] peer 10:3::11 as-number 65022
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] pic
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] peer 10.3.0.11 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] pic
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] peer 10:3::11 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER fast reroute for the IS-IS process.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] bier enable
[PE1-isis-1] bier fast-reroute enable
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute lfa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute ti-lfa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
4. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 2.2.2.2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 0
[PE2-LoopBack0] ip address 2.2.2.2 32
[PE2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[PE2-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2::2
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:3:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 2, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE2] bier
[PE2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 2
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:3::5 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:3::5
# Configure detecting the reachability of the primary next hop through BFD session of echo packets.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] primary-path-detect bfd echo
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:2
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE2] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 1:3::34
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] warm-root-standby
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] src-dt6 locator aaa sid 1:3::35
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] warm-root-standby
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/18 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] ip address 10.4.0.2 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] ipv6 address 10:4::2 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] ipv6 pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis cost 1200
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 10:5::2 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis cost 100
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 address 10:7::2 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Associate Loopback 1 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 1.2.3.3 32
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 1:2:3::3 128
[PE2-LoopBack1] pim sm
[PE2-LoopBack1] ipv6 pim sm
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure Loopback 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP.
[PE2] pim vpn-instance a
[PE2-pim-a] c-bsr 1.2.3.3
[PE2-pim-a] c-rp 1.2.3.3
[PE2-pim-a] quit
[PE2] ipv6 pim vpn-instance a
[PE2-pim6-a] c-bsr 1:2:3::3
[PE2-pim6-a] c-rp 1:2:3::3
[PE2-pim6-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 2.2.2.2
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 7::7 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 7::7 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 7::7 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 8::8 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 8::8 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 8::8 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 7::7 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 8::8 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 7::7 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 8::8 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] pic
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 advertise-community
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 7::7 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 7::7 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 8::8 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 8::8 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4::4 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] pic
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 advertise-community
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 7::7 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 7::7 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 8::8 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 8::8 prefix-sid
[PE2–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-bgp-default-a] peer 10.4.0.22 as-number 65022
[PE2-bgp-default-a] peer 10:4::22 as-number 65022
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] pic
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] peer 10.4.0.22 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] pic
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] peer 10:4::22 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER fast reroute for the IS-IS process.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] bier enable
[PE2-isis-1] bier fast-reroute enable
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute lfa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute ti-lfa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
5. Configure P 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P1> system-view
[P1] router id 3.3.3.3
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface loopback 1
[P1-LoopBack0] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[P1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 3::3 128
[P1-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[P1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[P1] segment-routing ipv6
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3::3
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:4:: 96 static 8
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign P 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 3, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[P1] bier
[P1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 3
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:4::5 as the End.RGB SID.
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:4::5
# Configure detecting the reachability of the primary next hop through BFD session of echo packets.
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] primary-path-detect bfd echo
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis cost 100
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 address 10:6::3 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis cost 1300
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 10:8::3 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[P1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 10:9::3 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Configure BGP.
[P1] bgp 100
[P1-bgp-default] router-id 3.3.3.3
[P1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[P1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[P1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P1-bgp-default] peer 10:9::5 as-number 200
[P1-bgp-default] peer 10:9::5 ebgp-max-hop 10
[P1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] import-bier isisv6 1
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 10:9::5 enable
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 10:9::5 capability bier
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 next-hop-local
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2::2 enable
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2::2 next-hop-local
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[P1–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER fast reroute for the IS-IS process.
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] bier enable
[P1-isis-1] bier fast-reroute enable
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] import-bier bgp4+
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] import-route bgp4+
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute lfa
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute ti-lfa
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
6. Configure P 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P2> system-view
[P2] router id 4.4.4.4
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P2] isis 1
[P2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[P2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface loopback 0
[P2-LoopBack0] ip address 4.4.4.4 32
[P2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 4::4 128
[P2-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[P2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[P2] segment-routing ipv6
[P2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 4::4
[P2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:5:: 96 static 8
[P2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign P 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 4, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[P2] bier
[P2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 4
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:5::5 as the End.RGB SID.
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:5::5
# Configure detecting the reachability of the primary next hop through BFD session of echo packets.
[P2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] primary-path-detect bfd echo
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis cost 100
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 address 10:7::4 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis cost 1300
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 10:8::4 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[P2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 10:10::4 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Configure BGP.
[P2] bgp 100
[P2-bgp-default] router-id 4.4.4.4
[P2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[P2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P2-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[P2-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P2-bgp-default] peer 10:10::6 as-number 200
[P2-bgp-default] peer 10:10::6 ebgp-max-hop 10
[P2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[P2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-bier isisv6 1
[P2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[P2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 next-hop-local
[P2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2::2 enable
[P2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2::2 next-hop-local
[P2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 10:10::6 enable
[P2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 10:10::6 capability bier
[P2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[P2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER fast reroute for the IS-IS process.
[P2] isis 1
[P2-isis-1] bier enable
[P2-isis-1] bier fast-reroute enable
[P2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] import-bier bgp4+
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] import-route bgp4+
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute lfa
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute ti-lfa
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P2-isis-1] quit
7. Configure P 3:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P3> system-view
[P3] router id 5.5.5.5
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P3] isis 1
[P3-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P3-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P3-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0005.00
[P3-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P3-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P3-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[P3] interface loopback 0
[P3-LoopBack0] ip address 5.5.5.5 32
[P3-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 5::5 128
[P3-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[P3-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P3-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[P3] segment-routing ipv6
[P3-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 5::5
[P3-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:6:: 96 static 8
[P3-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign P 3 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 5, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[P3] bier
[P3-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 5
[P3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[P3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:6::5 as the End.RGB SID.
[P3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:6::5
# Configure detecting the reachability of the primary next hop through BFD session of echo packets.
[P3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] primary-path-detect bfd echo
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[P3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 10:9::5 64
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis cost 1400
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 10:11::5 64
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] port link-mode route
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis cost 100
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 address 10:12::5 64
[P3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Configure BGP.
[P3] bgp 200
[P3-bgp-default] router-id 5.5.5.5
[P3-bgp-default] peer 7::7 as-number 200
[P3-bgp-default] peer 7::7 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P3-bgp-default] peer 8::8 as-number 200
[P3-bgp-default] peer 8::8 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P3-bgp-default] peer 10:9::3 as-number 100
[P3-bgp-default] peer 10:9::3 ebgp-max-hop 10
[P3-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P3-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[P3-bgp-default-ipv6] import-bier isisv6 1
[P3-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 7::7 enable
[P3-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 7::7 next-hop-local
[P3-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 8::8 enable
[P3-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 8::8 next-hop-local
[P3-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 10:9::3 enable
[P3-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 10:9::3 capability bier
[P3-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[P3–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER fast reroute for the IS-IS process.
[P3] isis 1
[P3-isis-1] bier enable
[P3-isis-1] bier fast-reroute enable
[P3-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P3-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P3-isis-1-ipv6] import-bier bgp4+
[P3-isis-1-ipv6] import-route bgp4+
[P3-isis-1-ipv6]fast-reroute lfa
[P3-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute ti-lfa
[P3-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P3-isis-1] quit
8. Configure P 4:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P4> system-view
[P4] router id 6.6.6.6
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P4] isis 1
[P4-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P4-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P4-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0006.00
[P4-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P4-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P4-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[P4] interface loopback 0
[P4-LoopBack0] ip address 6.6.6.6 32
[P4-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 6::6 128
[P4-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[P4-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P4-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[P4] segment-routing ipv6
[P4-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 6::6
[P4-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:7:: 96 static 8
[P4-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign P 4 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 6, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[P4] bier
[P4-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 6
[P4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[P4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:7::5 as the End.RGB SID.
[P4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:7::5
# Configure detecting the reachability of the primary next hop through BFD session of echo packets.
[P4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] primary-path-detect bfd echo
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[P4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 10:10::6 64
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis cost 1400
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 10:11::6 64
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] port link-mode route
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis cost 100
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 address 10:13::6 64
[P4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Configure BGP.
[P4] bgp 200
[P4-bgp-default] router-id 6.6.6.6
[P4-bgp-default] peer 7::7 as-number 200
[P4-bgp-default] peer 7::7 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P4-bgp-default] peer 8::8 as-number 200
[P4-bgp-default] peer 8::8 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P4-bgp-default] peer 10:10::4 as-number 100
[P4-bgp-default] peer 10:10::4 ebgp-max-hop 10
[P4-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P4-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[P4-bgp-default-ipv6] import-bier isisv6 1
[P4-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 7::7 enable
[P4-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 7::7 next-hop-local
[P4-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 8::8 enable
[P4-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 8::8 next-hop-local
[P4-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 10:10::4 enable
[P4-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 10:10::4 capability bier
[P4-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[P4–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER fast reroute for the IS-IS process.
[P4] isis 1
[P4-isis-1] bier enable
[P4-isis-1] bier fast-reroute enable
[P4-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P4-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P4-isis-1-ipv6] import-bier bgp4+
[P4-isis-1-ipv6] import-route bgp4+
[P4-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute lfa
[P4-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute ti-lfa
[P4-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P4-isis-1] quit
9. Configure PE 3:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE3> system-view
[PE3] router id 7.7.7.7
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE3] isis 1
[PE3-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE3-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE3-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0007.00
[PE3-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE3-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE3] interface loopback 0
[PE3-LoopBack0] ip address 7.7.7.7 32
[PE3-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 7::7 128
[PE3-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[PE3-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE3-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE3] segment-routing ipv6
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 7::7
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:8:: 96 static 8
[PE3-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 3 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 7, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE3] bier
[PE3-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 7
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:8::5 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:8::5
# Configure detecting the reachability of the primary next hop through BFD session of echo packets.
[PE3-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] primary-path-detect bfd echo
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE3] ip vpn-instance a
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:7
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE3] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE3-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE3] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE3-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE3] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE3-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 1:8::34
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv4] warm-root-standby
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE3-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv6] src-dt6 locator aaa sid 1:8::35
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv6] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv6] warm-root-standby
[PE3-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM, IGMP, and MLD on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 7.13.1.11 24
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 7:13:1::11 64
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] igmp enable
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mld enable
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] port link-mode route
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis cost 100
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 address 10:12::7 64
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis cost 1500
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 10:14::7 64
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE3] bgp 200
[PE3-bgp-default] router-id 7.7.7.7
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 1::1 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 2::2 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 5::5 as-number 200
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 5::5 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 6::6 as-number 200
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 6::6 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 2::2 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 2::2 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] pic
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2::2 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2::2 prefix-sid
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 5::5 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv6] pic
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 2::2 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 2::2 prefix-sid
[PE3–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE3-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] pic
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE3-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6-a] pic
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE3-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE3–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER fast reroute for the IS-IS process.
