- Table of Contents
-
- 15-BRAS Services Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-AAA configuration
- 02-ANCP configuration
- 03-PPP configuration
- 04-DHCP configuration
- 05-DHCPv6 configuration
- 06-User profile configuration
- 07-Connection limit configuration
- 08-L2TP configuration
- 09-PPPoE configuration
- 10-IPoE configuration
- 11-802.1X configuration (Layer 3)
- 12-UCM configuration
- 13-Value-added services configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 06-User profile configuration | 172.09 KB |
About session group profiles and user group profiles
Restrictions and guidelines: User profile configuration
Prerequisites for user profile
Configuring a session group profile
Configuring a user group profile
Applying a user profile to an interface
Applying a user profile to a PW
Applying a user profile to a VSI LDP PW
Applying a user profile to a VSI static PW
Applying a user profile to a cross-connect PW
Applying a user profile to an auto-discovery VSI LDP signaling PW
Applying a user profile to an auto-discovery VSI BGP signaling PW
Display and maintenance commands for user profiles
User profile configuration examples
Example: Configuring hierachical scheduing for multiple users in the same user group
Configuring user profiles
About user profiles
A user profile defines a set of parameters, such as a QoS policy, for a single user or interface. A user profile can be reused when a user connected to the network on a different interface.
You can use user profiles in the following ways:
· Authorize a user profile to a user. Each time a user passes authentication, the server sends the device the name of the user profile specified for the user. The device applies the parameters in the user profile to the user. For more information about authorizing a user profile to a user, see AAA in Security Configuration Guide. In this way, user profiles are typically used for the following purposes:
¡ Resource allocation per user—Interface-based traffic policing limits the total amount of bandwidth available to all users that are connected through one interface. However, user-profile-based traffic policing can limit the amount of bandwidth available to a single user.
¡ User access control—When a user passes authentication but the account is overdue, only the resources defined by the ACL permit rules in the free rules are accessible for this user.
· Apply a user profile to an interface. The user profile takes effect on all traffic on the interface.
About session group profiles and user group profiles
Concepts
A session group profile is a particular type of user profile used to authorize multiple users in an AAA scenario.
A user group profile is also used to authorize multiple users, but it can be applied to an interface in addition to being used in an AAA scenario.
A user group profile or session group profile can include multiple users and multiple services. For example, you can configure a session group profile or user group profile to limit the total bandwidth for the user group in addition to configuring a user profile for each user.
A session group profile and a user group profile implement the same function. However, the ways they associate user profiles differ.
· A session group profile is associated with a user profile when they are authorized to the same online user. The online user is subject to both the user profile and session group profile.
· A user group profile is associated with a user profile by using CLI command. The authentication server authorizes only the user profile to the online user. The online user is subject to both the user profile and the user group profile associated with the user profile.
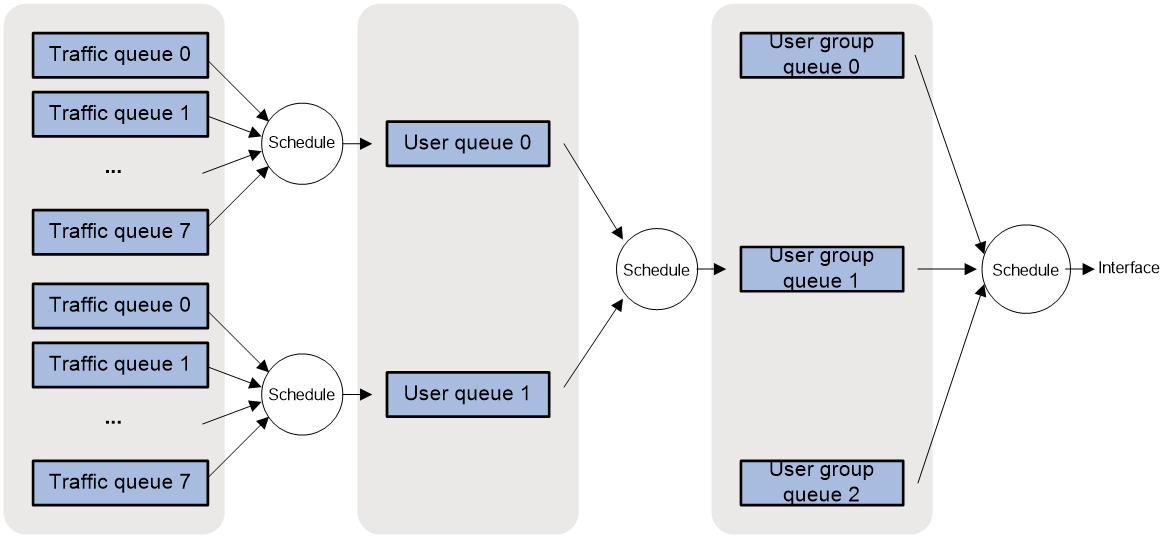
Hierarchical scheduling
A user profile limits traffic of a single online user. A session group profile or user group profile limits the total traffic of multiple online users. The following queue types are available for hierarchical scheduling:
· Traffic queue—Caches packets of different priorities of a user. You can apply a queue scheduing profile to a user profile to schedule the packets of a traffic queue.
