- Table of Contents
-
- 07-IP Multicast Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Multicast overview
- 02-IGMP snooping configuration
- 03-PIM snooping configuration
- 04-Multicast VLAN configuration
- 05-Multicast routing and forwarding configuration
- 06-IGMP configuration
- 07-PIM configuration
- 08-MSDP configuration
- 09-Multicast VPN overview
- 10-MDT-based MVPN configuration
- 11-RSVP-TE-based MVPN configuration
- 12-mLDP-based MVPN configuration
- 13-BIER-based MVPN configuration
- 14-MVPN extranet configuration
- 15-MLD snooping configuration
- 16-IPv6 PIM snooping configuration
- 17-IPv6 multicast VLAN configuration
- 18-IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding configuration
- 19-MLD configuration
- 20-IPv6 PIM configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 09-Multicast VPN overview | 98.70 KB |
Multicast VPN overview
Multicast VPN implements multicast delivery in VPNs. Comware uses the MVPN solution to implement multicast VPN. The greatest advantage of this solution is that only PEs need to support multiple instances, while the operator's public network supports multicast functionality. There is no need to modify the existing PIM configurations on CE and P devices, meaning this solution is transparent to both CE and P devices.
Background
The application of IP multicast is becoming widespread, and the Virtual Private Network (VPN) technology is increasingly common in enterprise networks. Almost all current e-government networks, power data networks, and other enterprise networks are based on the BGP/MPLS VPN architecture, which isolates data by dividing different departments into different VPNs. Similarly, multicast services within departments, such as video conferencing and data sharing, also require VPN isolation, making multicast VPN demand increasingly urgent. However, RFC 4364 only proposes solutions for unicast VPN services and does not provide specific planning or recommendations for multicast VPN services. Therefore, applying the multicast technology in VPN environments has become a critical issue.
Internet service providers (ISPs) aim to offer multicast VPN services to users using the existing BGP/MPLS VPN infrastructure, which should be scalable and leverage the backbone's multicast capabilities. VPN users want each site's CEs to establish PIM neighbor relationships only with the corresponding PE, without involving remote site's CEs. Additionally, users expect their network configurations and existing multicast application plans (for example, PIM modes, RP location, and RP discovery mechanisms) to remain unchanged. Besides, the following issues must be addressed when delivering multicast services over BGP/MPLS VPN networks:
· Overlapping private address spaces: BGP/MPLS VPN networks allow overlapping private address spaces across different VPNs, so multicast source and group addresses might overlap. The PE must correctly forward private network multicast data to users within the same VPN.
· Public network multicast support: Private network multicast data should be forwarded in the public network where possible to significantly reduce public network data load and save bandwidth.
· RPF checks for private multicast data in the public network: Multicast data forwarding relies on the source address and incoming interface. In BGP/MPLS VPN networks, Public Equipment (P) cannot directly forward private network multicast data due to the lack of private network routes.
· On-demand transmission of private multicast data: A VPN consists of multiple sites connected to different PEs, but not every site requires multicast data. Private multicast data should only flow to PEs that need it, reducing the load on PEs.
To address these issues, you can deploy the multicast VPN technology in BGP/MPLS VPN networks, enabling the transmission of private multicast data via the public network to remote private sites.
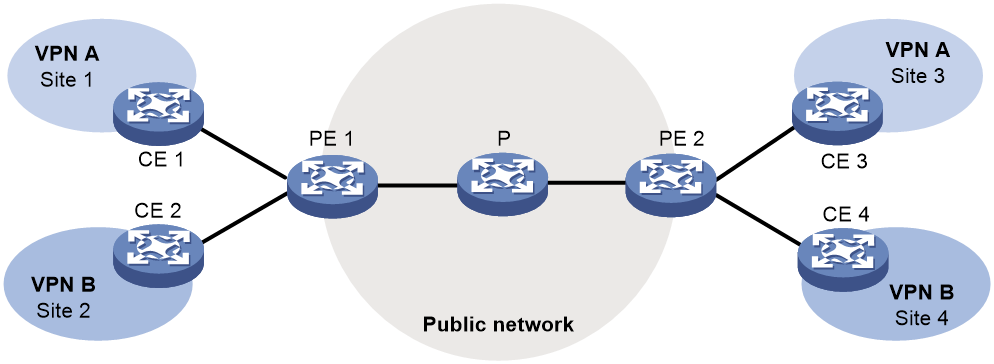
Typical network diagram
As shown in Figure 1, VPN A contains Site 1 and Site 3, and VPN B contains Site 2 and Site 4.
Figure 1 Typical network diagram for multicast VPN
VPN multicast traffic between the PEs and the CEs is transmitted on a per-VPN-instance basis. The public network multicast traffic between the PEs and the P device is transmitted through the public network. Multicast VPN provides independent multicast services for the public network, VPN A, and VPN B.
For more information about CEs, PEs and Ps, see MPLS Configuration Guide.
MVPN scheme
MVPN is used to implement multicast VPN. MVPN only requires the PEs to support multiple VPN instances and the public network provided by the service provider to support multicast. There is no need to upgrade CEs and Ps or change their PIM configurations. The MVPN scheme is transparent to CEs and Ps.
