- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 04-Automatic IRF Setup Configuration Examples | 152.03 KB |
Contents
General restrictions and guidelines
Example: Using Python script to set up an IRF fabric automatically
Configuring Device C (the DHCP server)
Introduction
This document provides examples for using Python script to set up an IRF fabric automatically.
Prerequisites
The configuration examples in this document were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
This document assumes that the candidate IRF devices are operating in standalone mode.
This document assumes that you have basic knowledge of IRF, Python, and automatic IRF setup.
General restrictions and guidelines
The switch can form an IRF fabric only with switches of the same model. Make sure the following items are the same across all member devices:
· Number of cards.
· Card models.
· Slot number for cards of the same model.
· Operating mode for the same slot (set by using the switch-mode command).
Example: Using Python script to set up an IRF fabric automatically
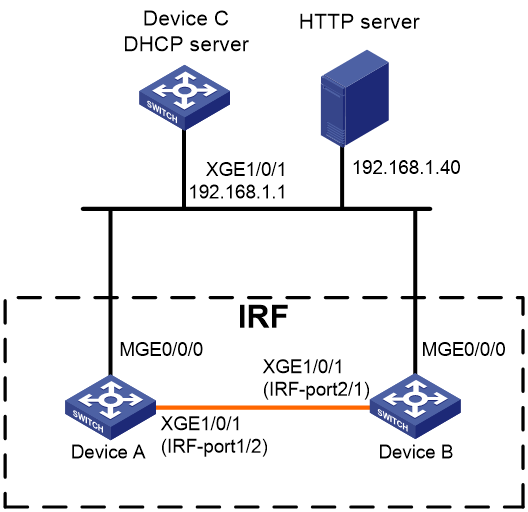
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 1, the administrator has only remote access to Device A and Device B, which have been physically connected for IRF setup. To have the two devices automatically configured into an IRF fabric:
· Edit a Python script file to configure Device A and Device B as follows:
¡ Enable the devices to merge into an IRF fabric automatically.
¡ Enable Telnet access to the IRF fabric, and configure password authentication on VTY lines.
· Store the Python file on an HTTP file server.
· Issue the Python script file to the devices through a DHCP server.
Restrictions and guidelines
When you set up an IRF fabric by using Python script, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· To do a successful automatic IRF setup, make sure the network environment has been set up as planned before you power on the candidate IRF member devices.
In this example, make sure the network has been set up as shown in Figure 1 before you power on Device A and Device B.
· The devices can start python-based automatic IRF setup only upon initial power-on or when they do not have next-startup configuration files.
· Two devices must run the same software version for a successful IRF setup. To ensure a successful IRF setup, edit the script to have the IRF member devices load the same software version.
· As a best practice, do not edit the content format of the Python script file provided in this document. If the file contains errors such as redundant spaces or characters, you will receive the File "autocfgjuQccA", line n error message. The message indicates that the command at line n has failed to execute.
· The IRF setup script contains steps to verify validity of the configuration files and software image file.
¡ If file validity check is desirable, save the configuration and software image files along with their correct MD5 files to the HTTP file server. Invalid MD5 files will result in a file download failure.
¡ If file validity check is not desirable, you do not need to save the MD5 files for the configuration and software image files on the server. The system will skip file validity check and continue with subsequent steps. In this situation, you will receive an MD5 file retrieval failure message, which does not require administrative action.
Procedures
Preparing files
1. Create the Python script file for IRF setup and then store it on the HTTP server. In this example, the script file is named device.py.
Use the script to have each member device perform the following operations:
a. (Optional.) Verifies that the flash memory has sufficient storage space for the downloaded files.
b. Downloads the files for IRF setup from the HTTP server, including the configuration file, the software image file, and the sn.txt.
c. Sets the software image file as the main startup image file.
d. Assigns a unique IRF member ID to each member device based on their SNs.
e. Specifies the configuration file as the main next-startup configuration file.
f. Reboots.
