- Table of Contents
-
- 03-Layer 3 Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-ARP Configuration
- 02-IP Addressing Configuration
- 03-DHCP Configuration
- 04-DNS Configuration
- 05-IP Performance Optimization Configuration
- 06-UDP Helper Configuration
- 07-IPv6 Basics Configuration
- 08-IP Routing Basics Configuration
- 09-Static Routing Configuration
- 10-IPv6 Static Routing Configuration
- 11-RIP Configuration
- 12-RIPng Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 10-IPv6 Static Routing Configuration | 111.31 KB |
IPv6 static routing configuration
Introduction to IPv6 static routing
Features of IPv6 static routes
Configuring an IPv6 static route
Displaying and maintaining IPv6 static routes
IPv6 static routing configuration example
This chapter includes these sections:
· Introduction to IPv6 static routing
· Configuring an IPv6 static route
· Displaying and maintaining IPv6 static routes
· IPv6 static routing configuration example
|
|
NOTE: · The term "switch" or "device" in this chapter refers to the switching engine on a WX3000E wireless switch. · The WX3000E series comprises WX3024E and WX3010E wireless switches. · The port numbers in this chapter are for illustration only. |
Introduction to IPv6 static routing
Static routes are manually configured. They work well in simple networks. Configuring and using them properly can improve network performance and ensure enough bandwidth for important applications.
However, static routes also have limitations. Any topology changes require the network administrator to manually configure and modify the relevant static routes.
Features of IPv6 static routes
Similar to IPv4 static routes, IPv6 static routes work well in simple IPv6 network environments.
Their major difference lies in the destination and next hop addresses. IPv6 static routes use IPv6 addresses, whereas IPv4 static routes use IPv4 addresses.
Default IPv6 route
An IPv6 static route with a destination prefix of ::/0 is a default IPv6 route. The default route is used to forward packets that match no specific routes in the routing table.
Configuring an IPv6 static route
In small IPv6 networks, IPv6 static routes can be used to forward packets. In comparison to dynamic routes, it helps to save network bandwidth.
Configuration prerequisites
· Configure parameters for the related interfaces
· Configure link layer attributes for the related interfaces
· Enable IPv6 packet forwarding
· Ensure that the neighboring nodes can reach each other
Configuration procedure
Follow these steps to configure an IPv6 static route:
|
To do… |
Use the commands… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Configure an IPv6 static route |
ipv6 route-static ipv6-address prefix-length [ interface-type interface-number ] next-hop-address [ preference preference-value ] |
Required Use either approach. The default preference of IPv6 static routes is 60. |
|
|
NOTE: If the output interface of a static route is a broadcast interface, such as a VLAN interface, the next hop address must be specified, and must be a link-local address. |
Displaying and maintaining IPv6 static routes
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Display IPv6 static route information |
display ipv6 routing-table protocol static [ inactive | verbose ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view |
|
Remove all IPv6 static routes |
delete ipv6 static-routes all |
Available in system view |
|
|
NOTE: · Using the undo ipv6 route-static command can delete a single IPv6 static route. Using the delete ipv6 static-routes all command deletes all IPv6 static routes including the default route. · For more information about the display ipv6 routing-table protocol static [ inactive | verbose ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] command, see the Layer 3 Command Reference. |
IPv6 static routing configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 1, configure IPv6 static routes so that hosts can reach one another.
Figure 1 Network diagram for IPv6 static route configuration
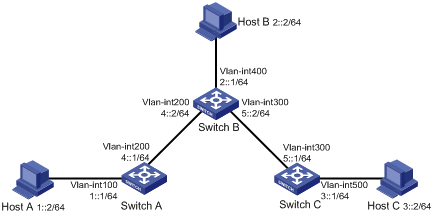
Configuration procedure
1. Configure the IPv6 addresses for all VLAN interfaces (omitted)
2. Configure IPv6 static routes.
# Configure a default IPv6 static route on SwitchA.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] ipv6
[SwitchA] ipv6 route-static :: 0 4::2
# Configure two IPv6 static routes on SwitchB.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] ipv6
[SwitchB] ipv6 route-static 1:: 64 4::1
[SwitchB] ipv6 route-static 3:: 64 5::1
# Configure a default IPv6 static route on SwitchC.
<SwitchC> system-view
[SwitchC] ipv6
[SwitchC] ipv6 route-static :: 0 5::2
3. Configure the IPv6 addresses and gateways for hosts.
Configure the IPv6 addresses for all the hosts based on the network diagram, configure the default gateway of Host A as 1::1, that of Host B as 2::1, and that of Host C as 3::1.
4. Display configuration information
# Display the IPv6 routing table of SwitchA.
[SwitchA] display ipv6 routing-table
Routing Table :
Destinations : 5 Routes : 5
Destination : :: Protocol : Static
NextHop : 4::2 Preference : 60
Interface : Vlan-interface200 Cost : 0
Destination : ::1/128 Protocol : Direct
NextHop : ::1 Preference : 0
Interface : InLoop0 Cost : 0
Destination : 1::/64 Protocol : Direct
NextHop : 1::1 Preference : 0
Interface : Vlan-interface100 Cost : 0
Destination : 1::1/128 Protocol : Direct
NextHop : ::1 Preference : 0
Interface : InLoop0 Cost : 0
Destination : FE80::/10 Protocol : Direct
NextHop : :: Preference : 0
Interface : NULL0 Cost : 0
# Verify the connectivity with the ping command.
[SwitchA] ping ipv6 3::1
PING 3::1 : 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
Reply from 3::1
bytes=56 Sequence=1 hop limit=254 time = 63 ms
Reply from 3::1
bytes=56 Sequence=2 hop limit=254 time = 62 ms
Reply from 3::1
bytes=56 Sequence=3 hop limit=254 time = 62 ms
Reply from 3::1
bytes=56 Sequence=4 hop limit=254 time = 63 ms
Reply from 3::1
bytes=56 Sequence=5 hop limit=254 time = 63 ms
--- 3::1 ping statistics ---
5 packet(s) transmitted
5 packet(s) received
0.00% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 62/62/63 ms
