- Table of Contents
-
- 07-IP Multicast Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Multicast overview
- 02-IGMP snooping configuration
- 03-PIM snooping configuration
- 04-Multicast VLAN configuration
- 05-Multicast routing and forwarding configuration
- 06-IGMP configuration
- 07-PIM configuration
- 08-MSDP configuration
- 09-Multicast VPN overview
- 10-MDT-based MVPN configuration
- 11-RSVP-TE-based MVPN configuration
- 12-mLDP-based MVPN configuration
- 13-BIER-based MVPN configuration
- 14-MVPN extranet configuration
- 15-MLD snooping configuration
- 16-IPv6 PIM snooping configuration
- 17-IPv6 multicast VLAN configuration
- 18-IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding configuration
- 19-MLD configuration
- 20-IPv6 PIM configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 12-mLDP-based MVPN configuration | 899.86 KB |
Inclusive tunnel establishment
Selective tunnel establishment and tunnel switchover
mLDP-based MVPN tasks at a glance
Prerequisites for configuring mLDP-based MVPN
Enabling IP multicast routing for a VPN instance
Configuring BGP IPv4 MVPN route exchange
Configuring BGP IPv6 MVPN route exchange
Creating an mLDP-based MVPN instance
Creating an MVPN IPv4 address family
Specifying the MVPN source interface
Enabling inclusive tunnel creation
Enabling selective tunnel creation
Setting the tunnel switchover delay
Enabling inter-AS auto-discovery
Display and maintenance commands for mLDP-based MVPN
mLDP-based MVPN configuration examples
Example: Configuring intra-AS mLDP-based MVPN
Example: Configuring inter-AS option A mLDP-based MVPN
Configuring mLDP-based MVPN
mLDP-based MVPN overview
Basic concepts
This section introduces the following concepts in mLDP-based MVPN:
· MVPN—An MVPN logically defines the transmission boundary of the multicast traffic of a VPN over the public network. It also physically identifies all the PEs that support that VPN instance on the public network. Different VPN instances correspond to different MVPNs. All PEs in an MVPN are MVPN peers.
· Inclusive tunnel—Transmits all multicast packets (including multicast protocol packets and multicast data packets of all multicast groups) for an MVPN. Only one inclusive tunnel can be established between two PEs in the MVPN. A PE encapsulates multicast data packets and PIM BSMs of an MVPN into public network multicast data packets and sends them over the public network through the inclusive tunnel.
· Selective tunnel—Transmits multicast packets of one or more multicast groups for an MVPN. Multiple selective tunnels can be established between two PEs in the MVPN.
mLDP-based MVPN operation
The operation of mLDP-based MVPN is similar to that of RSVP-TE-based MVPN. They differ in the direction in which the public network P2MP tunnel is created.
· RSVP-TE-based MVPN—Starting from the ingress PE, the upstream devices use RSVP to establish RSVP-TE P2MP tunnels with downstream devices. In this mode, the ingress PE needs to know the IP address of the egress PE.
· mLDP-based MVPN—Starting from the egress PE, the downstream devices use LDP to establish mLDP P2MP tunnels with downstream devices. In this mode, the egress PE needs to the IP address of the ingress PE.
For more information about the RSVP-TE-based MVPN operation, see "Configuring RSVP-TE-based MVPN."
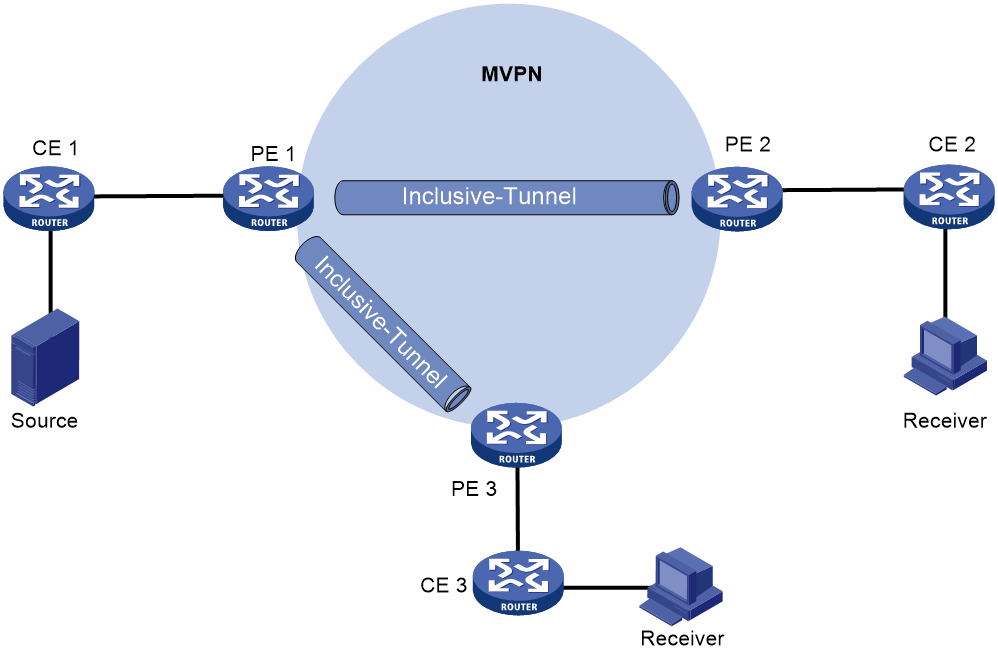
Inclusive tunnel establishment
As shown in Figure 1, the private network runs PIM, and the public network uses MPLS backbone. The inclusive tunnels are established as follows:
1. PE 1, PE 2, and PE 3 mutually establish IBGP neighbor relationship and exchange routing information.
2. PE 1 (the source of the tunnel) advertises the inclusive tunnel information to PE 2 and PE 3.
3. PE 2 and PE 3 each uses LDP to establish an inclusive mLDP tunnel with PE 1. The inclusive tunnel on the public network does not rely on PIM running on the private network.
Figure 1 Establishment of the inclusive tunnel
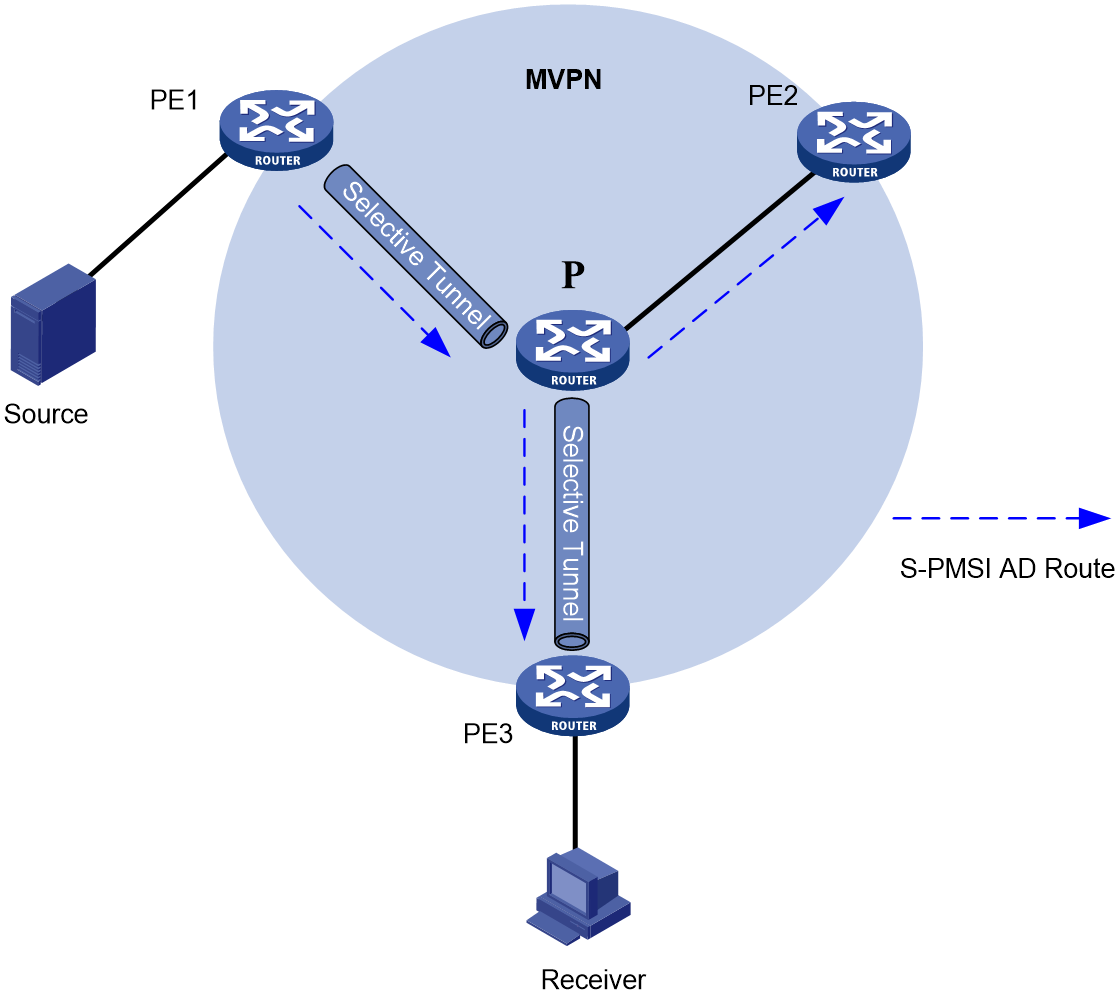
Selective tunnel establishment and tunnel switchover
mLDP-based MVPN supports switchover from the inclusive tunnel to selective tunnels to off-load traffic for specific (S, G) entries from the inclusive tunnel. An MVPN can have multiple selective tunnels.
As shown in Figure 2, the process of selective tunnel creation and the tunnel switchover is as follows:
1. Upon receiving a multicast packet for the (S, G) entry that meets the tunnel switchover criterion, the multicast source-side PE 1 sends an S-PMSI A-D route to PE 2 and PE 3.
2. PE 2 does not respond to the route because it has no receivers of the (S,G) entry attached.
3. PE 3 which has a receiver attached uses LDP to establish a selective tunnel with PE 1.
4. Subsequent multicast packets for the (S,G) entry are transmitted over the selective tunnel instead of the inclusive tunnel on the public network.
Figure 2 Selective tunnel establishment and tunnel switchover
Inter-AS mLDP-based MVPN
In an inter-AS VPN networking scenario, VPN sites are located in multiple ASs. These sites must be interconnected. Inter-AS VPN provides the following solutions:
· VRF-to-VRF connections between ASBRs—This solution is also called inter-AS option A.
· EBGP redistribution of labeled VPN-IPv4 routes between ASBRs—ASBRs advertise VPN-IPv4 routes to each other through MP-EBGP. This solution is also called inter-AS option B.
· Multihop EBGP redistribution of labeled VPN-IPv4 routes between PE devices—PEs advertise VPN-IPv4 routes to each other through MP-EBGP. This solution is also called inter-AS option C.
For more information about the three inter-AS VPN solutions, see MPLS L3VPN configuration in MPLS Configuration Guide.
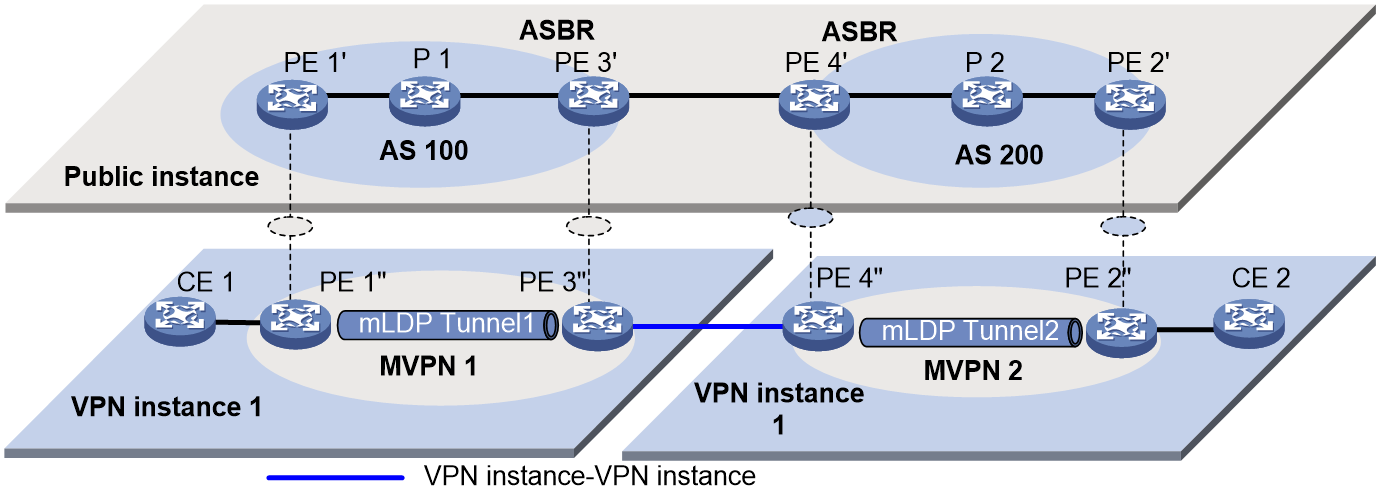
Inter-AS option A mLDP-based MVPN
As shown in Figure 3:
· A VPN instance spans AS 100 and AS 200.
