- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-WLAN high availability configuration | 144.96 KB |
Restrictions and guidelines: Dual-link backup configuration
Dual-link backup tasks at a glance
Setting AP connection priority and specifying a backup AC
Configuring master CAPWAP tunnel preemption
Verifying and maintaining WLAN VSRP
Displaying information about clients kept online by client persistence
Clearing clients kept online by client persistence
Dual-link backup configuration examples
Example: Configuring dual-link backup
Restrictions and guidelines: Client backup configuration
Prerequisites for client backup
Setting the client backup delay
Display and maintenance commands for client backup
Configuring dual-link backup
About dual-link backup
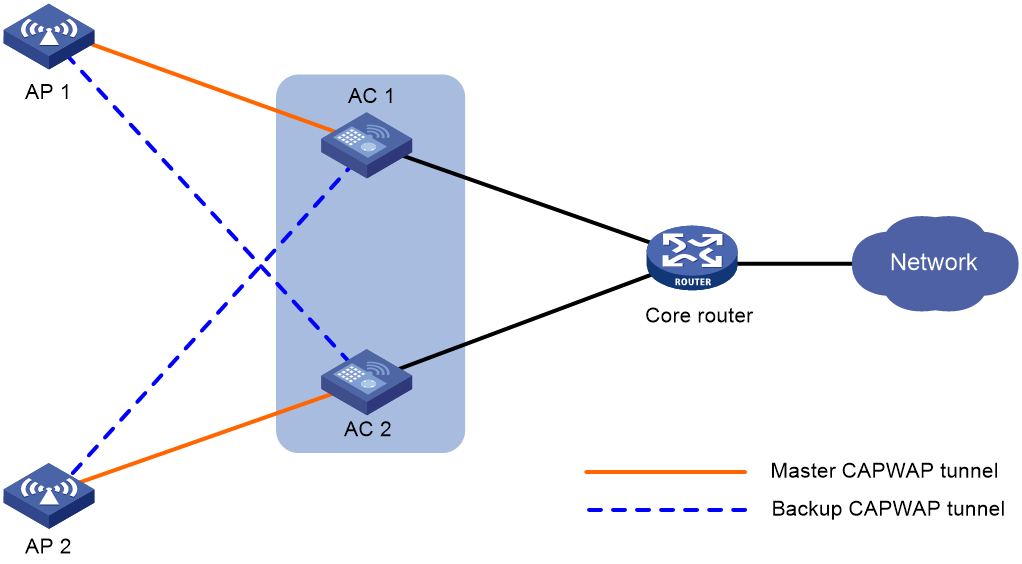
Dual-link backup enables two ACs to back up each other to reduce risks of service interruption caused by single-AC failures.
Dual-link backup is applicable to networks that are service continuity insensitive.
Figure 1 Network diagram for dual-link backup
Restrictions and guidelines: Dual-link backup configuration
For the dual-link backup feature to function correctly, configure auto AP or manual APs on the two ACs. The manual AP configuration must be identical on both ACs. For more information, see "Managing APs."
You can configure APs by using the following methods:
· Configure APs one by one in AP view.
· Assign APs to an AP group and configure the AP group in AP group view.
· Configure all APs in global configuration view.
For an AP, the settings made in these views for the same parameter take effect in descending order of AP view, AP group view, and global configuration view.
Dual-link backup tasks at a glance
To configure dual-link backup, perform the following tasks:
1. Setting AP connection priority and specifying a backup AC
2. (Optional.) Configuring master CAPWAP tunnel preemption
3. (Optional.) Enabling client persistence
Setting AP connection priority and specifying a backup AC
About this task
Set a higher AP connection priority for the master AC to ensure that APs can associate with the master AC first.
After an AP establishes a CAPWAP tunnel with the master AC, the AP will establish a backup CAPWAP tunnel with the specified backup AC.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view or AP group view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Enter AP group view.
wlan ap-group group-name
3. Set the AP connection priority.
priority priority
By default:
¡ In AP view, an AP uses the configuration in AP group view.
¡ In AP group view, the AP connection priority is 4.
4. Specify a backup AC.
backup-ac { ip ipv4-address | ipv6 ipv6-address }
By default:
¡ In AP view, an AP uses the configuration in AP group view.
¡ In AP group view, no backup AC is specified.
Configuring master CAPWAP tunnel preemption
About this task
This feature enables a backup CAPWAP tunnel to become a master tunnel after 10 minutes if the backup AC has higher AP connection priority than the master AC.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter AP view, AP group view, or global configuration view.
