- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 06-Anti-virus | 162.14 KB |
This help contains the following topics:
¡ Configure an anti-virus profile
¡ Configure the cloud query server
Introduction
Anti-virus identifies viruses in the application layer of packets based on an up-to-date virus signature library and takes actions to prevent a network from being infected. This feature is typically deployed on a gateway to insulate the internal network from viruses and protect the internal data.
Anti-virus supports inspecting packets transported through FTP, HTTP, IMAP, NFS, POP3, SMB, or SMTP.
Application scenario
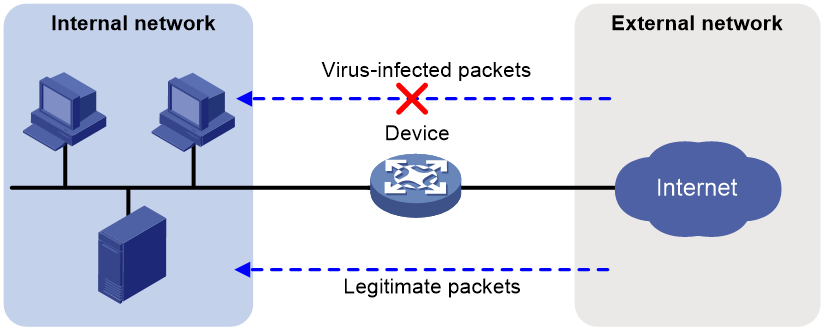
As shown in Figure 1, the device is the gateway of an internal network. Internal users access the external network and download data from the external network. The internal server accepts data uploaded by external users.
In this scenario, you can configure anti-virus on the gateway to protect the internal network. Anti-virus inspects incoming packets, permits legitimate packets to pass, and takes actions, such as alert, block, or redirect, on packets containing viruses.
Figure 1 Anti-virus application scenario
Basic concepts
Virus signature
A virus signature is a character string that uniquely identifies a specific virus. The virus signature library contains the predefined virus signatures.
MD5 rules
An MD5 rule is generated by the system based on the virus signatures in the virus signature library to identify virus-infected files.
Virus exception
Typically, anti-virus takes anti-virus actions on packets matching virus signatures. If a virus proves to be a false alarm, you can set the virus signature as a virus exception. Packets matching the virus exception are permitted to pass.
Application exception
Typically, anti-virus action is protocol specific and applies to all applications carried by the protocol. To take a different action on an application, you can set the application as an exception and specify a different anti-virus action for the application. Application exceptions use application-specific actions and the other applications use protocol-specific actions. For example, the anti-virus action for HTTP is permit. To block the games carried by HTTP, you can set the games as application exceptions and specify the block action for them.
MD5 value exception
If a packet is detected to contain a virus but actually the packet is safe, you can set the MD5 value of the virus as an MD5 value exception. The device will permit subsequent packets matching the MD5 value exception to pass.
You can get the MD5 value of a virus through the threat log.
Anti-virus action
Anti-virus actions apply to the packets that match virus signatures. The actions include the following types:
· Alarm—Permits matching packets and generates logs.
· Block—Blocks matching packets and generates logs.
· Redirect—Redirects matching HTTP connections to a URL and generates logs.
· Permit—Permits matching packets.
Virus detection methods
The device supports the following virus detection methods:
· Virus signature-based detection—The device matches packets against virus signatures in the virus signature library, and determines that a packet contains viruses if a match is found.
· MD5 rule-based detection—The device generates an MD5 hash value for a file to be inspected and compares the value with the system-defined MD5 rules. If a match is found, the file is identified to be virus-infected.
Cloud query
You can enable cloud query in an anti-virus profile. If the file in a packet does not match any local virus signature or MD5 rule, the device will send the MD5 value of the file to the cloud server for cloud query. The device determines the action to apply according to the query result returned from the cloud server.
· If the MD5 value of the file matches an MD5 rule, the file is considered to be virus-infected and the anti-virus action will apply.
· If no matching rule is found for the MD5 value or if the file is verified to be virus-free, the packet will be permitted to pass through.
