- Table of Contents
-
- 03-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Security zone configuration
- 02-Security policy configuration
- 03-Object group configuration
- 04-Object policy configuration
- 05-AAA configuration
- 06-IPoE configuration
- 07-Portal configuration
- 08-User identification configuration
- 09-Password control configuration
- 10-Public key management
- 11-PKI configuration
- 12-SSH configuration
- 13-SSL configuration
- 14-ASPF configuration
- 15-APR configuration
- 16-Session management
- 17-Connection limit configuration
- 18-Attack detection and prevention configuration
- 19-DDoS protection configuration
- 20-uRPF configuration
- 21-ARP attack protection configuration
- 22-ND attack defense configuration
- 23-IP-MAC binding configuration
- 24-Keychain configuration
- 25-Crypto engine configuration
- 26-SMS configuration
- 27-Terminal identification configuration
- 28-Flow manager configuration
- 29-Trusted access control configuration
- 30-Location identification configuration
- 31-Server connection detection configuration
- 32-MAC authentication configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 30-Location identification configuration | 182.37 KB |
Contents
Configuring location identification
Location identification tasks at a glance
Updating the location signature library
Display and maintenance commands for location identification
Example: Configuring location identification
Configuring location identification
About location identification
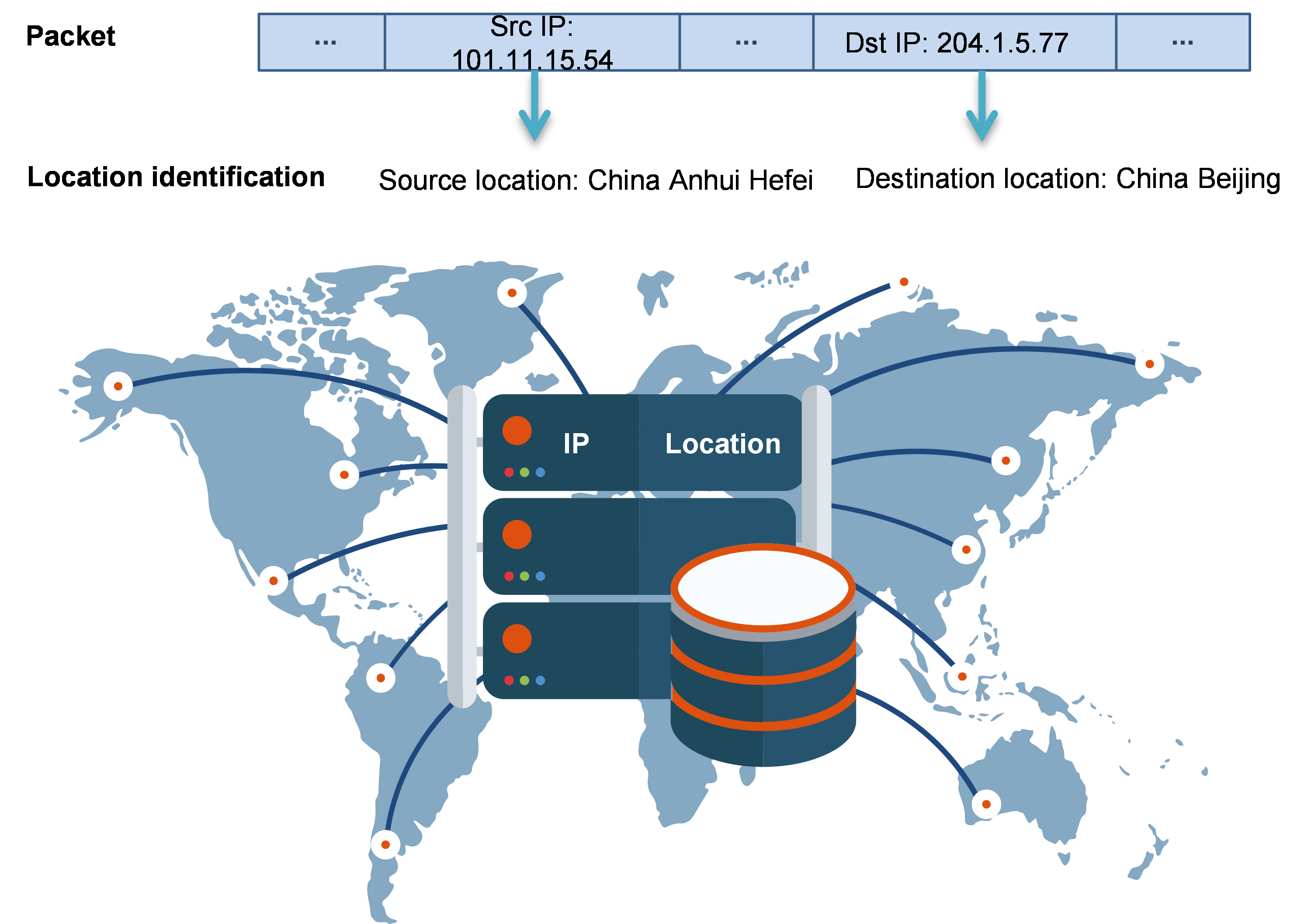
This feature identifies the locations of the source and destination IP addresses of packets and works with a security policy to implement location-based packet control.