· User queue—Schedules packets of traffic queues by using a queue scheduling profile applied to the user profile, and rate limits the packets of the user queue by using QoS policy and traffic policing settings.
· User group queue—Schedules packets of user queues by using a queue scheduling profile applied to the user group profile or session group profile, and rate limits the packets of the user group queue by using QoS policy, traffic policing, traffic shaping settings.
Traffic queues are physical queues and have cache units. User queues and user group queues are virtual queues that participate in hierarchical scheduling and do not have cache units.
Figure 1 Hierarchical scheduling
Restrictions and guidelines: User profile configuration
Because a session group profile and a user group profile implement the same function, a user profile cannot be associated with both a session group profile and a user group profile.
You can configure traffic regulation, QoS policy, traffic scheduling, queue scheduling profile, connection limits, and auth-free rule for a user profile as required.
Prerequisites for user profile
If a user profile is applied to an interface, no authentication settings are required.
If a user profile works with authentication, you must configure authentication settings for a user profile. For information about supported authentication methods, see the configuration guides for the related authentication modules.
Configuring a user profile
About this task
For information about CAR policies and QoS policies, see ACL and QoS Configuration Guide.
For information about connection limits, see "Configuring connection limits."
Restrictions and guidelines
The system supports authorizing users profiles to users and supports the following settings in the user profile:
· Traffic regulation.
· QoS policy.
· Traffic scheduling.
· Queue scheduling profile for user queues.
· Connection limits.
· Auth-free rule.
The system supports applying user profiles to interfaces and supports only rate regulation and queue scheduling profile settings in the user profile.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a user profile and enter user profile view.
user-profile profile-name
3. Configure traffic regulation. Choose the options to configure as needed:
If the qos user-queue qmprofile command is used for traffic scheduling, only the qos user-queue command is supported for traffic regulation.
¡ Configure a CAR policy for the user profile.
qos car { inbound | outbound } any cir committed-information-rate [ cbs committed-burst-size [ ebs excess-burst-size ] ]
qos car { inbound | outbound } any cir committed-information-rate [ cbs committed-burst-size ] pir peak-information-rate [ ebs excess-burst-size ]
By default, no CAR policy is configured for a user profile.
¡ Configure rate limiting for the user profile.
qos user-queue { cir committed-information-rate [ cbs committed-burst-size [ ebs excess-burst-size ] ] [ queue-length queue-length ] } * outbound
qos user-queue { cir committed-information-rate [ cbs committed-burst-size ] pir peak-information-rate [ ebs excess-burst-size ] [ queue-length queue-length ] } * outbound
qos user-queue { cir committed-information-rate [ cbs committed-burst-size [ ebs excess-burst-size ] ] } inbound
qos user-queue { cir committed-information-rate [ cbs committed-burst-size ] pir peak-information-rate [ ebs excess-burst-size ] } inbound
By default, rate limiting is not configured for a user profile.
4. Apply an existing QoS policy to the user profile.
qos apply policy policy-name { inbound | outbound }
By default, no QoS policy is applied to a user profile.
5. Configure queue scheduling for user queues.
¡ Specify a queue for session packets that use the user profile.
qos queue { queue-id | queue-name }
By default, no queue for session packets is specified for a user profile.
Session packets are scheduled based on the scheduling priority of the specified queue, implementing session-based congestion management.
¡ Set the outbound weight value for the user profile.
qos weight weight-value outbound
By default, no outbound weight value is set for a user profile.
Bandwidth resources are allocated based on the weight value.
6. Specify an existing queue scheduling profile for the user profile.
qos user-queue qmprofile qmprofile-name { inbound | outbound }
By default, no queue scheduling profile is specified for a user profile.