Anti-virus mechanism
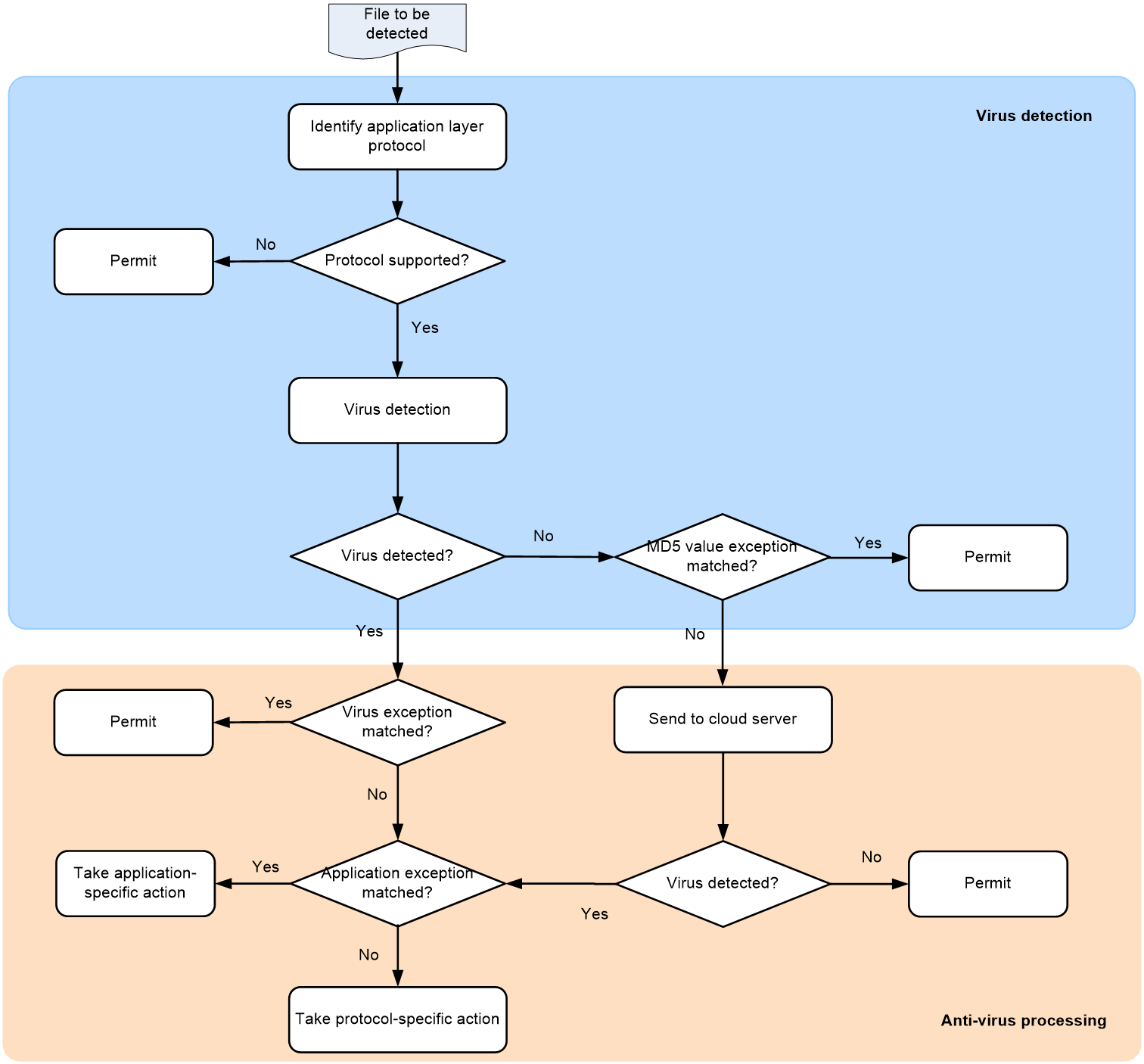
As shown in Figure 2, upon receiving a packet, the anti-virus device performs the following operations:
1. The device compares the packet with the security policies.
If the packet matches a security policy that is associated with an anti-virus profile, the device continues to identify the application layer protocol of the packet.
2. The device identifies whether the anti-virus supports the application layer protocol of the packet.
¡ If not, the device allows the packet to pass without anti-virus inspection.
¡ If yes, the device compares the packet with the virus signatures and MD5 rules.