The following is the sample Python script file content:
#!usr/bin/python
import comware
from time import strftime,gmtime,sleep
import signal
import os
import string
import commands
import hashlib
#python_config_file_mode
#'python_static'
#python_serial_number
#U can use 2 modes to obtain the config file
#- 'python_static'
#- 'python_serial_number'
python_config_file_mode = "python_serial_number"
#specify the minimum amount of storage space (in KB) required for saving the files
required_space = 500000
#transfer information
username = ""
password = ""
hostname = "192.168.1.40"
protocol = "http"
vrf = ""
config_timeout = 120
irf_timeout = 120
image_timeout = 2100
#Server file path
server_path = ""
#Local file path
local_path = "flash:/"
#Local config file name
config_local_name = "startup.cfg"
#Config file name on the server
config_server_name = "startup.cfg"
#Local boot file name (use the S10500X switch series as an exmaple)
boot_local_name = "s10500X.ipe"
#Boot file name on the server (use the S10500X switch series as an exmaple)
boot_server_name = "s10500X.ipe"
#Local SN file name
irf_local_name = "sn.txt"
#SN file name on the server
irf_server_name = "sn.txt"
python_log_name = ""
#Write the log file
def write2Log(info):
global python_log_name, local_path
if python_log_name == "":
try:
python_log_name = "%s%s_python_%s_script.log" %(local_path, strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S", gmtime()), os.getpid())
except Exception as inst:
print inst
fd = open(python_log_name, "a")
fd.write(info)
fd.flush()
fd.close()
#Get the file path according to the chassis ID and slot ID
def getPath(chassisID, slotID):
global local_path
path = ""
obj = comware.get_self_slot()
if (obj[0] == chassisID) and (obj[1] == slotID):
return local_path
if chassisID != -1:
path = "chassis%d#" % chassisID
if slotID != -1:
path = "%sslot%d#%s" %(path, slotID, local_path)
return path
#Remove files
def removeFile(filename):
try:
os.remove(filename)
except os.error:
pass
#Clear device temp files
def cleanDeviceFiles(str, oDevNode):
global config_local_name, boot_local_name, irf_local_name
sFilePath = getPath(oDevNode[0], oDevNode[1])
if str == "error":
removeFile("%s%s" %(sFilePath, config_local_name))
removeFile("%s%s" %(sFilePath, boot_local_name))
removeFile("%s%s" %(sFilePath, irf_local_name))
removeFile("%s%s.md5" %(sFilePath, config_local_name))
removeFile("%s%s.md5" %(sFilePath, boot_local_name))
removeFile("%s%s.md5" %(sFilePath, irf_local_name))
write2Log("\ndelete %s all files\n" %sFilePath)
print "\ndelete %s all files" %sFilePath
#Clear files
def cleanupFiles(str):
aSlotRange = []
if ("get_standby_slot" in dir(comware)):
aSlotRange = aSlotRange + comware.get_standby_slot()
aSlotRange.append(comware.get_self_slot())
i = 0
while i < len(aSlotRange):
if(aSlotRange[i] != None):
cleanDeviceFiles(str, aSlotRange[i])
i = i + 1
#Verify if free space is available for downloading the configuration file and software image file
def verifyfreespace(path):
global required_space
try:
s = os.statvfs(path)
freespace = (s.f_bavail * s.f_frsize) /1024
write2Log("\nthe %s free space is %s" %(path, freespace))
print "\n####the %s free space is %s####" %(path, freespace)
if required_space > freespace:
write2Log("\nthe %s space is not enough" % path)
print "\n####the %s space is not enough####" % path
return False
except Exception as inst:
write2Log("\nverify %s free space exception: %s" % (path, inst))
print "\n####verify %s free space exception: %s####" % (path, inst)
return False
return True
#Verify if the free space is sufficient.
def verifyDeviceFree(obj):
path = getPath(obj[0], obj[1])
if True != verifyfreespace(path):
return False
return True
#Check the free space of all MPUs
def verifyAllFreeSpace():
aSlotRange = []
if ("get_standby_slot" in dir(comware)):
aSlotRange = aSlotRange + comware.get_standby_slot()
aSlotRange.append(comware.get_self_slot())
bAllEnough = True
i = 0
while i < len(aSlotRange):
if(aSlotRange[i] != None) and (True != verifyDeviceFree(aSlotRange[i])):
bAllEnough = False
i = i + 1
return bAllEnough
def doExit(str):
if str == "success":
write2Log("\nThe script is running success!")
print "\n#### The script is running success! ####"
cleanupFiles("success")
comd = "reboot force"
comware.CLI(comd, False)
exit(0)
if str == "error":
write2Log("\nThe script is running failed!")