7. Configure connection limits.
¡ Set the maximum number of user connections.
connection-limit amount amount
By default, the number of user connections is not limited for a user profile.
¡ Set the maximum connection establishment rate.
connection-limit rate rate
By default, the connection establishment rate is not limited for a user profile.
8. Create a user profile free rule.
free-rule acl [ ipv6 ] { acl-number | name acl-name }
By default, no user profile free rule is configured for a user profile.
Configuring a session group profile
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Identify a session group on the interface.
qos session-group identify { customer-vlan | service-vlan | customer-service-vlan | subscriber-id }
By default, no session group is identified on the interface.
The interface identifies packets according to the specified method and classifies packets with the same characteristics to the same user group.
4. Return to system view.
quit
5. Create a session group profile and enter session group profile view.
user-profile profile-name type session-group
You can use the command to enter the view of an existing session group profile.
6. Configure traffic regulation.
¡ Configure GTS for the session group profile.
qos gts { any | queue queue-id } cir committed-information-rate [ cbs committed-burst-size [ ebs excess-burst-size ] ] [ queue-length queue-length ]
qos gts { any | queue queue-id } cir committed-information-rate [ cbs committed-burst-size ] pir peak-information-rate [ ebs excess-burst-size ] [ queue-length queue-length ]
By default, no GTS is configured for a session group profile.
7. Apply an existing queue scheduling profile to the session group profile.
qos apply qmprofile profile-name
By default, no queue scheduling profile is applied to a session group profile.
For information about GTS and queue scheduling profiles, see ACL and QoS Configuration Guide.
Configuring a user group profile
Restrictions and guidelines
After you execute the qos session-group identify command on an interface, the system can identify the user group to which users in the same home belong. When authorizing user profiles for different users, you can use the following methods to limit the bandwidth available to all users in the same home:
· Use AAA to limit the total traffic rate for all users in the same home through RADIUS subattributes 114, 115, 116, and 117. For information about RADIUS subattributes, see AAA in BRAS Services Configuration Guide.
· Use the qos user-queue user-group-profile command to associate the user profiles with the same user group profile.
If you associate the user profiles for users from the same home with different user group profiles, the total bandwidth available to the users will change among the bandwidth limits configured for the user group profiles. Suppose you associate user profile A and user profile B with user group profile A and with user group profile B, respectively. When user A first comes online, the total bandwidth for user A and user B is the bandwidth limit configured for user group profile A. When user B comes online later, the total bandwidth for user A and user B changes to the bandwidth limit configured for user group profile B. If user A goes offline and then comes online, the total bandwidth for user A and user B changes back to the bandwidth limit configured for user group profile A.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Identify a session group on the interface.
qos session-group identify { customer-vlan | service-vlan | customer-service-vlan | subscriber-id }
By default, no session group is identified on the interface.
The interface identifies packets according to the specified method and classifies packets with the same characteristics to the same user group.
4. Return to system view.
quit
5. Create a user group profile and enter user group profile view.
user-group-profile profile-name
6. Configure traffic regulation.
¡ Configure GTS for the user group profile.
qos gts [ inbound ] any cir committed-information-rate [ cbs committed-burst-size [ ebs excess-burst-size ] ] [ queue-length queue-length ]
qos gts [ inbound ] any cir committed-information-rate [ cbs committed-burst-size ] pir peak-information-rate [ ebs excess-burst-size ] [ queue-length queue-length ]
By default, no GTS is configured for a user group profile.
If you have configured rate limiting by using the qos user-queue command for a user profile and associated the user profile with a user group profile, the queue-length queue-length option in GTS cannot take effect for the user group profile.
7. Apply an existing queue scheduling profile to the user group profile.
qos apply qmprofile profile-name
By default, no queue scheduling profile is applied to a user group profile.
8. Set the outbound weight value for the user group profile.
qos weight weight-value outbound
By default, no outbound weight value is set for a user group profile.
Bandwidth resources are allocated among user group profiles based on the weight value.
9. Return to system view.
quit
10. Enter user profile view.
user-profile profile-name
11. Associate the user profile with the user group profile.
qos user-queue user-group-profile user-group-profile-name outbound
By default, a user profile is not associated with any user group profile.
For information about GTS and queue scheduling profiles, see ACL and QoS Configuration Guide.