· PE 3 and PE 4 are ASBRs for AS 100 and AS 200, respectively.
· PE 3 and PE 4 are interconnected through their respective VPN instance and treat each other as a CE.
Figure 3 Inter-AS option A mLDP-based MVPN
To implement inter-AS option A mLDP-based MVPN, a separate MVPN must be created in each AS. Multicast data of the VPN instance is transmitted across the ASs through the separate MVPNs in each AS.
Multicast packets of the VPN instance are delivered as follows:
1. CE 1 forwards a multicast packet of VPN instance 1 to PE 1.
2. PE 1 encapsulates the multicast packet into an MPLS packet and forwards it to PE 3 through mLDP tunnel 1.
3. PE 3 considers PE 4 as a CE of MVPN 1, so PE 3 decapsulates the MPLS packet and forwards the multicast packet to PE 4.
4. PE 4 considers PE 2 as a CE of MVPN 2, so PE 4 encapsulates the multicast packet into an MPLS packet and then forwards the packet to PE 2 through mLDP tunnel 2.
5. PE 2 decapsulates the MPLS packet and then forwards the multicast packet to CE 2.
In inter-AS option A, PEs in different ASs cannot advertise Source Active A-D routes to each other. Therefore, you must configure MSDP or Anycast-RP between RPs to allow Source Active A-D routes to be advertised across ASs.
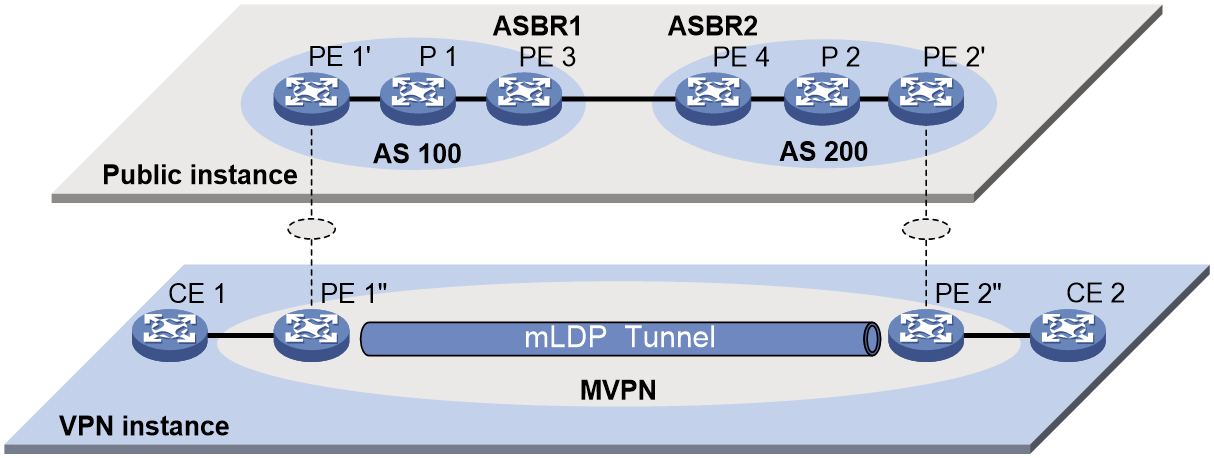
Inter-AS option B mLDP-based MVPN
As shown in Figure 4:
· A VPN instance spans AS 100 and AS 200.
· PE 3 and PE 4 are the ASBRs for AS 100 and AS 200, respectively.
· PE 3 and PE 4 are interconnected through MP-EBGP and treat each other as a P device.
· PE 3 and PE 4 advertise VPN-IPv4 routes to each other through MP-EBGP.
Figure 4 Inter-AS option B mLDP-based MVPN
To implement inter-AS option B mLDP-based MVPN, only one MVPN needs to be established across all ASs. VPN multicast data is transmitted across the ASs through this MVPN.
Multicast packets of the VPN instance are transmitted as follows:
1. Upon receiving a multicast packet of a multicast group in the VPN instance, CE 1 advertises the RP information for this group to PE 1 as follows:
¡ If the RP is PE 1, CE 1 directly sends a register message to PE 1 to advertise the RP information.
¡ If the RP is CE 1 or CE 2, CE 1 advertises the RP information to PE 1 through MSDP or Anycast-RP depending on the actual configuration.
2. PE 1 sends a Source Active A-D route to PE 3, PE 4, and PE 2 through BGP.
3. PE 2 sends a C-multicast route to join the multicast group if it has a receiver attached. The C-multicast route will be advertised to PE 4, PE 3, and PE 1 through BGP.
4. Upon receiving the C-multicast route, PE 1 encapsulates the multicast packet into an MPLS packet and then sends the packet to PE 2 through the mLDP tunnel.
5. PE 2 decapsulates the MPLS packet and then sends the multicast packet to CE 2.
Inter-AS option C mLDP-based MVPN
As shown in Figure 5:
· A VPN instance spans AS 100 and AS 200.
· PE 3 and PE 4 are the ASBRs for AS 100 and AS 200, respectively.
· PE 3 and PE 4 are interconnected through MP-EBGP and treat each other as a P device.
· PEs in different ASs establish a multihop MP-EBGP session to advertise VPN-IPv4 routes to each other.
Figure 5 Inter-AS option C mLDP-based MVPN
To implement inter-AS option C mLDP-based MVPN, only one MVPN needs to be created cross all ASs. Multicast data is transmitted across the ASs through this MVPN.
Multicast packets of the VPN instance are delivered as follows:
1. Upon receiving a multicast packet of a multicast group in the VPN instance, CE 1 advertises the RP information for this group to PE 1 as follows:
¡ If the RP is PE 1, CE 1 directly sends a register message to PE 1 to advertise the RP information.
¡ If the RP is CE 1 or CE 2, CE 1 advertises the RP information to PE 1 through MSDP or Anycast-RP depending on the actual configuration.
2. PE 1 sends a source-active A-D route to PE 2 through BGP.
3. PE 2 sends a C-multicast route to join the multicast group if it has a receiver attached. The C-multicast route will be advertised to PE 1 through BGP.
4. PE 1 encapsulates the multicast packet into an MPLS packet and then sends the packet to PE 2 through the mLDP tunnel.
5. PE 2 decapsulates the MPLS packet and then sends the multicast packet to CE 2.
mLDP-based MVPN tasks at a glance
To configure mLDP-based MVPN, perform the following tasks on PEs:
1. Enabling IP multicast routing for a VPN instance
2. Configuring BGP IPv4 MVPN route exchange
3. Configuring BGP IPv6 MVPN route exchange
6. Creating an mLDP-based MVPN instance
7. Creating an MVPN IPv4 address family
8. Specifying the MVPN source interface
9. Enabling inclusive tunnel creation
10. (Optional.) Enabling selective tunnel creation
11. (Optional.) Setting the tunnel switchover delay
12. (Optional.) Enabling inter-AS auto-discovery
Configuring mLDP-based MVPN
Prerequisites for configuring mLDP-based MVPN
Before you configure mLDP-based MVPN, complete the following tasks:
· Configure a unicast routing protocol on the public network.
· Configure MPLS LDP on the public network.
· Configure BGP to enable PEs to mutually establish neighbor relationship.
Enabling IP multicast routing for a VPN instance
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a VPN instance and enter its view.
ip vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
For more information about this command, see MPLS L3VPN commands in MPLS Command Reference.
3. Configure an RD for the VPN instance.
route-distinguisher route-distinguisher
For more information about this command, see MPLS L3VPN commands in MPLS Command Reference.
4. Return to system view.
quit
5. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
6. Associate the interface with the VPN instance.
ip binding vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
By default, an interface is associated with no VPN instance and belongs to the public network.
For more information about this command, see MPLS L3VPN commands in MPLS Command Reference.
7. Return to system view.
quit
8. Enable IP multicast routing for the VPN instance and enter MRIB view of the VPN instance.
IPv4:
multicast routing vpn-instance vpn-instance-name
By default, IP multicast routing is disabled for a VPN instance.
For more information about the commands, see multicast routing and forwarding commands in IP Multicast Command Reference.
Configuring BGP IPv4 MVPN route exchange
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter BGP instance view.
bgp as-number [ instance instance-name ]
3. Specify a BGP MVPN peer and its AS number.
peer ipv4-address as-number as-number
4. Enter BGP IPv4 MVPN address family view.
address-family ipv4 mvpn
5. Enable BGP to exchange IPv4 unicast routing information with BGP peers.
peer ipv4-address enable
By default, BGP cannot exchange IPv4 unicast routing information with BGP peers.
For more information about this command, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
6. (Optional.) Specify the maximum number of routes that a router can receive from a peer or peer group.
peer { group-name | ipv4-address [ mask-length ] } route-limit prefix-number [ { alert-only | discard | reconnect reconnect-time } | percentage-value ] *
By default, the number of routes that a router can receive from a peer or peer group is not limited.
For more information about this command, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
7. (Optional.) Configure the BGP Additional Paths feature.
a. Configure the BGP Additional Paths capabilities.
peer { group-name | ipv4-address [ mask-length ] | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] } additional-paths { receive | send } *
By default, no BGP Additional Paths capabilities are configured
b. Set the maximum number of Add-Path optimal routes that can be advertised to a peer or peer group.
peer { group-name | ipv4-address [ mask-length ] | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] } advertise additional-paths best number
By default, a maximum number of one Add-Path optimal route can be advertised to a peer or peer group.
c. Set the maximum number of Add-Path optimal routes that can be advertised to all peers.
additional-paths select-best best-number
By default, a maximum number of one Add-Path optimal route can be advertised to all peers.
For more information about the commands in this step, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
8. (Optional.) Advertise the COMMUNITY or Large Community attribute to a peer or peer group.
¡ Advertise the COMMUNITY attribute to a peer or peer group.
peer { group-name | ipv4-address [ mask-length ] } advertise-community
By default, the COMMUNITY attribute advertisement to a peer or peer group is disabled.
¡ Advertise the Large Community attribute to a peer or peer group.
peer { group-name | ipv4-address [ mask-length ] } advertise-large-community
By default, the Large Community attribute advertisement to a peer or peer group is disabled.
For more information about the commands in this step, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
9. (Optional.) Disable route target filtering of received BGP IPv4 MVPN routes.
undo policy vpn-target
By default, a PE device filters route targets for received BGP IPv4 MVPN routes.
10. (Optional.) Set the optimal route selection delay timer.
route-select delay delay-value
By default, the optimal route selection delay timer is 0 seconds, which means optimal route selection is not delayed.
For more information about this command, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
11. Prefer routes learned from the specified peer or peer group during optimal route selection.
peer { group-name | ipv4-address [ mask-length ] | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] } high-priority [ preferred ]
By default, BGP does not prefer routes learned from any peer or peer groups during optimal route selection.
For more information about this command, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
12. (Optional.) Prefer BGP routes of a specific next hop IP type during optimal route selection.
bestroute nexthop-priority { ipv4 | ipv6 } [ preferred ]
By default, BGP prefers routes with IPv4 next hops during optimal route selection.
For more information about this command, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
Configuring BGP IPv6 MVPN route exchange
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter BGP instance view.
bgp as-number [ instance instance-name ]
3. Specify a BGP MVPN peer and its AS number.
peer ipv6-address as-number as-number
4. Enter BGP IPv6 MVPN address family view.
address-family ipv6 mvpn
5. Enable BGP to exchange IPv6 unicast routing information with dynamic BGP peers.
peer ipv4-address enable
By default, BGP cannot exchange IPv6 unicast routing information with dynamic BGP peers.
For more information about this command, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
6. (Optional.) Specify the maximum number of routes that a router can receive from a peer or peer group.
peer { group-name | ipv4-address [ mask-length ] } route-limit prefix-number [ { alert-only | discard | reconnect reconnect-time } | percentage-value ] *
By default, the number of routes that a router can receive from a peer or peer group is not limited.