print "\n#### The script is running failed! ####"
cleanupFiles("error")
exit(1)
else:
exit(0)
#Get Chassis and Slot
def getChassisSlot(style):
if style == "master":
obj = comware.get_self_slot()
if len(obj) <= 0:
write2Log("\nget %s chassis and slot failed" % style)
print "\n####get %s chassis and slot failed####" % style
return None
return obj
#Signal terminal handler function
def sig_handler_no_exit(signum, function):
write2Log("\nSIGTERM Handler while configuring boot-loader variables")
print "\n####SIGTERM Handler while configuring boot-loader variables####"
#Signal terminal handler
def sigterm_handler(signum, function):
write2Log("\nSIGTERM Handler")
print "\n####SIGTERM Handler####"
cleanupFiles("error")
doExit("error")
#Transfer files
def doCopyFile(src = "", des = "", login_timeout = 10):
global username, password, hostname, protocol, vrf
print "INFO: Starting Copy of %s" % src
try:
removeFile(des)
obj = comware.Transfer(protocol, hostname, src, des, vrf, login_timeout, username, password)
if obj.get_error() != None:
write2Log("\ncopy %s failed: %s" % (src, obj.get_error()))
print "\n####copy %s failed: %s####" % (src, obj.get_error())
return False
except Exception as inst:
write2Log("\ncopy %s exception: %s" % (src, inst))
print "\n####copy %s exception: %s####" % (src, inst)
return False
write2Log("\ncopy file %s to %s success" % (src, des))
print "INFO: Completed Copy of %s" % src
return True
#Get MD5SUM from md5ConfigFile
def getMD5SumGiven(keyword, filename):
try:
file = open(filename, "r")
line = file.readline()
while "" != line:
if not string.find(line, keyword, 0, len(keyword)):
line = line.split("=")
line = line[1]
line = line.strip()
file.close()
return line
line = file.readline()
file.close()
except Exception as inst:
write2Log("\nget %s md5 exception: %s" % (filename, inst))
print "\n####get %s md5 exception: %s####" % (filename, inst)
return ""
#Verify MD5SUM of the file
def verifyMD5sumofFile(md5sumgiven, filename):
if md5sumgiven == "":
write2Log("\nverify %s md5 error: the %s md5 file is error" %(filename, filename))
print "\n####verify %s md5 error: the %s md5 file is error####" %(filename, filename)
return False
try:
m = hashlib.md5()
f = open(filename, 'rb')
buffer = 8192
while 1:
chunk = f.read(buffer)
if not chunk:
break
m.update(chunk)
f.close()
md5calculated = m.hexdigest()
except Exception as inst:
write2Log("\nverify %s md5 exception: %s" % (filename, inst))
print "\n####verify %s md5 exception: %s####" % (filename, inst)
return False
if md5sumgiven == md5calculated:
return True
write2Log("\nverify %s md5 error: md5sumgiven is %s filemd5 is %s" %(filename, md5sumgiven, md5calculated))
print "\n####verify %s md5 error: md5sumgiven is %s filemd5 is %s####" %(filename, md5sumgiven, md5calculated)
return False
#Check MD5 file
def checkFile(src, dest):
src = "%s.md5" % src
destmd5 = "%s.md5" % dest
bFlag = doCopyFile(src, destmd5, 120)
if (True == bFlag) and (True == verifyMD5sumofFile(getMD5SumGiven("md5sum", destmd5), dest)):
write2Log("\ncheckFile success: %s" % destmd5)
print "\n####checkFile success: %s####" % destmd5
return True
elif (True != bFlag):
write2Log("\n%s is not exist! Don't verify the MD5 file!" % destmd5)
print "INFO: %s is not exist! Don't verify the MD5 file!" % destmd5
return True
return False
#Get config file according to the mode
def getCfgFileName():
global config_server_name
if (python_config_file_mode == "python_serial_number") and (os.environ.has_key('DEV_SERIAL')):
config_server_name = "%s.cfg" % os.environ['DEV_SERIAL']
return config_server_name
else:
return config_server_name
#Copy file to all standby slots
def syncFileToStandby(sSrcFile, sFileName):
try:
aSlotRange = []
if ("get_standby_slot" in dir(comware)):
aSlotRange = aSlotRange + comware.get_standby_slot()
i = 0
while i < len(aSlotRange):