Applying a user profile to an interface
Restrictions and guidelines
A user profile applied to an interface supports only traffic policing, rate limiting, and queue scheduling profiles.
The following rules apply if you specify a direction when applying a user profile to an interface:
· The settings in the user profile take effect only if the direction of the settings is the same as the application direction.
· Only one user profile can be applied to the same direction.
The following rules apply if you do not specify a direction when applying a user profile to an interface:
· The settings in the user profile take effect in the direction as they are configured.
· No other user profile can be applied to the interface, regardless of whether it is applied with a direction.
This feature is mutually exclusive with any of the following configurations:
· Bind the interface to a VSI by using the xconnect vsi command.
· Bind the interface to a cross-connect by using the ac interface command.
· Enable IPoE on the interface and configure an IPoE access mode for users by using the ip subscriber enable command.
If a user profile containing a CAR policy is applied to an interface:
· The CAR policy is mutually exclusive with traffic policing configured on an interface by using the qos car command.
· The CAR policy on a main interface does not take effect on its subinterfaces.
· The CAR policy does not take effect on member ports of an aggregation group.
· The CAR policy supports only the single rate two color algorithm. If you configure the pir peak-information-rate option, tokens are put into the token bucket at the PIR.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Apply a user profile to the interface.
qos apply user-profile profile-name [ inbound | outbound ]
By default, no user profile is applied to an interface.
Applying a user profile to a PW
Restrictions and guidelines
You can apply a user profile to a PW to perform rate limiting and queue scheduling.
· You can use the qos user-queue command to configure rate limiting for a user profile. Only the single rate two color mechanism is supported.
· You can use the qos user-queue qmprofile command to specify a queue scheduling profile for a user profile. In the queue scheduling profile, do not configure a maximum allowed bandwidth in percentage, a minimum guaranteed bandwidth in percentage, or the maximum bandwidth allowed for a group.
If you configure both this feature and traffic policing (qos car) for a PW, only this feature takes effect.
You can apply only one user profile to a PW. The settings in the user profile take effect only if the direction of the settings is the same as the application direction.
Applying a user profile to a VSI LDP PW
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter VSI view.
vsi vsi-name [ hub-spoke ]
3. Specify LDP signaling for PWs, and enter VSI LDP signaling view.
pwsignaling ldp
By default, no PW signaling protocol is specified.
4. Configure an LDP PW, and enter VSI LDP PW view.
peer ip-address [ pw-id pw-id ] [ dci | hub | ignore-standby-state | no-split-horizon | pw-class class-name | tunnel-policy tunnel-policy-name ] *
5. Apply a user profile to the VSI LDP PW.
qos apply user-profile profile-name outbound
By default, no user profile is applied to a VSI LDP PW.
Applying a user profile to a VSI static PW
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter VSI view.
vsi vsi-name [ hub-spoke ]
3. Specify static signaling for PWs, and enter VSI static view.
pwsignaling static
By default, no PW signaling protocol is specified.
4. Configure a static PW and enter VSI static PW view.
peer ip-address [ pw-id pw-id ] [ in-label label-value out-label label-value ] [ dci | hub | no-split-horizon | pw-class class-name | tunnel-policy tunnel-policy-name ] *
5. Apply a user profile to the VSI static PW.
qos apply user-profile profile-name outbound
By default, no user profile is applied to a VSI static PW.
Applying a user profile to a cross-connect PW
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter cross-connect group view.
xconnect-group group-name
3. Enter cross-connect view.
connection connection-name
4. Configure an LDP or static PW and enter cross-connect PW view.
¡ Configure an LDP PW and enter cross-connect PW view.
peer ip-address pw-id pw-id [ ignore-standby-state ] [ admin | pw-class class-name | tunnel-policy tunnel-policy-name ] *
¡ Configure a static PW and enter cross-connect PW view.
peer ip-address pw-id pw-id in-label label-value out-label label-value [ admin | pw-class class-name | tunnel-policy tunnel-policy-name ] *
5. Apply a user profile to the cross-connect PW.
qos apply user-profile profile-name outbound
By default, no user profile is applied to a cross-connect PW.
Applying a user profile to an auto-discovery VSI LDP signaling PW
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter VSI view.
vsi vsi-name [ hub-spoke ]
3. Configure the VSI to automatically discover neighbors through BGP and enter auto-discovery VSI view.
auto-discovery bgp
By default, a VSI does not automatically discover neighbors through BGP.
