- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-Text | 571.83 KB |
About recommended BIOS settings
BIOS parameters for different workload modes
Introduction to workload modes
General Peak Frequency Compute
General Power Efficient Compute
Virtualization-Power Efficient
Transactional Application Processing
Configuring a workload profile
Entering the BIOS setup utility
Accessing the Advanced Power Management Configuration submenu
Overview
To meet the diverse needs of users in different workload modes, this document describes the configuration guide for setting BIOS parameters based on the services running on the server. It also describes the application scenarios and configuration instructions for the related workload modes."
About the BIOS
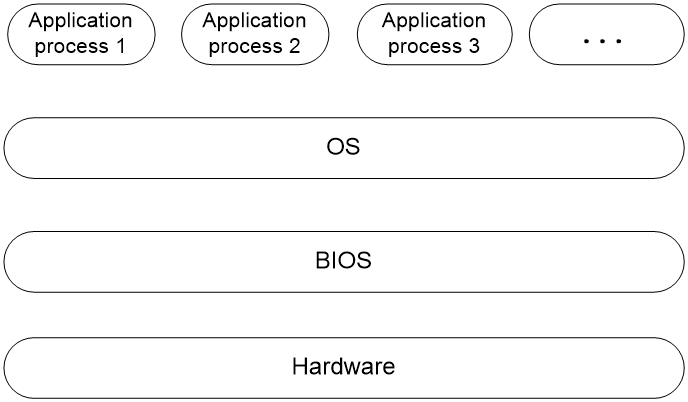
The Basic Input and Output System (BIOS) is a non-volatile firmware stored in the system ROM of a server. It is used to perform hardware initialization during server booting and provide runtime services for the operating systems. As shown in Figure 1, the BIOS interacts between the server hardware and the operating system (OS).
Figure 1 Layered architecture of a server system
Applicable products
This document is applicable to the following products:
· H3C UniServer B5700 G5
· H3C UniServer R4300 G5
· H3C UniServer R4700 G5
· H3C UniServer R4700LC G5
· H3C UniServer R4900 G5
· H3C UniServer R4900LC G5
· H3C UniServer R5300 G5
· H3C UniServer R5500 G5 Intel
· H3C UniServer R5500LC G5
· H3C UniServer R6900 G5
Applicable versions
This document is applicable to BIOS-5.57 and later.
Using this document
The information in this document is subject to change over time. You can access the H3C website to obtain the most recent version of the BIOS.
The information in this document might differ from your product if it contains custom configuration options or features.
Recommended BIOS settings
About recommended BIOS settings
A workload profile is a set of configuration options to deploy BIOS settings for server applications. The BIOS provides several profiles to match the selected workload. You can find the Workload Profile Configuration item from the Advanced > Socket Configuration > Advanced Power Management Configuration screen. The pre-configured parameter values in a profile are recommended values applicable to the corresponding scenario.
BIOS parameters for different workload modes
The BIOS parameter configurations recommended for different workload modes are shown in Table 1 and Table 2, which are the workload profile dependencies matrixes. An "X" means that the option setting has no requirement for the profile and can be modified. By default, "X" uses the default value of the corresponding device model and the default value varies by device model. When you apply a new profile to the device, the value of "X" will be restored to the default.
Not all the options listed are shown on the BIOS. However, the options of profiles default to the values shown here.
For information about application scenarios and configuration of different workload modes, see "Introduction to workload modes."