if(aSlotRange[i] != None):
sDestFile = "%s%s" %(getPath(aSlotRange[i][0], aSlotRange[i][1]), sFileName)
removeFile(sDestFile)
open(sDestFile,"wb").write(open(sSrcFile,"rb").read())
write2Log("\nsync file to standby %s" % (sDestFile))
print "\n####sync file to standby %s####" % (sDestFile)
i = i + 1
except Exception as inst:
write2Log("\nsync file to standby %s exception: %s" % (sSrcFile, inst))
print "\n####sync file to standby %s exception: %s####" % (sSrcFile, inst)
#Procedure to copy config file by using global information
def copyAndCheckFile(src, dest, timeout):
global server_path, local_path
srcTmp = "%s%s" % (server_path, src)
sDestFile = "%s%s" % (local_path, dest)
if (True == doCopyFile(srcTmp, sDestFile, timeout)) and (True == checkFile(srcTmp, sDestFile)):
syncFileToStandby(sDestFile, dest)
return True
else:
srcTmp = "%sdefault_%s" %(server_path, src)
if (True == doCopyFile(srcTmp, sDestFile, timeout)) and (True == checkFile(srcTmp, sDestFile)):
syncFileToStandby(dest)
return True
return False
# Split the Chassis and Slot
def splitChassisSlot(chassisID, slotID):
chassis_slot = ""
if chassisID != -1:
chassis_slot = " chassis %d" % chassisID
if slotID != -1:
chassis_slot = "%s slot %d" %(chassis_slot, slotID)
return chassis_slot
#download startup image package from the HTTP server
def copyBootImage():
global image_timeout, local_path, boot_server_name, boot_local_name
src = "%s" % boot_server_name
return copyAndCheckFile(src, boot_local_name, image_timeout)
#download the configuration file from the HTTP server
def copyCfgFile():
global config_timeout, local_path, config_local_name
src = "%s" % getCfgFileName()
return copyAndCheckFile(src, config_local_name, config_timeout)
#download the sn.txt file from the HTTP server
def copyIrfStack():
global irf_timeout, local_path, irf_local_name, irf_server_name
src = "%s" % irf_server_name
return copyAndCheckFile(src, irf_local_name, config_timeout)
# Procedure to install boot image
def installBoot(chassis_slot, sFile, style):
result = None
write2Log("\ninstall%s%s begin" %(chassis_slot, style))
print "INFO: Install%s%s Start, Please Wait..." %(chassis_slot, style)
comd = "boot-loader file %s%s%s" % (sFile, chassis_slot, style)
try:
result = comware.CLI(comd, False)
if result == None:
write2Log("\nboot-loader file %s%s%s failed" % (sFile, chassis_slot, style))
print "\n####boot-loader file %s%s%s failed####" % (sFile, chassis_slot, style)
return False
except Exception as inst:
write2Log("\nboot-loader %s exception: %s" % (sFile, inst))
print "\n####boot-loader %s exception: %s####" % (sFile, inst)
return False
return True
#Procedure to install boot image
def installBootImage():
global boot_local_name
aSlotRange = [comware.get_self_slot()]
if ("get_standby_slot" in dir(comware)):
aSlotRange = aSlotRange + comware.get_standby_slot()
bInstallOk = True
i = 0
while i < len(aSlotRange):
sFile = "%s%s" %(getPath(aSlotRange[0][0], aSlotRange[0][1]), boot_local_name)
if False == installBoot(splitChassisSlot(aSlotRange[i][0], aSlotRange[i][1]), sFile, " main"):
bInstallOk = False
i = i + 1
return bInstallOk
#execute the startup saved-configuration command to specify the next-startup configuration file
def startupCfg():
global local_path, config_local_name
result = None
dest = "%s%s" %(local_path, config_local_name)
write2Log("\nstartup saved-configuration %s begin" %dest)
print "INFO: Startup Saved-configuration Start"
comd = "startup saved-configuration %s main" % dest
try:
result = comware.CLI(comd, False)
if result == None:
write2Log("\nstartup saved-configuration %s failed" % dest)
print "\n####startup saved-configuration %s failed####" % dest
return False
except Exception as inst:
write2Log("\nstartup %s exception: %s" % (dest, inst))
print "\n####startup %s exception: %s####" % (dest, inst)