[PE3] isis 1
[PE3-isis-1] bier enable
[PE3-isis-1] bier fast-reroute enable
[PE3-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute lfa
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute ti-lfa
[PE3-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE3-isis-1] quit
10. Configure PE 4:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE4> system-view
[PE4] router id 8.8.8.8
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE4] isis 1
[PE4-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE4-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE4-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0008.00
[PE4-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE4-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE4-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE4] interface loopback 0
[PE4-LoopBack0] ip address 8.8.8.8 32
[PE4-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 8::8 128
[PE4-LoopBack0] isis enable 1
[PE4-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE4-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE4] segment-routing ipv6
[PE4-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 8::8
[PE4-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:9:: 96 static 8
[PE4-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 4 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 8, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE4] bier
[PE4-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 8
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:9::5 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:9::5
# Configure detecting the reachability of the primary next hop through BFD session of echo packets.
[PE4-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] primary-path-detect bfd echo
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE4] ip vpn-instance a
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:8
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE4] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE4-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE4] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE4-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE4] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 1:9::34
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv4] warm-root-standby
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv6] src-dt6 locator aaa sid 1:9::35
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv6] warm-root-standby
[PE4-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM, IGMP, and MLD on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 7.13.1.12 24
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 7:13:1::12 64
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] igmp enable
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mld enable
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] port link-mode route
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] isis cost 100
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ipv6 address 10:13::8 64
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis cost 1500
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 10:14::8 64
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE4] bgp 200
[PE4-bgp-default] router-id 8.8.8.8
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 1::1 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 2::2 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 5::5 as-number 200
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 5::5 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 6::6 as-number 200
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 6::6 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE4-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 2::2 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE4-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 2::2 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE4-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv4] pic
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2::2 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2::2 prefix-sid
[PE4-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 5::5 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE4-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv6] pic
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 2::2 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 2::2 prefix-sid
[PE4–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE4-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] pic
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE4-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6-a] pic
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE4-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER fast reroute for the IS-IS process.
[PE4] isis 1
[PE4-isis-1] bier enable
[PE4-isis-1] bier fast-reroute enable
[PE4-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE4-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE4-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute lfa
[PE4-isis-1-ipv6] fast-reroute ti-lfa
[PE4-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE4-isis-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display PIM routing entries for VPN instance a on PE 1 and PE 2.
[PE1] display pim vpn-instance a routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entries; 1 (S, G) entries
(7.12.1.10, 225.0.0.1)
RP: 1.2.3.3
Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT ACT RC SRC-ACT IDF-MN
UpTime: 00:02:49
Upstream interface: Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
Upstream neighbor: 10.3.0.11
RPF prime neighbor: 10.3.0.11
Downstream interface information:
Total number of downstream interfaces: 1
1: BIERVOif2
Protocol: MD, UpTime: 00:02:40, Expires: -
[PE2] display pim vpn-instance a routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entries; 1 (S, G) entries
(7.12.1.10, 225.0.0.1)
RP: 1.2.3.3 (local)
Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT 2MSDP ACT RC SRC-ACT 2MVPN SC IDF-BU
UpTime: 00:05:55
Upstream interface: Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/18
Upstream neighbor: 10.4.0.22
RPF prime neighbor: 10.4.0.22
Downstream interface information:
Total number of downstream interfaces: 1
1: BIERVOif2 (Inactive)
Protocol: MD, UpTime: 00:05:46, Expires: -
# Display the BIER information of BFR prefixes on PE 1.
[PE1] display bier routing-table
Sub-domain 0
Total BFERs: 6
BFR ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1::1(Local)
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: N/A
BFR ID: 2
BFR prefix: 2::2
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 2
BFR prefix: 2::2
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/17 FE80::280E:94FF:FE96:F0A Invalid
BFR prefix: 4::4
NBRFlag: B
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/18 FE80::280E:9DFF:FE8C:100B 2147483651
BFR ID: 3
BFR prefix: 3::3
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 2
BFR prefix: 3::3
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/18 FE80::280E:9DFF:FE8C:100B Invalid
BFR prefix: 4::4
NBRFlag: B
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/17 FE80::280E:94FF:FE96:F0A 2147483652
BFR ID: 4
BFR prefix: 4::4
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 2
BFR prefix: 2::2
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/17 FE80::280E:94FF:FE96:F0A Invalid
BFR prefix: 4::4
NBRFlag: B
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/18 FE80::280E:9DFF:FE8C:100B Invalid
BFR ID: 5
BFR prefix: 5::5
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 2
BFR prefix: 3::3
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/18 FE80::280E:9DFF:FE8C:100B Invalid
BFR prefix: 4::4
NBRFlag: B
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/17 FE80::280E:94FF:FE96:F0A 2147483652
BFR ID: 6
BFR prefix: 6::6
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 2
BFR prefix: 2::2
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/17 FE80::280E:94FF:FE96:F0A Invalid
BFR prefix: 4::4
NBRFlag: B
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/18 FE80::280E:9DFF:FE8C:100B Invalid
# Display cross-AS BIRT information on PE 1.
[PE1] display bier inter-as routing-table
Sub-domain 0
BFR ID: 7
BFR prefix: 5::5
AS: --
Protocol: IS-IS
Preference: --
BFR ID: 8
BFR prefix: 5::5
AS: --
Protocol: IS-IS
Preference: --
Example: Configuring prefix retaining for inter-AS (IS-IS-EBGP-IS-IS) BIER-based MVPN (MSR6 encapsulation)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 25, configure prefix retaining for inter-AS (IS-IS-EBGP-IS-IS) BIER-based MVPN with the MSR6 encapsulation to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Functions |
· An ASBR device does not replace the BIER prefix when advertising routing information from another AS to its own AS. · In AS 100 and AS 200, BIER information is carried in IS-IS packets. |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 and Loopback 1 belong to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and BIER |
· Configure IS-IS in AS 100 and AS 200 on the public network, and establish EBGP peer connections between ASBR 1 and ASBR 2. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and ASBR 1 on their respective Loopback 0. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 2 and ASBR 2 on their respective Loopback 0. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and PE 2 on their respective Loopback 0. · Configure BIER on the public network: sub-domain 0, BSL 128, and max-SI 32. · Configure the BFR prefixes of PE 1, ASBR 1, ASBR 2, and PE 2 as the IPv6 addresses for their respective Loopback 0, and configure the End.RGB SID for each device. |
|
IP multicast routing |
Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1 and PE 2. |
|
IGMP |
Enable IGMP on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 of PE 2. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on all private interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on PE 1 and PE 2. · Configure Loopback 1 of PE 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a to provide services for all multicast groups. |
Table 13 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
7.12.1.10/24 |
ASBR 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
113.1.1.4/24 113::4/64 |
|
R 1 |
— |
7.13.1.10/24 |
ASBR 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
14.1.1.4/24 14.1.1.4/64 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
7.12.1.12/24 100:2:2::2/64 |
ASBR 2 |
Loop0 |
4.4.4.4/32 4::4/128 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
11.1.1.1/24 11::1/64 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
15.1.1.5/24 15::5/64 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop0 |
1.1.1.1/32 1::1/128 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
14.1.1.5/24 14::5/64 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
11.11.11.11/32 11::11/128 |
P 2 |
Loop0 |
5.5.5.5/32 5::5/128 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
11.1.1.2/24 11::2/64 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
15.1.1.6/24 15::6/64 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
12.1.1.2/24 12::2/64 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
7.13.1.12/24 100:3:3::2/64 |
|
P 1 |
Loop0 |
2.2.2.2/32 2::2/128 |
PE 2 |
Loop0 |
6.6.6.6/32 6::6/128 |
|
ASBR 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
113.1.1.3/24 113::3/64 |
|
|
|
|
ASBR 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
12.1.1.3/24 12::3/64 |
|
|
|
|
ASBR 1 |
Loop0 |
1.1.1.1/32 1::1/128 |
|
|
|
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 0
[PE1-LoopBack0] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:2:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 1, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE1] bier
[PE1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:2::1
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 1:2::2
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] src-dt6 locator aaa sid 1:2::3
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
[PE1-mvpn-a] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 7.12.1.12 255.255.255.0
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 100:2:2::2 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 11::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Loopback 1 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 11::11 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure Loopback 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP.
[PE1] pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim-a] c-bsr 11.11.11.11
[PE1-pim-a] c-rp 11.11.11.11
[PE1-pim-a] quit
[PE1] ipv6 pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim6-a] c-bsr 11::11
[PE1-pim6-a] c-rp 11::11
[PE1-pim6-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 6::6 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 6::6 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] bier enable
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
2. Configure P 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P1> system-view
[P1] router id 2.2.2.2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 11.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 11::2 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 12.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 12::2 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface loopback 0
[P1-LoopBack0] ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
[P1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[P1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-LoopBack0] quit
3. Configure ASBR 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<ASBR1> system-view
[ASBR1] router id 3.3.3.3
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[ASBR1] isis 1
[ASBR1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[ASBR1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[ASBR1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00
[ASBR1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR1] interface loopback 0
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 3::3 128
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[ASBR1] segment-routing ipv6
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3::3
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 3:2:: 96 static 8
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign ASBR 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 3, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[ASBR1] bier
[ASBR1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 3
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 3:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 3:2::1
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[ASBR1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 113.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 113::3 64
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 12.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 12::3 64
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[ASBR1] bgp 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] router-id 3.3.3.3
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 113::4 as-number 200
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 113::4 ebgp-max-hop 10
[ASBR1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] import-bier isisv6 1
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 next-hop-local
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 capability bier
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::4 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::4 capability bier
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[ASBR1] isis 1
[ASBR1-isis-1] bier enable
[ASBR1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] import-bier bgp4+
# Redistribute IPv6 BGP routes into IS-IS.
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] import-route bgp4+
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-isis-1] quit
4. Configure ASBR 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<ASBR2> system-view
[ASBR2] router id 4.4.4.4
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[ASBR2] isis 1
[ASBR2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[ASBR2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[ASBR2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[ASBR2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR2] interface loopback 0
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] ip address 4.4.4.4 32
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 4::4 128
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[ASBR2] segment-routing ipv6
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 4::4
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 4:2:: 96 static 8
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign ASBR 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 4, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[ASBR2] bier
[ASBR2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 4
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 4:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 4:2::1
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[ASBR2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 113.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 113::4 64
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 14.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 14::4 64
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[ASBR2] bgp 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] router-id 4.4.4.4
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 6::6 as-number 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 6::6 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 113::3 as-number 100
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 113::3 ebgp-max-hop 10
[ASBR2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-bier isisv6 1
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 next-hop-local
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::3 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::3 capability bier
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[ASBR2] isis 1
[ASBR2-isis-1] bier enable
[ASBR2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] import-bier bgp4+
# Redistribute IPv6 BGP routes into IS-IS.
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] import-route bgp4+
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-isis-1] quit
5. Configure P 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P2> system-view
[P2] router id 5.5.5.5
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P2] isis 1
[P2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0005.00
[P2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 15.1.1.5 255.255.255.0
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 15::5 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 14.1.1.5 255.255.255.0
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 14::5 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface loopback 0
[P2-LoopBack0] ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255
[P2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 5::5 128
[P2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-LoopBack0] quit
6. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 6.6.6.6
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0006.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 0
[PE2-LoopBack0] ip address 6.6.6.6 32
[PE2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 6::6 128
[PE2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 6::6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 6:2:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 6, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE2] bier
[PE2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 6:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 6:2::1
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:6
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE2] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 6:2::2
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] src-dt6 locator aaa sid 6:2::3
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
[PE2-mvpn-a] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM, IGMP, and MLD on the interface.
[PE2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 7.13.1.12 255.255.255.0
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 100:3:3::2 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] igmp enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mld enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 15.1.1.6 255.255.255.0
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 15::6 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 200
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 6.6.6.6
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4::4 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] bier enable
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display the BFR ID range in the BGP routing table on ASBR 1 and ASBR 2.
