- Table of Contents
-
- 03-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Security zone configuration
- 02-Security policy configuration
- 03-Object group configuration
- 04-Object policy configuration
- 05-AAA configuration
- 06-IPoE configuration
- 07-Portal configuration
- 08-User identification configuration
- 09-Password control configuration
- 10-Public key management
- 11-PKI configuration
- 12-SSH configuration
- 13-SSL configuration
- 14-ASPF configuration
- 15-APR configuration
- 16-Session management
- 17-Connection limit configuration
- 18-Attack detection and prevention configuration
- 19-DDoS protection configuration
- 20-uRPF configuration
- 21-ARP attack protection configuration
- 22-ND attack defense configuration
- 23-IP-MAC binding configuration
- 24-Keychain configuration
- 25-Crypto engine configuration
- 26-SMS configuration
- 27-Terminal identification configuration
- 28-Flow manager configuration
- 29-Trusted access control configuration
- 30-Location identification configuration
- 31-Server connection detection configuration
- 32-MAC authentication configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 27-Terminal identification configuration | 106.27 KB |
Contents
Configuring terminal identification
How terminal identification works
Prerequisites for terminal identification
Terminal identification tasks at a glance
Specifying the operating mode of terminal identification
Configuring an object group for identifying terminal addresses
Enabling terminal identification logging
Configuring the terminal identification allowlist
Approving terminals as legal terminals
Display and maintenance commands for terminal identification
Configuring terminal identification
About terminal identification
Identifying terminals, such as cameras and sensors, is fundamental to establish secure Internet of Things (IoT) connections.
When the terminal traffic passes through a device, the device performs the following tasks:
· Analyzes and extracts the terminal information, such as the vendor, model ,and MAC address information, and displays terminal information on the Web interface.
· Identifies the terminal based on the terminal information.
· Controls identified terminals.
· Generates a log when a terminal is identified for the first time or the terminal information changes.
Operating mode
Terminal identification supports the following operating modes:
· Alarm—In this mode, the system permits traffic of all terminals. When the system identifies a terminal for the first time or detects a terminal information change, it sends a log message to the user. This mode is applicable to scenarios that do not have strict security requirements.
· Allowlist—In this mode, the system permits traffic of only terminals in the allowlist. When the system detects a terminal information change, it sends a log message to the user. This mode is applicable to scenarios that have strict security requirements.
How terminal identification works
Signature library
Terminal identification identifies terminals based on the APR signature library. For information about the APR signature library, see APR in Security Configuration Guide.
Workflow
Terminal identification works as follows:
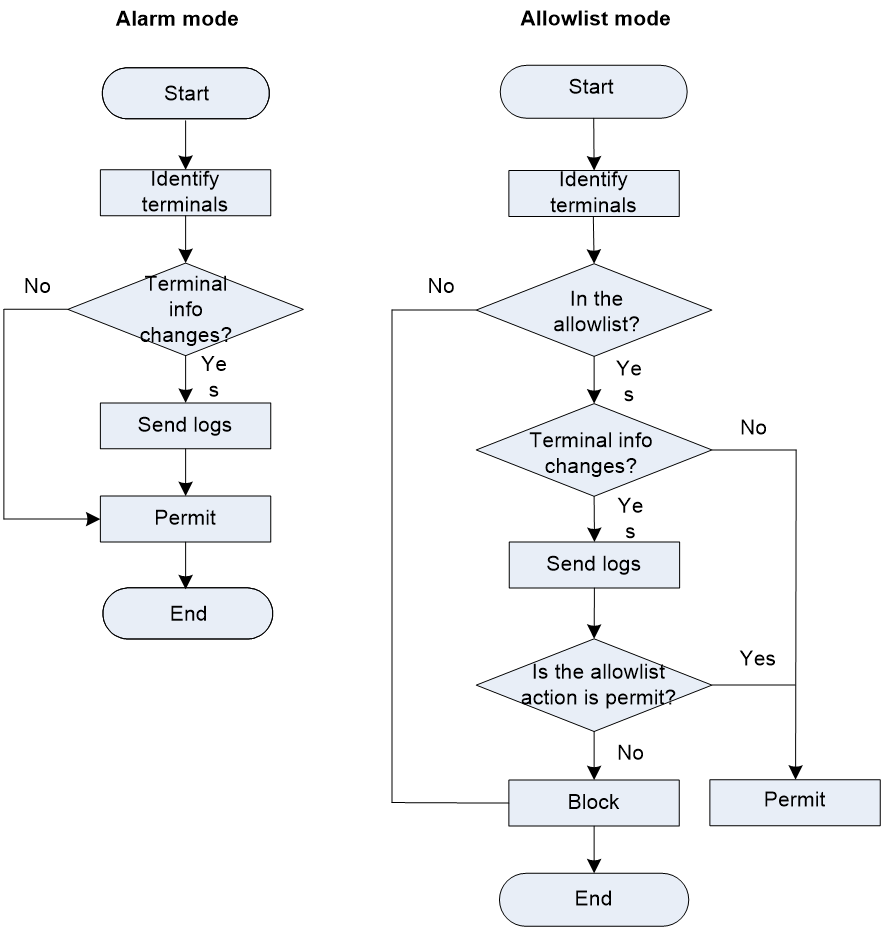
· Alarm mode—As shown in Figure 1, the system identifies each terminal and permits traffic of all terminals. When the system detects a terminal for the first time or detects that the information about an existing terminal changes, the system sends a log message.