return False
write2Log("\nstartup saved-configuration %s success" % dest)
print "INFO: Completed Startup Saved-configuration"
return True
def getIrfCfg(line, num):
line = line.split()
number = None
if 3 == len(line):
number = line[num]
else :
number = None
return number
def getMemberID():
aMemId = comware.get_self_slot()
memId = None
if aMemId[0] == -1 :
memId = aMemId[1]
else :
memId = aMemId[0]
return memId
def getNewMemberID():
global irf_local_name, local_path, env
filename = "%s%s" %(local_path, irf_local_name)
serNum = os.environ['DEV_SERIAL']
reNum = None
try:
file = open(filename, "r")
line = file.readline()
while "" != line:
if (serNum == getIrfCfg(line, 0)):
file.close()
reNum = getIrfCfg(line, 2)
return reNum
line = file.readline()
file.close()
except Exception as inst:
write2Log("\nget renumberID exception: %s" % inst)
print "\n####get renumberID exception: %s####" % inst
write2Log("\nget %s renumberID failed" % filename)
print "\n#### get %s renumberID failed ####" % filename
return reNum
#determine whether the IRF fabric has been built successfully
def isIrfDevice():
try:
result = comware.CLI("display irf", False)
if result == None:
return False
except Exception as inst:
return False
return True
#parse the sn.txt file and renumber the member ID as configured in the file
def getIrfComd():
comd = None
newMemberID = getNewMemberID()
aMemId = comware.get_self_slot()
if None == newMemberID:
return None
if False == isIrfDevice():
comd = "system-view ; irf member %s ; chassis convert mode irf" % newMemberID
else:
comd = "system-view ; irf member %s renumber %s" % (getMemberID(), newMemberID)
return comd
def stackIrfCfg():
global env
if (not os.environ.has_key('DEV_SERIAL')):
write2Log("\nenviron variable 'DEV_SERIAL' is not found!")
print "\n####environ variable 'DEV_SERIAL' is not found!####"
return False
comd = getIrfComd()
if None == comd:
return False
result = None
write2Log("\nstartup stack irf begin")
print "INFO: Startup stack irf Start"
try:
result = comware.CLI(comd, False)
if result == None:
write2Log("\nstartup stack irf failed: %s" % comd)
print "\n####startup stack irf failed: %s####" %comd
return False
except Exception as inst:
write2Log("\nstartup stack irf exception: %s command: %s" % (inst, comd))
print "\n####startup stack irf exception: %s command: %s####" % (inst, comd)
return False
write2Log("\nstartup stack irf success")
print "INFO: Completed Startup Stack Irf"
return True
#Check if all standby slots are ready
def ifAllStandbyReady():
if (("get_slot_range" in dir(comware)) == False):
return True
aSlotRange = comware.get_slot_range()
bAllReady = True
for i in range(aSlotRange["MinSlot"], aSlotRange["MaxSlot"]):
oSlotInfo = comware.get_slot_info(i)
if (oSlotInfo != None) and (oSlotInfo["Role"] == "Standby") and (oSlotInfo["Status"] == "Fail"):
bAllReady = False
write2Log("\nSlot %s is not ready!" %i)
print "\n####Slot %s is not ready!####" %i
return bAllReady
# If any standby slots are not ready, wait
def waitStandbyReady():
while ifAllStandbyReady() == False:
sleep(10)
#python main
# User can stop the script when downloading files
waitStandbyReady()
signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, sigterm_handler)
if (True == verifyAllFreeSpace()) and (True == copyBootImage()) and (True == copyCfgFile()) and (True == copyIrfStack()):
# User cannot stop the script after downloading files
signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, sig_handler_no_exit)
if (True == installBootImage()) and (True == startupCfg()) and (True == stackIrfCfg()):
doExit("success")
doExit("error")
2. Create a configuration file for each device and save the configuration files to the HTTP server.
Name the configuration files in serial_number.cfg format, where the serial_number argument represents the serial number of the device.
