- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 02-Static LSP configuration | 84.02 KB |
Overview
A static label switched path (LSP) is established by manually specifying the incoming label and outgoing label on each node (ingress, transit, or egress node) of the forwarding path.
Static LSPs consume fewer resources, but they cannot automatically adapt to network topology changes. Therefore, static LSPs are suitable for small and stable networks with simple topologies.
Follow these guidelines to establish a static LSP:
· The ingress node performs the following operations:
a. Determines an FEC for a packet according to the destination address.
b. Adds the label for that FEC into the packet.
c. Forwards the packet to the next hop or out of the outgoing interface.
Therefore, on the ingress node, you must specify the outgoing label for the destination address (the FEC) and the next hop or the outgoing interface.
· A transit node swaps the label carried in a received packet with a specific label, and forwards the packet to the next hop or out of the outgoing interface. Therefore, on each transit node, you must specify the incoming label, the outgoing label, and the next hop or the outgoing interface.
· If the penultimate hop popping function is not configured, an egress node pops the incoming label of a packet, and performs label forwarding according to the inner label or IP forwarding. Therefore, on the egress node, you only need to specify the incoming label.
· The outgoing label specified on an LSR must be the same as the incoming label specified on the directly-connected downstream LSR.
Configuration prerequisites
Before you configure a static LSP, perform the following tasks:
· Identify the ingress node, transit nodes, and egress node of the LSP.
· Enable MPLS on all interfaces that participate in MPLS forwarding. For more information, see "Configuring basic MPLS."
· Make sure the ingress node has a route to the destination address of the LSP. This is not required on transit and egress nodes.
Configuration guidelines
When you configure a static LSP, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· If you specify a next hop for a static LSP on the ingress or transit node, make sure the ingress node or transit node has an active route to the specified next hop address.
· On the ingress or transit node of a static LSP, the device does not support the outgoing interface specified by the outgoing-interface interface-type interface-number option.
· On the egress node of a static LSP, you do not need to configure the static-lsp egress command if the outgoing label configured on the penultimate hop of the static LSP is 0 or 3.
Configuration procedure
To configure a static LSP:
|
Step |
Command |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
|
2. Configure the ingress node of the static LSP. |
static-lsp ingress lsp-name destination dest-addr { mask | mask-length } { nexthop next-hop-addr | outgoing-interface interface-type interface-number } out-label out-label |
|
3. Configure the transit node of the static LSP. |
static-lsp transit lsp-name in-label in-label { nexthop next-hop-addr | outgoing-interface interface-type interface-number } out-label out-label |
|
4. Configure the egress node of the static LSP. |
static-lsp egress lsp-name in-label in-label |
Displaying static LSPs
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display static LSP information. |
display mpls static-lsp [ lsp-name lsp-name ] |
Static LSP configuration example
By default, Ethernet, VLAN, and aggregate interfaces are shut down. You must use the undo shutdown command to bring them up. This example assumes that all these interfaces are already up.
Network requirements
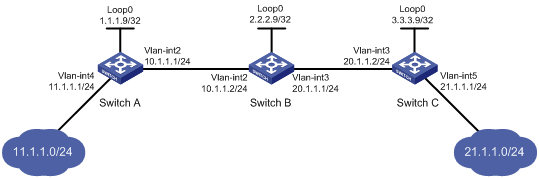
Switch A, Switch B, and Switch C all support MPLS.
Establish static LSPs between Switch A and Switch C, so that subnets 11.1.1.0/24 and 21.1.1.0/24 can access each other over MPLS.
Configuration restrictions and guidelines
· For an LSP, the outgoing label specified on an LSR must be identical with the incoming label specified on the downstream LSR.
· LSPs are unidirectional. You must configure an LSP for each direction of the data forwarding path.
· A route to the destination address of the LSP must be available on the ingress node, but it is not needed on transit and egress nodes. Therefore, you do not need to configure a routing protocol to ensure IP connectivity among all switches.
Configuration procedure
1. Create VLANs and configure IP addresses for all interfaces, including the loopback interfaces, as shown in Figure 1. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure a static route to the destination address of each LSP:
# On Switch A, configure a static route to network 21.1.1.0/24.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] ip route-static 21.1.1.0 24 10.1.1.2
# On Switch C, configure a static route to network 11.1.1.0/24.
<SwitchC> system-view
[SwitchC] ip route-static 11.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 20.1.1.1
3. Configure basic MPLS on the switches:
# Configure Switch A.
[SwitchA] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 2
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface2] mpls enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface2] quit
# Configure Switch B.
[SwitchB] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 2
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] mpls enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] quit
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 3
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface3] mpls enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface3] quit
# Configure Switch C.
[SwitchC] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 3
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface3] mpls enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface3] quit
4. Configure a static LSP from Switch A to Switch C:
# Configure the LSP ingress node, Switch A.
[SwitchA] static-lsp ingress AtoC destination 21.1.1.0 24 nexthop 10.1.1.2 out-label 30
# Configure the LSP transit node, Switch B.
[SwitchB] static-lsp transit AtoC in-label 30 nexthop 20.1.1.2 out-label 50
# Configure the LSP egress node, Switch C.
[SwitchC] static-lsp egress AtoC in-label 50
5. Configure a static LSP from Switch C to Switch A:
# Configure the LSP ingress node, Switch C.
[SwitchC] static-lsp ingress CtoA destination 11.1.1.0 24 nexthop 20.1.1.1 out-label 40
# Configure the LSP transit node, Switch B.
[SwitchB] static-lsp transit CtoA in-label 40 nexthop 10.1.1.1 out-label 70
# Configure the LSP egress node, Switch A.
[SwitchA] static-lsp egress CtoA in-label 70
Verifying the configuration
# Display static LSP information on switches, for example, on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display mpls static-lsp
Total: 2
Name FEC In/Out Label Nexthop/Out Interface State
AtoC 21.1.1.0/24 NULL/30 10.1.1.2 Up
CtoA -/- 70/NULL - Up
# Test the connectivity of the LSP from Switch A to Switch C.
[SwitchA] ping mpls -a 11.1.1.1 ipv4 21.1.1.0 24
MPLS Ping FEC: 21.1.1.0/24 : 100 data bytes
100 bytes from 20.1.1.2: Sequence=1 time=4 ms
100 bytes from 20.1.1.2: Sequence=2 time=1 ms
100 bytes from 20.1.1.2: Sequence=3 time=1 ms
100 bytes from 20.1.1.2: Sequence=4 time=1 ms
100 bytes from 20.1.1.2: Sequence=5 time=1 ms
--- FEC: 21.1.1.0/24 ping statistics ---
5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
# Test the connectivity of the LSP from Switch C to Switch A.
[SwitchC] ping mpls -a 21.1.1.1 ipv4 11.1.1.0 24
MPLS Ping FEC: 11.1.1.0/24 : 100 data bytes
100 bytes from 10.1.1.1: Sequence=1 time=5 ms
100 bytes from 10.1.1.1: Sequence=2 time=1 ms
100 bytes from 10.1.1.1: Sequence=3 time=1 ms
100 bytes from 10.1.1.1: Sequence=4 time=1 ms
100 bytes from 10.1.1.1: Sequence=5 time=1 ms
--- FEC: 11.1.1.0/24 ping statistics ---
5 packets transmitted, 5 packets received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/5 ms