For more information about this command, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
7. (Optional.) Configure the BGP Additional Paths feature.
a. Configure the BGP Additional Paths capabilities.
peer { group-name | ipv4-address [ mask-length ] | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] } additional-paths { receive | send } *
By default, no BGP Additional Paths capabilities are configured
b. Set the maximum number of Add-Path optimal routes that can be advertised to a peer or peer group.
peer { group-name | ipv4-address [ mask-length ] | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] } advertise additional-paths best number
By default, a maximum number of one Add-Path optimal route can be advertised to a peer or peer group.
c. Set the maximum number of Add-Path optimal routes that can be advertised to all peers.
additional-paths select-best best-number
By default, a maximum number of one Add-Path optimal route can be advertised to all peers.
For more information about the commands in this step, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
8. (Optional.) Advertise the COMMUNITY or Large Community attribute to a peer or peer group.
¡ Advertise the COMMUNITY attribute to a peer or peer group.
peer { group-name | ipv4-address [ mask-length ] } advertise-community
By default, the COMMUNITY attribute advertisement to a peer or peer group is disabled.
¡ Advertise the Large Community attribute to a peer or peer group.
peer { group-name | ipv4-address [ mask-length ] } advertise-large-community
By default, the Large Community attribute advertisement to a peer or peer group is disabled.
For more information about the commands in this step, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
9. (Optional.) Disable route target filtering of received BGP IPv6 MVPN routes.
undo policy vpn-target
By default, a PE device filters route targets for received BGP IPv6 MVPN routes.
10. (Optional.) Set the optimal route selection delay timer.
route-select delay delay-value
By default, the optimal route selection delay timer is 0 seconds, which means optimal route selection is not delayed.
For more information about this command, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
11. Prefer routes learned from the specified peer or peer group during optimal route selection.
peer { group-name | ipv4-address [ mask-length ] | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] } high-priority [ preferred ]
By default, BGP does not prefer routes learned from any peer or peer groups during optimal route selection.
For more information about this command, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
12. (Optional.) Prefer BGP routes of a specific next hop IP type during optimal route selection.
bestroute nexthop-priority { ipv4 | ipv6 } [ preferred ]
By default, BGP prefers routes with IPv4 next hops during optimal route selection.
For more information about this command, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
Allowing the device to add extended community attributes to C-multicast routes sent to BGP VPNv4 peers
About this task
The following BGP extended community attributes are used to identify the route originator of a BGP VPNv4 route:
· Source AS—Carries the number of AS where the MVPN source resides. The format of this attribute is 32-bit AS number:0, for example, 100:0.
· VRF Route Import—Carries the originating address and the VPN instance to which the BGP VPNv4 route belongs. The format of the attribute is 32-bit originating address:VPN instance index, for example, 192.168.122.15:1. The value of the originating address depends on the MVPN source interface configuration.
¡ If the source command is used to specify the MVPN source interface, the originating address is the IP address of the MVPN source interface.
¡ If the source command is not used, the originating address is the router ID of the BGP instance to which the device belongs.
Prerequisites
Before you perform this task, you must establish BGP VPNv4 peer relationship and BGP IPv4 MVPN neighbor relationship between the device and other devices.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter BGP instance view.
bgp as-number [ instance instance-name ]
3. Enter BGP VPNv4 address family view.
address-family vpnv4
For more information about this command, see BGP commands in Layer 3-IP Routing Command Reference.
4. Allow the device to add Source AS and VRF Route Import extended community attributes to routes sent to BGP VPNv4 peers.
mvpn-advertise-rt-import
By default, the device is disabled from adding Source AS and RF Route Import extended community attributes to routes sent to BGP VPNv4 peers.
Allowing the device to add extended community attributes to C-multicast routes sent to BGP VPNv6 peers
About this task
The following BGP extended community attributes are used to identify the route originator of a BGP VPNv6 route:
· Source AS—Carries the number of the AS where the MVPN source resides. The format of this attribute is 32-bit AS number:0, for example, 100:0.
· VRF Route Import—Carries the originating address and the VPN instance to which the BGP VPNv6 route belongs. The format of the attribute is 32-bit originating address:VPN instance index, for example, 192.168.122.15:1. The value of the originating address depends on the MVPN source interface configuration.
¡ If the source command is used to specify the MVPN source interface, the originating address is the IP address of the MVPN source interface.
¡ If the source command is not used, the originating address is the router ID of the BGP instance to which the device belongs.
Prerequisites
Before you perform this task, you must establish BGP VPNv6 peer relationship and BGP IPv6 MVPN neighbor relationship between the device and other devices.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter BGP instance view.
bgp as-number [ instance instance-name ]
3. Enter BGP VPNv6 address family view.
address-family vpnv6
For more information about this command, see BGP commands in Layer 3-IP Routing Command Reference.
4. Allow the device to add Source AS and VRF Route Import extended community attributes to routes sent to BGP VPNv6 peers.
mvpn-advertise-rt-import
By default, the device is disabled from adding Source AS and RF Route Import extended community attributes to routes sent to BGP VPNv6 peers.
Creating an mLDP-based MVPN instance
About this task
You can create one or more mLDP-based MVPN instances on a PE device.
A VPN instance supports only one MVPN mode.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create an mLDP-based MVPN instance and enter its view.
multicast-vpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name mode mldp
Creating an MVPN IPv4 address family
Restrictions and guidelines
Configurations in MVPN IPv4 address family view apply only to IPv4 multicast.
Configurations in MVPN IPv6 address family view apply only to IPv6 multicast.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter MVPN view.
multicast-vpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name mode mldp
3. Create an MVPN address family and enter its view.
IPv4:
address-family ipv4
IPv6:
address-family ipv6
Specifying the MVPN source interface
About this task
An mLDP tunnel uses the IP address of the MVPN source interface as the source address to encapsulate multicast packets from the private network.
Restrictions and guidelines
For the PE to obtain correct routing information, you must specify the interface used for establishing BGP peer relationship as the MVPN source interface.
For an MVPN that transmits both IPv4 and IPv6 multicast packets, you must specify the same MVPN source interface in MVPN IPv4 and IPv6 address family views.
The MVPN source interface can be configured to borrow the IP address of a loopback interface. As a best practice, specify the mask length for the loopback interface address as 32.
To use IP unnumbered, you must also configure OSPF, IS-IS, and LLDP. For information about configuring OSPF, IS-IS, and LLDP, see "Configuring PIM."
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter MVPN view.
multicast-vpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name mode mldp
3. Enter MVPN address family view.
IPv4:
address-family ipv4
IPv6:
address-family ipv6
4. Specify the MVPN source interface.
source interface-type interface-number
By default, no MVPN source interface is specified.
Enabling inclusive tunnel creation
Restrictions and guidelines
Once created, the inclusive tunnel always exists no matter whether multicast traffic is present or not.
Only one inclusive tunnel can be established between two PEs in an MVPN.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter MVPN view.
multicast-vpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name mode mldp
3. Enter MVPN address family view.
IPv4:
address-family ipv4
IPv6:
address-family ipv6
4. Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation.
inclusive-tunnel dynamic
By default, dynamic inclusive tunnel creation is disabled.
Enabling selective tunnel creation
About this task
Multicast traffic that matches the tunnel switchover criterion is switched over to selective tunnels from the inclusive tunnel after selective tunnel are created.
Restrictions and guidelines
Selective tunnels are created only after the multicast traffic is transmitted over the inclusive tunnel.
Multicast packets for multiple (S, G) entries can share the same selective tunnel.
Multiple selective tunnels can be created between two PEs in an MVPN. These selective tunnels are independent from one another.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter MVPN view.
multicast-vpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name mode mldp
3. Enter MVPN address family view.
IPv4:
address-family ipv4
IPv6:
address-family ipv6
4. Enable dynamic selective tunnel creation.
MVPN IPv4 address family:
selective-tunnel dynamic [ acl { acl ipv4-acl-number | name ipv4-acl-name } ]
MVPN IPv6 address family:
selective-tunnel dynamic [ acl { ipv6-acl-number | name ipv6-acl-name } ]
By default, dynamic selective tunnel creation is disabled.
Setting the tunnel switchover delay
About this task
To avoid multicast data loss during tunnel switchover, adjust the delay time for multicast data to switch over from the inclusive tunnel to selective tunnels.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter MVPN view.
multicast-vpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name mode mldp
3. Enter MVPN address family view.
IPv4:
address-family ipv4
IPv6:
address-family ipv6
4. Set the tunnel switchover delay.
selective-tunnel delay delay
By default, the tunnel switchover delay is 3 seconds.
Enabling inter-AS auto-discovery
About this task
This feature inhibits the device from carrying the NO_EXPORT attribute in intra-AS A-D routes and S-PMSI A-D routes sent to BGP. Use this feature on the multicast source-side PE in an inter-AS MVPN scenario so that these routes can be discovered on the devices out of the local AS.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter MVPN view.
multicast-vpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name mode mldp
3. Enter MVPN address family view.
IPv4:
address-family ipv4
IPv6:
address-family ipv6
4. Enable inter-AS auto-discovery.
auto-discovery inter-as
By default, inter-AS auto-discovery is disabled.
Display and maintenance commands for mLDP-based MVPN
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
|
|
Display BGP MVPN peer group information. |
display bgp [ instance instance-name ] group ipv4 mvpn [ group-name group-name ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] group ipv6 mvpn [ group-name group-name ] |
|
|
|
Display information about BGP MVPN peers or peer groups. |
display bgp [ instance instance-name ] peer ipv4 mvpn [ ip-address mask-length | { ip-address | group-name group-name } log-info | [ ip-address ] verbose ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] peer ipv6 mvpn [ ip-address mask-length | { ip-address | group-name group-name } log-info | [ ip-address ] verbose ] |
|
|
|
Display information about BGP IPv4 MVPN routes. |
display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv4 mvpn [ { public | route-distinguisher route-distinguisher } [ route-type { intra-as I inter-as | s-pmsi | leaf | source-active | shared-tree | source-tree } ] [ mvpn-prefix ] | statistics ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv4 mvpn [ public | route-distinguisher route-distinguisher ] [ mvpn-prefix [ advertise-info ] ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv4 mvpn [ route-type { intra-as I inter-as | s-pmsi | leaf | source-active | shared-tree | source-tree } [ statistics ] ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv4 mvpn peer ip-address { advertised-routes | received-routes } [ mvpn-prefix [ verbose ] | statistics ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv4 mvpn { as-path-acl { as-path-acl-number | as-path-acl-name } | as-path-regular-expression regular-expression } display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv4 mvpn { public | route-distinguisher route-distinguisher } route-type { inter-as | intra-as | leaf | s-pmsi | shared-tree | source-active | source-tree } time-range min-time max-time |
|
|
|
Display information about BGP IPv6 MVPN routes. |
display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv6 mvpn [ { public | route-distinguisher route-distinguisher } [ route-type { inter-as |intra-as | leaf | s-pmsi | shared-tree | source-active | source-tree } ] [ mvpn-prefix ] | statistics ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv6 mvpn [ public | route-distinguisher route-distinguisher ] [ mvpn-prefix [ advertise-info ] ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv6 mvpn [ route-type { inter-as |intra-as | leaf | s-pmsi | shared-tree | source-active | source-tree } [ statistics ] ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv6 mvpn peer { ipv4-address | ipv6-address } { advertised-routes | received-routes } [ mvpn-prefix [ verbose ] | statistics ] display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv6 mvpn { as-path-acl { as-path-acl-number | as-path-acl-name } | as-path-regular-expression regular-expression } display bgp [ instance instance-name ] routing-table ipv6 mvpn { public | route-distinguisher route-distinguisher } route-type { inter-as | intra-as | leaf | s-pmsi | shared-tree | source-active | source-tree } time-range min-time max-time |
|
|
|
Display the contents of the Source AS and VRF Route Import extended community attributes added to BGP routes. |
display bgp [ instance instance-name ] { ipv4 | ipv6 } route-target mvpn |
|
|
|
Display information about C-multicast A-D routes for RSVP-TE-based MVPN. |
display multicast-vpn { vpn-instance vpn-instance-name| public-instance } [ ipv6 ] c-multicast routing-table [ group-address [ mask { mask-length | mask } ] | source-address [ mask { mask-length | mask } ] | outgoing-interface { exclude | include | match } interface-type interface-number ] |
|
|
|
Display information about the inclusive tunnel for a VPN instance. |
display multicast-vpn { vpn-instance vpn-instance-name | public-instance } [ ipv6 ] inclusive-tunnel { local | remote } |
|
|
|
Display information about selective tunnels for a VPN instance. |
display multicast-vpn { vpn-instance vpn-instance-name | public-instance } [ ipv6 ] selective-tunnel { local [ interface interface-type interface-number ] | remote } |
||
|
Reset BGP sessions for BGP IPv4 MVPN address family. |
reset bgp [ instance instance-name ] { as-number | ipv4-address [ mask-length ] | all | external | group group-name | internal } ipv4 mvpn reset bgp [ instance instance-name ] ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] ipv4 mvpn |
|
|
|
Reset BGP sessions for BGP IPv6 MVPN address family. |
reset bgp [ instance instance-name ] { as-number | ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] | all | external | group group-name | internal } ipv6 mvpn reset bgp [ instance instance-name ] ipv4-address [ mask-length ] ipv6 mvpn |
|
|
For more information about the display bgp group, display bgp peer, display bgp update-group, and reset bgp commands, see BGP commands in Layer 3—IP Routing Command Reference.
