- Table of Contents
-
- H3C iMC Database Installation Guide-5W103
- 01-MySQL 8.0.xx Installation and Configuration Guide (for Linux)
- 02-MySQL 8.0.xx Installation and Configuration Guide (for Windows)
- 03-Oracle 11g Installation and Configuration Guide
- 04-Oracle 11g R2 Installation and Configuration Guide
- 05-Oracle 12c Installation and Configuration Guide
- 06-Oracle 12c R2 Installation and Configuration Guide
- 07-Oracle 18c Installation and Configuration Guide
- 08-SQL Server 2016 Installation and Configuration Guide
- 09-SQL Server 2017 Installation and Configuration Guide
- 10-SQL Server 2019 Installation and Configuration Guide
- 11-SQL Server 2022 Installation and Configuration Guide
- 12-MariaDB 10.x.x Installation Guide (Linux)
- 13-MariaDB 10.x.x Installation Guide (Windows)
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 13-MariaDB 10.x.x Installation Guide (Windows) | 2.79 MB |
|
|
|
|
|
MariaDB 10.x.x |
|
Installation Guide (Windows) |
|
|
|
|
|
New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. http://www.h3c.com
Document version: 5W100-20250415 Software version: IMC PLAT 7.3 (E0708) |
Copyright © 2025, New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. and its licensors All rights reserved
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. All contents in this document, including statements, information, and recommendations, are believed to be accurate, but they are presented without warranty of any kind, express or implied. H3C shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Preface
This document includes the following topics:
· Introduction—Introduces MariaDB versions and usage guidelines.
· Installation—Introduces the installation procedure of MariaDB.
· Start/Stop—Introduces how to start and stop the MariaDB database service.
· Configuration—Introduces the essential configurations for MariaDB.
· Uninstallation—Introduces the uninstallation procedure of MariaDB.
· FAQ—Introduces common frequently asked questions about MariaDB installation and configuration.
This preface includes the following topics about the documentation:
· Audience
Audience
This documentation is intended for:
· Network planners.
· Field technical support and servicing engineers.
· Network operators, administrators, and maintainers.
Conventions
The following information describes the conventions used in the documentation.
GUI conventions
|
Convention |
Description |
|
Boldface |
Window names, button names, field names, and menu items are in Boldface. For example, the New User window opens; click OK. |
|
> |
Multi-level menus are separated by angle brackets. For example, File > Create > Folder. |
Symbols
|
Convention |
Description |
|
An alert that calls attention to important information that if not understood or followed can result in personal injury. |
|
|
An alert that calls attention to important information that if not understood or followed can result in data loss, data corruption, or damage to hardware or software. |
|
|
An alert that calls attention to essential information. |
|
|
NOTE: |
An alert that contains additional or supplementary information. |
|
An alert that provides helpful information. |
Documentation feedback
You can e-mail your comments about product documentation to [email protected].
We appreciate your comments.
Contents
Configure the environment variables
Test the connectivity with the server
Modify parameters in the my.ini file
Introduction
This document describes how to install and configure the MariaDB database on the Windows Server 2019 operating system when Intelligent Management Center (IMC) uses the MariaDB database, and the restrictions and guidelines. This document applies to the installation of MariaDB 10.5.x, MariaDB 10.3.x, and MariaDB 5.5.x. The installation procedures for other versions are similar, though the interface might slightly differ. (Details not shown.)
When you use the MariaDB database with IMC, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· You can proceed to install IMC only after you successfully install and start MariaDB.
· When you deploy IMC in distributed mode, all primary and backup IMC servers must use the same MariaDB as the database server.
Installation
Prepare for installation
This chapter describes the installation of MariaDB. Before installation, copy the installation file to the server. You can obtain the installation file from the official website of MariaDB. This document uses MariaDB 10.5.2 as an example.
When you install MariaDB, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· When IMC uses a local database, you only need to install MariaDB on the IMC server.
· When IMC uses a remote database, install MariaDB on the remote database server. When you configure the database connection parameters for IMC, select other server from the Database Location list and enter the IP address of the remote database server in the Database Server Address field.
· The MariaDB database can manage up to 2000 devices. Before installation, see the hardware requirements in the specific operating system guide.