[ASBR1] display bgp routing-table ipv6 4::4 128
BGP local router ID: 3.3.3.3
Local AS number: 100
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 4::4/128:
From : 113::4 (4.4.4.4)
Rely nexthop : 113::4
Original nexthop: 113::4
Out interface : Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
Route age : 00h00m08s
OutLabel : NULL
RxPathID : 0x0
TxPathID : 0x0
BIER Path : <Sub-domain ID 0, BFR-ID 4, MSR6 encap><BSL info: [128,32]><
END.RGB SID 4:2::1><BFR-ID [start,range], range count 1, [6,
1]>
AS-path : 200
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, pref-val 0
State : valid, external, best
IP precedence : N/A
QoS local ID : N/A
Traffic index : N/A
Tunnel policy : NULL
Rely tunnel IDs : N/A
[ASBR2] display bgp routing-table ipv6 3::3 128
BGP local router ID: 4.4.4.4
Local AS number: 200
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 3::3/128:
From : 113::3 (3.3.3.3)
Rely nexthop : 113::3
Original nexthop: 113::3
Out interface : Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
Route age : 00h01m47s
OutLabel : NULL
RxPathID : 0x0
TxPathID : 0x0
BIER Path : <Sub-domain ID 0, BFR-ID 3, MSR6 encap><BSL info: [128,32]><
END.RGB SID 3:2::1><BFR-ID [start,range], range count 1, [1,
1]>
AS-path : 100
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, pref-val 0
State : valid, external, best
IP precedence : N/A
QoS local ID : N/A
Traffic index : N/A
Tunnel policy : NULL
Rely tunnel IDs : N/A
# Display the BIER information of BFR prefixes on PE 1.
[PE1] display bier routing-table
Sub-domain 0
Total BFERs: 3
BFR ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1::1(Local)
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: N/A
BFR ID: 3
BFR prefix: 3::3
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 3::3
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::424B:FF:FECA:1C06 Invalid
BFR ID: 4
BFR prefix: 4::4
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 3::3
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::424B:FF:FECA:1C06 Invalid
# Display cross-AS BIRT information on PE 1.
[PE1] display bier inter-as routing-table
Sub-domain 0
BFR ID: 6
BFR prefix: 4::4
AS: --
Protocol: IS-IS
Preference: --
# Display the BIER information of BFR prefixes on PE 2.
[PE2] display bier routing-table
Sub-domain 0
Total BFERs: 3
BFR ID: 6
BFR prefix: 6::6(Local)
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: N/A
BFR ID: 3
BFR prefix: 3::3
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 4::4
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::4255:82FF:FEF0:608 Invalid
BFR ID: 4
BFR prefix: 4::4
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 4::4
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::4255:82FF:FEF0:608 Invalid
# Display cross-AS BIRT information on PE 2.
[PE2] display bier inter-as routing-table
Sub-domain 0
BFR ID: 1
BFR prefix: 3::3
AS: --
Protocol: IS-IS
Preference: --
Example: Configuring prefix retaining for inter-AS (IBGP (proxy)-EBGP-IS-IS) BIER-based MVPN (MSR6 encapsulation)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 26, configure prefix retaining for inter-AS (IBGP (proxy)-EBGP-IS-IS) BIER-based MVPN with the MSR6 encapsulation to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Functions |
· An ASBR device does not replace the BIER prefix when advertising routing information from another AS to its own AS. · In AS 100, BIER information is carried in BGP packets. In AS 200, BIER information is carried in IS-IS packets. |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 and Loopback 1 belong to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and BIER |
· Configure IBGP in AS 100 on the public network, configure IS-IS in AS 200, and establish EBGP peer connections between ASBR 1 and ASBR 2. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and P 1 on their respective Loopback 0, establish BGP peer connections between P 1 and ASBR 1 on their respective Loopback 0, and establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and ASBR 1 on their respective Loopback 0. · Establish BGP peer connections on between PE 2 and ASBR 2 on their respective Loopback 0. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and PE 2 on their respective Loopback 0. · Configure BIER on the public network: sub-domain 0, BSL 128, and max-SI 32. · Configure the BFR prefixes of PE 1, ASBR 1, ASBR 2, and PE 2 as the IPv6 addresses for their respective Loopback 0, and configure the End.RGB SID for each device. |
|
IP multicast routing |
Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1 and PE 2. |
|
IGMP |
Enable IGMP on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 of PE 2. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on all private interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on PE 1 and PE 2. · Configure Loopback 1 of PE 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a to provide services for all multicast groups. |
Table 14 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
7.12.1.10/24 |
ASBR 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
113.1.1.4/24 113::4/64 |
|
R 1 |
— |
7.13.1.10/24 |
ASBR 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
14.1.1.4/24 14.1.1.4/64 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
7.12.1.12/24 100:2:2::2/64 |
ASBR 2 |
Loop0 |
4.4.4.4/32 4::4/128 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
11.1.1.1/24 11::1/64 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
15.1.1.5/24 15::5/64 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop0 |
1.1.1.1/32 1::1/128 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
14.1.1.5/24 14::5/64 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
11.11.11.11/32 11::11/128 |
P 2 |
Loop0 |
5.5.5.5/32 5::5/128 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
11.1.1.2/24 11::2/64 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
15.1.1.6/24 15::6/64 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
12.1.1.2/24 12::2/64 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
7.13.1.12/24 100:3:3::2/64 |
|
P 1 |
Loop0 |
2.2.2.2/32 2::2/128 |
PE 2 |
Loop0 |
6.6.6.6/32 6::6/128 |
|
ASBR 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
113.1.1.3/24 113::3/64 |
|
|
|
|
ASBR 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
12.1.1.3/24 12::3/64 |
|
|
|
|
ASBR 1 |
Loop0 |
1.1.1.1/32 1::1/128 |
|
|
|
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 0
[PE1-LoopBack0] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:2:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 1, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE1] bier
[PE1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:2::1
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 1:2::2
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] src-dt6 locator aaa sid 1:2::3
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
[PE1-mvpn-a] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 7.12.1.12 255.255.255.0
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 100:2:2::2 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 11::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Loopback 1 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 11::11 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure Loopback 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP.
[PE1] pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim-a] c-bsr 11.11.11.11
[PE1-pim-a] c-rp 11.11.11.11
[PE1-pim-a] quit
[PE1] ipv6 pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim6-a] c-bsr 11::11
[PE1-pim6-a] c-rp 11::11
[PE1-pim6-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 6::6 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2::2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 capability bier
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 6::6 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] quit
# Apply locator aaa to IS-IS process 1.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
2. Configure P 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P1> system-view
[P1] router id 2.2.2.2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 11.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 11::2 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 12.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 12::2 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface loopback 0
[P1-LoopBack0] ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
[P1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[P1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure BGP.
[P1] bgp 100
[P1-bgp-default] router-id 2.2.2.2
[P1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[P1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[P1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 enable
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[P1–bgp-default] quit
3. Configure ASBR 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<ASBR1> system-view
[ASBR1] router id 3.3.3.3
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[ASBR1] isis 1
[ASBR1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[ASBR1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[ASBR1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00
[ASBR1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR1] interface loopback 0
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 3::3 128
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[ASBR1] segment-routing ipv6
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3::3
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 3:2:: 96 static 8
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign ASBR 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 3, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[ASBR1] bier
[ASBR1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 3
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 3:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 3:2::1
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[ASBR1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 113.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 113::3 64
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 12.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 12::3 64
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[ASBR1] bgp 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] router-id 3.3.3.3
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 113::4 as-number 200
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 113::4 ebgp-max-hop 10
[ASBR1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 next-hop-local
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 capability bier
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2::2 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2::2 next-hop-local
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::4 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::4 capability bier
# Enable BGP BFR prefix proxying.
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] bier bfr-prefix proxy
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1–bgp-default] quit
# Apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[ASBR1] isis 1
[ASBR1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-isis-1] quit
4. Configure ASBR 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<ASBR2> system-view
[ASBR2] router id 4.4.4.4
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[ASBR2] isis 1
[ASBR2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[ASBR2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[ASBR2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[ASBR2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR2] interface loopback 0
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] ip address 4.4.4.4 32
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 4::4 128
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[ASBR2] segment-routing ipv6
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 4::4
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 4:2:: 96 static 8
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign ASBR 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 4, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[ASBR2] bier
[ASBR2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 4
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 4:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 4:2::1
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[ASBR2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 113.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 113::4 64
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 14.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 14::4 64
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[ASBR2] bgp 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] router-id 4.4.4.4
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 6::6 as-number 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 6::6 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 113::3 as-number 100
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 113::3 ebgp-max-hop 10
[ASBR2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-bier isisv6 1
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 next-hop-local
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::3 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::3 capability bier
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[ASBR2] isis 1
[ASBR2-isis-1] bier enable
[ASBR2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] import-bier bgp4+
# Redistribute IPv6 BGP routes into IS-IS.
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] import-route bgp4+
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-isis-1] quit
5. Configure P 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P2> system-view
[P2] router id 5.5.5.5
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P2] isis 1
[P2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0005.00
[P2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 15.1.1.5 255.255.255.0
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 15::5 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 14.1.1.5 255.255.255.0
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 14::5 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface loopback 0
[P2-LoopBack0] ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255
[P2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 5::5 128
[P2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-LoopBack0] quit
6. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 6.6.6.6
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0006.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 0
[PE2-LoopBack0] ip address 6.6.6.6 32
[PE2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 6::6 128
[PE2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 6::6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 6:2:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 6, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE2] bier
[PE2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 6:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 6:2::1
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:6
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE2] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 6:2::2
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] src-dt6 locator aaa sid 6:2::3
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
[PE2-mvpn-a] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM, IGMP, and MLD on the interface.
[PE2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 7.13.1.12 255.255.255.0
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 100:3:3::2 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] igmp enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mld enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 15.1.1.6 255.255.255.0
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 15::6 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 200
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 6.6.6.6
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4::4 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] bier enable
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display the BFR ID range in the BGP routing table on ASBR 1 and ASBR 2.