mLDP-based MVPN configuration examples
Example: Configuring intra-AS mLDP-based MVPN
Network configuration
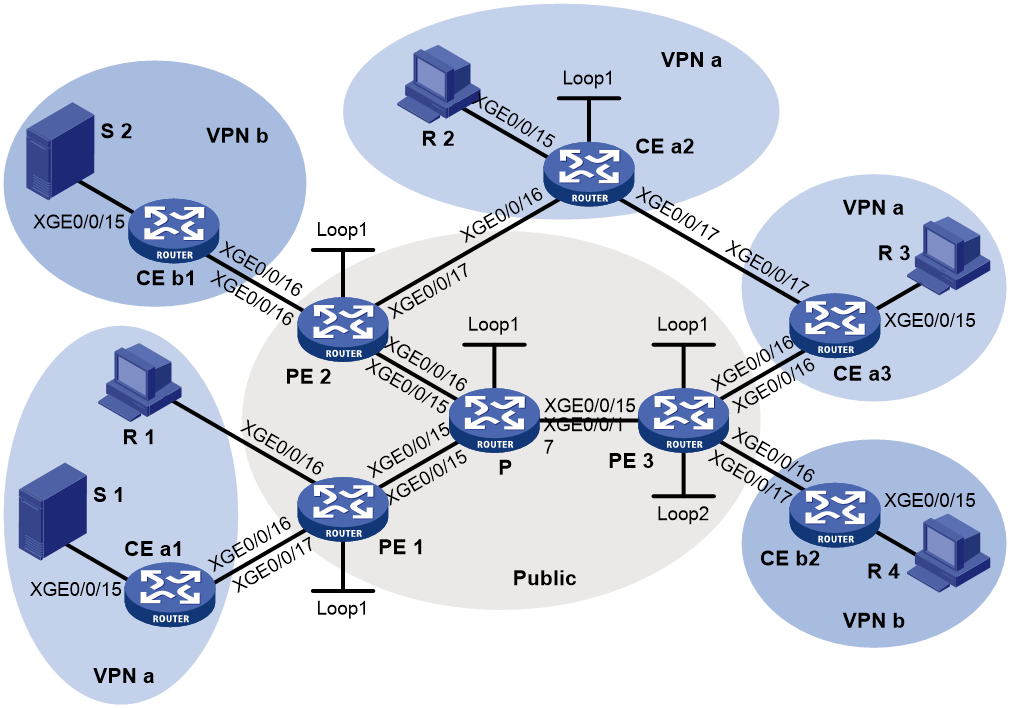
As shown in Figure 6, configure intra-AS mLDP-based MVPN to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
· In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 1, R 2, and R 3 are receivers. · In VPN instance b, S 2 is a multicast source, and R 4 is a receiver. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 and Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 belong to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance b. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 3: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 and Loopback 2 belong to VPN instance b. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and MPLS |
· Configure OSPF on the public network, and configure RIP between the PEs and the CEs. · Establish BGP peer connections between PE 1, PE 2, and PE 3 on their respective Loopback 1. · Configure MPLS LDP on the public network. |
|
IP multicast routing |
· Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1, PE 2, and PE 3. · Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b on PE 2 and PE 3. · Enable IP multicast routing on CE a1, CE a2, CE a3, CE b1, and CE b2. |
|
IGMP |
· Enable IGMPv2 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 of PE 1. · Enable IGMPv2 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE a2, CE a3, and CE b2. |
|
PIM |
· Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on PE 1, PE 2, and PE 3. · Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on CE a1, CE a2, CE a3, CE b1, and CE b2. · Configure Loopback 1 of CE a2 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a to provide services for all multicast groups. · Configure Loopback 2 of PE 3 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance b to provide services for all multicast groups. |
|
MSDP |
· Enable MSDP on CE a2, and specify Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 as the local MSDP connection interface. · Enable MSDP on PE 2 for VPN instance a, and specify Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 as the local MSDP connection interface. |
Table 1 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
10.110.7.2/24 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/15 |
192.168.8.1/24 |
|
S 2 |
— |
10.110.8.2/24 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.5.1/24 |
|
R 1 |
— |
10.110.1.2/24 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10.110.6.1/24 |
|
R 2 |
— |
10.110.9.2/24 |
PE 3 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.3/32 |
|
R 3 |
— |
10.110.10.2/24 |
PE 3 |
Loop2 |
33.33.33.33/32 |
|
R 4 |
— |
10.110.11.2/24 |
CE a1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.110.7.1/24 |
|
P |
XGE0/0/15 |
192.168.6.2/24 |
CE a1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.2.2/24 |
|
P |
XGE0/0/16 |
192.168.7.2/24 |
CE a2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.110.9.1/24 |
|
P |
XGE0/0/17 |
192.168.8.2/24 |
CE a2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.4.2/24 |
|
P |
Loop1 |
2.2.2.2/32 |
CE a2 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10.110.12.1/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
192.168.6.1/24 |
CE a2 |
Loop1 |
22.22.22.22/32 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.1.1/24 |
CE a3 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.110.10.1/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10.110.2.1/24 |
CE a3 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.5.2/24 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.1/32 |
CE a3 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10.110.12.2/24 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
192.168.7.1/24 |
CE b1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.110.8.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.3.1/24 |
CE b1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.3.2/24 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10.110.4.1/24 |
CE b2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.110.11.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.2/32 |
CE b2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.110.6.2/24 |
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable MPLS LDP and mLDP P2MP globally.
[PE1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1] mpls ldp
[PE1-ldp] mldp p2mp
[PE1-ldp] quit
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing in VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 192.168.6.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable IGMP on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.1.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] igmp enable
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 10.110.2.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.2 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.2 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.3 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.3 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1.1.1.2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1.1.1.3 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.3 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route rip 2
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[PE1] ospf 1
[PE1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE1-ospf-1] quit
# Configure RIP.
[PE1] rip 2 vpn-instance a
[PE1-rip-2] network 10.110.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-rip-2] network 10.110.2.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-rip-2] import-route bgp
[PE1-rip-2] quit
2. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 1.1.1.2
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable MPLS LDP and mLDP P2MP globally.
[PE2] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.2
[PE2] mpls ldp
[PE2-ldp] mldp p2mp
[PE2-ldp] quit
# Create a VPN instance named b, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance b
[PE2-vpn-instance-b] route-distinguisher 200:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b.
[PE2] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib-a] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance b.
[PE2] multicast-vpn vpn-instance b mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance b.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance b.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation and dynamic selective tunnel creation for VPN instance b.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] quit
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib-a] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 192.168.7.1 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance b, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance b
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.3.1 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 10.110.4.1 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.2 32
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.3 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.3 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1.1.1.1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1.1.1.3 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.3 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route rip 2
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance b
[PE2-bgp-default-b] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route rip 3
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-b] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-b] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[PE2] ospf 1
[PE2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.2 0.0.0.0
[PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.7.0 0.0.0.255
[PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE2-ospf-1] quit
# Configure RIP.
[PE2] rip 2 vpn-instance a
[PE2-rip-2] network 10.110.4.0 0.0.0.255
[PE2-rip-2] import-route bgp
[PE2-rip-2] quit
[PE2] rip 3 vpn-instance b
[PE2-rip-3] network 10.110.3.0 0.0.0.255
[PE2-rip-3] import-route bgp
[PE2-rip-3] quit
3. Configure PE 3:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE3> system-view
[PE3] router id 1.1.1.3
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable MPLS LDP and mLDP P2MP globally.
[PE3] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.3
[PE3] mpls ldp
[PE3-ldp] mldp p2mp
[PE3-ldp] quit
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE3] ip vpn-instance a
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a.
[PE3] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE3-mrib-a] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE3] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Create a VPN instance named b, and configure an RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE3] ip vpn-instance b
[PE3-vpn-instance-b] route-distinguisher 200:1
[PE3-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity
[PE3-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity
[PE3-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b.
[PE3] multicast routing vpn-instance b
[PE3-mrib-b] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance b.
[PE3] multicast-vpn vpn-instance b mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance b.
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance b.
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] source loopback 1
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] quit
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 192.168.8.1 24
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.5.1 24
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance b, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip binding vpn-instance b
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 10.110.6.1 24
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[PE3] interface loopback 1
[PE3-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.3 32
[PE3-LoopBack1] quit
# Associate Loopback 2 with VPN instance b, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE3] interface loopback 2
[PE3-LoopBack2] ip binding vpn-instance b
[PE3-LoopBack2] ip address 33.33.33.33 32
[PE3-LoopBack2] pim sm
[PE3-LoopBack2] quit
# Configure Loopback 2 as a C-BSR and a C-RP.
[PE3] pim vpn-instance b
[PE3-pim-b] c-bsr 33.33.33.33
[PE3-pim-b] c-rp 33.33.33.33
[PE3-pim-b] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE3] bgp 100
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.2 as-number 100
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.2 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1.1.1.1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1.1.1.2 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.2 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE3–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE3-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route rip 2
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE3-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE3–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance b
[PE3-bgp-default-b] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route rip 3
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route direct
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-b] quit
[PE3-bgp-default-b] quit
[PE3–bgp-default] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[PE3] ospf 1
[PE3-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.3 0.0.0.0
[PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.8.0 0.0.0.255
[PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE3-ospf-1] quit
# Configure RIP.
[PE3] rip 2 vpn-instance a
[PE3-rip-2] network 10.110.5.0 0.0.0.255
[PE3-rip-2] import-route bgp
[PE3-rip-2] quit
[PE3] rip 3 vpn-instance b
[PE3-rip-3] network 10.110.6.0 0.0.0.255
[PE3-rip-3] network 33.33.33.33 0.0.0.0
[PE3-rip-3] import-route bgp
[PE3-rip-3] quit
4. Configure P:
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable MPLS LDP and mLDP P2MP globally.
<P> system-view
[P] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2
[P] mpls ldp
[P-ldp] mldp p2mp
[P-ldp] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[P] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 192.168.6.2 24
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[P] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 192.168.7.2 24
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls enable
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls ldp enable
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[P] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 192.168.8.2 24
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] mpls enable
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] mpls ldp enable
[P-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[P] interface loopback 1
[P-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.2 32
[P-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[P] ospf 1
[P-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
[P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255
[P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.7.0 0.0.0.255
[P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.8.0 0.0.0.255
[P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[P-ospf-1] quit
5. Configure CE a1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEa1> system-view
[CEa1] multicast routing
[CEa1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.110.7.1 24
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.2.2 24
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure RIP.
[CEa1] rip 2
[CEa1-rip-2] network 10.110.2.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa1-rip-2] network 10.110.7.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa1-rip-2] quit
6. Configure CE b1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEb1> system-view
[CEb1] multicast routing
[CEb1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.110.8.1 24
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.3.2 24
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure RIP.
[CEb1] rip 3
[CEb1-rip-3] network 10.110.3.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb1-rip-3] network 10.110.8.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb1-rip-2] quit
7. Configure CE a2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEa2> system-view
[CEa2] multicast routing
[CEa2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IGMP on the interface.
[CEa2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.110.9.1 24
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.4.2 24
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 10.110.12.1 24
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa2] interface loopback 1
[CEa2-LoopBack1] ip address 22.22.22.22 32
[CEa2-LoopBack1] pim sm
[CEa2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure Loopback 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP.
[CEa2] pim vpn-instance a
[CEa2-pim] c-bsr 22.22.22.22
[CEa2-pim] c-rp 22.22.22.22
[CEa2-pim] quit
# Configure MSDP.
[CEa2] msdp
[CEa2-msdp] peer 10.110.4.1 connect-interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEa2-msdp] quit
# Configure RIP.
[CEa2] rip 2
[CEa2-rip-2] network 10.110.4.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa2-rip-2] network 10.110.9.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa2-rip-2] network 10.110.12.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa2-rip-2] network 22.22.22.22 0.0.0.0
[CEa2-rip-2] quit
8. Configure CE a3:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEa3> system-view
[CEa3] multicast routing
[CEa3-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IGMP on the interface.