Installation procedure
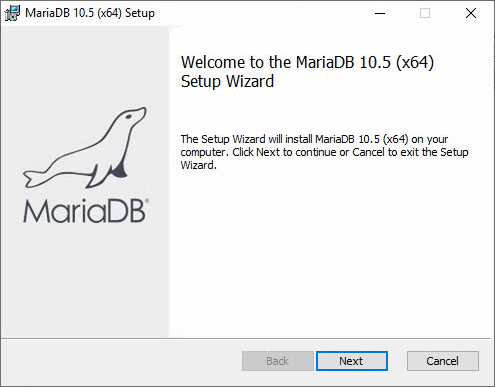
1. Double-click the MariaDB installation file to start the installer.
Figure 1 Start the installer
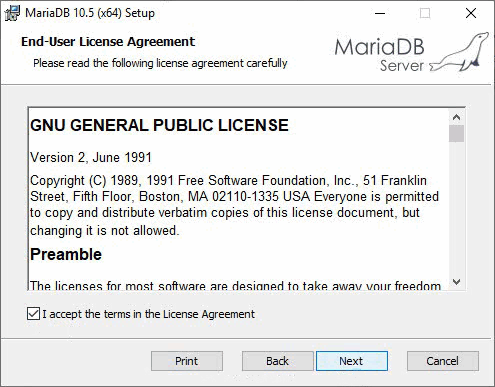
2. Click Next to access the End-User License Agreement page.
3. To proceed with the installation, select the I accept the terms in the License Agreement option. If you disagree with the terms in the license agreement, click Cancel to exit the installer. In this example, select the I accept the terms in the License Agreement option. Click Next to access the Custom Setup page.
Figure 2 End-User License Agreement
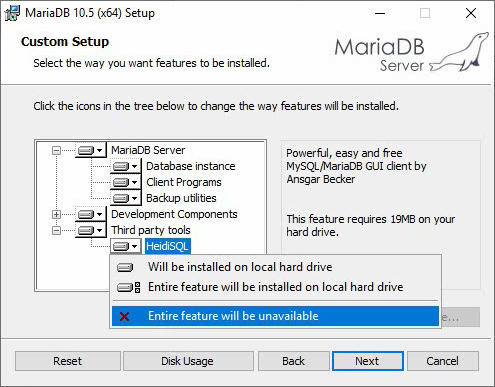
4. In this example, you only need to install
the database, and you do not need to install the graphical interface tool
HeidiSQL. Click the ![]() icon to the left of HeidiSQL, and select Entire
feature will be unavailable from the menu that opens, as shown in Figure 3.
icon to the left of HeidiSQL, and select Entire
feature will be unavailable from the menu that opens, as shown in Figure 3.
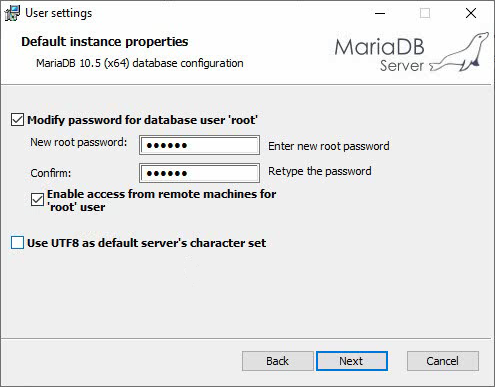
5. Click Next to access the Default instance properties page and configure the following settings:
¡ In the Modify password for database user 'root' section, set the password for the root user.
¡ When the IMC server uses a remote database, it must use a remote root user to connect to the database. Select Enable access from remote machines for 'root' user.
|
CAUTION: For the password to be correctly detected during the subsequent IMC installation, make sure the password does not contain spaces, tabs, or the following characters: `'"!()&|\$;@<>/^. |
Figure 4 Default instance properties-1
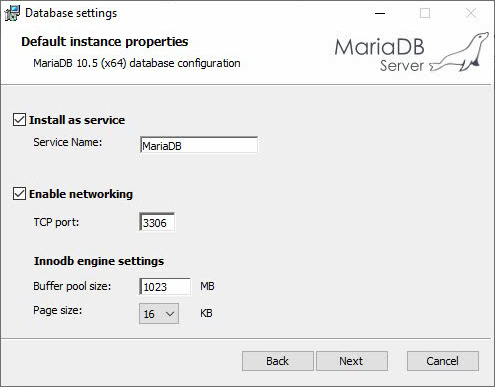
6. Click Next to access the page for other configuration items, and configure the service name, port number, and other information as needed. In this example, use the default settings for these configuration items.