Table 1 Workload profile dependencies matrix
|
Dependency |
Virtualization-Power Efficient |
Virtualization-Performance |
Low Latency |
Fixed Turbo Frequency |
High Performance Compute |
General Peak Frequency Compute |
|
Hyper-Threading [ALL] |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
X |
Enabled |
Enabled |
|
Hardware Prefetcher |
Disabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
X |
Enabled |
Enabled |
|
Adjacent Cache Prefetch |
Disabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
X |
Enabled |
Enabled |
|
DCU Streamer Prefetcher |
Disabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
X |
Enabled |
Enabled |
|
DCU IP Prefetcher |
Disabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
X |
Enabled |
Enabled |
|
LLC Prefetch |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
X |
Enabled |
Disabled |
|
XPT Prefetcher |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
X |
Enabled |
Disabled |
|
EIST (P-States) |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
|
Energy Efficient Turbo |
Enabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
|
Turbo Mode |
Disabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
|
Hardware P-States |
Native Mode |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Out of Band Mode |
Disabled |
Disabled |
|
EPP profile |
X |
X |
X |
Performance |
X |
X |
|
Enable Monitor MWAIT |
Enabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
|
CPU C6 Report/report |
Enabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
|
Enhanced Halt State (C1E) |
Enabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
|
Package C State |
C6(non Retention) state |
C0/C1 state |
C0/C1 state |
X |
C0/C1 state |
C0/C1 state |
|
Power Performance Tuning |
BIOS Controls EPB |
OS Controls EPB |
OS Controls EPB |
X |
OS Controls EPB |
OS Controls EPB |
|
ENERGY_PERF_BIAS_CFG mode |
Power |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
VMX |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
X |
Disabled |
X |
|
Intel VT for Directed I/O |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
X |
Disabled |
X |
|
SR-IOV Support |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
X |
Disabled |
X |
|
Numa |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
X |
Enabled |
Enabled |
|
SNC (Sub NUMA) |
Disabled |
Enable SNC2 (2-clusters) - G5 2P |
Enable SNC2 (2-clusters) - G5 2P |
X |
Enable SNC2 (2-clusters) - G5 2P |
Disabled |
|
ADDDC Sparing |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
Patrol Scrub |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
Note: The Virtualization-Performance profile requires Enable Monitor MWAIT option to be set to Enabled when using it in a VMware EVC mode scenario. |
||||||
Table 2 Workload profile dependencies matrix (2)
|
Dependency |
General Power Efficient Compute |
Transactional Application Processing |
General Throughput Compute |
Advanced Reliability Mode |
Graphic Processing |
IO Throughput |
|
Hyper-Threading [ALL] |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
|
Hardware Prefetcher |
Disabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
|
Adjacent Cache Prefetch |
Disabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
|
DCU Streamer Prefetcher |
Disabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
|
DCU IP Prefetcher |
Disabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
|
LLC Prefetch |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
|
XPT Prefetcher |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
|
EIST (P-States) |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
|
Energy Efficient Turbo |
Enabled |
Disabled |
Enabled |
X |
Disabled |
Enabled |
|
Turbo Mode |
Disabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Disabled |
|
Hardware P-States |
Native Mode |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
|
EPP profile |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
Enable Monitor MWAIT |
Enabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
|
CPU C6 Report/report |
Enabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Enabled |
|
Enhanced Halt State (C1E) |
Enabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Enabled |
|
Package C State |
C6(non Retention) state |
C0/C1 state |
C0/C1 state |
C0/C1 state |
C0/C1 state |
C0/C1 state |
|
Power Performance Tuning |
BIOS Controls EPB |
OS Controls EPB |
OS Controls EPB |
OS Controls EPB |
OS Controls EPB |
OS Controls EPB |
|
ENERGY_PERF_BIAS_CFG mode |
Power |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
VMX |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Enabled |
X |
Disabled |
Enabled |
|
Intel VT for Directed I/O |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Enabled |
X |
Disabled |
Enabled |
|
SR-IOV Support |
Disabled |
Disabled |
Enabled |
X |
Disabled |
Enabled |
|
Numa |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
Enabled |
|
SNC (Sub NUMA) |
Disabled |
Enable SNC2 (2-clusters) - G5 2P |
Enable SNC2 (2-clusters) - G5 2P |
Disabled |
Enable SNC2 (2-clusters) - G5 2P |
Enable SNC2 (2-clusters) - G5 2P |
|
ADDDC Sparing |
X |
X |
X |
Enabled |
X |
X |
|
Patrol Scrub |
X |
X |
X |
Enabled |
X |
X |
Introduction to workload modes
The following information describes the application scenarios and configuration instructions of workload profile for different workload modes.
|
|
NOTE: The BIOS configuration schemes for different application scenarios are for general use. You configure the settings as needed. |
Fixed Turbo Frequency
Application scenarios
The Fixed Turbo Frequency profile enables all present processors to operate at the Turbo frequency through out-of-band management.
Configuration instructions
The operating system does not participate in frequency adjustment.
General Peak Frequency Compute
Application scenarios
The General Peak Frequency Compute profile is intended for scenarios that do not require high overall system performance.
Configuration instructions
By disabling Turbo boost, this profile allows the operating system to control frequency adjustment for the system to operate at the CPU base frequency.
Low Latency
Application scenarios
The Low Latency profile is intended to be used in latency-sensitive environments, such as a system featuring a large data volume, real-time service monitoring, and extensive message spreading.
Configuration instructions
This type of systems requires quick responses to maximize the real-time value of data. By disabling power saving and hyper-threading that might introduce computational latency, this profile allows the operating system to control frequency so that the system can operate at the Turbo frequency.
High Performance Compute
Application scenarios
The High Performance Compute profile is intended for intensive computing scenarios.
Configuration instructions
This profile is similar to the low latency profile but is mostly used to process concurrent tasks. As a best practice, enable hyper-threading. By disabling power saving, this profile enables the operating system to control frequency adjustment for the system to operate at the Turbo frequency.
General Power Efficient Compute
Application scenarios
The General Power Efficient Compute profile is intended for scenarios that have high power consumption.