[ASBR1] display bgp routing-table ipv6 4::4 128
BGP local router ID: 3.3.3.3
Local AS number: 100
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 4::4/128:
From : 113::4 (4.4.4.4)
Rely nexthop : 113::4
Original nexthop: 113::4
Out interface : Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
Route age : 00h08m09s
OutLabel : NULL
RxPathID : 0x0
TxPathID : 0x0
BIER Path : <Sub-domain ID 0, BFR-ID 4, MSR6 encap><BSL info: [128,32]><
END.RGB SID 3:2::1><BFR-ID [start,range], range count 1, [6,
1]>
AS-path : 200
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, pref-val 0
State : valid, external, best
IP precedence : N/A
QoS local ID : N/A
Traffic index : N/A
Tunnel policy : NULL
Rely tunnel IDs : N/A
[ASBR2] display bgp routing-table ipv6 3::3 128
BGP local router ID: 4.4.4.4
Local AS number: 200
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 3::3/128:
From : 113::3 (3.3.3.3)
Rely nexthop : 113::3
Original nexthop: 113::3
Out interface : Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
Route age : 00h01m37s
OutLabel : NULL
RxPathID : 0x0
TxPathID : 0x0
BIER Path : <Sub-domain ID 0, BFR-ID 3, MSR6 encap><BSL info: [128,32]><
END.RGB SID 3:2::1><BFR-ID [start,range], range count 1, [1,
1]>
AS-path : 100
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, pref-val 0
State : valid, external, best
IP precedence : N/A
QoS local ID : N/A
Traffic index : N/A
Tunnel policy : NULL
Rely tunnel IDs : N/A
# Display the BIER information of BFR prefixes on PE 1.
[PE1] display bier routing-table
Sub-domain 0
Total BFERs: 2
BFR ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1::1(Local)
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: N/A
BFR ID: 3
BFR prefix: 3::3
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 3::3
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::424B:FF:FECA:1C06 Invalid
BFR ID: 4
BFR prefix: 4::4
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 3::3
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::424B:FF:FECA:1C06 Invalid
# Display cross-AS BIRT information on PE 1.
[PE1] display bier inter-as routing-table
Sub-domain 0
BFR ID: 4
BFR prefix: 4::4
AS: 200
Protocol: IBGP
Preference: --
BFR ID: 6
BFR prefix: 4::4
AS: 200
Protocol: IBGP
Preference: --
# Display the BIER information of BFR prefixes on PE 2.
[PE2] display bier routing-table
Sub-domain 0
Total BFERs: 3
BFR ID: 6
BFR prefix: 6::6(Local)
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: N/A
BFR ID: 3
BFR prefix: 3::3
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 4::4
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::4255:82FF:FEF0:608 Invalid
BFR ID: 4
BFR prefix: 4::4
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 4::4
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::4255:82FF:FEF0:608 Invalid
# Display cross-AS BIRT information on PE 2.
[PE2] display bier inter-as routing-table
Sub-domain 0
BFR ID: 1
BFR prefix: 3::3
AS: --
Protocol: IS-IS
Preference: --
Example: Configuring prefix retaining for inter-AS (IBGP (proxy)-EBGP-IBGP (proxy)) BIER-based MVPN (MSR6 encapsulation)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 27, configure prefix retaining for inter-AS (IBGP (proxy)-EBGP-IBGP (proxy)) BIER-based MVPN with the MSR6 encapsulation to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Functions |
· An ASBR device does not replace the BIER prefix when advertising routing information from another AS to its own AS. · In AS 100 and AS 200, BIER information is carried in BGP packets. |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 and Loopback 1 belong to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and BIER |
· Configure IBGP in AS 100 and AS 200 on the public network, and establish EBGP peer connections between ASBR 1 and ASBR 2. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and P 1 on their respective Loopback 0, establish BGP peer connections between P 1 and ASBR 1 on their respective Loopback 0, and establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and ASBR 1 on their respective Loopback 0. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 2 and P 2 on their respective Loopback 0, establish BGP peer connections between P 2 and ASBR 2 on their respective Loopback 0, and establish BGP peer connections between PE 2 and ASBR 2 on their respective Loopback 0. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and PE 2 on their respective Loopback 0. · Configure BIER on the public network: sub-domain 0, BSL 128, and max-SI 32. · Configure the BFR prefixes of PE 1, ASBR 1, ASBR 2, and PE 2 as the IPv6 addresses for their respective Loopback 0, and configure the End.RGB SID for each device. |
|
IP multicast routing |
Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1 and PE 2. |
|
IGMP |
Enable IGMP on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 of PE 2. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on all private interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on PE 1 and PE 2. · Configure Loopback 1 of PE 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a to provide services for all multicast groups. |
Table 15 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
7.12.1.10/24 |
ASBR 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
113.1.1.4/24 113::4/64 |
|
R 1 |
— |
7.13.1.10/24 |
ASBR 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
14.1.1.4/24 14.1.1.4/64 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
7.12.1.12/24 100:2:2::2/64 |
ASBR 2 |
Loop0 |
4.4.4.4/32 4::4/128 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
11.1.1.1/24 11::1/64 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
15.1.1.5/24 15::5/64 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop0 |
1.1.1.1/32 1::1/128 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
14.1.1.5/24 14::5/64 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
11.11.11.11/32 11::11/128 |
P 2 |
Loop0 |
5.5.5.5/32 5::5/128 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
11.1.1.2/24 11::2/64 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
15.1.1.6/24 15::6/64 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
12.1.1.2/24 12::2/64 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
7.13.1.12/24 100:3:3::2/64 |
|
P 1 |
Loop0 |
2.2.2.2/32 2::2/128 |
PE 2 |
Loop0 |
6.6.6.6/32 6::6/128 |
|
ASBR 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
113.1.1.3/24 113::3/64 |
|
|
|
|
ASBR 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
12.1.1.3/24 12::3/64 |
|
|
|
|
ASBR 1 |
Loop0 |
1.1.1.1/32 1::1/128 |
|
|
|
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 0
[PE1-LoopBack0] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:2:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 1, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE1] bier
[PE1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:2::1
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 1:2::2
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] src-dt6 locator aaa sid 1:2::3
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
[PE1-mvpn-a] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM, IGMP, and MLD on the interface.
[PE1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 7.12.1.12 255.255.255.0
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 100:2:2::2 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] igmp enable
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mld enable
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 11::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Loopback 1 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 11::11 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure Loopback 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP.
[PE1] pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim-a] c-bsr 11.11.11.11
[PE1-pim-a] c-rp 11.11.11.11
[PE1-pim-a] quit
[PE1] ipv6 pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim6-a] c-bsr 11::11
[PE1-pim6-a] c-rp 11::11
[PE1-pim6-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 6::6 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2::2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 capability bier
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 6::6 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] quit
# Apply locator aaa to IS-IS process 1.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
2. Configure P 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P1> system-view
[P1] router id 2.2.2.2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 11.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 11::2 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 12.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 12::2 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface loopback 0
[P1-LoopBack0] ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
[P1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[P1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure BGP.
[P1] bgp 100
[P1-bgp-default] router-id 2.2.2.2
[P1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[P1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[P1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 enable
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[P1–bgp-default] quit
3. Configure ASBR 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<ASBR1> system-view
[ASBR1] router id 3.3.3.3
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[ASBR1] isis 1
[ASBR1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[ASBR1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[ASBR1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00
[ASBR1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR1] interface loopback 0
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 3::3 128
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[ASBR1] segment-routing ipv6
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3::3
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 3:2:: 96 static 8
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign ASBR 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 3, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[ASBR1] bier
[ASBR1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 3
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 3:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 3:2::1
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[ASBR1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 113.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 113::3 64
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 12.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 12::3 64
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[ASBR1] bgp 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] router-id 3.3.3.3
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 113::4 as-number 200
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 113::4 ebgp-max-hop 10
[ASBR1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 next-hop-local
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 capability bier
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2::2 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2::2 next-hop-local
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::4 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::4 capability bier
# Enable BGP BFR prefix proxying.
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] bier bfr-prefix proxy
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1–bgp-default] quit
# Apply locator aaa to IS-IS process 1.
[ASBR1] isis 1
[ASBR1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-isis-1] quit
4. Configure ASBR 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<ASBR2> system-view
[ASBR2] router id 4.4.4.4
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[ASBR2] isis 1
[ASBR2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[ASBR2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[ASBR2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[ASBR2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR2] interface loopback 0
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] ip address 4.4.4.4 32
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 4::4 128
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[ASBR2] segment-routing ipv6
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 4::4
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 4:2:: 96 static 8
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign ASBR 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 4, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[ASBR2] bier
[ASBR2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 4
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 4:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 4:2::1
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[ASBR2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 113.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 113::4 64
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 14.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 14::4 64
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[ASBR2] bgp 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] router-id 4.4.4.4
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 5::5 as-number 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 5::5 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 6::6 as-number 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 6::6 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 113::3 as-number 100
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 113::3 ebgp-max-hop 10
[ASBR2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 5::5 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 5::5 next-hop-local
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 next-hop-local
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 capability bier
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::3 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::3 capability bier
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
# Enable BGP BFR prefix proxying.
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] bier bfr-prefix proxy
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2–bgp-default] quit
# Apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[ASBR2] isis 1
[ASBR2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-isis-1] quit
5. Configure P 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P2> system-view
[P2] router id 5.5.5.5
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P2] isis 1
[P2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0005.00
[P2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 15.1.1.5 255.255.255.0
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 15::5 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 14.1.1.5 255.255.255.0
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 14::5 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface loopback 0
[P2-LoopBack0] ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255
[P2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 5::5 128
[P2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure BGP.
[P2] bgp 200
[P2-bgp-default] router-id 5.5.5.5
[P2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 as-number 200
[P2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P2-bgp-default] peer 6::6 as-number 200
[P2-bgp-default] peer 6::6 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[P2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4::4 enable
[P2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 enable
[P2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[P2–bgp-default] quit
6. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 6.6.6.6
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0006.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 0
[PE2-LoopBack0] ip address 6.6.6.6 32
[PE2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 6::6 128
[PE2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 6::6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 6:2:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 6, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE2] bier
[PE2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 6:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 6:2::1
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:6
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE2] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 6:2::2
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] src-dt6 locator aaa sid 6:2::3
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
[PE2-mvpn-a] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM, IGMP, and MLD on the interface.
[PE2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 7.13.1.12 255.255.255.0
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 100:3:3::2 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] igmp enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mld enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 15.1.1.6 255.255.255.0
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 15::6 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 200
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 6.6.6.6
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 5::5 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 5::5 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4::4 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4::4 capability bier
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 5::5 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Apply locator aaa to IS-IS process 1.
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display the BFR ID range in the BGP routing table on ASBR 1 and ASBR 2.
[ASBR1] display bgp routing-table ipv6 4::4 128
BGP local router ID: 3.3.3.3
Local AS number: 100
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 4::4/128:
From : 113::4 (4.4.4.4)
Rely nexthop : 113::4
Original nexthop: 113::4
Out interface : Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
Route age : 00h00m40s
OutLabel : NULL
RxPathID : 0x0
TxPathID : 0x0
BIER Path : <Sub-domain ID 0, BFR-ID 4, MSR6 encap><BSL info: [128,32]><
END.RGB SID 3:2::1><BFR-ID [start,range], range count 1, [6,
1]>
AS-path : 200
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, pref-val 0
State : valid, external, best
IP precedence : N/A
QoS local ID : N/A
Traffic index : N/A
Tunnel policy : NULL
Rely tunnel IDs : N/A
[ASBR2] display bgp routing-table ipv6 3::3 128
BGP local router ID: 4.4.4.4
Local AS number: 200
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 3::3/128:
From : 113::3 (3.3.3.3)
Rely nexthop : 113::3
Original nexthop: 113::3
Out interface : Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
Route age : 00h12m39s
OutLabel : NULL
RxPathID : 0x0
TxPathID : 0x0
BIER Path : <Sub-domain ID 0, BFR-ID 3, MSR6 encap><BSL info: [128,32]><
END.RGB SID 4:2::1><BFR-ID [start,range], range count 1, [1,
1]>
AS-path : 100
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, pref-val 0
State : valid, external, best
IP precedence : N/A
QoS local ID : N/A
Traffic index : N/A
Tunnel policy : NULL
Rely tunnel IDs : N/A
# Display the BIER information of BFR prefixes on PE 1.
[PE1] display bier routing-table
Sub-domain 0
Total BFERs: 2
BFR ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1::1(Local)