Figure 5 Default instance properties-2
7. Click Next to access the Ready to install MariaDB 10.5 (x64) page.
Figure 6 Ready to install MariaDB 10.5 (x64)
8. Click Install to start installing MariaDB.
Figure 7 Installing MariaDB 10.5 (x64)
9. Click Finish to complete the MariaDB installation.
Figure 8 Installation completed
Configure the environment variables
To directly execute all MariaDB management commands (for example, mysqld, mysqlshow, and mysqladmin) at the command line interface (CLI), add the MariaDB installation path to the environment variables. The following example describes how to modify environment variables in Windows Server 2019. When you modify the environment variables for other operating system versions, the procedure might slightly differ. For more information, see the official documentation for the specific version.
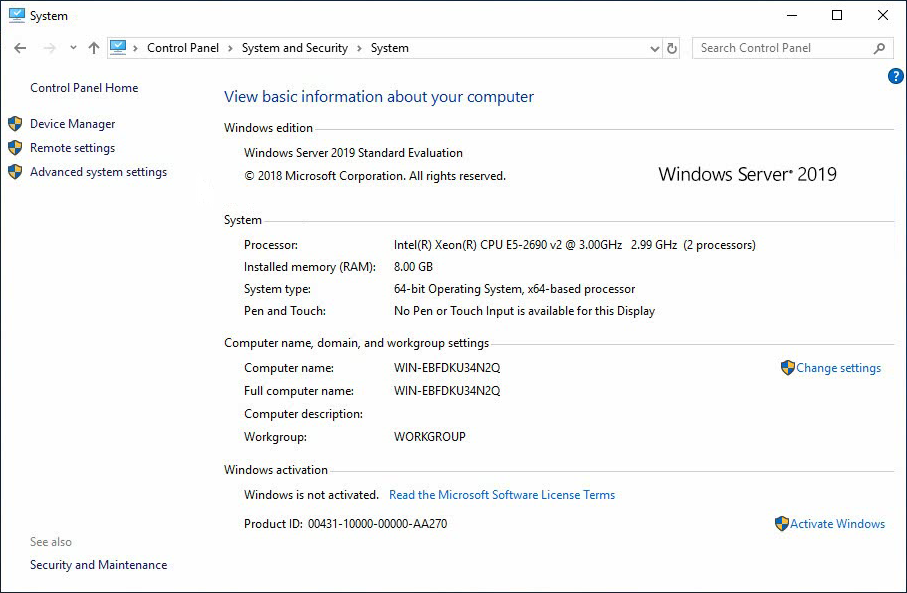
1. Click Start and select Control Panel to open the control panel. Then, select System and Security > System to access the View basic information about your computer page.