[CEa3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEa3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.110.10.1 24
[CEa3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CEa3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEa3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.5.2 24
[CEa3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEa3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[CEa3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 10.110.12.2 24
[CEa3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[CEa3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Configure RIP.
[CEa3] rip 2
[CEa3-rip-2] network 10.110.5.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa3-rip-2] network 10.110.10.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa3-rip-2] network 10.110.12.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa3-rip-2] quit
9. Configure CE b2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEb2> system-view
[CEb2] multicast routing
[CEb2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IGMP on the interface.
[CEb2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.110.11.1 24
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.110.6.2 24
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure RIP.
[CEb2] rip 3
[CEb2-rip-3] network 10.110.6.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb2-rip-3] network 10.110.11.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb2-rip-2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about the mLDP inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: mLDP
Tunnel interface: LSPVOif0
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000000>
Tunnel state: Up
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000000
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: 1.1.1.2
2: 1.1.1.3
# Display information about mLDP selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnel in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: mLDP
Tunnel interface: LSPVOif1
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000001>
Tunnel state: Up
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000001
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
# Display C-multicast A-D route information for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a c-multicast routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(10.110.7.2, 225.0.0.1)
CreateTime: 02:54:43
Tunnel Information: LSPVOif1
# Display information about the mLDP inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 2.
[PE2] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel remote
Tunnel interface: --
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000000>
Tunnel state: --
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000000
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: 1.1.1.2 (local)
# Display information about mLDP selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 2.
[PE2] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel remote
Tunnel interface: --
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000001>
Tunnel state: --
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000001
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: 1.1.1.2 (local)
# Display information about the mLDP inclusive tunnel for VPN instance b on PE 2.
[PE2] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: mLDP
Tunnel interface: LSPVOif0
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000000>
Tunnel state: Up
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000000
Root: 1.1.1.2 (local)
Leafs:
1: 1.1.1.1
2: 1.1.1.3
# Display information about mLDP selective tunnels for VPN instance b on PE 2.
[PE2] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnel in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: mLDP
Tunnel interface: LSPVOif1
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000001>
Tunnel state: Up
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000001
Root: 1.1.1.2 (local)
# Display C-multicast A-D route information for VPN instance b on PE 2.
[PE2] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b c-multicast routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(10.110.8.2, 225.0.0.2)
CreateTime: 02:54:43
Tunnel Information: LSPVOif1
# Display information about the mLDP inclusive tunnel for VPN instance b on PE 3.
[PE3] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b inclusive-tunnel remote
Tunnel interface: --
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000000>
Tunnel state: --
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000000
Root: 1.1.1.2
Leaf:
1: 1.1.1.3 (local)
# Display information about mLDP selective tunnels for VPN instance b on PE 3.
[PE3] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b selective-tunnel remote
Tunnel interface: --
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000001>
Tunnel state: --
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000001
Root: 1.1.1.2
Leaf:
1: 1.1.1.3 (local)
Example: Configuring inter-AS option A mLDP-based MVPN
Network configuration
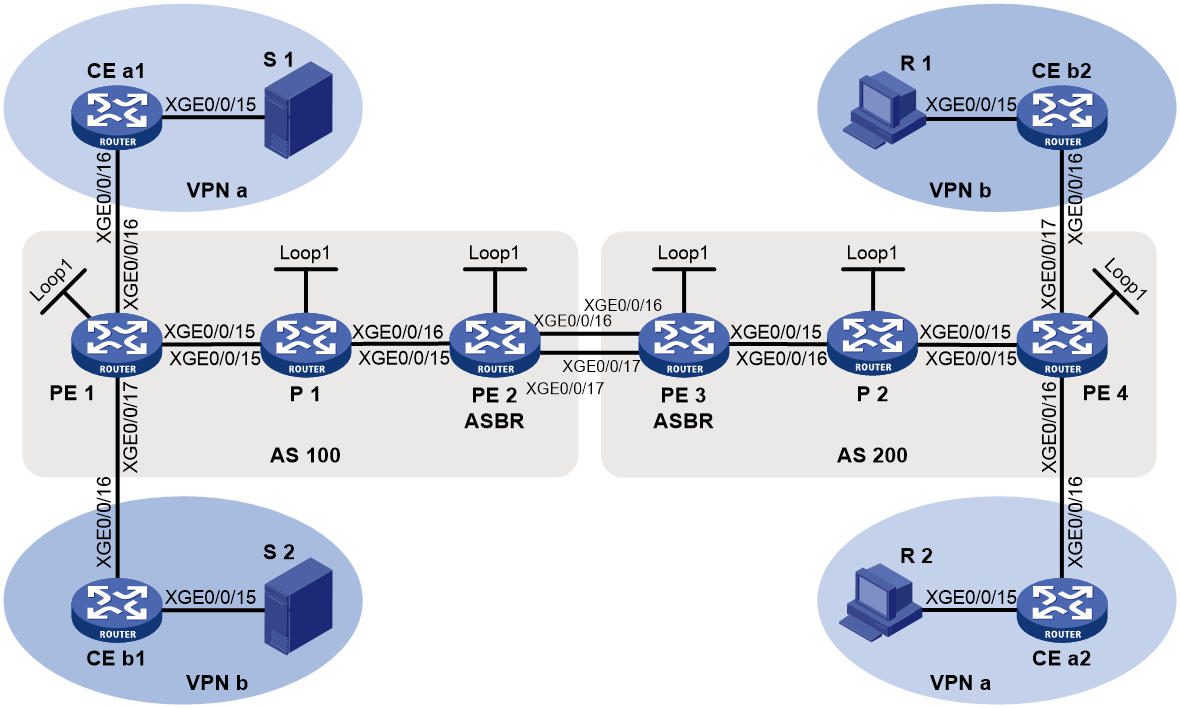
As shown in Figure 7, configure inter-AS option A mLDP-based MVPN to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
· In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 2 is a receiver. · In VPN instance b, S 2 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 belongs to VPN instance b. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 belongs to VPN instance b. · PE 3: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 belongs to VPN instance b. · PE 4: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 belongs to VPN instance b. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and MPLS |
· Configure OSPF in AS 100 and AS 200, and configure OSPF between the PEs and CEs. · Establish IBGP peer connections between PE 1, PE 2, PE 3, and PE 4 on their respective Loopback 1. · Establish EBGP peer connections between Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 on PE 2 and PE 3. · Configure BGP IPv4 MVPN peer connections between PE 1, PE 2, PE 3, and PE 4 on their respective Loopback 1. · Configure MPLS in AS 100 and AS 200. · Enable MPLS on P 1 and P 2. |
|
IP multicast routing |
· Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1 and PE 4. · Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b on PE 1 and PE 4. · Enable IP multicast routing on CE a1, CE a2, CE b1, and CE b2. |
|
IGMP |
· Enable IGMPv2 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE a2. · Enable IGMPv3 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE b2. |
|
PIM |
Enable PIM-SM for VPN instances a and b: · Enable PIM-SM on all private network interfaces of PE 1 and PE 4. · Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on CE a1, CE a2, CE b1, and CE b2. · Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 of CE a1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a in AS 100 to provide services for all multicast groups. · Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 of CE b1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance b in AS 200 to provide services for all multicast groups. |
|
MSDP |
Enable MSDP on CE a1, and specify Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 as the local MSDP connection interface. Enable MSDP on CE a2, and specify Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 as the local MSDP connection interface. |
Table 2 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
12.1.1.100/24 |
R 1 |
— |
12.4.1.100/24 |
|
S 2 |
— |
12.2.1.100/24 |
R 2 |
— |
12.3.1.100/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.4.1.1/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.1.1.1/24 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.3.1.2/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/17 |
11.2.1.1/24 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10.6.1.2/24 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.1/32 |
PE 3 |
Loop1 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.2.1.2/24 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.5.1.2/24 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.3.1.1/24 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.3.1.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/17 |
10.6.1.1/24 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/17 |
11.4.1.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
2.2.2.2/32 |
PE 4 |
Loop1 |
4.4.4.4/24 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.5.1.1/24 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.2.1.1/24 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.4.1.2/24 |
|
P 1 |
Loop1 |
5.5.5.5/32 |
P 2 |
Loop1 |
6.6.6.6/32 |
|
CE a1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.1.1.1/24 |
CE b1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.2.1.1/24 |
|
CE a1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.1.1.2/24 |
CE b1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.2.1.2/24 |
|
CE a2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.3.1.1/24 |
CE b2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.4.1.1/24 |
|
CE a2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.3.1.2/24 |
CE b2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.4.1.2/24 |
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
[PE1] quit
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable LDP and mLDP P2MP globally.
[PE1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1] mpls ldp
[PE1-ldp] mldp p2mp
[PE1-ldp] quit
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure the RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation, dynamic selective tunnel creation, and inter-AS auto-discovery for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Create a VPN instance named b, and configure the RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance b
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] route-distinguisher 200:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance b
[PE1-mrib-b] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance b.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance b mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance b.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance b.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation, dynamic selective tunnel creation, and inter-AS auto-discovery for VPN instance b.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.1.1.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.1.1.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance b, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip binding vpn-instance b
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 11.2.1.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 2.2.2.2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2.2.2.2 enable
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2.2.2.2 next-hop-local
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route ospf 2
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance b
[PE1-bgp-default-b] address-family ipv4
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route ospf 3
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-b] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[PE1] ospf 1
[PE1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE1-ospf-1] quit
[PE1] ospf 2 vpn-instance a
[PE1-ospf-2] area 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE1-ospf-2] quit
[PE1] ospf 3 vpn-instance b
[PE1-ospf-3] area 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE1-ospf-3] quit
2. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 2.2.2.2
[PE2] quit
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable LDP and mLDP P2MP globally.
[PE2] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2
[PE2] mpls ldp
[PE2-ldp] mldp p2mp
[PE2-ldp] quit
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure the RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE2-mrib-a] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE2] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic
# Enable dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Create a VPN instance named b, and configure the RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance b
[PE2-vpn-instance-b] route-distinguisher 200:1
[PE2-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity
[PE2-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b.
[PE2] multicast routing vpn-instance b
[PE2-mrib-b] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance b.
[PE2] multicast-vpn vpn-instance b mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance b.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance b.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic
# Enable dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] quit
[PE2-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.2.1.2 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, and assign an IP address to the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.3.1.1 24
# Enable PIM-SM on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and configure the interface as a PIM-SM domain border.
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim bsr-boundary
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance b, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip binding vpn-instance b
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 10.6.1.1 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.2 32
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1.1.1.1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.1 next-hop-local
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE2-bgp-default-a] peer 10.3.1.2 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] peer 10.3.1.2 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance b
[PE2-bgp-default-b] peer 10.6.1.2 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default-b] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route direct
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-b] peer 10.6.1.2 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4-b] quit
[PE2-bgp-default-b] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[PE2] ospf 1
[PE2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
[PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE2-ospf-1] quit
3. Configure PE 3:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE3> system-view
[PE3] router id 3.3.3.3
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable LDP and mLDP P2MP globally.
[PE3] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3
[PE3] mpls ldp
[PE3-ldp] mldp p2mp
[PE3-ldp] quit
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure the RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE3] ip vpn-instance a
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 300:1
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE3-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a.
[PE3] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE3-mrib-a] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE3] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation, dynamic selective tunnel creation, and inter-AS auto-discovery for VPN instance a.
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Create a VPN instance named b, and configure the RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE3] ip vpn-instance b
[PE3-vpn-instance-b] route-distinguisher 400:1
[PE3-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity
[PE3-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity
[PE3-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b.
[PE3] multicast routing vpn-instance b
[PE3-mrib-b] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance b.
[PE3] multicast-vpn vpn-instance b mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance b.
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance b.
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation, dynamic selective tunnel creation, and inter-AS auto-discovery for VPN instance b.
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] quit
[PE3-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.4.1.1 24
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, and assign an IP address to the interface
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.3.1.2 24
# Enable PIM-SM on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and configure the interface as a PIM-SM domain border.