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: N/A
BFR ID: 3
BFR prefix: 3::3
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 3::3
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::424B:FF:FECA:1C06 Invalid
BFR ID: 4
BFR prefix: 4::4
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 3::3
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::424B:FF:FECA:1C06 Invalid
# Display cross-AS BIRT information on PE 1.
[PE1] display bier inter-as routing-table
Sub-domain 0
BFR ID: 4
BFR prefix: 4::4
AS: 200
Protocol: IBGP
Preference: --
BFR ID: 6
BFR prefix: 4::4
AS: 200
Protocol: IBGP
Preference: --
# Display the BIER information of BFR prefixes on PE 2.
[PE2] display bier routing-table
Sub-domain 0
Total BFERs: 2
BFR ID: 6
BFR prefix: 6::6(Local)
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: N/A
BFR ID: 4
BFR prefix: 4::4
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 4::4
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::4255:82FF:FEF0:608 Invalid
# Display cross-AS BIRT information on PE 2.
[PE2] display bier inter-as routing-table
Sub-domain 0
BFR ID: 1
BFR prefix: 3::3
AS: 100
Protocol: IBGP
Preference: --
BFR ID: 3
BFR prefix: 3::3
AS: 100
Protocol: IBGP
Preference: --
Example: Configuring prefix retaining for inter-AS (IBGP/IS-IS-EBGP-IS-IS) BIER-based MVPN (MSR6 encapsulation)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 28, configure prefix retaining for inter-AS (IBGP/IS-IS-EBGP-IS-IS) BIER-based MVPN N with the MSR6 encapsulation to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Functions |
· An ASBR device does not replace the BIER prefix when advertising routing information from another AS to its own AS. · In AS 100, BIER information is carried in BGP or IS-IS packets. In AS 200, BIER information is carried in IS-IS packets. |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 and Loopback 1 belong to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and BIER |
· Configure IS-IS in AS 100 and AS 200 on the public network, and establish EBGP peer connections between ASBR 1 and ASBR 2. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and ASBR 1 on their respective Loopback 0. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 2 and ASBR 2 on their respective Loopback 0. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and PE 2 on their respective Loopback 0. · Configure BIER on the public network: sub-domain 0, BSL 128, and max-SI 32. · Configure the BFR prefixes of PE 1, ASBR 1, ASBR 2, and PE 2 as the IPv6 addresses for their respective Loopback 0, and configure the End.RGB SID for each device. |
|
IP multicast routing |
Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1 and PE 2. |
|
IGMP |
Enable IGMP on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 of PE 2. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on all private interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on PE 1 and PE 2. · Configure Loopback 1 of PE 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a to provide services for all multicast groups. |
Table 16 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
7.12.1.10/24 |
ASBR 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
113.1.1.4/24 113::4/64 |
|
R 1 |
— |
7.13.1.10/24 |
ASBR 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
14.1.1.4/24 14.1.1.4/64 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
7.12.1.12/24 100:2:2::2/64 |
ASBR 2 |
Loop0 |
4.4.4.4/32 4::4/128 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
11.1.1.1/24 11::1/64 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
15.1.1.5/24 15::5/64 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop0 |
1.1.1.1/32 1::1/128 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
14.1.1.5/24 14::5/64 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
11.11.11.11/32 11::11/128 |
P 2 |
Loop0 |
5.5.5.5/32 5::5/128 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
11.1.1.2/24 11::2/64 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
15.1.1.6/24 15::6/64 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
12.1.1.2/24 12::2/64 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
7.13.1.12/24 100:3:3::2/64 |
|
P 1 |
Loop0 |
2.2.2.2/32 2::2/128 |
PE 2 |
Loop0 |
6.6.6.6/32 6::6/128 |
|
ASBR 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
113.1.1.3/24 113::3/64 |
|
|
|
|
ASBR 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
12.1.1.3/24 12::3/64 |
|
|
|
|
ASBR 1 |
Loop0 |
1.1.1.1/32 1::1/128 |
|
|
|
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 0
[PE1-LoopBack0] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:2:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 1, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE1] bier
[PE1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 1:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 1:2::1
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 1:2::2
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] src-dt6 locator aaa sid 1:2::3
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
[PE1-mvpn-a] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 7.12.1.12 255.255.255.0
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 100:2:2::2 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 11::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Loopback 1 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 11::11 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure Loopback 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP.
[PE1] pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim-a] c-bsr 11.11.11.11
[PE1-pim-a] c-rp 11.11.11.11
[PE1-pim-a] quit
[PE1] ipv6 pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim6-a] c-bsr 11::11
[PE1-pim6-a] c-rp 11::11
[PE1-pim6-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 6::6 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 capability bier
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 6::6 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] bier enable
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
2. Configure P 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P1> system-view
[P1] router id 2.2.2.2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface loopback 0
[P1-LoopBack0] ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
[P1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[P1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[P1] segment-routing ipv6
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 2::2
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 2:2:: 96 static 8
[P1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign P 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 2, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[P1] bier
[P1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 2
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 2:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[P1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 2:2::1
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 11.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 11::2 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 12.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 12::2 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] bier enable
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
3. Configure ASBR 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<ASBR1> system-view
[ASBR1] router id 3.3.3.3
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[ASBR1] isis 1
[ASBR1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[ASBR1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[ASBR1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00
[ASBR1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR1] interface loopback 0
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 3::3 128
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[ASBR1] segment-routing ipv6
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3::3
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 3:2:: 96 static 8
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign ASBR 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 3, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[ASBR1] bier
[ASBR1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 3
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 3:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 3:2::1
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[ASBR1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 113.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 113::3 64
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 12.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 12::3 64
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[ASBR1] bgp 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] router-id 3.3.3.3
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 113::4 as-number 200
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 113::4 ebgp-max-hop 10
[ASBR1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] import-bier isisv6 1
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 next-hop-local
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 capability bier
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::4 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::4 capability bier
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[ASBR1] isis 1
[ASBR1-isis-1] bier enable
[ASBR1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] import-bier bgp4+
# Redistribute IPv6 BGP routes into IS-IS.
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] import-route bgp4+
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-isis-1] quit
4. Configure ASBR 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<ASBR2> system-view
[ASBR2] router id 4.4.4.4
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[ASBR2] isis 1
[ASBR2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[ASBR2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[ASBR2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[ASBR2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR2] interface loopback 0
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] ip address 4.4.4.4 32
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 4::4 128
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[ASBR2] segment-routing ipv6
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 4::4
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 4:2:: 96 static 8
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign ASBR 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 4, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[ASBR2] bier
[ASBR2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 4
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 4:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 4:2::1
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[ASBR2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 113.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 113::4 64
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 14.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 14::4 64
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[ASBR2] bgp 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] router-id 4.4.4.4
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 6::6 as-number 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 6::6 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 113::3 as-number 100
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 113::3 ebgp-max-hop 10
[ASBR2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-bier isisv6 1
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 next-hop-local
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::3 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::3 capability bier
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[ASBR2] isis 1
[ASBR2-isis-1] bier enable
[ASBR2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] import-bier bgp4+
# Redistribute IPv6 BGP routes into IS-IS.
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] import-route bgp4+
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-isis-1] quit
5. Configure P 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P2> system-view
[P2] router id 5.5.5.5
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P2] isis 1
[P2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0005.00
[P2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 15.1.1.5 255.255.255.0
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 15::5 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 14.1.1.5 255.255.255.0
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 14::5 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface loopback 0
[P2-LoopBack0] ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255
[P2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 5::5 128
[P2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-LoopBack0] quit
6. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 6.6.6.6
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0006.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 0
[PE2-LoopBack0] ip address 6.6.6.6 32
[PE2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 6::6 128
[PE2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 6::6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 6:2:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 6, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE2] bier
[PE2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the MSR6 encapsulation.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type msr6 bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 6:2::1 as the End.RGB SID.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] end-rgb locator aaa sid 6:2::1
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:6
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE2] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] src-dt4 locator aaa sid 6:2::2
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] src-dt6 locator aaa sid 6:2::3
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
[PE2-mvpn-a] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM, IGMP, and MLD on the interface.
[PE2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 7.13.1.12 255.255.255.0
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 100:3:3::2 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] igmp enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mld enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 15.1.1.6 255.255.255.0
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 15::6 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 200
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 6.6.6.6
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4::4 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] bier enable
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display the BFR ID range in the BGP routing table on ASBR 1 and ASBR 2.
[ASBR1] display bgp routing-table ipv6 4::4 128
BGP local router ID: 3.3.3.3
Local AS number: 100
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 4::4/128:
From : 113::4 (4.4.4.4)
Rely nexthop : 113::4
Original nexthop: 113::4
Out interface : Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
Route age : 00h00m40s
OutLabel : NULL
RxPathID : 0x0
TxPathID : 0x0
BIER Path : <Sub-domain ID 0, BFR-ID 4, MSR6 encap><BSL info: [128,32]><
END.RGB SID 4:2::1><BFR-ID [start,range], range count 1, [6,
1]>
AS-path : 200
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, pref-val 0
State : valid, external, best
IP precedence : N/A
QoS local ID : N/A
Traffic index : N/A
Tunnel policy : NULL
Rely tunnel IDs : N/A
[ASBR2] display bgp routing-table ipv6 3::3 128
BGP local router ID: 4.4.4.4
Local AS number: 200
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 3::3/128:
From : 113::3 (3.3.3.3)
Rely nexthop : 113::3
Original nexthop: 113::3
Out interface : Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
Route age : 00h02m34s
OutLabel : NULL
RxPathID : 0x0
TxPathID : 0x0
BIER Path : <Sub-domain ID 0, BFR-ID 3, MSR6 encap><BSL info: [128,32]><
END.RGB SID 3:2::1><BFR-ID [start,range], range count 1, [1,
2]>
AS-path : 100
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, pref-val 0
State : valid, external, best
IP precedence : N/A
QoS local ID : N/A
Traffic index : N/A
Tunnel policy : NULL
Rely tunnel IDs : N/A
# Display the BIER information of BFR prefixes on PE 1.
[PE1] display bier routing-table
Sub-domain 0
Total BFERs: 4
BFR ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1::1(Local)
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: N/A
BFR ID: 2
BFR prefix: 2::2
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 2::2
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::424B:FF:FECA:1C06 Invalid
BFR ID: 3
BFR prefix: 3::3
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 2::2
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::424B:FF:FECA:1C06 Invalid
BFR ID: 4
BFR prefix: 4::4
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 2::2
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::424B:FF:FECA:1C06 Invalid
# Display cross-AS BIRT information on PE 1.
[PE1] display bier inter-as routing-table
Sub-domain 0
BFR ID: 6
BFR prefix: 4::4
AS: --
Protocol: IS-IS
Preference: --
# Display the BIER information of BFR prefixes on PE 2.
[PE2] display bier routing-table
Sub-domain 0
Total BFERs: 4
BFR ID: 6
BFR prefix: 6::6(Local)
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: N/A
BFR ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1::1
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 4::4
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::4255:82FF:FEF0:608 Invalid
BFR ID: 3
BFR prefix: 3::3
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 4::4
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::4255:82FF:FEF0:608 Invalid
BFR ID: 4
BFR prefix: 4::4
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 4::4
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::4255:82FF:FEF0:608 Invalid