Figure 9 View basic information about your computer
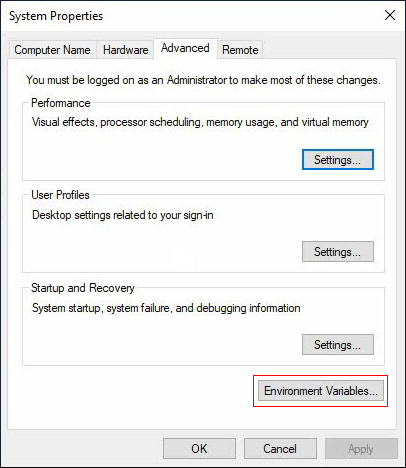
2. Click the Advanced system settings link to open the System Properties window.
Figure 10 System Properties
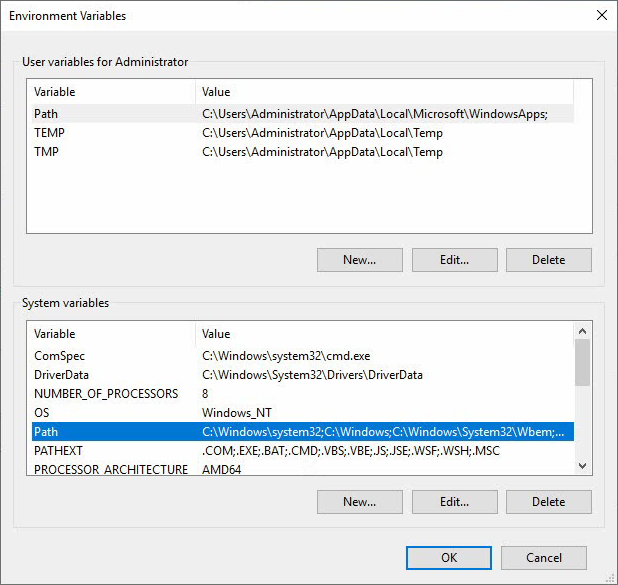
3. Click Environment Variables… on the Advanced tab to open the Environment Variables window.
Figure 11 Environment Variables
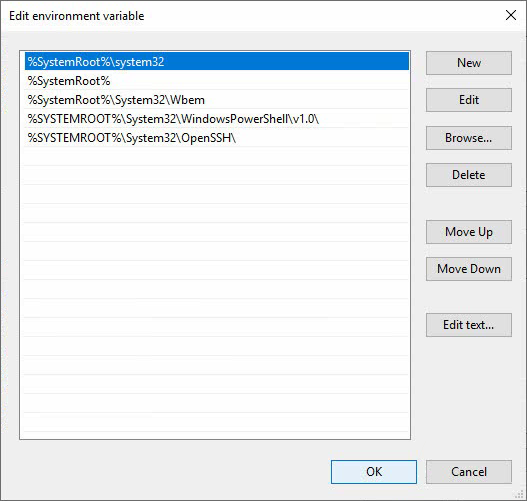
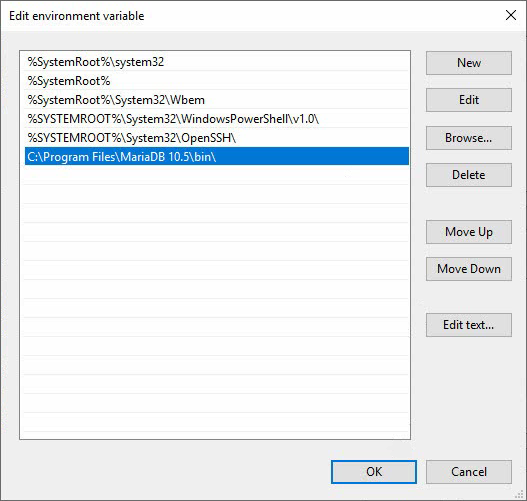
4. In the System variables area, select Path and click Edit… to open the Edit environment variable window.
Figure 12 Edit environment variable
5. Click New to create a path for the bin folder under the MariaDB installation directory, as shown in Figure 13. The default bin folder path is C:\Program Files\MariaDB 10.5\bin\ for MariaDB 10.5, C:\Program Files\MariaDB 10.3\bin\ for MariaDB 10.3, and C:\Program Files\MariaDB 5.5\bin\ for MariaDB 5.5.
6. After you add the path, click OK on the Edit environment variable, Environment Variables, and System Properties windows to save the environment variable changes.
7. After you configure the environment variables, restart the operating system to have the new environment variables take effect.
Test the connectivity with the server
After you configure the environment variables, make sure MariaDB has started on the remote database server. Then, follow these steps to test connectivity with MariaDB.
1. Click Start and select Run. Enter cmd in the Run window, and click OK. The command line window opens.
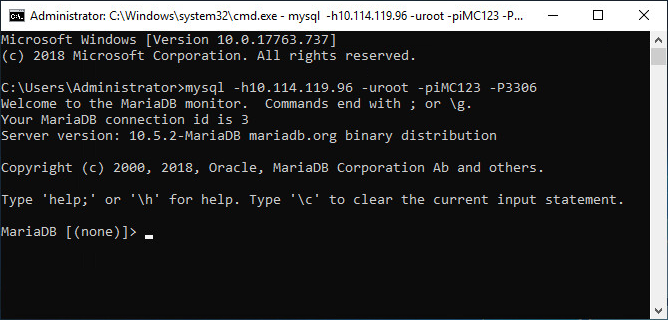
2. In the command line window, enter the following command to test connectivity with the server.
mysql -h10.114.119.96 -uroot –piMC123 -P3306
In this command, 10.114.119.96 is the IP address of the database server, root is the remote username for MariaDB, IMC123 is the password for the remote root user, and 3306 is the default port number for the MariaDB database.
3. If you can enter the command line mode of the MariaDB server, it means you can successfully connect to the MariaDB server, as shown in Figure 14.
Figure 14 Test the connectivity with the server
Start/Stop
On a server with MariaDB installed, you can start or stop the MariaDB service through Windows Service Manager.