Configuration instructions
This profile is similar to the virtualization-power efficient profile but virtualization-related options are disabled. In this profile, power saving is enabled and CPU cores can enter sleep mode, which increases latency and causes performance degrade in case of processor mode change.
Virtualization-Power Efficient
Application scenarios
The Virtualization-Power Efficient profile is intended to be used for virtualization environments and scenarios that have strict power consumption requirements.
Configuration instructions
The profile enables all virtualization-related options. By enabling power saving, the profile manages to maintain the system power consumption to a low level in idle state at the cost of high speed.
Virtualization-Performance
Application scenarios
The Virtualization-Performance profile is intended to be used in virtualization environments that require high performance.
Configuration instructions
The profile enables all virtualization-related options. By disabling power saving, the profile allows the system to operate at a high speed and a high frequency.
Advanced Reliability Mode
Application scenarios
The Advanced Reliability Mode profile is intended for scenarios that require high system stability and maintainability.
Configuration instructions
By enabling advanced RAS features and disabling power saving, this profile shortens the response time for system errors. As a best practice, use x4 memory chips.
Transactional Application Processing
Application scenarios
The Transactional Application Processing profile is intended to be used for upper-layer service application scenarios such as database systems.
Configuration instructions
The profile configuration is the same as the HPC profile settings, which is applicable to most scenarios. If the service data are random and the data set has a large volume, disable prefetch options and NUMA to facilitate application service execution as a best practice.
General Throughput Compute
Application scenarios
The General Throughput Compute profile is intended to be used for workloads where the total maximum sustained workload throughput is needed.
Configuration instructions
By disabling prefetch options and Turbo boost, this profile reduces the processor idle cycles caused by waiting, balances peak frequency management and throughput, and improves I/O throughput.
Graphic Processing
Application scenarios
The Graphic Processing profile is intended for workloads that are run on servers installed with GPUs.
Configuration instructions
The profile configuration is similar to the HPC profile settings, which is applicable to most scenarios. By disabling virtualization, this profile improves the processor core frequency, which enhances data processing ability and improves system performance.
IO Throughput
Application scenarios
The IO Throughput profile is intended for workloads that require improved IO and memory throughput.
Configuration instructions
This is achieved by disabling prefetch options, turning off turbo boost, enabling some power-saving options, reducing the number of stalled cycles caused by CPU waiting, balancing peak frequency management, and throughput requirements. The end result is improved IO and memory throughput.
Custom
Application scenarios
The Custom profile uses the default BIOS settings.
Configuration instructions
If you select this profile, the system loads the default BIOS settings and you can modify the settings as needed. For information about the default settings, see the BIOS user guide.
Configuring a workload profile
Entering the BIOS setup utility
1. Connect a keyboard, a mouse, and a monitor to the server or enable the remote console from the HDM Web interface.
For information about enabling the remote console, see H3C Servers HDM User Guide.