3. If a matching signature or matching MD5 rule is found, the device performs the following operations:
a. Determines if the matching signature is an exception. If yes, the device permits the packet to pass. If not, the device examines whether the application is an exception.
b. If the application is an exception, the device takes the application-specific action (alert, block, or permit). If the application is not an exception, the device takes the protocol-specific action (alert, block, or redirect).
4. If no matching signature or MD5 rule is found, the device performs the following operations:
a. Determines if the MD5 value of the file in the packet is an MD5 value exception.
- If yes, the device permits the packet to pass.
- If not, the device sends the MD5 value of the file in the packet to the cloud server.
b. If cloud query is disabled in the anti-virus policy, the device permits the packet to pass.
c. If cloud query is enabled in the anti-virus policy but the cloud server does not detect any virus, the device permits the packet to pass.
d. If cloud query is enabled in the anti-virus policy and the cloud server detects the virus, the device determines if the application is an exception.
- If yes, the device takes the application-specific action (alert, block, or permit).
- If not, the device takes the protocol-specific action (alert, block, or redirect).
Restrictions and guidelines
· The cloud query feature is available only for HTTP, IMAP, NFS (read operations only), POP3, and SMTP traffic.
· After you create, edit, or delete an anti-virus profile, the configuration will automatically take effect after 40 seconds by default. To make the configuration take effect immediately, click Submit.
· The anti-virus feature requires a license to run on the device. If the license expires, the anti-virus feature is still available but you can no longer update the virus signature library. For more information about licenses, see the license online help.
Configure anti-virus
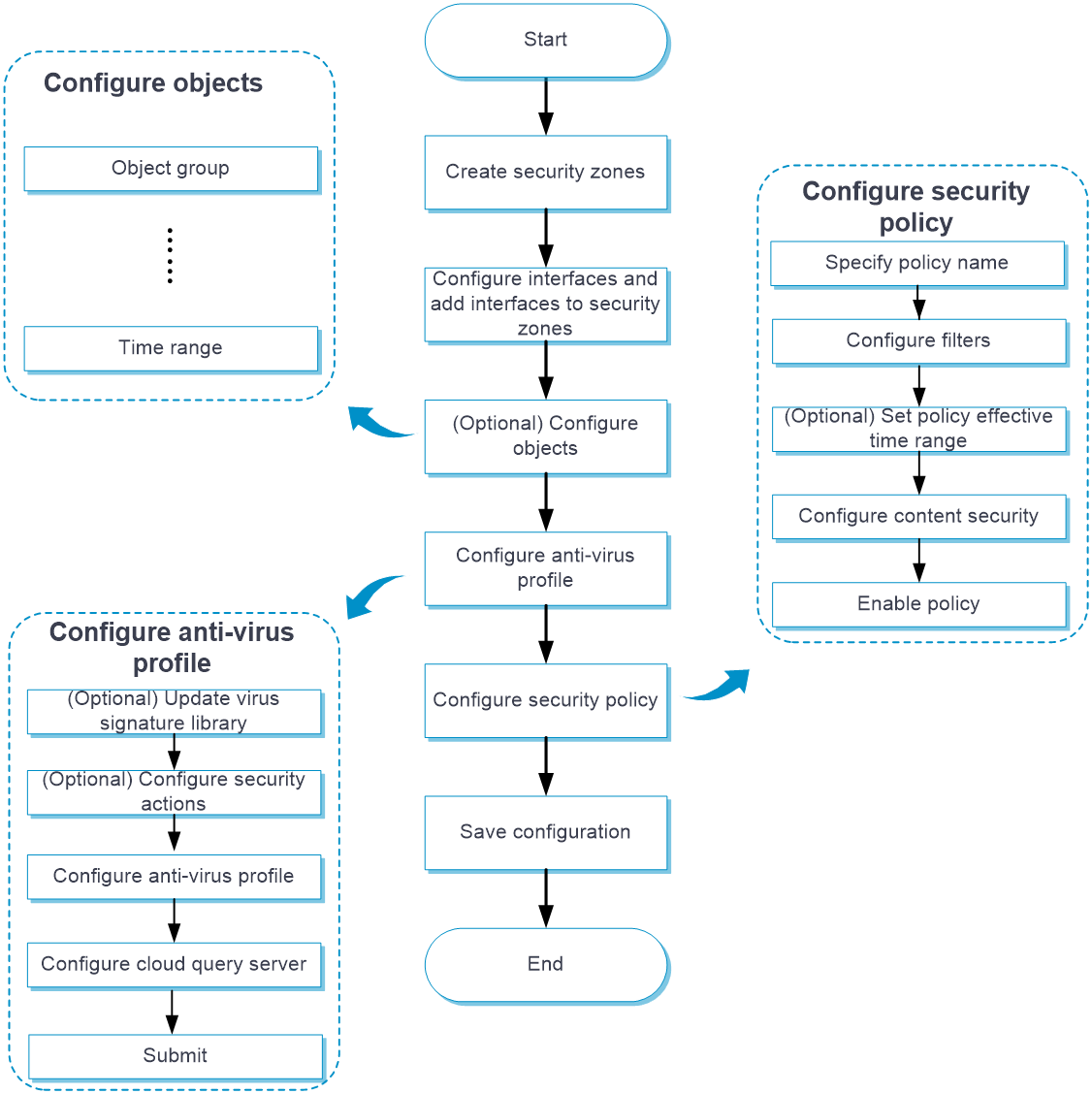
Configure anti-virus as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 Anti-virus configuration procedure
Configure an anti-virus profile
By default, the device provides a predefined anti-virus profile named default, which cannot be modified or deleted.
You can customize anti-virus profiles as needed.
For all protocols that anti-virus supports, the connection requests are always initiated by the client. For anti-virus to work correctly, make sure the security policy that uses the anti-virus profile meets the following requirements:
· The security zone where the client resides is set as the source security zone.
· The security zone where the server resides is set as the destination security zone.
Procedure
1. Click the Objects tab.
2. In the navigation pane, select APPSecurity > Anti-Virus > Profile.
3. Click Create.
4. Create an anti-virus profile.