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim bsr-boundary
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance b, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.3.1.2 24
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[PE3] interface loopback 1
[PE3-LoopBack1] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[PE3-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE3] bgp 200
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 4.4.4.4 as-number 200
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 4.4.4.4 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 4.4.4.4 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4.4.4.4 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4.4.4.4 next-hop-local
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE3-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE3-bgp-default-a] peer 10.3.1.1 as-number 100
[PE3-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] peer 10.3.1.1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE3-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE3-bgp-default] ip vpn-instance b
[PE3-bgp-default-b] peer 10.6.1.1 as-number 100
[PE3-bgp-default-b] address-family ipv4 unicast
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route direct
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-b] peer 10.6.1.1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4-b] quit
[PE3-bgp-default-b] quit
[PE3–bgp-default] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[PE3] ospf 1
[PE3-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
[PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE3-ospf-1] quit
4. Configure PE 4:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE4> system-view
[PE4] router id 4.4.4.4
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable LDP and mLDP P2MP globally.
[PE4] mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.4
[PE4] mpls ldp
[PE4-ldp] mldp p2mp
[PE4-ldp] quit
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure the RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE4] ip vpn-instance a
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 300:1
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a.
[PE4] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE4-mrib-a] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE4] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Create a VPN instance named b, and configure the RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE4] ip vpn-instance b
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] route-distinguisher 400:1
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b.
[PE4] multicast routing vpn-instance b
[PE4-mrib-b] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance b,.
[PE4] multicast-vpn vpn-instance b mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance b.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance b.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] source loopback 1
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] quit
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.5.1.2 24
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.3.1.1 24
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance b, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip binding vpn-instance b
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 11.4.1.1 24
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE4] interface loopback 1
[PE4-LoopBack1] ip address 4.4.4.4 32
[PE4-LoopBack1] pim sm
[PE4-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE4] bgp 200
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 200
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE4-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 3.3.3.3 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 3.3.3.3 enable
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 3.3.3.3 next-hop-local
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE4–bgp-default -vpnv4] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE4-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route ospf 2
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE4-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance b
[PE4-bgp-default-b] address-family ipv4
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route ospf 3
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route direct
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] quit
[PE4-bgp-default-b] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[PE4] ospf 1
[PE4-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[PE4-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0
[PE4-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.5.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE4-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE4-ospf-1] quit
[PE4] ospf 2 vpn-instance a
[PE4-ospf-2] import-route bgp 200
[PE4-ospf-2] area 0.0.0.0
[PE4-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE4-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE4-ospf-2] quit
[PE4] ospf 3 vpn-instance b
[PE4-ospf-3] import-route bgp 200
[PE4-ospf-3] area 0.0.0.0
[PE4-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE4-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE4-ospf-3] quit
5. Configure P 1:
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable LDP and mLDP P2MP globally.
<P1> system-view
[P1] mpls lsr-id 5.5.5.5
[P1] mpls ldp
[P1-ldp] mldp p2mp
[P1-ldp] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[P1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.1.1.2 24
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[P1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.2.1.1 24
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls enable
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls ldp enable
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[P1] interface loopback 1
[P1-LoopBack1] ip address 5.5.5.5 32
[P1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[P1] ospf 1
[P1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[P1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 5.5.5.5 0.0.0.0
[P1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[P1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
6. Configure P 2:
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable LDP and mLDP P2MP globally.
<P2> system-view
[P2] mpls lsr-id 6.6.6.6
[P2] mpls ldp
[P2-ldp] mldp p2mp
[P2-ldp] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[P2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.5.1.1 24
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[P2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.4.1.2 24
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls enable
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls ldp enable
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[P2] interface loopback 1
[P2-LoopBack1] ip address 6.6.6.6 32
[P2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[P2] ospf 1
[P2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[P2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 6.6.6.6 0.0.0.0
[P2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[P2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.5.1.0 0.0.0.255
7. Configure CE a1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEa1> system-view
[CEa1] multicast routing
[CEa1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.1.1.1 24
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.1.1.2 24
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 as a C-BSR and a C-RP.
[CEa1] pim
[CEa1-pim] c-bsr 11.1.1.2
[CEa1-pim] c-rp 11.1.1.2
# Configure OSPF.
[CEa1] ospf 1
[CEa1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEa1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEa1-ospf-1] quit
# Configure MSDP.
[CEa1] msdp
[CEa1-msdp] peer 11.3.1.2 connect-interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEa1-msdp] quit
8. Configure CE b1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEb1> system-view
[CEb1] multicast routing
[CEb1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.2.1.1 24
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.2.1.2 24
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEb1] ospf 1
[CEb1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEb1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEb1-ospf-1] quit
9. Configure CE a2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEa2> system-view
[CEa2] multicast routing
[CEa2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IGMP on the interface.
[CEa2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.3.1.1 24
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.3.1.2 24
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 as a C-BSR and a C-RP.
[CEa2] pim
[CEa2-pim] c-bsr 11.3.1.2
[CEa2-pim] c-rp 11.3.1.2
[CEa2-pim] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEa2] ospf 1
[CEa2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEa2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEa2-ospf-1] quit
# Configure MSDP.
[CEa2] msdp
[CEa2-msdp] peer 11.1.1.2 connect-interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEa2-msdp] quit
10. Configure CE b2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEb2> system-view
[CEb2] multicast routing
[CEb2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IGMPv3 on the interface.
[CEb2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.4.1.1 24
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp version 3
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.4.1.2 24
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEb2] ospf 1
[CEb2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEb2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEb2-ospf-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about the mLDP inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: mLDP
Tunnel interface: LSPVOif0
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000000>
Tunnel state: Up
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000000
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: 2.2.2.2
# Display information about mLDP selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnel in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: mLDP
Tunnel interface: LSPVOif1
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000001>
Tunnel state: Up
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000001
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
# Display C-multicast A-D route information for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a c-multicast routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(12.1.1.100, 225.0.0.1)
CreateTime: 02:54:43
Tunnel Information: LSPVOif1
# Display information about the mLDP inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 2.
[PE2] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel remote
Tunnel interface: --
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000000>
Tunnel state: --
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000000
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: 2.2.2.2(local)
# Display information about mLDP selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 2.
[PE2] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel remote
Tunnel interface: --
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000001>
Tunnel state: --
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000001
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: 2.2.2.2 (local)
# Display PIM routing entries for VPN instance a on PE 2.
[PE2] display pim vpn-instance a routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entries; 1 (S, G) entries
(12.1.1.100, 225.0.0.1)
RP: 11.1.1.2
Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT ACT SC
UpTime: 00:56:25
Upstream interface: LSPVIif0(1.1.1.1)
Upstream neighbor: 1.1.1.1
RPF prime neighbor: 1.1.1.1
Downstream interface information:
Total number of downstream interfaces: 1
1: Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
Protocol: pim-sm, UpTime: 00:56:25, Expires: 00:03:17
# Display information about the mLDP inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 3.
[PE3] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: mLDP
Tunnel interface: LSPVOif0
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000000>
Tunnel state: Up
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000000
Root: 3.3.3.3 (local)
Leafs:
1: 4.4.4.4
# Display information about mLDP selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 3.
[PE3] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnel in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: mLDP
Tunnel interface: LSPVOif1
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000001>
Tunnel state: Up
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000001
Root: 3.3.3.3 (local)
# Display C-multicast A-D route information for VPN instance a on PE 3.
[PE3] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a c-multicast routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(12.1.1.100, 225.0.0.1)
CreateTime: 02:54:43
Tunnel Information: LSPVOif1
# Display PIM routing entries for VPN instance a on PE 3.
[PE3] display pim vpn-instance a routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entries; 1 (S, G) entries
(12.1.1.100, 225.0.0.1)
RP: 11.3.1.2
Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT ACT RC
UpTime: 00:54:22
Upstream interface: Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
Upstream neighbor: 10.3.1.1
RPF prime neighbor: 10.3.1.1
Downstream interface information:
Total number of downstream interfaces: 1
1: LSPVOif1
Protocol: MD, UpTime: 00:54:18, Expires: -
# Display information about the mLDP inclusive tunnel for VPN instance b on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b inclusive-tunnel remote
Tunnel interface: --
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000000>
Tunnel state: --
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000000
Root: 3.3.3.3
Leaf:
1: 4.4.4.4 (local)
# Display information about mLDP selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel remote
Tunnel interface: --
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000001>
Tunnel state: --
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000001
Root: 3.3.3.3
Leaf:
1: 4.4.4.4 (local)
Example: Configuring inter-AS option B mLDP-based MVPN
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 8, configure inter-AS option B mLDP-based MVPN to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
· In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 2 is a receiver. · In VPN instance b, S 2 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 belongs to VPN instance b. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 3: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 4: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 belongs to VPN instance b. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and MPLS |
· Configure OSPF in AS 100 and AS 200, and configure OSPF between the PEs and CEs. · Establish IBGP peer connections between PE 1, PE 2, PE 3, and PE 4 on their respective Loopback 1. · Establish EBGP peer connections between Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 on PE 2 and PE 3. · Configure a static route on PE 2 and PE 3. · Configure MPLS in AS 100 and AS 200. · Enable MPLS on P 1 and P 2. |
|
IP multicast routing |
· Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1 and PE 4. · Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b on PE 1 and PE 4. · Enable IP multicast routing on CE a1, CE a2, CE b1, and CE b2. |
|
IGMP |
· Enable IGMPv2 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE a2. · Enable IGMPv3 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE b2. |
|
PIM |
Enable PIM-SM for VPN instances a and b: · Enable PIM-SM on all private network interfaces of PE 1 and PE 4. · Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on CE a1, CE a2, CE b1, and CE b2. · Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 of PE 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a to provide services for all multicast groups. |
Table 3 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
12.1.1.100/24 |
R 1 |
— |
12.4.1.100/24 |
|
S 2 |
— |
12.2.1.100/24 |
R 2 |
— |
12.3.1.100/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.4.1.1/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.1.1.1/24 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.3.1.2/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/17 |
11.2.1.1/24 |
PE 3 |
Loop1 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.1/32 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.5.1.2/24 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.2.1.2/24 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.3.1.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.3.1.1/24 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/17 |
11.4.1.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
2.2.2.2/32 |
PE 4 |
Loop1 |
4.4.4.4/32 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.5.1.1/24 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.2.1.1/24 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.4.1.2/24 |
|
P 1 |
Loop1 |
5.5.5.5/32 |
P 2 |
Loop1 |
6.6.6.6/32 |
|
CE a1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.1.1.1/24 |
CE b1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.2.1.1/24 |
|
CE a1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.1.1.2/24 |
CE b1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.2.1.2/24 |
|
CE a2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.3.1.1/24 |
CE b2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.4.1.1/24 |
|
CE a2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.3.1.2/24 |
CE b2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.4.1.2/24 |
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable LDP and mLDP P2MP globally.
[PE1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1] mpls ldp
[PE1-ldp] mldp p2mp
[PE1-ldp] quit
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure the RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation, dynamic selective tunnel creation, and inter-AS auto-discovery for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Create a VPN instance named b, and configure the RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance b
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] route-distinguisher 200:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance b
[PE1-mrib-b] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance b.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance b mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance b.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance b.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation, dynamic selective tunnel creation, and inter-AS auto-discovery for VPN instance b.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and then enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.1.1.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and then enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.1.1.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance b, assign an IP address to the interface, and then enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip binding vpn-instance b
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 11.2.1.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 as a C-BSR and a C-RP.
[PE1] pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim-a] c-bsr 11.1.1.1
[PE1-pim-a] c-rp 11.1.1.1
[PE1-pim-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1–bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 2.2.2.2 enable
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 2.2.2.2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route ospf 2
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance b
[PE1-bgp-default-b] address-family ipv4
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route ospf 3
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-b] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[PE1] ospf 1
[PE1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE1-ospf-1] quit
[PE1] ospf 2 vpn-instance a
[PE1-ospf-2] area 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE1-ospf-2] quit
[PE1] ospf 3 vpn-instance b
[PE1-ospf-3] area 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE1-ospf-3] quit
2. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 2.2.2.2
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable LDP and mLDP P2MP globally.
[PE2] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2
[PE2] mpls ldp
[PE2-ldp] mldp p2mp
[PE2-ldp] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.2.1.2 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.3.1.1 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls ldp enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.2 32
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 10.3.1.2 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 10.3.1.2 connect-interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] undo policy vpn-target
[PE2–bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 10.3.1.2 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] undo policy vpn-target
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1.1.1.1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 10.3.1.2 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Configure a static route.
[PE2] ip route-static 3.3.3.3 32 ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16 10.3.1.2
# Configure OSPF.
[PE2] ospf 1
[PE2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
[PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE2-ospf-1] quit
3. Configure PE 3:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE3> system-view
[PE3] router id 3.3.3.3
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable LDP, mLDP P2MP, and mLDP recursive FEC globally.