4. Use LDP to create a PW to an automatically discovered remote PE and enter auto-discovery VSI LDP signaling view.
signaling-protocol ldp
By default, no signaling protocol is specified.
5. (Optional.) Configure an auto-discovery VSI LDP signaling PW and enter its view.
peer ip-address
By default, no PWs exist for auto-discovery VSI LDP signaling PW.
6. Apply a user profile to the auto-discovery VSI LDP signaling PW.
qos apply user-profile profile-name outbound
By default, no user profile is applied to an auto-discovery VSI LDP signaling PW.
Applying a user profile to an auto-discovery VSI BGP signaling PW
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter VSI view.
vsi vsi-name [ hub-spoke ]
3. Configure the VSI to automatically discover neighbors through BGP and enter auto-discovery VSI view.
auto-discovery bgp
By default, a VSI does not automatically discover neighbors through BGP.
4. Use BGP to create a PW to an automatically discovered remote PE and enter auto-discovery VSI LDP signaling view.
signaling-protocol bgp
By default, no signaling protocol is specified.
5. (Optional.) Configure an auto-discovery VSI BGP signaling PW and enter its view.
peer ip-address
By default, no PWs exist for auto-discovery VSI BGP signaling PW.
6. Apply a user profile to the auto-discovery VSI BGP signaling PW.
qos apply user-profile profile-name outbound
By default, no user profile is applied to an auto-discovery VSI BGP signaling PW.
Display and maintenance commands for user profiles
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display the configuration and traffic policing statistics for a user profile applied to an interface. |
In standalone mode: display user-profile interface [ interface-type interface-number ] [ slot slot-number ] [ inbound | outbound ] In IRF mode: display user-profile interface [ interface-type interface-number ] [ chassis chassis-number slot slot-number ] [ inbound | outbound ] |
|
Display the configuration and statistics for a user profile applied to a PW. |
In standalone mode: display user-profile l2vpn-pw [ vsi vsi-name peer ip-address [ pw-id pw-id | remote-site-id remote-site-id ] | xconnect-group group-name connection connection-name peer ip-address pw-id pw-id ] { outbound } [ slot slot-number ] In IRF mode: display user-profile l2vpn-pw [ vsi vsi-name peer ip-address [ pw-id pw-id | remote-site-id remote-site-id ] | xconnect-group group-name connection connection-name peer ip-address pw-id pw-id ] { outbound } [ chassis chassis-number slot slot-number ] |
|
Display configuration and online user information for the specified user group profile or all user group profiles. |
In standalone mode: display user-group-profile [ name profile-name ] [ slot slot-number ] In IRF mode: display user-group-profile [ name profile-name ] [ chassis chassis-number slot slot-number ] |
|
Display configuration and online user information for the specified user profile or all user profiles. |
In standalone mode: display user-profile [ session-group ] [ name profile-name ] [ slot slot-number ] In IRF mode: display user-profile [ session-group ] [ name profile-name ] [ chassis chassis-number slot slot-number ] |
|
Clear the traffic policing statistics for a user profile applied to an interface. |
reset user-profile interface [ interface-type interface-number ] [ inbound | outbound ] |
User profile configuration examples
Example: Configuring hierachical scheduing for multiple users in the same user group
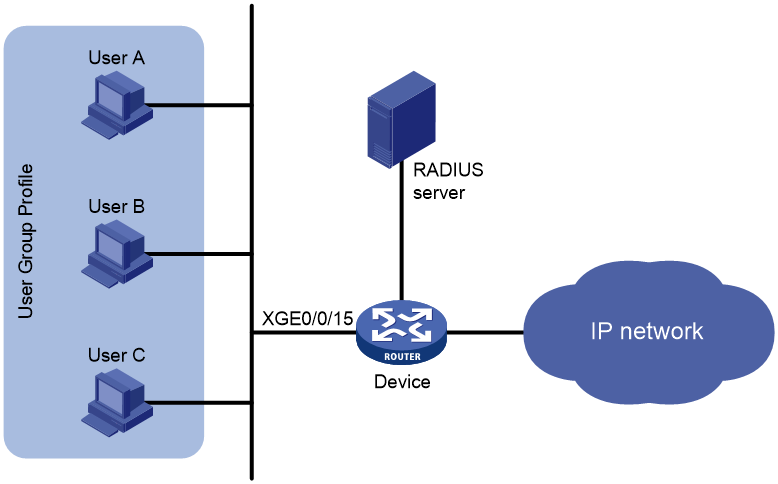
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, the RADIUS server performs authentication, authorization,a nd accounting for the home user group accessing the network.