· Whitelist mode
a. As shown in Figure 1, the system identifies each terminal and checks whether the IP address of each terminal (including terminals classified as other category) is in the allowlist. An unidentifiable terminal is classified as other category.
b. If the IP address of a terminal is not in the allowlist, the system drops the traffic of the terminal. If the IP address of a terminal is in the allowlist, the system checks whether the terminal information changes. If the terminal information does not change, the system permits the traffic.
c. If the terminal information changes, the system sends a log message and check whether the allowlist action is permit.
d. If the allowlist action is permit, the system permits the traffic. Otherwise, the system drops the traffic.
Figure 1 Terminal identification workflow
Prerequisites for terminal identification
Before configuring terminal identification, update the APR signature library to the latest version (see "Configuring APR").
Terminal identification tasks at a glance
To configure terminal identification, perform the following tasks:
1. Specifying the operating mode of terminal identification
2. (Optional.) Configuring a terminal group
3. Configuring an object group for identifying terminal addresses
4. Enabling terminal identification logging
5. Configuring the terminal identification allowlist
6. (Optional.) Approving terminals as legal terminals
7. (Optional.) Reidentifying terminals
Specifying the operating mode of terminal identification
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter terminal identification view.
terminal-identification
3. Specify the operating mode.
work-mode { allowlist | warning }
The default setting is warning.
Configuring a terminal group
About this task
A terminal group is a set of terminals with similar characteristics. A packet belongs to a terminal group if it is from a terminal member of this group.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter terminal identification view.
terminal-identification
3. Create a terminal group and enter its view.
terminal-group group-name
4. (Optional.) Configure a description for the terminal group.
description text
By default, a terminal group is described as "User-defined terminal group".
5. Add terminals to the terminal group.
include terminal terminal-name
Configuring an object group for identifying terminal addresses
About this task
This task allows you to identify terminals accurately. By default, the device identifies the packet source IP address as the terminal IP address, which is sometimes inaccurate. If you know terminal IP addresses or manager IP addresses, configure an object group of the corresponding type for accurate terminal address identification. The device supports the following address object groups:
· Terminal address object group—A set of terminal IP addresses. If the packet source or destination IP address matches this group, the source or destination IP address is the terminal IP address.
· Manager address object group—A set of terminal manager IP addresses. If the packet source or destination IP address matches this group, the destination or source IP address is the terminal IP address.
The manager address object group has higher priority over the terminal address object group. If a packet matches a manager address object group, the matching process stops. If a packet does not match a manager address object group, the device continues to match terminal address object groups. If neither the source nor the destination IP address of a packet is in any address object groups, the device identifies the source IP address as the terminal IP address.
Prerequisites
Before configuring an object group for identifying terminal addresses, make sure the specified IPv4 or IPv6 address object group already exists. For more information about IPv4 or IPv6 address object groups, see object group configuration in Security Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter terminal identification view.
terminal-identification
3. Configure an object group for identifying terminal addresses. Choose the options to configure as needed:
¡ Configure the terminal address object group.
terminal object-group { ipv4 | ipv6 } object-group-name
By default, no terminal address object group is configured.
¡ Configure the manager address object group.
manage object-group { ipv4 | ipv6 } object-group-name
By default, no manager address object group is configured.
Enabling terminal identification logging
About this task
This feature allows the device to fast output logs to log hosts upon detecting the changes of terminal information, such as the vendor and model changes. For more information about fast log output and log hosts, see configuring fast log output in Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter terminal identification view.
terminal-identification
3. Enable terminal identification logging.
logging enable
By default, terminal identification logging is disabled.
Configuring the terminal identification allowlist
About this task
The device permits the traffic of a terminal if the IP address of the terminal is in the terminal identification allowlist. Otherwise, the device drops the traffic of a terminal. The terminal identification allowlist supports the following actions:
· Permit—Permits the traffic of a terminal all the time.
· Block—Drops the traffic of a terminal all the time only after the terminal information changes.
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature takes effect only in allowlist mode.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter terminal identification view.
terminal-identification
3. Specify an IPv4 address object group for generating the allowlist.
allowlist object-group ipv4 object-group-name
By default, no IPv4 address object group is specified.
4. Specify an action.
allowlist action { drop | permit }
The default action is permit.
Approving terminals as legal terminals
About this task
If you are sure identified terminals are accurate and trusted, you can perform this task to approve them as legal terminals displays terminal information on the Web interface.
In allowlist mode with the drop action, the system drops traffic of a terminal in the allowlist when the terminal comes online for the first time. To permits the traffic of the terminal, you can approve it as a legal terminal.
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature takes effect only in allowlist mode.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter terminal identification view.
terminal-identification
3. Approve terminals as legal terminals.
approved { all | ipv4 ipv4-address }
By default, no terminals are approved as legal terminals.
Reidentifying terminals
About this task
If you consider that terminal information is inaccurate, you can perform this task to clear all identified terminal information and reidentifies terminals.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter terminal identification view.
terminal-identification
3. Reidentify terminals.
reidentify { all | ipv4 ipv4-address }
Display and maintenance commands for terminal identification
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display information about predefined terminals. |
display terminal-identification terminal predefined |
|
Display information about terminal groups. |
display terminal-identification terminal-group |