[PE3] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3
[PE3] mpls ldp
[PE3-ldp] mldp p2mp
[PE3-ldp] mldp recursive-fec
[PE3-ldp] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.4.1.1 24
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.3.1.2 24
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls enable
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls ldp enable
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[PE3] interface loopback 1
[PE3-LoopBack1] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[PE3-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE3] bgp 200
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 4.4.4.4 as-number 200
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 4.4.4.4 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 10.3.1.1 as-number 100
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 10.3.1.1 connect-interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] undo policy vpn-target
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4.4.4.4 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 10.3.1.1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn] undo policy vpn-target
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 4.4.4.4 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 10.3.1.1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE3–bgp-default] quit
# Configure a static route.
[PE3] ip route-static 2.2.2.2 32 ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16 10.3.1.1
# Configure OSPF.
[PE3] ospf 1
[PE3-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
[PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE3-ospf-1] quit
4. Configure PE 4:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE4> system-view
[PE4] router id 4.4.4.4
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable LDP, mLDP P2MP, and mLDP recursive FEC globally.
[PE4] mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.4
[PE4] mpls ldp
[PE4-ldp] mldp p2mp
[PE4-ldp] mldp recursive-fec
[PE4-ldp] quit
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure the RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE4] ip vpn-instance a
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 300:1
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a.
[PE4] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE4-mrib-a] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE4] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic
# Enable dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Create a VPN instance named b, and configure the RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE4] ip vpn-instance b
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] route-distinguisher 400:1
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b.
[PE4] multicast routing vpn-instance b
[PE4-mrib-b] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance b,.
[PE4] multicast-vpn vpn-instance b mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance b.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance b.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic
# Enable dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] quit
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.5.1.2 24
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.3.1.1 24
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance b, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip binding vpn-instance b
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 11.4.1.1 24
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE4] interface loopback 1
[PE4-LoopBack1] ip address 4.4.4.4 32
[PE4-LoopBack1] pim sm
[PE4-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE4] bgp 200
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 200
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE4–bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 3.3.3.3 enable
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE4-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 3.3.3.3 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE4-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route ospf 2
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE4-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance b
[PE4-bgp-default-b] address-family ipv4
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route ospf 3
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route direct
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] quit
[PE4-bgp-default-b] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] quit
[PE4–bgp] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[PE4] ospf 1
[PE4-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[PE4-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0
[PE4-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.5.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE4-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE4-ospf-1] quit
[PE4] ospf 2 vpn-instance a
[PE4-ospf-2] import-route bgp 200
[PE4-ospf-2] area 0.0.0.0
[PE4-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE4-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE4-ospf-2] quit
[PE4] ospf 3 vpn-instance b
[PE4-ospf-3] import-route bgp 200
[PE4-ospf-3] area 0.0.0.0
[PE4-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE4-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE4-ospf-3] quit
5. Configure P 1:
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable LDP and mLDP P2MP globally.
<P1> system-view
[P1] mpls lsr-id 5.5.5.5
[P1] mpls ldp
[P1-ldp] mldp p2mp
[P1-ldp] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[P1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.1.1.2 24
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[P1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.2.1.1 24
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls enable
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls ldp enable
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[P1] interface loopback 1
[P1-LoopBack1] ip address 5.5.5.5 32
[P1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[P1] ospf 1
[P1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[P1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 5.5.5.5 0.0.0.0
[P1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[P1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
6. Configure P 2:
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable LDP, mLDP P2MP, and mLDP recursive FEC globally.
<P2> system-view
[P2] mpls lsr-id 6.6.6.6
[P2] mpls ldp
[P2-ldp] mldp p2mp
[PE3-ldp] mldp recursive-fec
[P2-ldp] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[P2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.5.1.1 24
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[P2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.4.1.2 24
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls enable
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls ldp enable
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[P2] interface loopback 1
[P2-LoopBack1] ip address 6.6.6.6 32
[P2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[P2] ospf 1
[P2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[P2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 6.6.6.6 0.0.0.0
[P2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[P2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.5.1.0 0.0.0.255
7. Configure CE a1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEa1> system-view
[CEa1] multicast routing
[CEa1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.1.1.1 24
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.1.1.2 24
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEa1] ospf 1
[CEa1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEa1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEa1-ospf-1] quit
8. Configure CE b1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEb1> system-view
[CEb1] multicast routing
[CEb1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.2.1.1 24
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.2.1.2 24
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEb1] ospf 1
[CEb1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEb1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEb1-ospf-1] quit
9. Configure CE a2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEa2> system-view
[CEa2] multicast routing
[CEa2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IGMP on the interface.
[CEa2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.3.1.1 24
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.3.1.2 24
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEa2] ospf 1
[CEa2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEa2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEa2-ospf-1] quit
10. Configure CE b2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEb2> system-view
[CEb2] multicast routing
[CEb2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IGMPv3 on the interface.
[CEb2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.4.1.1 24
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp version 3
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.4.1.2 24
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEb2] ospf 1
[CEb2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEb2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEb2-ospf-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about the mLDP inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: mLDP
Tunnel interface: LSPVOif0
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000000>
Tunnel state: Up
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000000
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: 4.4.4.4
# Display information about mLDP selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnel in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: mLDP
Tunnel interface: LSPVOif2
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000002>
Tunnel state: Up
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000002
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
# Display C-multicast A-D route information for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a c-multicast routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(12.1.1.100, 225.0.0.1)
CreateTime: 02:54:43
Tunnel Information: LSPVOif2
# Display PIM routing entries for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display pim vpn-instance a routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entries; 1 (S, G) entries
(12.1.1.100, 225.0.0.1)
RP: 11.1.1.1 (local)
Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT 2MSDP ACT RC SRC-ACT 2MVPN
UpTime: 00:00:43
Upstream interface: Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
Upstream neighbor: 11.1.1.2
RPF prime neighbor: 11.1.1.2
Downstream interface information:
Total number of downstream interfaces: 1
1: LSPVOif2
Protocol: MD, UpTime: 00:00:30, Expires: -
# Display information about the mLDP inclusive tunnel for VPN instance b on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: mLDP
Tunnel interface: LSPVOif1
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000001>
Tunnel state: up
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000001
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: 4.4.4.4
# Display information about mLDP selective tunnels for VPN instance b on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnel in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: mLDP
Tunnel interface: LSPVOif3
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000003>
Tunnel state: Up
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000003
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
# Display PIM routing entries for VPN instance b on PE 1.
[PE1] display pim vpn-instance b routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entries; 1 (S, G) entries
(12.2.1.100, 232.0.0.0)
Protocol: pim-ssm, Flag: RC
UpTime: 00:26:06
Upstream interface: Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17
Upstream neighbor: 11.2.1.2
RPF prime neighbor: 11.2.1.2
Downstream interface information:
Total number of downstream interfaces: 1
1: LSPVOif3
Protocol: MD, UpTime: 00:25:56, Expires: -
# Display information about the mLDP inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel remote
Tunnel interface: --
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000000>
Tunnel state: --
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000000
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: 4.4.4.4 (local)
# Display information about mLDP selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel remote
Tunnel interface: --
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000002>
Tunnel state: --
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000002
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:1:
4.4.4.4 (local)
# Display information about the mLDP inclusive tunnel for VPN instance b on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b inclusive-tunnel remote
Tunnel interface: --
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000001>
Tunnel state: --
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000001
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: 4.4.4.4 (local)
# Display information about mLDP selective tunnels for VPN instance b on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b selective-tunnel remote
Tunnel interface: --
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000003>
Tunnel state: --
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000003
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: 4.4.4.4 (local)
Example: Configuring inter-AS option C mLDP-based MVPN
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 9, configure inter-AS option C mLDP-based MVPN to meet the following requirements:
|
Item |
Network configuration |
|
Multicast sources and receivers |
· In VPN instance a, S 1 is a multicast source, and R 2 is a receiver. · In VPN instance b, S 2 is a multicast source, and R 1 is a receiver. |
|
VPN instances to which PE interfaces belong |
· PE 1: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 belongs to VPN instance b. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 2: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 3: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. · PE 4: Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 belongs to VPN instance a. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 belongs to VPN instance b. Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 and Loopback 1 belong to the public network. |
|
Unicast routing protocols and MPLS |
· Configure OSPF in AS 100 and AS 200, and configure OSPF between the PEs and CEs. · Establish IBGP peer connections between PE 1, PE 2, PE 3, and PE 4 on their respective Loopback 1. · Establish EBGP peer connections between Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 on PE 2 and PE 3. · Configure MPLS in AS 100 and AS 200. · Enable MPLS on P 1 and P 2. |
|
IP multicast routing |
· Enable IP multicast routing on the public network on PE 1, PE 2, PE 3, and PE 4. · Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a on PE 1 and PE 4. · Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b on PE 1 and PE 4. · Enable IP multicast routing on CE a1, CE a2, CE b1, and CE b2. |
|
IGMP |
· Enable IGMPv2 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE a2. · Enable IGMPv3 on Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15 of CE b2. |
|
PIM |
Enable PIM-SM for VPN instances a and b: · Enable PIM-SM on all private network interfaces of PE 1 and PE 4. · Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces that do not have attached receiver hosts on CE a1, CE a2, CE b1, and CE b2. · Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 of PE 1 as a C-BSR and a C-RP for VPN instance a to provide services for all multicast groups. |
Table 4 Interface and IP address assignment
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
S 1 |
— |
12.1.1.100/24 |
R 1 |
— |
12.4.1.100/24 |
|
S 2 |
— |
12.2.1.100/24 |
R 2 |
— |
12.3.1.100/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.4.1.1/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.1.1.1/24 |
PE 3 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.3.1.2/24 |
|
PE 1 |
XGE0/0/17 |
11.2.1.1/24 |
PE 3 |
Loop1 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
|
PE 1 |
Loop1 |
1.1.1.1/32 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.5.1.2/24 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.2.1.2/24 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.3.1.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.3.1.1/24 |
PE 4 |
XGE0/0/17 |
11.4.1.1/24 |
|
PE 2 |
Loop1 |
2.2.2.2/32 |
PE 4 |
Loop1 |
4.4.4.4/24 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
10.5.1.1/24 |
|
P 1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.2.1.1/24 |
P 2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
10.4.1.2/24 |
|
P 1 |
Loop1 |
5.5.5.5/32 |
P 2 |
Loop1 |
6.6.6.6/32 |
|
CE a1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.1.1.1/24 |
CE b1 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.2.1.1/24 |
|
CE a1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.1.1.2/24 |
CE b1 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.2.1.2/24 |
|
CE a2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.3.1.1/24 |
CE b2 |
XGE0/0/15 |
12.4.1.1/24 |
|
CE a2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.3.1.2/24 |
CE b2 |
XGE0/0/16 |
11.4.1.2/24 |
Procedure
1. Configure PE 1:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE1> system-view
[PE1] router id 1.1.1.1
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable LDP and mLDP P2MP globally.
[PE1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1
[PE1] mpls ldp
[PE1-ldp] mldp p2mp
[PE1-ldp] quit
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure the RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 100:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE1-mrib-a] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation, dynamic selective tunnel creation, and inter-AS auto-discovery for VPN instance a.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Create a VPN instance named b, and configure the RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance b
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] route-distinguisher 200:1
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity
[PE1-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b.
[PE1] multicast routing vpn-instance b
[PE1-mrib-b] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance b.
[PE1] multicast-vpn vpn-instance b mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance b.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance b.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation, dynamic selective tunnel creation, and inter-AS auto-discovery for VPN instance b.
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] auto-discovery inter-as
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] quit
[PE1-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and then enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.1.1.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and then enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.1.1.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance b, assign an IP address to the interface, and then enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip binding vpn-instance b
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 11.2.1.1 24
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[PE1] interface loopback 1
[PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[PE1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 as a C-BSR and a C-RP.
[PE1] pim vpn-instance a
[PE1-pim-a] c-bsr 11.1.1.1
[PE1-pim-a] c-rp 11.1.1.1
[PE1-pim-a] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE1] bgp 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4.4.4.4 as-number 200
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4.4.4.4 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE1-bgp-default] peer 4.4.4.4 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE1–bgp-default] address-family ipv4
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 2.2.2.2 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 2.2.2.2 label-route-capability
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] peer 4.4.4.4 enable
[PE1-bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 4.4.4.4 enable
[PE1–bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE1-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route ospf 2
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE1–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance b
[PE1-bgp-default-b] address-family ipv4
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route ospf 3
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route direct
[PE1-bgp-default-ipv4-b] quit
[PE1-bgp-default-b] quit
[PE1-bgp-default] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[PE1] ospf 1
[PE1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE1-ospf-1] quit
[PE1] ospf 2 vpn-instance a
[PE1-ospf-2] import-route bgp
[PE1-ospf-2] area 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE1-ospf-2] quit
[PE1] ospf 3 vpn-instance b
[PE1-ospf-3] import-route bgp
[PE1-ospf-3] area 0.0.0.0
[PE1-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE1-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE1-ospf-3] quit
2. Configure PE 2:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE2> system-view
[PE2] router id 2.2.2.2
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable LDP and mLDP P2MP globally.