In the configuration files, specify the configuration for IRF setup and parameters for device login (telnet in this example), including login authentication settings.
|
|
NOTE: To obtain the serial number, use one of the following methods: · Examine the label on the chassis rear panel. · Execute the display device manuinfo command. |
This example uses the following configuration files:
¡ 210235A045B05B0004354.cfg:
#
telnet server enable
#
irf mac-address persistent timer
irf auto-update enable
undo irf link-delay
irf member 1 priority 1
irf mode normal
#
irf-port 1/2
port group mdc 1 interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1 mode enhanced
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
#
interface M-GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 192.168.0.63 255.255.255.0
#
line vty 0 63
user-role network-admin
set authentication password simple 123
#
¡ 210235A045B05B0004350.cfg:
#
telnet server enable
#
irf mac-address persistent timer
irf auto-update enable
undo irf link-delay
irf member 2 priority 1
irf mode normal
#
irf-port 2/1
port group mdc 1 interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1 mode enhanced
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
#
interface M-GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 192.168.0.63 255.255.255.0
#
line vty 0 63
user-role network-admin
set authentication password simple 123
#
3. Create the sn.txt file to store serial number and member ID mappings for the member devices, and then save the file to the HTTP server. The device will run the python script to parse the sn.txt file, change its member ID as configured, and then self-configure with the settings for that member ID.
sn Irf group Irf number
210235A045B05B0004354 100 1
210235A045B05B0004350 100 2
|
Column |
Description |
|
sn |
Serial numbers of the member devices. Each SN uniquely represents a device. The script uses these SNs to assign a unique IRF member ID to each member device and configure the member devices based on their member IDs. To obtain the serial number, use one of the following methods: · Examine the label on the chassis rear panel. · Execute the display device manuinfo command. |
|
Irf group |
IRF group number administratively used for easy identification of IRF fabric memberships. This number is not used for IRF setup. You can use any numbering plan for your management purposes. |
|
Irf number |
IRF member ID. Each device must use a unique member ID. |
4. Save the startup software image file (s10500X.ipe in this example) to the HTTP server. (Details not shown.)
You must upgrade software for consistency if the member devices use different versions of software.
5. Save MD5 files for the configuration files and software image file to the HTTP server if file verification is required. You must save the MD5 files in the same directory as the configuration files and software image file. (Details not shown.)
Configuring Device C (the DHCP server)
# Enable DHCP. Configure an address pool to assign IP addresses to the subnet that contains the member switches. This example uses the 192.168.1.0/24 subnet.
<DeviceC> system-view
[DeviceC] dhcp enable
[DeviceC] dhcp server ip-pool 1
[DeviceC-dhcp-pool-1] network 192.168.1.0 24
# Specify the URL of the script file for the clients.
[DeviceC-dhcp-pool-1] bootfile-name http://192.168.1.40/device.py
[DeviceC-dhcp-pool-1] quit
Configuring the HTTP server
# Configure the HTTP server and enable HTTP service, as described in the HTTP server user guide. (Details not shown.)
Verifying the configuration
Telnet to any one of the IRF member devices to verify the IRF setup. In this example, telnet to a port on Device A.
# Verify that you can use the configured password to Telnet to the IRF fabric.
Password:
******************************************************************************
* Copyright (c) 2004-2019 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. *
* Without the owner's prior written consent, *
* no decompiling or reverse-engineering shall be allowed. *
******************************************************************************
<DeviceA>
# Verify that Device A and Device B have formed an IRF fabric.
<DeviceA> display irf
MemberID Slot Role Priority CPU-Mac Description
1 1 Standby 1 00e0-fc0f-8c02 ---
*+2 1 Master 1 00e0-fc0f-8c14 ---
--------------------------------------------------
* indicates the device is the master.
+ indicates the device through which the user logs in.
The Bridge MAC of the IRF is: 000c-1000-1111
Auto upgrade : yes
Mac persistent : 6 min
Domain ID : 0
Auto merge : yes
IRF mode : normal
Configuration files
· Device A and Device B:
#
telnet server enable
#
irf mac-address persistent timer
irf auto-update enable
undo irf link-delay
irf member 1 priority 1
irf member 2 priority 1
irf mode normal
#
irf-port 1/2
port group mdc 1 interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1 mode enhanced
#
irf-port 2/1
port group mdc 1 interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1 mode enhanced
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
#
interface M-GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 192.168.0.63 255.255.255.0
#
line vty 0 63
user-role network-admin
set authentication password hash $h$6$40hhbS6PeVJORuQu$X/9nQ9PSpPbtGDukVYGOW2Ao
9yJaekVbzovWv23pEKCVwzqqRP8Elnm1qRm4TEIbAetmwQG5gWyREMC3zRCOaQ==
#
· Device C:
#
dhcp enable
#
dhcp server ip-pool 1
network 192.168.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
bootfile-name http://192.168.1.40/device.py
#