# Display cross-AS BIRT information on PE 2.
[PE2] display bier inter-as routing-table
Sub-domain 0
BFR ID: 2
BFR prefix: 3::3
AS: --
Protocol: IS-IS
Preference: --
Example: Configuring prefix replacement for inter-AS (IS-IS-EBGP-IS-IS) BIER-based MVPN (G-BIER encapsulation)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 29, configure prefix replacement for inter-AS (IS-IS-EBGP-IS-IS) BIER-based MVPN with the G-BIER encapsulation to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Functions |
· An ASBR device does not replace the BIER prefix with its own BIER prefix when advertising routing information from another AS to its own AS. · In AS 100 and AS 200, BIER information is carried in IS-IS packets. |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 and Loopback 1 belong to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and BIER |
· Configure IS-IS in AS 100 and AS 200 on the public network, and establish EBGP peer connections between ASBR 1 and ASBR 2. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and ASBR 1 on their respective Loopback 0. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 2 and ASBR 2 on their respective Loopback 0. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and PE 2 on their respective Loopback 0. · Configure BIER on the public network: sub-domain 0, BSL 128, and max-SI 32. · Configure the BFR prefixes of PE 1, ASBR 1, ASBR 2, and PE 2 as the IPv6 addresses for their respective Loopback 0, and configure the multicast policy reserved address for each device. |
|
IP multicast routing |
Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1 and PE 2. |
|
IGMP |
Enable IGMP on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 of PE 2. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on all private interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on PE 1 and PE 2. · Configure Loopback 1 of PE 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a to provide services for all multicast groups. |
Table 17 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
7.12.1.10/24 |
ASBR 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
113.1.1.4/24 113::4/64 |
|
R 1 |
— |
7.13.1.10/24 |
ASBR 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
14.1.1.4/24 14.1.1.4/64 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
7.12.1.12/24 100:2:2::2/64 |
ASBR 2 |
Loop0 |
4.4.4.4/32 4::4/128 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
11.1.1.1/24 11::1/64 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
15.1.1.5/24 15::5/64 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop0 |
1.1.1.1/32 1::1/128 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
14.1.1.5/24 14::5/64 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
11.11.11.11/32 11::11/128 |
P 2 |
Loop0 |
5.5.5.5/32 5::5/128 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
11.1.1.2/24 11::2/64 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
15.1.1.6/24 15::6/64 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
12.1.1.2/24 12::2/64 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
7.13.1.12/24 100:3:3::2/64 |
|
P 1 |
Loop0 |
2.2.2.2/32 2::2/128 |
PE 2 |
Loop0 |
6.6.6.6/32 6::6/128 |
|
ASBR 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
113.1.1.3/24 113::3/64 |
|
|
|
|
ASBR 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
12.1.1.3/24 12::3/64 |
|
|
|
|
ASBR 1 |
Loop0 |
1.1.1.1/32 1::1/128 |
|
|
|
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 0
[PE1-LoopBack0] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:2:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 1, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE1] bier
[PE1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5001::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5001::1
# Configure multicast service prefix information.
[PE1] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1234:1:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 12
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 14
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
[PE1-mvpn-a] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 7.12.1.12 255.255.255.0
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 100:2:2::2 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 11::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Loopback 1 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 11::11 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure Loopback 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP.
[PE1] pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim-a] c-bsr 11.11.11.11
[PE1-pim-a] c-rp 11.11.11.11
[PE1-pim-a] quit
[PE1] ipv6 pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim6-a] c-bsr 11::11
[PE1-pim6-a] c-rp 11::11
[PE1-pim6-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 6::6 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 6::6 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] bier enable
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
2. Configure P 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P1> system-view
[P1] router id 2.2.2.2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 11.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 11::2 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 12.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 12::2 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface loopback 0
[P1-LoopBack0] ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
[P1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[P1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-LoopBack0] quit
3. Configure ASBR 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<ASBR1> system-view
[ASBR1] router id 3.3.3.3
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[ASBR1] isis 1
[ASBR1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[ASBR1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[ASBR1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00
[ASBR1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR1] interface loopback 0
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 3::3 128
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[ASBR1] segment-routing ipv6
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3::3
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 3:2:: 96 static 8
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign ASBR 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 3, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[ASBR1] bier
[ASBR1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 3
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5003::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5003::1
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[ASBR1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 113.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 113::3 64
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 12.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 12::3 64
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[ASBR1] bgp 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] router-id 3.3.3.3
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 113::4 as-number 200
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 113::4 ebgp-max-hop 10
[ASBR1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] import-bier isisv6 1
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 next-hop-local
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 capability bier
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::4 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::4 capability bier
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[ASBR1] isis 1
[ASBR1-isis-1] bier enable
[ASBR1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] import-bier bgp4+
# Redistribute IPv6 BGP routes into IS-IS.
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] import-route bgp4+
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-isis-1] quit
4. Configure ASBR 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<ASBR2> system-view
[ASBR2] router id 4.4.4.4
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[ASBR2] isis 1
[ASBR2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[ASBR2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[ASBR2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[ASBR2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR2] interface loopback 0
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] ip address 4.4.4.4 32
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 4::4 128
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[ASBR2] segment-routing ipv6
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 4::4
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 4:2:: 96 static 8
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign ASBR 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 4, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[ASBR2] bier
[ASBR2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 4
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5004::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5004::1
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[ASBR2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 113.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 113::4 64
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 14.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 14::4 64
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[ASBR2] bgp 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] router-id 4.4.4.4
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 6::6 as-number 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 6::6 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 113::3 as-number 100
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 113::3 ebgp-max-hop 10
[ASBR2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-bier isisv6 1
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 next-hop-local
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::3 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::3 capability bier
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[ASBR2] isis 1
[ASBR2-isis-1] bier enable
[ASBR2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] import-bier bgp4+
# Redistribute IPv6 BGP routes into IS-IS.
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] import-route bgp4+
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-isis-1] quit
5. Configure P 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P2> system-view
[P2] router id 5.5.5.5
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P2] isis 1
[P2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0005.00
[P2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 15.1.1.5 255.255.255.0
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 15::5 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 14.1.1.5 255.255.255.0
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 14::5 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface loopback 0
[P2-LoopBack0] ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255
[P2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 5::5 128
[P2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-LoopBack0] quit
6. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 6.6.6.6
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0006.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 0
[PE2-LoopBack0] ip address 6.6.6.6 32
[PE2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 6::6 128
[PE2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 6::6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 6:2:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 6, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE2] bier
[PE2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5006::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5006::1
# Configure multicast service prefix information.
[PE2] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1234:6:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:6
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE2] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 13
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 15
[PE2-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
[PE2-mvpn-a] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM, IGMP, and MLD on the interface.
[PE2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 7.13.1.12 255.255.255.0
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 100:3:3::2 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] igmp enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mld enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 15.1.1.6 255.255.255.0
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 15::6 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 200
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 6.6.6.6
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4::4 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] bier enable
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display the BFR ID range in the BGP routing table on ASBR 1 and ASBR 2.
[ASBR1] display bgp routing-table ipv6 4::4 128
BGP local router ID: 3.3.3.3
Local AS number: 100
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 4::4/128:
From : 113::4 (4.4.4.4)
Rely nexthop : 113::4
Original nexthop: 113::4
Out interface : Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
Route age : 00h00m19s
OutLabel : NULL
RxPathID : 0x0
TxPathID : 0x0
BIER Path : <Sub-domain ID 0, BFR-ID 4, G-BIER encap><BSL info: [128,32]
><MPRA 5004::1><BFR-ID range, count 1, [6, 6]>
AS-path : 200
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, pref-val 0
State : valid, external, best
IP precedence : N/A
QoS local ID : N/A
Traffic index : N/A
Tunnel policy : NULL
Rely tunnel IDs : N/A
[ASBR2] display bgp routing-table ipv6 3::3 128
BGP local router ID: 4.4.4.4
Local AS number: 200
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 3::3/128:
From : 113::3 (3.3.3.3)
Rely nexthop : 113::3
Original nexthop: 113::3
Out interface : Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
Route age : 00h02m42s
OutLabel : NULL
RxPathID : 0x0
TxPathID : 0x0
BIER Path : <Sub-domain ID 0, BFR-ID 3, G-BIER encap><BSL info: [128,32]
><MPRA 5003::1><BFR-ID range, count 1, [1, 1]>
AS-path : 100
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, pref-val 0
State : valid, external, best
IP precedence : N/A
QoS local ID : N/A
Traffic index : N/A
Tunnel policy : NULL
Rely tunnel IDs : N/A
# Display the BIER information of BFR prefixes on PE 1.
[PE1] display bier routing-table
Sub-domain 0
Total BFERs: 2
BFR ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1::1(Local)
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: N/A
BFR ID: 3
BFR prefix: 3::3
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 3::3
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::424B:FF:FECA:1C06 Invalid
BFR ID: 4
BFR prefix: 4::4
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 3::3
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::424B:FF:FECA:1C06 Invalid
# Display cross-AS BIRT information on PE 1.
[PE1] display bier inter-as routing-table
Sub-domain 0
BFR ID: 4
BFR prefix: 3::3
AS: --
Protocol: IS-IS
Preference: --
BFR ID: 6
BFR prefix: 3::3
AS: --
Protocol: IS-IS
Preference: --
# Display the BIER information of BFR prefixes on PE 2.
[PE2] display bier routing-table
Sub-domain 0
Total BFERs: 2
BFR ID: 6
BFR prefix: 6::6(Local)
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: N/A
BFR ID: 4
BFR prefix: 4::4
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 4::4
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::4255:82FF:FEF0:608 Invalid
# Display cross-AS BIRT information on PE 2.
[PE2] display bier inter-as routing-table
Sub-domain 0
BFR ID: 1
BFR prefix: 4::4
AS: --
Protocol: IS-IS
Preference: --
BFR ID: 3
BFR prefix: 4::4
AS: --
Protocol: IS-IS
Preference: --
Example: Configuring prefix replacement for inter-AS (IBGP (proxy)-EBGP-IS-IS) BIER-based MVPN (G-BIER encapsulation)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 30, configure prefix replacement for inter-AS (IBGP (proxy)-EBGP-IS-IS) BIER-based MVPN N with the G-BIER encapsulation to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Functions |
· An ASBR device does not replace the BIER prefix with its own BIER prefix when advertising routing information from another AS to its own AS. · In AS 100, BIER information is carried in BGP packets. In AS 200, BIER information is carried in IS-IS packets. |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 and Loopback 1 belong to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and BIER |
· Configure IBGP in AS 100 on the public network, configure IS-IS in AS 200, and establish EBGP peer connections between ASBR 1 and ASBR 2. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and P 1 on their respective Loopback 0, establish BGP peer connections between P 1 and ASBR 1 on their respective Loopback 0, and establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and ASBR 1 on their respective Loopback 0. · Establish BGP peer connections on between PE 2 and ASBR 2 on their respective Loopback 0. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and PE 2 on their respective Loopback 0. · Configure BIER on the public network: sub-domain 0, BSL 128, and max-SI 32. · Configure the BFR prefixes of PE 1, ASBR 1, ASBR 2, and PE 2 as the IPv6 addresses for their respective Loopback 0, and configure the multicast policy reserved address for each device. |
|
IP multicast routing |
Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1 and PE 2. |
|
IGMP |
Enable IGMP on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 of PE 1 and PE 2. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on all private interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on PE 1 and PE 2. · Configure Loopback 1 of PE 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a to provide services for all multicast groups. |
Table 18 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
7.12.1.10/24 |
ASBR 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
113.1.1.4/24 113::4/64 |
|
R 1 |
— |
7.13.1.10/24 |
ASBR 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
14.1.1.4/24 14.1.1.4/64 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
7.12.1.12/24 100:2:2::2/64 |
ASBR 2 |
Loop0 |
4.4.4.4/32 4::4/128 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
11.1.1.1/24 11::1/64 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
15.1.1.5/24 15::5/64 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop0 |
1.1.1.1/32 1::1/128 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
14.1.1.5/24 14::5/64 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
11.11.11.11/32 11::11/128 |
P 2 |
Loop0 |
5.5.5.5/32 5::5/128 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
11.1.1.2/24 11::2/64 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
15.1.1.6/24 15::6/64 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
12.1.1.2/24 12::2/64 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
7.13.1.12/24 100:3:3::2/64 |
|
P 1 |
Loop0 |
2.2.2.2/32 2::2/128 |
PE 2 |
Loop0 |
6.6.6.6/32 6::6/128 |
|
ASBR 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
113.1.1.3/24 113::3/64 |
|
|
|
|
ASBR 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
12.1.1.3/24 12::3/64 |
|
|
|
|
ASBR 1 |
Loop0 |
1.1.1.1/32 1::1/128 |
|
|
|
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 0
[PE1-LoopBack0] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure an IPv6 static route.