[PE2] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2
[PE2] mpls ldp
[PE2-ldp] mldp p2mp
[PE2-ldp] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.2.1.2 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[PE2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.3.1.1 24
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls ldp enable
[PE2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[PE2] interface loopback 1
[PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.2 32
[PE2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure routing polices.
[PE2] route-policy map1 permit node 1
[PE2-route-policy-map1-1] apply mpls-label
[PE2-route-policy-map1-1] quit
[PE2] route-policy map2 permit node 1
[PE2-route-policy-map2-1] apply mpls-label
[PE2-route-policy-map2-1] if-match mpls-label
[PE2-route-policy-map2-1] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE2] bgp 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE2-bgp-default] peer 10.3.1.2 as-number 200
[PE2-bgp-default] address-family ipv4
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1.1.1.1 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1.1.1.1 route-policy map2 export
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 1.1.1.1 label-route-capability
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.3.1.2 enable
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.3.1.2 route-policy map1 export
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.3.1.2 label-route-capability
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route ospf 1
[PE2-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[PE2–bgp-default] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[PE2] ospf 1
[PE2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
[PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE2-ospf-1] quit
3. Configure PE 3:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE3> system-view
[PE3] router id 3.3.3.3
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable LDP, mLDP P2MP, and mLDP recursive FEC globally.
[PE3] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3
[PE3] mpls ldp
[PE3-ldp] mldp p2mp
[PE3-ldp] mldp recursive-fec
[PE3-ldp] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.4.1.1 24
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[PE3] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.3.1.2 24
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls enable
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls ldp enable
[PE3-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[PE3] interface loopback 1
[PE3-LoopBack1] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[PE3-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure routing policies.
[PE3] route-policy map1 permit node 1
[PE3-route-policy-map1-1] apply mpls-label
[PE3-route-policy-map1-1] quit
[PE3] route-policy map2 permit node 1
[PE3-route-policy-map2-1] apply mpls-label
[PE3-route-policy-map2-1] if-match mpls-label
[PE3-route-policy-map2-1] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE3] bgp 200
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 4.4.4.4 as-number 200
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 4.4.4.4 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE3-bgp-default] peer 10.3.1.1 as-number 100
[PE3-bgp-default] address-family ipv4
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 4.4.4.4 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 4.4.4.4 route-policy map2 export
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 4.4.4.4 label-route-capability
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.3.1.1 enable
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 10.3.1.1 route-policy map1 export
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route ospf 1
[PE3-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[PE3–bgp-default] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[PE3] ospf 1
[PE3-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
[PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE3-ospf-1] quit
4. Configure PE 4:
# Configure a global router ID.
<PE4> system-view
[PE4] router id 4.4.4.4
[PE4] multicast routing
[PE4-mrib] quit
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable LDP, mLDP P2MP, and mLDP recursive FEC globally.
[PE4] mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.4
[PE4] mpls ldp
[PE4-ldp] mldp p2mp
[PE4-ldp] mldp recursive-fec
[PE4-ldp] quit
# Create a VPN instance named a, and configure the RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE4] ip vpn-instance a
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] route-distinguisher 300:1
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance a.
[PE4] multicast routing vpn-instance a
[PE4-mrib-a] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance a.
[PE4] multicast-vpn vpn-instance a mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance a.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic
# Enable dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a-ipv4] quit
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-a] quit
# Create a VPN instance named b, and configure the RD and route targets for the VPN instance.
[PE4] ip vpn-instance b
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] route-distinguisher 400:1
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity
[PE4-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Enable IP multicast routing for VPN instance b.
[PE4] multicast routing vpn-instance b
[PE4-mrib-b] quit
# Create an mLDP-based MVPN for VPN instance b,.
[PE4] multicast-vpn vpn-instance b mode mldp
# Create an MVPN IPv4 address family for VPN instance b.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] address-family ipv4
# Specify the MVPN source interface for VPN instance b.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] source loopback 1
# Enable dynamic inclusive tunnel creation.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] inclusive-tunnel dynamic
# Enable dynamic selective tunnel creation.
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] selective-tunnel dynamic
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b-ipv4] quit
[PE4-mvpn-vpn-instance-b] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.5.1.2 24
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16 with VPN instance a, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip binding vpn-instance a
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.3.1.1 24
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Associate Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/17 with VPN instance b, assign an IP address to the interface, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[PE4] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/17
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip binding vpn-instance b
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] ip address 11.4.1.1 24
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] pim sm
[PE4-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[PE4] interface loopback 1
[PE4-LoopBack1] ip address 4.4.4.4 32
[PE4-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure BGP.
[PE4] bgp 200
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 200
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.1 ebgp-max-hop 10
[PE4-bgp-default] peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface loopback 1
[PE4-bgp-default] address-family ipv4
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 3.3.3.3 enable
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 3.3.3.3 label-route-capability
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] address-family ipv4 mvpn
[PE4–bgp-default-mvpn] peer 1.1.1.1 enable
[PE4–bgp-default-mvpn] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] address-family vpnv4
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] mvpn-advertise-rt-import
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.1 enable
[PE4–bgp-default-vpnv4] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance a
[PE4-bgp-default-a] address-family ipv4
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route ospf 2
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] import-route direct
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-a] quit
[PE4-bgp-default-a] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] ip vpn-instance b
[PE4-bgp-default-b] address-family ipv4
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route ospf 3
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] import-route direct
[PE4-bgp-default-ipv4-b] quit
[PE4-bgp-default-b] quit
[PE4–bgp-default] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[PE4] ospf 1
[PE4-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[PE4-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0
[PE4-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.5.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE4-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE4-ospf-1] quit
[PE4] ospf 2 vpn-instance a
[PE4-ospf-2] import-route bgp 200
[PE4-ospf-2] area 0.0.0.0
[PE4-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE4-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE4-ospf-2] quit
[PE4] ospf 3 vpn-instance b
[PE4-ospf-3] import-route bgp 200
[PE4-ospf-3] area 0.0.0.0
[PE4-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[PE4-ospf-3-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[PE4-ospf-3] quit
5. Configure P 1:
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable LDP and mLDP P2MP globally.
<P1> system-view
[P1] mpls lsr-id 5.5.5.5
[P1] mpls ldp
[P1-ldp] mldp p2mp
[P1-ldp] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[P1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.1.1.2 24
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[P1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.2.1.1 24
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls enable
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls ldp enable
[P1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[P1] interface loopback 1
[P1-LoopBack1] ip address 5.5.5.5 32
[P1-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[P1] ospf 1
[P1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[P1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 5.5.5.5 0.0.0.0
[P1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[P1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
6. Configure P 2:
# Configure an LSR ID, and enable LDP, mLDP P2MP, and mLDP recursive FEC globally.
<P2> system-view
[P2] mpls lsr-id 6.6.6.6
[P2] mpls ldp
[P2-ldp] mldp p2mp
[P2-ldp] mldp recursive-fec
[P2-ldp] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[P2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 10.5.1.1 24
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls enable
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] mpls ldp enable
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable MPLS and IPv4 LDP on the interface.
[P2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 10.4.1.2 24
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls enable
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] mpls ldp enable
[P2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to Loopback 1.
[P2] interface loopback 1
[P2-LoopBack1] ip address 6.6.6.6 32
[P2-LoopBack1] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[P2] ospf 1
[P2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[P2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 6.6.6.6 0.0.0.0
[P2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[P2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.5.1.0 0.0.0.255
7. Configure CE a1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEa1> system-view
[CEa1] multicast routing
[CEa1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.1.1.1 24
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.1.1.2 24
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEa1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEa1] ospf 1
[CEa1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEa1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEa1-ospf-1] quit
8. Configure CE b1:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEb1> system-view
[CEb1] multicast routing
[CEb1-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.2.1.1 24
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] pim sm
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb1] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.2.1.2 24
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEb1-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEb1] ospf 1
[CEb1-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEb1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEb1-ospf-1] quit
9. Configure CE a2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEa2> system-view
[CEa2] multicast routing
[CEa2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IGMP on the interface.
[CEa2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.3.1.1 24
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEa2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.3.1.2 24
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEa2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEa2] ospf 1
[CEa2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEa2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEa2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEa2-ospf-1] quit
10. Configure CE b2:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<CEb2> system-view
[CEb2] multicast routing
[CEb2-mrib] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/15, and enable IGMPv3 on the interface.
[CEb2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] ip address 12.4.1.1 24
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp enable
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] igmp version 3
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Assign an IP address to Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/16, and enable PIM-SM on the interface.
[CEb2] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/16
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] ip address 11.4.1.2 24
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] pim sm
[CEb2-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16] quit
# Configure OSPF.
[CEb2] ospf 1
[CEb2-ospf-1] area 0.0.0.0
[CEb2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.4.1.0 0.0.0.255
[CEb2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[CEb2-ospf-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about the mLDP inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: mLDP
Tunnel interface: LSPVOif0
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000000>
Tunnel state: Up
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000000
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: 4.4.4.4
# Display information about mLDP selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnel in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: mLDP
Tunnel interface: LSPVOif2
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000002>
Tunnel state: Up
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000002
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
# Display C-multicast A-D route information for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a c-multicast routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(12.1.1.100, 225.0.0.1)
CreateTime: 02:54:43
Tunnel Information: LSPVOif2
# Display PIM routing entries for VPN instance a on PE 1.
[PE1] display pim vpn-instance a routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entries; 1 (S, G) entries
(12.1.1.100, 225.0.0.1)
RP: 11.1.1.1 (local)
Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT 2MSDP ACT RC SRC-ACT 2MVPN
UpTime: 00:00:43
Upstream interface: Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/16
Upstream neighbor: 11.1.1.2
RPF prime neighbor: 11.1.1.2
Downstream interface information:
Total number of downstream interfaces: 1
1: LSPVOif2
Protocol: MD, UpTime: 00:00:30, Expires: -
# Display information about the mLDP inclusive tunnel for VPN instance b on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b inclusive-tunnel local
Tunnel type: mLDP
Tunnel interface: LSPVOif1
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000001>
Tunnel state: up
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000001
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
Leafs:
1: 4.4.4.4
# Display information about mLDP selective tunnels for VPN instance b on PE 1.
[PE1] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b selective-tunnel local
Total 1 selective tunnel in using
Total 0 selective tunnel in creating
Tunnel type: mLDP
Tunnel interface: LSPVOif3
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000003>
Tunnel state: Up
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000003
Root: 1.1.1.1 (local)
# Display PIM routing entries for VPN instance b on PE 2.
[PE1] display pim vpn-instance b routing-table
Total 0 (*, G) entries; 1 (S, G) entries
(12.2.1.100, 232.0.0.0)
Protocol: pim-ssm, Flag: RC
UpTime: 00:26:06
Upstream interface: Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/17
Upstream neighbor: 11.2.1.2
RPF prime neighbor: 11.2.1.2
Downstream interface information:
Total number of downstream interfaces: 1
1: LSPVOif3
Protocol: MD, UpTime: 00:25:56, Expires: -
# Display information about the mLDP inclusive tunnel for VPN instance a on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a inclusive-tunnel remote
Tunnel interface: --
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000000>
Tunnel state: --
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000000
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: 4.4.4.4 (local)
# Display information about mLDP selective tunnels for VPN instance a on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance a selective-tunnel remote
Tunnel interface: --
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000002>
Tunnel state: --
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000002
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: 4.4.4.4 (local)
# Display information about the mLDP inclusive tunnel for VPN instance b on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b inclusive-tunnel remote
Tunnel interface: --
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000001>
Tunnel state: --
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000001
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf:
1: 4.4.4.4 (local)
# Display information about mLDP selective tunnels for VPN instance b on PE 4.
[PE4] display multicast-vpn vpn-instance b inclusive-tunnel remote
Tunnel interface: --
Tunnel identifier: mLDP P2MP <0xe4000001>
Tunnel state: --
Opaque value: 0x010004e4000001
Root: 1.1.1.1
Leaf: