- Table of Contents
-
- 07-Layer 3—IP Routing Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Basic IP routing configuration
- 02-Static routing configuration
- 03-RIP configuration
- 04-OSPF configuration
- 05-IS-IS configuration
- 06-BGP configuration
- 07-Policy-based routing configuration
- 08-IPv6 static routing configuration
- 09-RIPng configuration
- 10-OSPFv3 configuration
- 11-IPv6 policy-based routing configuration
- 12-Guard route configuration
- 13-Routing policy configuration
- 14-MTR configuration
- 15-DCN configuration
- 16-RIR configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 12-Guard route configuration | 115.20 KB |
Restrictions and guidelines: guard route configuration
Display and maintenance commands for guard routes
Guard route configuration examples
Example: Configuring a guard route
Configuring guard routes
About guard routes
A guard route directs traffic to the guard device for filtering and cleaning. You can manually configure a guard route on the guard device, or use a script to automatically configure a guard route upon receipt of a notification.
Guard route characteristics
Guard routes use Null 0 as the outgoing interface.
Guard routes are inactive routes and will not be installed into the FIB.
You must configure a routing protocol, such as BGP, OSPF, or OSPFv3, to redistribute and advertise guard routes for directing traffic to the guard device.
Guard route mechanism
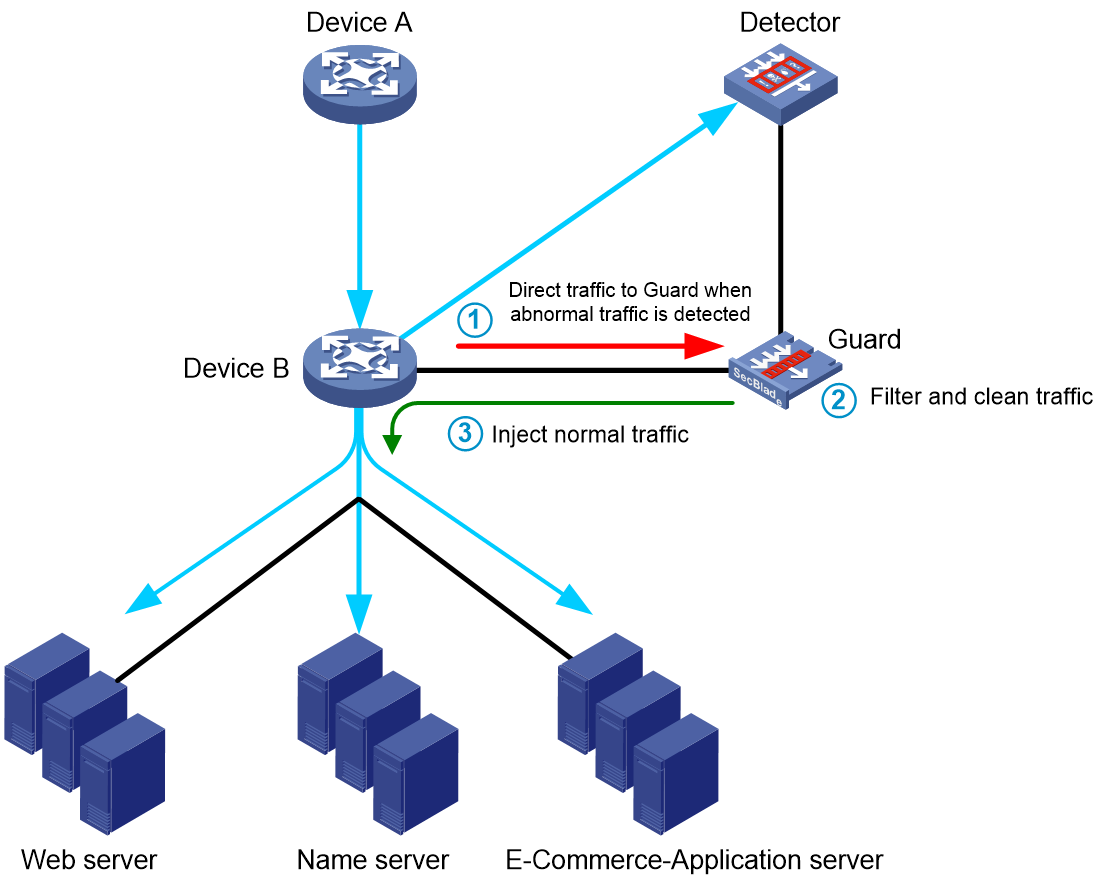
Figure 1 Guard route network diagram
As shown in Figure 1, Device B uses port mirroring to mirror traffic destined for the application servers to the detector for monitoring. It uses a routing protocol to redistribute guard routes from the guard device.
When no abnormal traffic is detected, Device B forwards traffic without the participation of the guard device.
When abnormal traffic is detected, the detector performs one of the following tasks:
· Sends a notification to the guard device. The guard device then automatically generates a guard route.
· Generates an alarm to notify the network administrator. The administrator then manually configures a guard route on the guard device.
The destination address of the guard route is the address to which the abnormal traffic is destined.
After the guard route is configured, the guard device advertises the route to Device B. Device B directs all traffic destined to the destination address of the guard route to the guard device. The guard device filters and cleans the traffic and then sends the normal traffic back to Device B.
Restrictions and guidelines: guard route configuration
A guard device is typically used for traffic filtering and cleaning. To avoid system consumption, configure a routing policy on the guard device or its connected device to disable receiving and advertising non-guard routes. For more information about routing policies, see "Configuring routing policies."
Configuring a guard route
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure a guard route.
IPv4:
ip route-guard ip-address { mask-length | mask }
By default, no IPv4 guard routes exist.
IPv6:
ipv6 route-guard ipv6-address prefix-length
By default, no IPv6 guard routes exist.
Display and maintenance commands for guard routes
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Commands |
|
Display IPv4 guard route information. |
display ip routing-table protocol guard [ inactive | verbose ] |
|
Display IPv6 guard route information. |
display ipv6 routing-table protocol guard [ inactive | verbose ] |
Guard route configuration examples
Example: Configuring a guard route
Network configuration
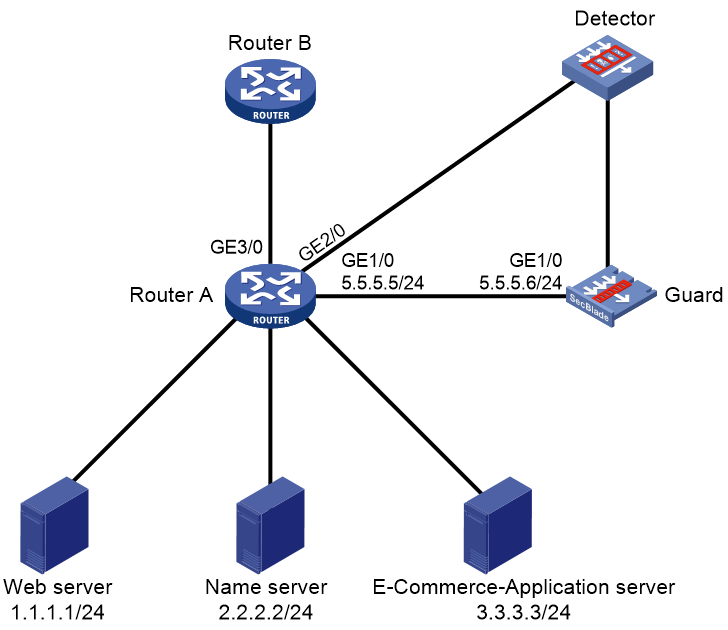
As shown in Figure 1, Router A communicates with the application servers through Router B.
Perform the following tasks to direct traffic destined to 1.1.1.1 to the guard device for filtering and cleaning:
· Configure port mirroring on Router B to mirror the traffic from Router A to the application servers to the detector for monitoring.
· Enable Router B to establish an IBGP peer relationship with the guard device, redistribute guard routes from the guard device, and advertise the guard routes to Router A.
· Configure a guard route destined to 1.1.1.1 on the guard device.
Figure 2 Network diagram
Procedure
1. Configure IP addresses and routes to ensure network connectivity. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure port mirroring on Router B:
# Create local mirroring group 1.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] mirroring-group 1 local
# Configure local mirroring group 1 to monitor the received packets of GigabitEthernet 3/0.
[RouterB] mirroring-group 1 mirroring-port gigabitethernet 3/0 inbound
# Configure GigabitEthernet 2/0 as the monitor port of local mirroring group 1.
GigabitEthernet 2/0 replicates packets of GigabitEthernet 3/0 and sends the packets to the detector.
[RouterB] mirroring-group 1 monitor-port gigabitethernet 2/0
3. Configure BGP on Router B:
# Create basic ACL 2000 with the deny mode.
[RouterB] acl basic 2000
[RouterB-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] rule 0 deny
[RouterB-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] quit
# Establish an IBGP peer relationship to the guard device.
[RouterB] bgp 100
[RouterB-bgp-default] router-id 2.2.2.2
[RouterB-bgp-default] peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 100
[RouterB-bgp-default] peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface loopback 0
[RouterB-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[RouterB-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 3.3.3.3 enable
[RouterB-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[RouterB-bgp-default] quit
[RouterB] ospf 1
[RouterB-ospf-1] area 0
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 5.5.5.0 0.0.0.255
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[RouterB-ospf-1] quit
# Filter routes advertised to peer 3.3.3.3 by using basic ACL 2000.
[RouterB] bgp 100
[RouterB-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[RouterB-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 3.3.3.3 filter-policy 2000 export
[RouterB-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[RouterB-bgp-default] quit
4. Configure the guard device:
# Configure node 0 in permit mode for routing policy guard-out to set the COMMUNITY attributes for BGP routes.
<Guard> system-view
[Guard] route-policy guard-out permit node 0
[Guard-route-policy] apply community 1:1 no-export no-advertise
[Guard-route-policy] quit
# Establish an IBGP peer relationship to Router B, and enable BGP to redistribute guard routes.
[Guard] bgp 100
[Guard-bgp-default] router-id 3.3.3.3
[Guard-bgp-default] peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100
[Guard-bgp-default] peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface loopback 0
[Guard-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[Guard-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 2.2.2.2 enable
[Guard-bgp-default-ipv4] import-route guard
[Guard-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[Guard-bgp-default] quit
[Guard] ospf 1
[Guard-ospf-1] area 0
[Guard-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
[Guard-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 5.5.5.0 0.0.0.255
[Guard-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[Guard-ospf-1] quit
# Apply routing policy guard-out to routes outgoing to peer 2.2.2.2, and advertise the COMMUNITY attribute to peer 2.2.2.2.
[Guard] bgp 100
[Guard-bgp-default] address-family ipv4 unicast
[Guard-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 2.2.2.2 route-policy guard-out export
[Guard-bgp-default-ipv4] peer 2.2.2.2 advertise-community
[Guard-bgp-default-ipv4] quit
[Guard-bgp-default] quit
# Configure a guard route with the destination address 1.1.1.1 on the guard device.
[Guard] ip route-guard 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
Verifying the configuration
# Display guard route information on the guard device.
[Guard] display ip routing-table protocol guard
Public Routing Table : Guard
Summary Count : 1
Guard Routing table Status : < Active>
Summary Count : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
1.1.1.1/32 Guard 40 0 0.0.0.0 NULL0
Guard Routing table Status : < Inactive>
Summary Count : 0
# Display information about route 1.1.1.1 on Router B.
[RouterB] display bgp routing-table ipv4 1.1.1.1
BGP local router ID: 2.2.2.2
Local AS number: 100
Paths: 1 available, 1 best
BGP routing table information of 1.1.1.1/32:
From : 3.3.3.3 (3.3.3.3)
Rely nexthop : 5.5.5.6
Original nexthop: 3.3.3.3
OutLabel : NULL
Community : <1:1>, No-Export, No-Advertise
AS-path : (null)
Origin : incomplete
Attribute value : MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0
State : valid, internal, best
IP precedence : N/A
QoS local ID : N/A
Traffic index : N/A
VPN-Peer UserID : N/A
DSCP : N/A
EXP : N/A
# Display advertisement information for route 1.1.1.1 on Router B.
[RouterB] display bgp routing-table ipv4 1.1.1.1 advertise-info
BGP local router ID: 2.2.2.2
Local AS number: 100
Paths: 1 best
BGP routing table information of 1.1.1.1/32:
Not advertised to any peers yet
The output shows that traffic destined to 1.1.1.1/32 will be directed to the guard device, and Router B will not advertise route 1.1.1.1/32.