[PE1] ipv6 route-static 6::6 128 11::2
# Configure SRv6.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:2:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 1, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE1] bier
[PE1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5001::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5001::1
# Configure multicast service prefix information.
[PE1] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1234:1:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 12
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 14
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
[PE1-mvpn-a] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 7.12.1.12 255.255.255.0
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 100:2:2::2 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 11::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Loopback 1 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 11::11 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure Loopback 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP.
[PE1] pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim-a] c-bsr 11.11.11.11
[PE1-pim-a] c-rp 11.11.11.11
[PE1-pim-a] quit
[PE1] ipv6 pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim6-a] c-bsr 11::11
[PE1-pim6-a] c-rp 11::11
[PE1-pim6-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 6::6 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2::2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 capability bier
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 6::6 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] quit
# Apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
2. Configure P 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P1> system-view
[P1] router id 2.2.2.2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
# Configure an IPv6 static route.
[P1] ipv6 route-static 6::6 128 12::3
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 11.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 11::2 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 12.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 12::2 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface loopback 0
[P1-LoopBack0] ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
[P1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[P1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure BGP.
[P1] bgp 100
[P1-bgp-default] router-id 2.2.2.2
[P1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[P1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[P1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 enable
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[P1–bgp-default] quit
3. Configure ASBR 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<ASBR1> system-view
[ASBR1] router id 3.3.3.3
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[ASBR1] isis 1
[ASBR1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[ASBR1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[ASBR1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00
[ASBR1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR1] interface loopback 0
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 3::3 128
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[ASBR1] segment-routing ipv6
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3::3
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 3:2:: 96 static 8
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign ASBR 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 3, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[ASBR1] bier
[ASBR1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 3
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5003::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5003::1
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[ASBR1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 113.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 113::3 64
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 12.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 12::3 64
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[ASBR1] bgp 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] router-id 3.3.3.3
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 113::4 as-number 200
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 113::4 ebgp-max-hop 10
[ASBR1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 next-hop-local
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 capability bier
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2::2 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2::2 next-hop-local
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::4 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::4 capability bier
# Enable BGP BFR prefix proxying.
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] bier bfr-prefix proxy
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1–bgp-default] quit
# Apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[ASBR1] isis 1
[ASBR1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-isis-1] quit
4. Configure ASBR 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<ASBR2> system-view
[ASBR2] router id 4.4.4.4
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[ASBR2] isis 1
[ASBR2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[ASBR2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[ASBR2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[ASBR2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR2] interface loopback 0
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] ip address 4.4.4.4 32
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 4::4 128
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure an IPv6 static route.
[ASBR2] ipv6 route-static 1::1 128 113::3
# Configure SRv6.
[ASBR2] segment-routing ipv6
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 4::4
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 4:2:: 96 static 8
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign ASBR 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 4, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[ASBR2] bier
[ASBR2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 4
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5004::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5004::1
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[ASBR2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 113.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 113::4 64
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 14.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 14::4 64
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[ASBR2] bgp 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] router-id 4.4.4.4
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 6::6 as-number 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 6::6 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 113::3 as-number 100
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 113::3 ebgp-max-hop 10
[ASBR2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-bier isisv6 1
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 next-hop-local
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::3 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::3 capability bier
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[ASBR2] isis 1
[ASBR2-isis-1] bier enable
[ASBR2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] import-bier bgp4+
# Redistribute IPv6 BGP routes into IS-IS.
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] import-route bgp4+
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-isis-1] quit
5. Configure P 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P2> system-view
[P2] router id 5.5.5.5
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P2] isis 1
[P2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0005.00
[P2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P2-isis-1] quit
# Configure an IPv6 static route.
[P2] ipv6 route-static 1::1 128 14::4
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 15.1.1.5 255.255.255.0
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 15::5 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 14.1.1.5 255.255.255.0
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 14::5 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface loopback 0
[P2-LoopBack0] ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255
[P2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 5::5 128
[P2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-LoopBack0] quit
6. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 6.6.6.6
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0006.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 0
[PE2-LoopBack0] ip address 6.6.6.6 32
[PE2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 6::6 128
[PE2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure an IPv6 static route.
[P2] ipv6 route-static 1::1 128 15::5
# Configure SRv6.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 6::6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 6:2:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 6, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE2] bier
[PE2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5006::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5006::1
# Configure multicast service prefix information.
[PE1] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1234:6:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:6
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 13
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 15
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
[PE1-mvpn-a] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM, IGMP, and MLD on the interface.
[PE2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 7.13.1.12 255.255.255.0
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 100:3:3::2 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] igmp enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mld enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 15.1.1.6 255.255.255.0
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 15::6 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 200
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 6.6.6.6
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4::4 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Enable BIER for an IS-IS process, and apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] bier enable
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display the BFR ID range in the BGP routing table on ASBR 1 and ASBR 2.
[ASBR1] display bgp routing-table ipv6 4::4 128
BGP local router ID: 3.3.3.3
Local AS number: 100
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 4::4/128:
From : 113::4 (4.4.4.4)
Rely nexthop : 113::4
Original nexthop: 113::4
Out interface : Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
Route age : 00h09m18s
OutLabel : NULL
RxPathID : 0x0
TxPathID : 0x0
BIER Path : <Sub-domain ID 0, BFR-ID 4, G-BIER encap><BSL info: [128,32]
><MPRA 5004::1><BFR-ID range, count 1, [6, 6]>
AS-path : 200
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, pref-val 0
State : valid, external, best
IP precedence : N/A
QoS local ID : N/A
Traffic index : N/A
Tunnel policy : NULL
Rely tunnel IDs : N/A
[ASBR2] display bgp routing-table ipv6 3::3 128
BGP local router ID: 4.4.4.4
Local AS number: 200
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 3::3/128:
From : 113::3 (3.3.3.3)
Rely nexthop : 113::3
Original nexthop: 113::3
Out interface : Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
Route age : 00h00m29s
OutLabel : NULL
RxPathID : 0x0
TxPathID : 0x0
BIER Path : <Sub-domain ID 0, BFR-ID 3, G-BIER encap><BSL info: [128,32]
><MPRA 5003::1><BFR-ID range, count 3, [1, 1],[4, 4],[6, 6]>
AS-path : 100
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, pref-val 0
State : valid, external, best
IP precedence : N/A
QoS local ID : N/A
Traffic index : N/A
Tunnel policy : NULL
Rely tunnel IDs : N/A
# Display the BIER information of BFR prefixes on PE 1.
[PE1] display bier routing-table
Sub-domain 0
Total BFERs: 2
BFR ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1::1(Local)
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: N/A
BFR ID: 3
BFR prefix: 3::3
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 3::3
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::424B:FF:FECA:1C06 Invalid
# Display cross-AS BIRT information on PE 1.
[PE1] display bier inter-as routing-table
Sub-domain 0
BFR ID: 4
BFR prefix: 3::3
AS: 100
Protocol: IBGP
Preference: --
BFR ID: 6
BFR prefix: 3::3
AS: 100
Protocol: IBGP
Preference: --
# Display the BIER information of BFR prefixes on PE 2.
[PE2] display bier routing-table
Sub-domain 0
Total BFERs: 2
BFR ID: 6
BFR prefix: 6::6(Local)
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: N/A
BFR ID: 4
BFR prefix: 4::4
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 4::4
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::4255:82FF:FEF0:608 Invalid
# Display cross-AS BIRT information on PE 2.
[PE2] display bier inter-as routing-table
Sub-domain 0
BFR ID: 1
BFR prefix: 4::4
AS: --
Protocol: IS-IS
Preference: --
BFR ID: 3
BFR prefix: 4::4
AS: --
Protocol: IS-IS
Preference: --
Example: Configuring prefix replacement for inter-AS (IBGP (proxy)-EBGP-IBGP) BIER-based MVPN (G-BIER encapsulation)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 31, configure prefix replacement for inter-AS (IBGP (proxy)-EBGP-IBGP) BIER-based MVPN with the G-BIER encapsulation to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Functions |
· An ASBR device does not replace the BIER prefix with its own BIER prefix when advertising routing information from another AS to its own AS. · In AS 100 and AS 200, BIER information is carried in BGP packets. |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 and Loopback 1 belong to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 0 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and BIER |
· Configure IBGP in AS 100 and AS 200 on the public network, and establish EBGP peer connections between ASBR 1 and ASBR 2. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and P 1 on their respective Loopback 0, establish BGP peer connections between P 1 and ASBR 1 on their respective Loopback 0, and establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and ASBR 1 on their respective Loopback 0. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 2 and P 2 on their respective Loopback 0, establish BGP peer connections between P 2 and ASBR 2 on their respective Loopback 0, and establish BGP peer connections between PE 2 and ASBR 2 on their respective Loopback 0. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1 and PE 2 on their respective Loopback 0. · Configure BIER on the public network: sub-domain 0, BSL 128, and max-SI 32. · Configure the BFR prefixes of PE 1, ASBR 1, ASBR 2, and PE 2 as the IPv6 addresses for their respective Loopback 1, and configure the multicast policy reserved address for each device. |
|
IP multicast routing |
Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1 and PE 2. |
|
IGMP |
Enable IGMP on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 of PE 2. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on all private interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on PE 1 and PE 2. · Configure Loopback 1 of PE 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a to provide services for all multicast groups. |
Table 19 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
7.12.1.10/24 |
ASBR 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
113.1.1.4/24 113::4/64 |
|
R 1 |
— |
7.13.1.10/24 |
ASBR 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
14.1.1.4/24 14.1.1.4/64 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
7.12.1.12/24 100:2:2::2/64 |
ASBR 2 |
Loop0 |
4.4.4.4/32 4::4/128 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
11.1.1.1/24 11::1/64 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
15.1.1.5/24 15::5/64 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop0 |
1.1.1.1/32 1::1/128 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
14.1.1.5/24 14::5/64 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
11.11.11.11/32 11::11/128 |
P 2 |
Loop0 |
5.5.5.5/32 5::5/128 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
11.1.1.2/24 11::2/64 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
15.1.1.6/24 15::6/64 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
12.1.1.2/24 12::2/64 |
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
7.13.1.12/24 100:3:3::2/64 |
|
P 1 |
Loop0 |
2.2.2.2/32 2::2/128 |
PE 2 |
Loop0 |
6.6.6.6/32 6::6/128 |
|
ASBR 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
113.1.1.3/24 113::3/64 |
|
|
|
|
ASBR 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
12.1.1.3/24 12::3/64 |
|
|
|
|
ASBR 1 |
Loop0 |
1.1.1.1/32 1::1/128 |
|
|
|
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 0
[PE1-LoopBack0] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 1::1 128
[PE1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure an IPv6 static route.