A location in this feature refers to a set of IP addresses in the location. You can add locations and their IP addresses to the location identification module by loading a location signature file or manually configuring locations. The device determines the source and destination locations of packets by examining the source and destination IP addresses of the packets. Then, the device works with a security policy to implement location-based packet control.
Figure 1 Location identification
Location identification tasks at a glance
To configure location identification, perform the following tasks:
2. Configuring a location group
3. Updating the location signature library
Configuring a location
About this task
Locations include the following types:
· Predefined locations—Locations defined in the location signature library, including countries, provinces, and cities.
· User-defined locations—Locations created by the user. This type of location can be used to define a smaller geographical area, such as a district or a street in a city.
· Unknown location—A particular location in the location signature library, which is used to store IP addresses that do not have a location.
Restrictions and guidelines
The name of a user-defined location cannot be the same as that of a predefined location.
The IPv4 addresses in different locations cannot be overlapping.
When manually added IPv4 addresses overlap with predefined IPv4 addresses, the predefined IPv4 addresses do not take effect.
Only user-defined locations can be configured with the longitude and latitude.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter location view.
geo-location { unknown | { pre-defined | user-defined } geo-location-name }
3. Add IPv4 addresses to the location.
ip address { ip-address { mask-length | mask } | range ip-address1 ip-address2 }
By default, only a predefined location or the unknown location contains IPv4 addresses.
The undo ip address command can only remove manually added IPv4 addresses.
4. (Optional.) Specify the longitude and latitude of the location.
coordinate longitude longitude-value latitude latitude-value
By default, the longitude and latitude are not specified.
5. (Optional.) Configure a description for the location.
description text
By default, no description is configured.
Configuring a location group
About this task
You can add multiple locations to a location group to process the packets of the locations in the same way. You can also add a location group to another location group.
Restrictions and guidelines
Two location groups cannot contain each other at the same time.
The system supports a maximum of three location group hierarchy layers. For example, if groups 1 and 2 are members of groups 2 and 3, respectively, group 3 cannot have members and group 1 cannot be members of another group.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter location group view.
geo-location-group geo-location-group-name
3. Add a location to the location group.
add geo-location geo-location-name
By default, a location group does not contain any locations.
4. Add a location group to the location group.
add geo-location-group geo-location-group-name
By default, a location group does not contain any location groups.
5. (Optional.) Configure a description for the location group.
description text
By default, no description is configured.
Updating the location signature library
About this task
The location signature library contains predefined countries, provinces, and cities as locations and contains public IP addresses of each location. The device is loaded with a location signature file by default. To update the location signature library, copy the latest signature file from the official website to the local root directory and load it.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Load a location signature file to update the location signature library.
geo-load file-name
Display and maintenance commands for location identification
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display information about locations. |
display geo-location { all | type { pre-defined | unknown | user-defined } | name geo-location-name } |
|
Display the location of an IP address. |
display geo-location ip ip-address |
|
Display information about location groups. |
display geo-location-group [ name geo-location-group-name ] |
Example: Configuring location identification
See "Configuring security policies."