Table 1 Anti-virus profile configuration items
|
Item |
Description |
|
Name |
Enter a name for the anti-virus profile. |
|
Description |
Enter a description for the anti-virus profile. |
|
Enable cloud query |
Select this item to enable cloud query. |
|
Upload |
Select this item for a protocol to apply the profile to the upload traffic of the protocol. This item is not available for the POP3 protocol. |
|
Download |
Select this item for a protocol to apply the profile to the download traffic of the protocol. This item is not available for the SMTP protocol. |
|
Action |
Select the action for matching packets from the Action list of a protocol. Supported actions are Alarm, Block, and Redirect. The IMAP protocol supports only the Alarm action. |
|
Application exceptions |
To set an application as an application exception, select the application, and then click Add to add it to the application exception list. On the application exception list, select the action for the application exception from the Action list. |
|
Virus exceptions |
To set a virus as a virus exception, enter the virus ID, and then click Add to add it to the virus exception list. |
|
MD5 value exceptions |
To set the MD5 value of a virus as an MD5 value exception, enter the MD5 value, and then click Add to add it to the MD5 value exception list. |
5. Click OK.
6. Use the anti-virus profile in a security policy. For more information about security policies, see security policy online help.
7. The configuration will automatically take effect after 40 seconds by default. To make the configuration take effect immediately, click Submit.
Configure the cloud query server
Perform this task to configure the cloud query server for anti-virus.
Procedure
1. Click the Objects tab.
2. In the navigation pane, select APPSecurity > Anti-Virus > Profile.
3. Click Configure next to the Cloud server connectivity field.
4. Configure the cloud query server.
Table 2 Cloud query server configuration items
|
Item |
Description |
|
Server address |
Enter the IP address or hostname of the cloud query server. Only the cloud query server of our company is supported. |
|
Max cached MD5 entries |
Specify the maximum number of MD5 entries that can be cached in the hit entry list and non-hit entry list. The non-hit entry list is a list of MD5 values submitted to the cloud server that cannot be determined as viruses. The hit entry list is a list of MD5 values that are determined as viruses. |
|
Min cache time |
Specify the minimum cache time for an MD5 entry in minutes. Setting the minimum cache time for MD5 entries ensures that the entries will not be deleted during the specified period of time. However, if the configured max cached MD5 entries is less than the currently cached entries, the system will delete the oldest cache entries even if their cache periods are equal to or less than the minimum cache time. |