¡ Enter AP view.
wlan ap ap-name
¡ Enter AP group view.
wlan ap-group group-name
¡ Enter global configuration view.
wlan global-configuration
3. Configure master CAPWAP tunnel preemption.
wlan tunnel-preempt { disable | enable }
By default:
¡ In AP view, an AP uses the configuration in AP group view. If no configuration exists in AP group view, the AP uses the configuration in global configuration view.
¡ In AP group view, an AP uses the configuration in global configuration view.
¡ In global configuration view, master CAPWAP tunnel preemption is disabled.
Enabling client persistence
About this task
In a dual-link network, when the backup AC becomes the master AC, it synchronizes all client entries with the master AC. During the synchronization, wireless clients will go offline simultaneously and it will take a long time for them to come online again. With this feature enabled, the backup AC synchronizes entries with the master AC slowly, allowing wireless clients to slowly go offline and come online, thereby keeping clients online.
To use this feature together with portal authentication, configure MAC-based quick portal authentication for users to complete authentication without awareness.
For this feature to take effect in a dual-link network, make sure the master AC, backup AC, and all APs use version SP5802 or higher.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter global configuration view.
wlan global-configuration
3. Enable client persistence.
client-persistence enable
By default, client persistence is disabled.
Verifying and maintaining WLAN VSRP
Displaying information about clients kept online by client persistence
To display information about clients kept online by client persistence, execute the following command in any view:
display wlan persistent-client
Clearing clients kept online by client persistence
To clear clients kept online by client persistence, execute the following command in user view:
reset wlan persistent-client
Dual-link backup configuration examples
Example: Configuring dual-link backup
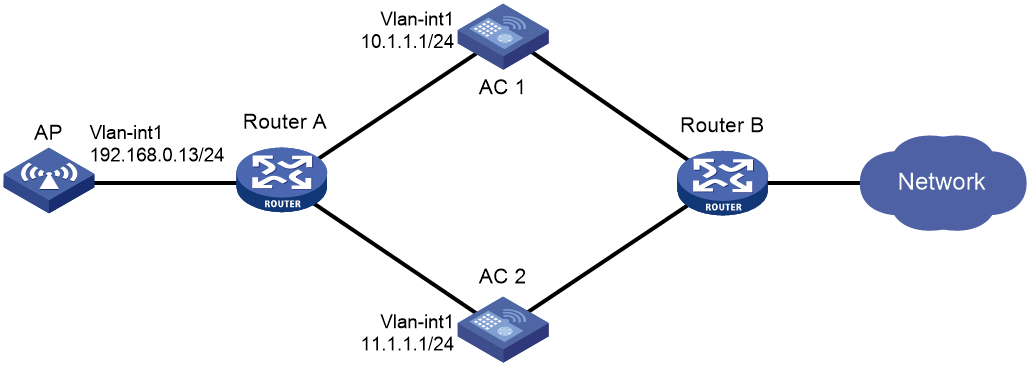
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, configure AC 1 to act as the master AC and AC 2 as the backup AC. When AC 1 fails and AC 2 takes over, the AP can communicate through AC 2. Configure the master CAPWAP tunnel preemption feature on the two ACs so that the AP reconnects to AC 1 when AC 1 recovers.
Procedure
1. Configure AC 1:
# Create VLAN-interface 1 and assign an IP address to it.
<AC1> system-view
[AC1] interface vlan-interface 1
[AC1-Vlan-interface1] ip address 10.1.1.1 24
[AC1-Vlan-interface1] quit
# Create an AP named ap1, and specify the AP model and serial ID. Set the AP connection priority to 7.
[AC1] wlan ap ap1 model WA6320
[AC1-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 219801A28N819CE0002T
[AC1-wlan-ap-ap1] priority 7
[AC1-wlan-ap-ap1] backup-ac ip 11.1.1.1
# Enable master CAPWAP tunnel preemption.
[AC1-wlan-ap-ap1] wlan tunnel-preempt enable
[AC1-wlan-ap-ap1] quit
2. Configure AC 2:
# Create VLAN-interface 1 and assign an IP address to it.
<AC2> system-view
[AC2] interface Vlan-interface 1
[AC2-Vlan-interface1] ip address 11.1.1.1 24
[AC2-Vlan-interface1] quit
# Create an AP named ap1, and specify the AP model and serial ID. Set the AP connection priority to 5.
[AC2] wlan ap ap1 model WA6320
[AC2-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 219801A28N819CE0002T
[AC2-wlan-ap-ap1] priority 5
# Specify a backup AC.
[AC2-wlan-ap-ap1] backup-ac ip 10.1.1.1
# Enable master CAPWAP tunnel preemption.
[AC2-wlan-ap-ap1] wlan tunnel-preempt enable
[AC2-wlan-ap-ap1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Get the AP online on AC 1. (Details not shown.)