The following information describes how to start or stop the MariaDB service through Windows Service Manager.
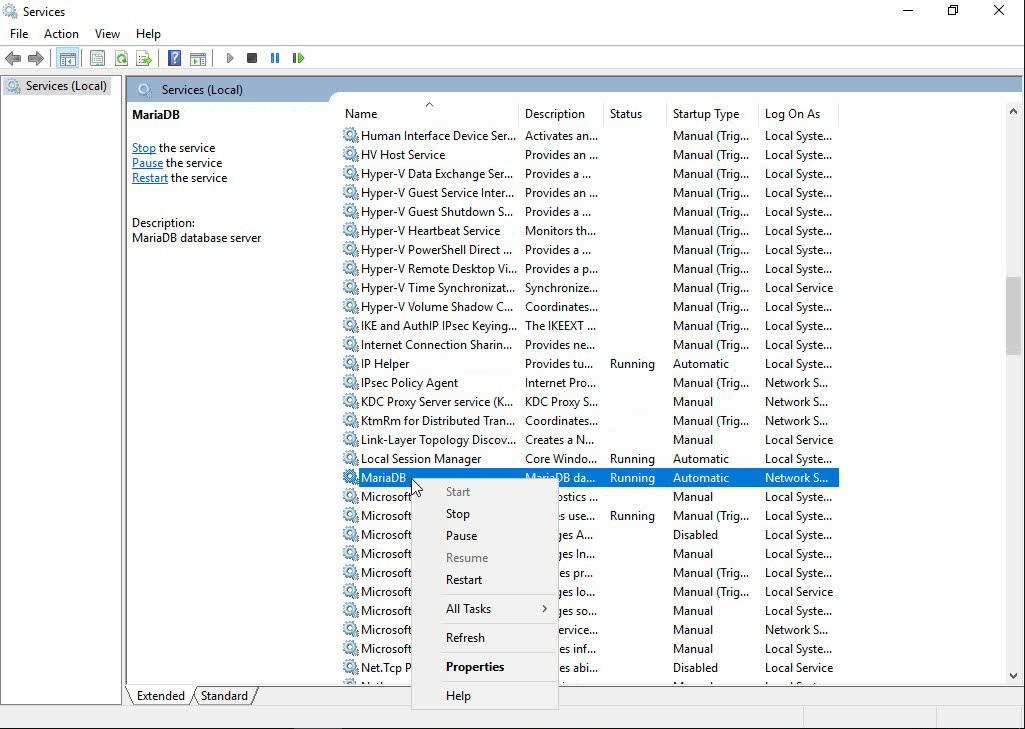
1. Click Start, and select All Programs > Administrative Tools > Services to access the Services page. Select the Windows service name for MariaDB (MariaDB for MariaDB 10.5 and MySQL for MariaDB 5.5 and MariaDB 10.3 by default), and right-click it. The shortcut menu opens, as shown in Figure 15.
Figure 15 Start/Stop the MariaDB service
2. To start MariaDB, select Start. This option is available only when MariaDB is not started. To stop MariaDB, select Stop. This option is available only when MariaDB is running.
Configuration
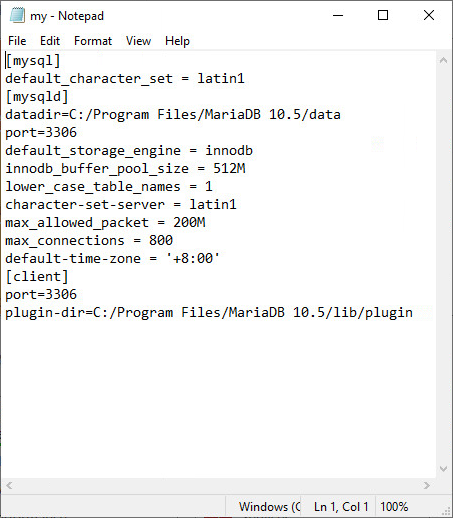
After MariaDB is installed, the system automatically generates the MariaDB configuration file named my.ini in the data path (C:\Program Files\MariaDB 10.5\data by default) set during installation. This file determines the functions and performance of MariaDB.
Modify parameters in the my.ini file
1. Before modifying the my.ini file, you must stop the MariaDB service first. For how to stop the MariaDB service, see "Start/Stop."