Configure common user profiles and a user group profile to meet the following requirements:
· Limit the total traffic rate to 100 Mbps for all users in the home user group.
· Limit the traffic rate to 40000 kbps for User A.
· Limit the traffic rate to 80000 kbps for User B.
· Limit the traffic rate to 20000 kbps for User C.
Procedure
1. Configure the RADIUS server:
a. Authorize user profiles a, b, and c for User A, User B, and User C. (Details not shown.)
b. Specify user group profile ugp for each user. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure the device:
# Create a queue scheduling profile named qm.
<Device> system-view
[Device] qos qmprofile qm
[Device-qmprofile-qm] quit
# Identify a session group on an interface.
[Device] interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/15
[Device-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] qos session-group identify service-vlan
This operation will affect online users from now on. Continue? [Y/N]:y
[Device-Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/15] quit
# Create a user group profile named ugp.
[Device] user-group-profile ugp
# Apply queue scheduling profile named qm to user group profile named ugp.
[Device-user-group-profile-ugp] qos apply qmprofile qm
# Configure GTS for all traffic, with the CIR as 100000 kbps.
[Device-user-group-profile-ugp] qos gts any cir 100000
[Device-user-group-profile-ugp] qos gts inbound any cir 100000
[Device-user-group-profile-ugp] quit
# Create a user profile named a, configure CAR (CIR 40000 kbps) for it, and associate it with user profile group ugp.
[Device] user-profile a
[Device-user-profile-a] qos car inbound any cir 40000
[Device-user-profile-a] qos car outbound any cir 40000
[Device-user-profile-a] qos user-queue user-group-profile ugp inbound
[Device-user-profile-a] qos user-queue user-group-profile ugp outbound
[Device-user-profile-a] quit
# Create a user profile named b, configure CAR (CIR 80000 kbps) for it, and associate it with user profile group ugp.
[Device] user-profile b
[Device-user-profile-b] qos car inbound any cir 80000
[Device-user-profile-b] qos car outbound any cir 80000
[Device-user-profile-b] qos user-queue user-group-profile ugp inbound
[Device-user-profile-b] qos user-queue user-group-profile ugp outbound
[Device-user-profile-b] quit
# Create a user profile named c, configure CAR (CIR 20000 kbps) for it, and associate it with user profile group ugp.
[Device] user-profile c
[Device-user-profile-c] qos car inbound any cir 20000
[Device-user-profile-c] qos car outbound any cir 20000
[Device-user-profile-c] qos user-queue user-group-profile ugp inbound
[Device-user-profile-c] qos user-queue user-group-profile ugp outbound
[Device-user-profile-c] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the user profiles are correctly configured and are effective on online users.
<Device> display user-profile
User Profile: a
Direction: Inbound
Committed Access Rate:
CIR 40000 (kbps), CBS 2500000 (Bytes), EBS 0 (Bytes)
User queue:
User group profile: ugp
Direction: Outbound
Committed Access Rate:
CIR 40000 (kbps), CBS 2500000 (Bytes), EBS 0 (Bytes)
User queue:
User group profile: ugp
User Profile: b
Direction: Inbound
Committed Access Rate:
CIR 80000 (kbps), CBS 5000000 (Bytes), EBS 0 (Bytes)
User queue:
User group profile: ugp
Direction: Outbound
Committed Access Rate:
CIR 80000 (kbps), CBS 5000000 (Bytes), EBS 0 (Bytes)
User queue:
User group profile: ugp
User Profile: c
Direction: Inbound
Committed Access Rate:
CIR 20000 (kbps), CBS 1250000 (Bytes), EBS 0 (Bytes)
User queue:
User group profile: ugp
Direction: Outbound
Committed Access Rate:
CIR 20000 (kbps), CBS 1250000 (Bytes), EBS 0 (Bytes)
User queue:
# Verify that user group profile upg is correctly configured and is active for users.
<Device> display user-group-profile name ugp
User Group Profile: ugp
Direction: Inbound
General Traffic Shaping:
If-match any:
CIR 100000 (kbps), CBS 6250000 (Bytes), EBS 0 (Bytes)
Direction: Outbound
General Traffic Shaping:
If-match any:
CIR 100000 (kbps), CBS 6250000 (Bytes), EBS 0 (Bytes)
QMProfile: qm