# Shut down VLAN-interface 1 on AC 1 and wait no longer than 3 minutes, during which service interruption occurs. (Details not shown.)
# Verify that the AP comes online on AC 2 and the AP state is R/M on AC 2. (Details not shown.)
# Bring up VLAN-interface 1 on AC 1. (Details not shown.)
# Verify that the AP comes online on AC 1 again and the AP state is R/M on AC 1 and R/B in AC 2. (Details not shown.)
Configuring AP backup
About AP backup
AP backup forms multiple ACs into a cloud clusterr to ensure centralized AP management and avoid wireless service interruption in case of AC failures.
AC roles
An AC has the following roles:
|
Role |
Description |
|
Master AC |
Master in a cloud clusterr. The master AC manages the entire cloud cluster. |
|
Subordinate AC |
Subordinate in a cloud clusterr. A subordinate AC processes services, forwards packets, and acts as a backup for the master AC. When the master AC fails, the system automatically elects a new master AC from the subordinate ACs in the cloud cluster. |
|
Active AC |
An AC that can establish CAPWAP tunnels with APs. The master AC is always an active AC. |
|
Non-active AC |
An AC that cannot establish CAPWAP tunnels with APs. Non-active ACs can only be subordinate ACs. When an active AC fails, a non-active AC will be elected as an active AC. |
|
Directly connected AC |
An AC that receives the first packet from an AP when the AP launches a CAPWAP tunnel establishment process. |
|
Non-directly connected AC |
An AC that does not receive the first packet from an AP when the AP launches a CAPWAP tunnel establishment process. |
AP backup and recovery
AP backup enables the active AC (master AC) in a cloud clusterr to synchronize information about connected APs to all the non-active ACs. When the active AC fails, one of the non-active ACs becomes active to provide services, ensuring service continuity.
Prerequisites for AP backup
Before configuring AP backup, set up a cloud clusterr for the target ACs. For information about cloud cluster, see Virtualization Configuration Guide.
Enabling AP backup
About this task
This feature enables the active AC to synchronize information about connected APs to all the non-active ACs. When the active AC fails, one of the non-active AC becomes active to provide services.
Restrictions and guidelines
Disabling this feature removes backup AP information from all ACs.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable AP backup.
wlan ap-backup hot-backup enable
By default, AP backup is disabled.
Configuring client backup
About client backup
Client backup enables cloud cluster member ACs to backup client information with each other to keep clients online in case of AC failures. Client backup is triggered every time client information changes.
Client backup must work with AP backup. After both features are enabled, active ACs back up connected AP and client information to other member ACs. When an active AC fails, the master AC will select another AC in the cloud cluster fabric to recover information of AP and clients connected to the failed AC. For information about AP backup and AC selection, see "Configuring AP backup."
Restrictions and guidelines: Client backup configuration
Active ACs back up client information only for clients that come online after client backup is enabled. Disabling client backup deletes client backup information from all member ACs.
Prerequisites for client backup
The client backup feature must be used in conjunction with the AP backup feature. Client backup takes effect only when both features are enabled.
After you enable AP backup and client backup, the active AC can back up all connected APs and client information to other ACs within the cloud cluster. If the active AC fails, the master AC selects another AC to restore the AP and client information from the failed AC. For more information about AP backup and the AC selection rules, see "Configuring AP backup."
Enabling client backup
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable client backup.
wlan client-backup hot-backup enable
By default, client backup is disabled.
Setting the client backup delay
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature takes effect only when client backup is enabled.
This feature takes effect only on clients that come online after the client backup delay is set.
If an active/standby switchover occurs during the delay time, online clients whose information has not been backed up will be logged off and need to come online again. An active/standby switchover can be triggered by a restart of the active AC process.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the client backup delay.
wlan client-backup hot-backup delay delay-time
By default, the client backup delay is 60 seconds.
Display and maintenance commands for client backup
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display backup information about 802.1X clients associated with the specified cloud cluster member device. |
display dot1x connection-backup [ ap ap-name [ radio radio-id ] ] slot slot-number |
|
Display backup information about MAC authentication clients associated with the specified cloud cluster member device. |
display mac-authentication connection-backup [ ap ap-name [ radio radio-id ] ] slot slot-number |
|
Display client backup information for the specified cloud cluster member device. |
display wlan client-backup [ ap ap-name [ radio radio-id ] | mac-address mac-address ] [ verbose ] [ slot slot-number ] |