MVPN supports the following modes: MDT, RSVP-TE, mLDP, and BIER. The RSVP-TE, mLDP, and BIER MVPNs are next-generation MVPNs (NG MVPN). For more information about each mode, see "Configuring MDT-based MVPN", "Configuring RSVP-TE-based MVPN", "Configuring mLDP-based MVPN", and "Configuring BIER-based MVPN.", The NG MVPN is a new solution for transporting multicast traffic over a BGP/MPLS L3VPN network. It uses MP-BGP to transmit private routes and uses tunnels to deliver multicast data packets and control packets to a private network over a public network.
Technical advantages
· Network upgrades are simple. Only PEs need to be upgraded. CE and P devices do not require upgrades or configuration changes, making MVPN transparent to them. The backbone network remains stable without detecting changes in private network multicast traffic.
· No changes are required for transmitting unicast routes in the private network. The MVPN scheme uses existing BGP/MPLS VPN technology to transmit routes of multicast sources within the VPN using VPN-IPv4 routes, allowing receivers and PE devices to obtain unicast routes to the multicast sources.
· The MDT-based MVPN addresses RPF check issues by utilizing the multicast forwarding capability of the public network. A PE encapsulates private network multicast packets into public multicast packets, leveraging the inherent multicast forwarding capability of the public network.
· In the NG MVPN, the public network uses BGP to transmit private network multicast protocol packets and routes, eliminating the need for other multicast protocols and simplifying network deployment and maintenance.
· In the NG MVPN, the public network uses mature MPLS label forwarding and tunnel protection technologies, enhancing the service quality and reliability of multicast traffic.
M6VPE
Only mLDP-based M6VPE is supported in the current software version.
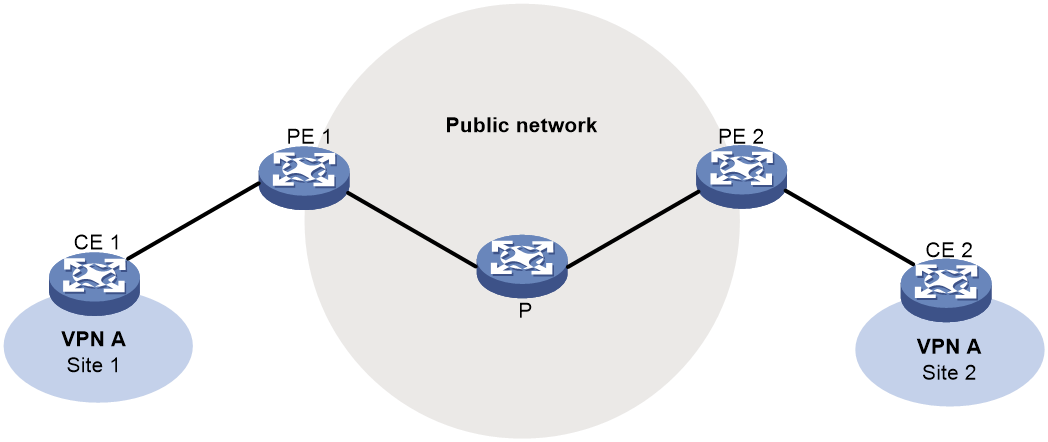
The multicast IPv6 VPN provider edge (M6VPE) feature enables PEs to transmit IPv6 multicast traffic of a VPN instance over the public network. Only the IPv4 network is available for the backbone network.
As shown in Figure 2, the public network runs IPv4 protocols, and sites of VPN instance VPN A run IPv6 multicast protocols. To transmit IPv6 multicast traffic between CE 1 and CE 2, configure M6VPE on the PEs.
IPv6 multicast traffic forwarding over the IPv4 public network is as follows:
1. CE 1 forwards an IPv6 multicast packet for VPN instance VPN A to PE 1.
2. PE 1 encapsulates the IPv6 multicast packet with an IPv4 packet header and transmits the IPv4 packet in the IPv4 backbone network.
3. PE 2 decapsulates the IPv4 packet and forwards the IPv6 multicast packet to CE 2.
Restrictions and guidelines: Multicast VPN configuration
PIM FRR and IPv6 PIM FRR periodically monitor multicast traffic on the primary and backup incoming interfaces of each multicast forwarding entry to detect link failures. Use this feature only in a scenario with continued high-speed forwarding of multicast traffic. To avoid multicast traffic forwarding failures when multicast VPN is used, do not enable PIM FRR and IPv6 PIM FRR. For more information about PIM FRR and IPv6 PIM FRR, see "Configuring PIM" and "Configuring IPv6 PIM", respectively.
The MTIs take effect only after the default group and the MVPN source interface are specified and the MVPN source interface obtains an public IP address.
The PIM mode on an MTI must be the same as the PIM mode running on the VPN instance to which the MTI belongs. When a minimum of one interface on the VPN instance is enabled with PIM, the MTI is enabled with PIM accordingly. When all interfaces on the VPN instance are disabled with PIM, PIM is also disabled on the MTI.
Configure multicast VPN on PEs.