- Table of Contents
-
- 03-Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-MAC address table configuration
- 02-PFC configuration
- 03-Bulk interface configuration
- 04-Ethernet interface configuration
- 05-Ethernet link aggregation configuration
- 06-M-LAG configuration
- 07-Port isolation configuration
- 08-VLAN configuration
- 09-MVRP configuration
- 10-Loopback, null, and inloopback interface configuration
- 11-QinQ configuration
- 12-VLAN mapping configuration
- 13-Loop detection configuration
- 14-Spanning tree configuration
- 15-LLDP configuration
- 16-L2PT configuration
- 17-Cut-through Layer 2 forwarding configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 02-PFC configuration | 59.90 KB |
Configuring PFC
About PFC
Priority-based flow control (PFC) provides a finer flow control mechanism to implement lossless packet transmission on Ethernet.
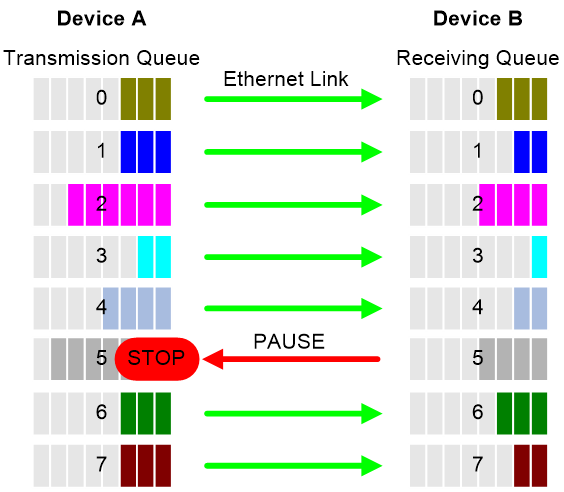
PFC performs flow control for packets based on the 802.1p priorities carried in packets. As shown in Figure 1, PFC establishes eight virtual channels over an Ethernet link, each corresponding to an 802.1p priority. Any virtual channel can be paused or restarted independent of the other channels. This mechanism allows multiple types of traffic to coexist on and share an Ethernet link.
Figure 1 How PFC works
When congestion occurs on the local end, the device determines how to process received packets based on the 802.1p priorities carried in packets as follows:
· If PFC is enabled for the 802.1p priority carried in a packet, the local end accepts the packet and sends PFC pause frames to notify the remote end to stop sending packets carrying the 802.1p priority. The remote end stops sending packets carrying the 802.1p priority after receiving the PFC pause frames. This process is repeated until congestion is eliminated.
· If PFC is not enabled for the 802.1p priority carried in a packet, the local end drops the packet.
Restrictions and guidelines
You can configure PFC in system view or Ethernet interface view. When you configure PFC in system view and Ethernet interface view multiple times, the most recent configuration takes effect.
If you do not enable PFC on an interface, the interface can receive but cannot process PFC pause frames. To make PFC take effect, you must enable PFC on both ends.
To avoid packet loss, apply the same PFC configuration to all interfaces that the packets pass through.
Generic flow control and PFC are mutually exclusive on an interface. For more information about generic flow control, see Ethernet interface configuration in Interface Configuration Guide.
In an IRF network, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· For IRF and other protocols to operate correctly, as a best practice, do not enable PFC for 802.1p priority 0, 6, or 7.
· To perform PFC on an IRF port, configure PFC on the IRF port and the IRF physical ports that are bound to the IRF port.
For information about IRF, see IRF configuration Guide.
For PFC to take effect in an overlay network, execute the qos trust tunnel-dot1p command. For information about the overlay network, see VXLAN Configuration Guide. For information about the qos trust tunnel-dot1p command, see ACL and QoS Command Reference.
Configuring PFC on interfaces
Configuring PFC on an Ethernet interface
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable PFC on all Ethernet interfaces.
priority-flow-control { auto | enable }
By default, PFC is disabled on all Ethernet interfaces.
3. Enable PFC for 802.1p priorities on all Ethernet interfaces.
priority-flow-control no-drop dot1p dot1p-list
By default, PFC is disabled for all 802.1p priorities on all Ethernet interfaces.
4. Enter Ethernet interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
5. Enable PFC on the Ethernet interface.
priority-flow-control { auto | enable }
By default, PFC is disabled.
6. Enable PFC for 802.1p priorities.
priority-flow-control no-drop dot1p dot1p-list
By default, PFC is disabled for all 802.1p priorities.
Verifying and maintaining PFC
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display the PFC information of interfaces. |
display priority-flow-control interface [ interface-type [ interface-number ] ] |