2. For MariaDB 10.5, select Start > MariaDB 10.5 (x64) > my.ini(MariaDB 10.5 (x64)). For MariaDB 10.3, select Start > MariaDB 10.3 (x64) > my.ini(MariaDB 10.3 (x64)). For MariaDB 5.5, select Start > MariaDB 5.5 (x64) > my.ini(MariaDB 5.5 (x64)). By default, the system opens the my.ini file by using Notepad.
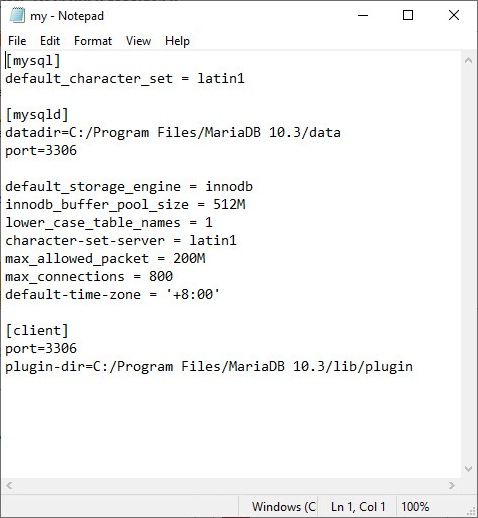
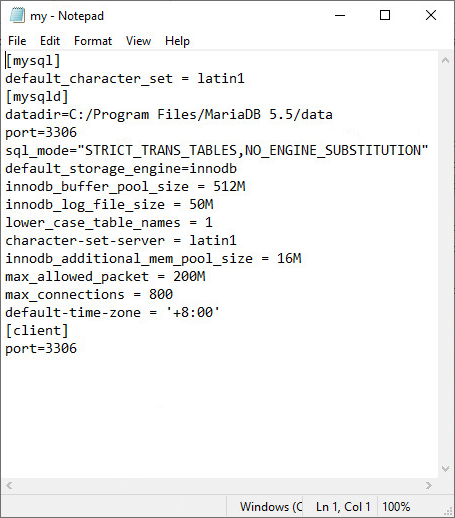
3. Modify the parameter values under [mysql] and [mysqld]. For more information about each parameter value, see Table 1.
Add the following information under [mysql]:
default_character_set = latin1
Add the following information under [mysqld]:
default_storage_engine = innodb
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 512M
lower_case_table_names = 1
character-set-server = latin1
innodb_additional_mem_pool_size = 16M (applicable to only MariaDB 5.5)
max_allowed_packet = 200M
max_connections = 800
default-time-zone = '+8:00'
Table 1 Configuration parameters
|
Parameter name |
Parameter |
Description |
|
Storage engine |
default_storage_engine |
Set the default storage engine. IMC supports only InnoDB. |
|
Whether the table names are case-insensitive |
lower_case_table_names |
Specify whether the table names are case-sensitive: 0 for yes and 1 for no. |
|
Character set |
default_character_set and character-set-server
|
Character set used by the database. For example, the character set is gbk for Chinese, latin1 for English, and sjis for Japanese. |
|
InnoDB buffer |
innodb_buffer_pool_size |
Capacity of the InnoDB buffer pool. |
|
innodb_additional_mem_pool_size |
Capacity of the InnoDB additional memory pool. |
|
|
Maximum packet capacity |
max_allowed_packet |
Maximum data packet capacity. |
|
Maximum number of connections |
max_connections |
Maximum number of connections allowed by the database. You can also adjust the maximum number of connections based on the number of components installed. For the connection count of each component or module, see Intelligent Management Center User Guide. |
|
Time zone |
default-time-zone |
You must specify a specific time zone for MariaDB. You can use a named time zone (such as Europe/Helsinki, America/Eastern, or MET) when you have created and populated the time zone information table in the MariaDB database. |
|
Transaction isolation level |
transaction_isolation |
When you install the EIA component, edit the configuration file named my.cnf/my_en.cnf and identify whether the transaction_isolation configuration item exists under the [mysqld] configuration: · If yes, change the value for the configuration item to READ-COMMITTED. · If not, add the transaction_isolation=READ-COMMITTED configuration to the configuration file. |
4. After you edit the my.ini file as shown in Figure 16, Figure 17, and Figure 18, save the file and restart MariaDB for the changes to take effect.