[PE1] ipv6 route-static 6::6 128 11::2
# Configure SRv6.
[PE1] segment-routing ipv6
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 1::1
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 1:2:: 96 static 8
[PE1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 1, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE1] bier
[PE1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 1
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5001::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[PE1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5001::1
# Configure multicast service prefix information.
[PE1] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1234:1:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 12
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 14
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
[PE1-mvpn-a] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 7.12.1.12 255.255.255.0
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 100:2:2::2 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 11::1 64
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Loopback 1 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 address 11::11 128
[PE1-LoopBack1] pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack1] ipv6 pim sm
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure Loopback 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP.
[PE1] pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim-a] c-bsr 11.11.11.11
[PE1-pim-a] c-rp 11.11.11.11
[PE1-pim-a] quit
[PE1] ipv6 pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim6-a] c-bsr 11::11
[PE1-pim6-a] c-rp 11::11
[PE1-pim6-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] router-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 6::6 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 6::6 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2::2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 capability bier
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 6::6 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 6::6 prefix-sid
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv6] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] quit
# Apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE1] isis 1
[PE1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE1-isis-1] quit
2. Configure P 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P1> system-view
[P1] router id 2.2.2.2
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P1] isis 1
[P1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00
[P1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P1-isis-1] quit
# Configure an IPv6 static route.
[P1] ipv6 route-static 6::6 128 12::3
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 11.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 11::2 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 12.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 12::2 64
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P1] interface loopback 0
[P1-LoopBack0] ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
[P1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 2::2 128
[P1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure BGP.
[P1] bgp 100
[P1-bgp-default] router-id 2.2.2.2
[P1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[P1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 as-number 100
[P1-bgp-default] peer 3::3 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 3::3 enable
[P1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[P1–bgp-default] quit
3. Configure ASBR 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<ASBR1> system-view
[ASBR1] router id 3.3.3.3
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[ASBR1] isis 1
[ASBR1-isis-1] is-level level-2
[ASBR1-isis-1] cost-style wide
[ASBR1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00
[ASBR1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR1] interface loopback 0
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 3::3 128
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR1-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure SRv6.
[ASBR1] segment-routing ipv6
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 3::3
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 3:2:: 96 static 8
[ASBR1-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign ASBR 1 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 3, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[ASBR1] bier
[ASBR1-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 3
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5003::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[ASBR1-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5003::1
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[ASBR1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 113.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 113::3 64
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 12.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 12::3 64
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[ASBR1] bgp 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] router-id 3.3.3.3
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 as-number 100
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 2::2 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 113::4 as-number 200
[ASBR1-bgp-default] peer 113::4 ebgp-max-hop 10
[ASBR1-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 next-hop-local
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 1::1 capability bier
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2::2 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 2::2 next-hop-local
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::4 enable
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::4 capability bier
# Enable BGP BFR prefix proxying.
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] bier bfr-prefix proxy
[ASBR1-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1–bgp-default] quit
# Apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[ASBR1] isis 1
[ASBR1-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[ASBR1-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR1-isis-1] quit
4. Configure ASBR 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<ASBR2> system-view
[ASBR2] router id 4.4.4.4
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[ASBR2] isis 1
[ASBR2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[ASBR2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[ASBR2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00
[ASBR2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR2] interface loopback 0
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] ip address 4.4.4.4 32
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 4::4 128
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure an IPv6 static route.
[ASBR2] ipv6 route-static 1::1 128 113::3
# Configure SRv6.
[ASBR2] segment-routing ipv6
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 4::4
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 4:2:: 96 static 8
[ASBR2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign ASBR 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 4, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[ASBR2] bier
[ASBR2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 4
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5004::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[ASBR2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5004::1
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[ASBR2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 113.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 113::4 64
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[ASBR2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 14.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 14::4 64
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[ASBR2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure BGP.
[ASBR2] bgp 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] router-id 4.4.4.4
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 5::5 as-number 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 5::5 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 6::6 as-number 200
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 6::6 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 113::3 as-number 100
[ASBR2-bgp-default] peer 113::3 ebgp-max-hop 10
[ASBR2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 5::5 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 5::5 next-hop-local
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 next-hop-local
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 capability bier
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::3 enable
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 113::3 capability bier
[ASBR2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2–bgp-default] quit
# Apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[ASBR2] isis 1
[ASBR2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[ASBR2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[ASBR2-isis-1] quit
5. Configure P 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<P2> system-view
[P2] router id 5.5.5.5
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[P2] isis 1
[P2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[P2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[P2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0005.00
[P2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[P2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[P2-isis-1] quit
# Configure an IPv6 static route.
[P2] ipv6 route-static 1::1 128 14::4
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] undo shutdown
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 15.1.1.5 255.255.255.0
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 15::5 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] undo shutdown
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 14.1.1.5 255.255.255.0
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 14::5 64
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[P2] interface loopback 0
[P2-LoopBack0] ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255
[P2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 5::5 128
[P2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[P2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure BGP.
[P2] bgp 200
[P2-bgp-default] router-id 5.5.5.5
[P2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 as-number 200
[P2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P2-bgp-default] peer 6::6 as-number 200
[P2-bgp-default] peer 6::6 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[P2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[P2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4::4 enable
[P2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 6::6 enable
[P2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[P2–bgp-default] quit
6. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 6.6.6.6
# Configure IPv6 IS-IS.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] is-level level-2
[PE2-isis-1] cost-style wide
[PE2-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0006.00
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Loopback 0, and enable IPv6 for IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface loopback 0
[PE2-LoopBack0] ip address 6.6.6.6 32
[PE2-LoopBack0] ipv6 address 6::6 128
[PE2-LoopBack0] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure an IPv6 static route.
[PE2] ipv6 route-static 1::1 128 15::5
# Configure SRv6.
[PE2] segment-routing ipv6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] encapsulation source-address 6::6
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] locator aaa ipv6-prefix 6:2:: 96 static 8
[PE2-segment-routing-ipv6] quit
# Assign PE 2 to sub-domain 0, configure the BFR ID as 6, and configure the BFR prefix as the IPv6 address of Loopback 0.
[PE2] bier
[PE2-bier] sub-domain 0 ipv6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-id 6
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] bfr-prefix interface LoopBack 0
# Configure BIER with the G-BIER encapsulation.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] encapsulation-type g-bier bsl 128 max-si 32
# Configure 5006::1 as the multicast policy reserved address.
[PE2-bier-sub-domain-0-ipv6] g-bier mpra 5006::1
# Configure multicast service prefix information.
[PE2] multicast-service-prefix ms1 ipv6-prefix 1234:6:: 64 service-id-length 10
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:6
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IPv4 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Enable IPv6 multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] ipv6 multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib6-a] quit
# Create a BIER-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode bier
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 13
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv4] quit
# Create an MVPN IPv6 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a] address-family ipv6
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] source loopback 0
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation, and enable multicast warm backup.
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] inclusive-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] selective-tunnel dynamic sub-domain 0 bsl 128
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] tunnel-source multicast-service-prefix ms1 service-id 15
[PE1-mvpn-a-ipv6] quit
[PE1-mvpn-a] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign IP addresses to the interface, and enable PIM-SM, IGMP, and MLD on the interface.
[PE2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 7.13.1.12 255.255.255.0
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 address 100:3:3::2 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ipv6 pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] igmp enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mld enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign IP addresses to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IS-IS on the interface.
[PE2] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] port link-mode route
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 15.1.1.6 255.255.255.0
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ipv6 address 15::6 64
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] isis ipv6 enable 1
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 200
[PE2-bgp-default] router-id 6.6.6.6
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 connect-interface loopback 0
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1::1 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 4::4 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 5::5 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 5::5 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv6
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] bier enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4::4 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 4::4 capability bier
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] peer 5::5 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] advertise srv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv6
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] peer 1::1 prefix-sid
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv6] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] segment-routing ipv6 best-effort
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv6-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Apply locator aaa to the IS-IS process.
[PE2] isis 1
[PE2-isis-1] address-family ipv6 unicast
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] segment-routing ipv6 locator aaa
[PE2-isis-1-ipv6] quit
[PE2-isis-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display the BFR ID range in the BGP routing table on ASBR 1 and ASBR 2.
[ASBR1] display bgp routing-table ipv6 4::4 128
BGP local router ID: 3.3.3.3
Local AS number: 100
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 4::4/128:
From : 113::4 (4.4.4.4)
Rely nexthop : 113::4
Original nexthop: 113::4
Out interface : Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
Route age : 00h01m14s
OutLabel : NULL
RxPathID : 0x0
TxPathID : 0x0
BIER Path : <Sub-domain ID 0, BFR-ID 4, G-BIER encap><BSL info: [128,32]
><MPRA 5004::1>
AS-path : 200
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, pref-val 0
State : valid, external, best
IP precedence : N/A
QoS local ID : N/A
Traffic index : N/A
Tunnel policy : NULL
Rely tunnel IDs : N/A
[ASBR2] display bgp routing-table ipv6 3::3 128
BGP local router ID: 4.4.4.4
Local AS number: 200
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 3::3/128:
From : 113::3 (3.3.3.3)
Rely nexthop : 113::3
Original nexthop: 113::3
Out interface : Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15
Route age : 00h00m04s
OutLabel : NULL
RxPathID : 0x0
TxPathID : 0x0
BIER Path : <Sub-domain ID 0, BFR-ID 3, G-BIER encap><BSL info: [128,32]
><MPRA 5003::1><BFR-ID range, count 3, [1, 1],[4, 4],[6, 6]>
AS-path : 100
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, pref-val 0
State : valid, external, best
IP precedence : N/A
QoS local ID : N/A
Traffic index : N/A
Tunnel policy : NULL
Rely tunnel IDs : N/A
# Display the BIER information of BFR prefixes on PE 1.
[PE1] display bier routing-table
Sub-domain 0
Total BFERs: 2
BFR ID: 1
BFR prefix: 1::1(Local)
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: N/A
BFR ID: 3
BFR prefix: 3::3
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 3::3
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::424B:FF:FECA:1C06 Invalid
# Display cross-AS BIRT information on PE 1.
[PE1] display bier inter-as routing-table
Sub-domain 0
BFR ID: 4
BFR prefix: 3::3
AS: 100
Protocol: IBGP
Preference: --
BFR ID: 6
BFR prefix: 3::3
AS: 100
Protocol: IBGP
Preference: --
# Display the BIER information of BFR prefixes on PE 2.
[PE2] display bier routing-table
Sub-domain 0
Total BFERs: 2
BFR ID: 6
BFR prefix: 6::6(Local)
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: N/A
BFR ID: 4
BFR prefix: 4::4
PHP: Disabled
Flag: Active
BFR-conflicted nodes: N/A
BFR neighbors: 1
BFR prefix: 4::4
NBRFlag:
Next hop list:
Out interface Next hop NhFlag Token
XGE0/0/15 FE80::4255:82FF:FEF0:608 Invalid
# Display cross-AS BIRT information on PE 2.
[PE2] display bier inter-as routing-table
Sub-domain 0
BFR ID: 1
BFR prefix: 3::3
AS: 100
Protocol: IBGP
Preference: --
BFR ID: 3
BFR prefix: 3::3
AS: 100
Protocol: IBGP
Preference: --