Figure 16 Partial content of the my.ini file for MariaDB 10.5
Figure 17 Partial content of the my.ini file for MariaDB 10.3
Figure 18 Partial content of the my.ini file for MariaDB 5.5
(Optional.) Backup the database
1. If mysqldump is used for database backup, data insertion might slow down, leading to data backlog. During the backup period, there might be no data or very little data. To resolve this issue, modify the my.ini configuration file, which is the configuration file of the database.
2. Open the my.ini file and add the following content.
[mysqldump]
single-transaction
3. After editing the my.ini file, save the file.
Uninstallation
To uninstall MariaDB, simply use the installer provided by MariaDB.
1. Double-click the MariaDB installation file to start the installer.
Figure 19 Start the installer
2. Click Next to access the Change, repair, or remove installation page.
Figure 20 Change, repair, or remove installation
3. Click Remove to access the Default Instance Properties page.
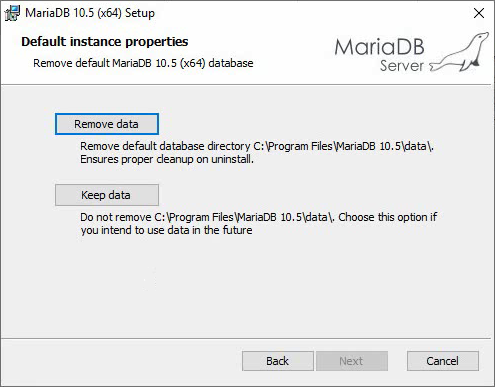
Figure 21 Default instance properties
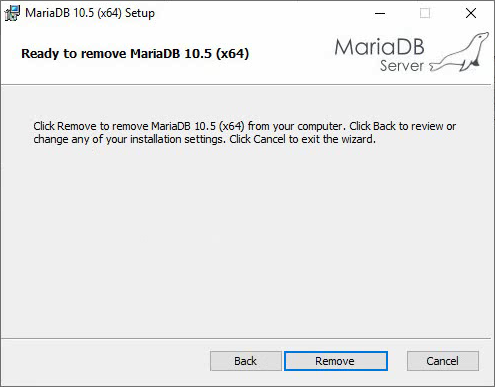
4. Click Remove data to access the Ready to remove MariaDB 10.5 (x64) page.
Figure 22 Ready to remove MariaDB 10.5 (x64)
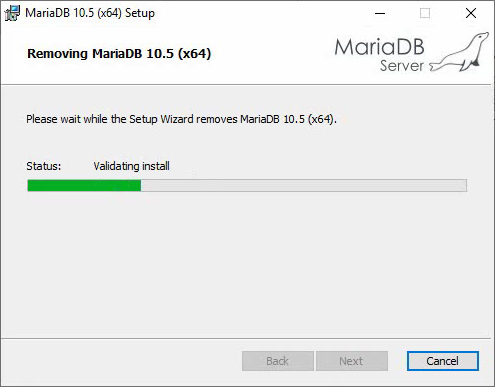
5. Click Remove to start uninstalling MariaDB.
Figure 23 Removing MariaDB 10.5 (x64)
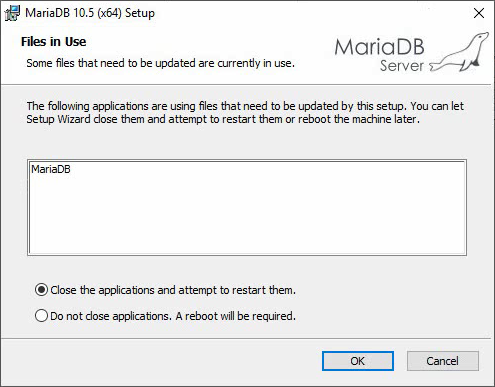
6. If the Files in Use window opens, select Close the applications and attempt to restart them, and then click OK to proceed with the uninstallation.
Figure 24 Files in Use
7. Click Finish to complete the MariaDB uninstallation.
Figure 25 Uninstallation completed
FAQ
Why does the database contain garbled characters?
When you install MariaDB, set the appropriate character set based on your current language environment. If you cannot do that, garbled characters might exist in the data in the database. To resolve this issue, change the values for the default_character_set and character-set-server parameters under [mysql] in the my.ini file, as described in "Modify parameters in the my.ini file." Table 2 shows the commonly used character sets. If the operating system uses any other language, set the correct character set according to the official MariaDB documentation.
|
Language environment |
Character set |
|
Chinese |
Gbk |
|
English |
latin1 |
|
Japanese |
Sjis |