2. Start or restart the server.
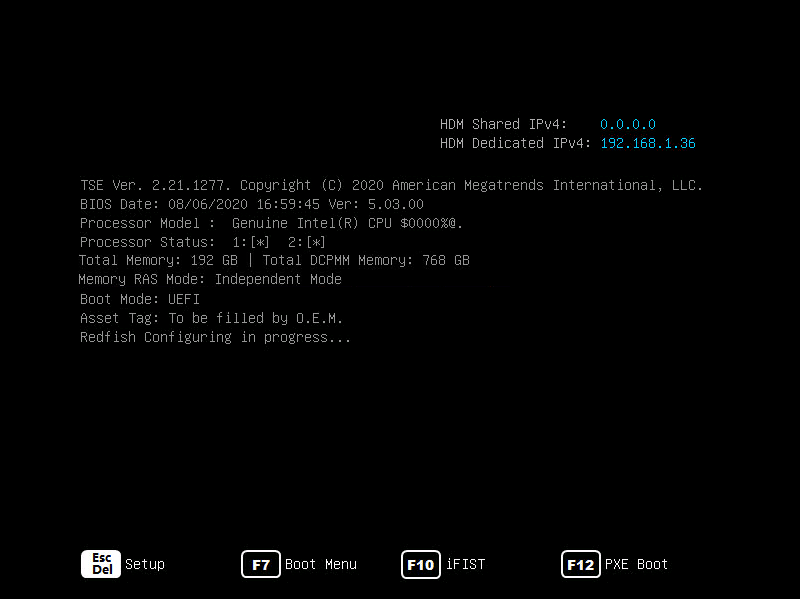
3. Press Del or Esc when the BIOS startup screen opens, as shown in Figure 2.
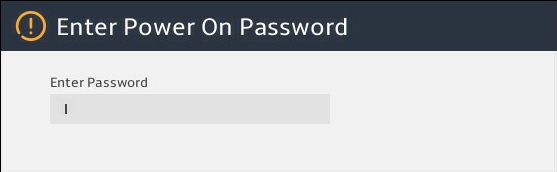
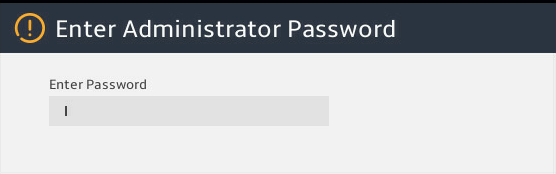
4. Enter the BIOS password if required during boot-up, as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 Entering the power on password
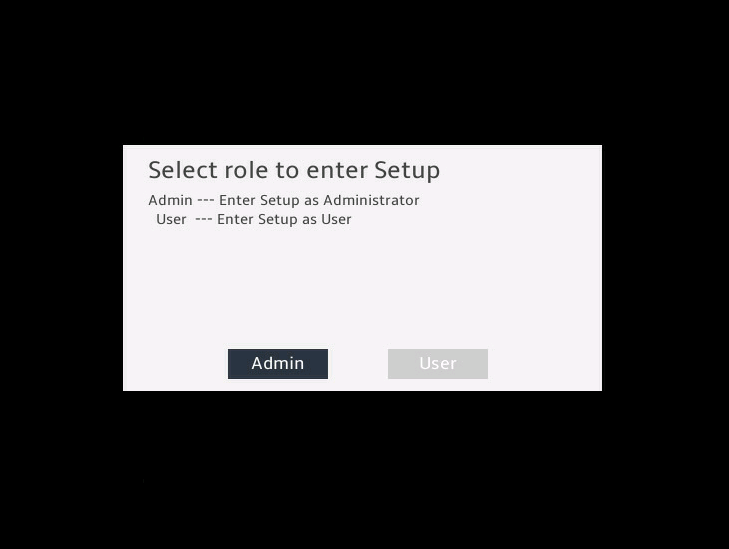
5. (Optional.) If you have set a BIOS administrator password and a user password, select the role before entering BIOS setup, as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4 Selecting a role to enter setup
6. Enter the password of the selected role, as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5 Entering the BIOS password
As shown in Figure 6, the BIOS setup utility screen opens.
Figure 6 BIOS setup utility screen
Accessing the Advanced Power Management Configuration submenu
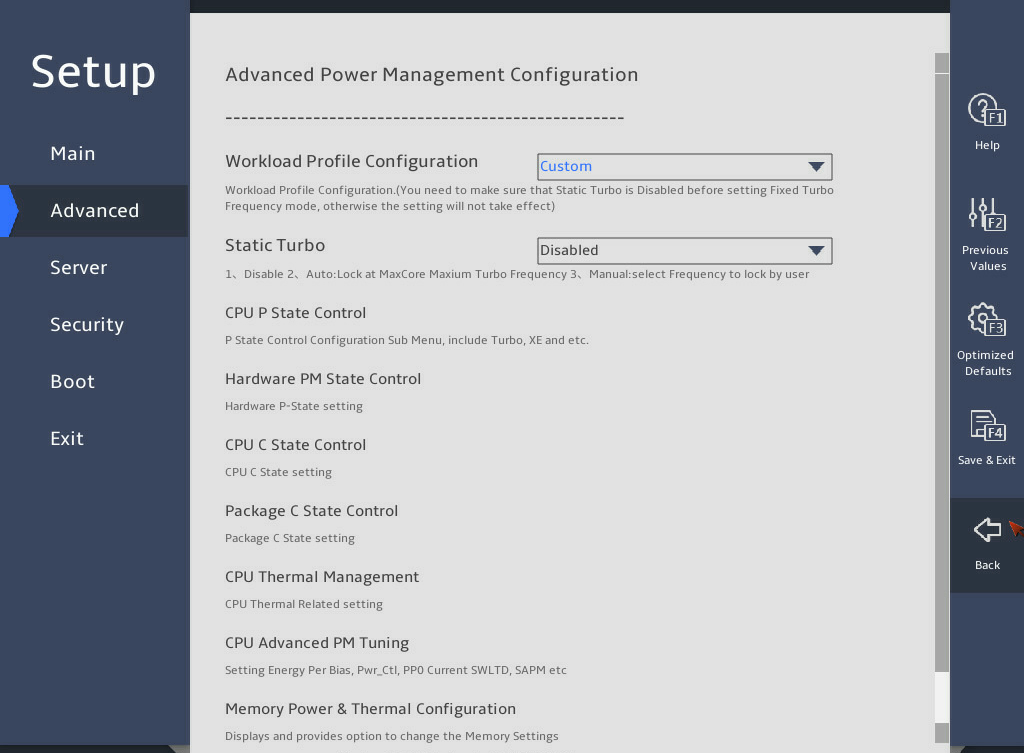
On the BIOS setup utility, click the Advanced tab, select Socket Configuration > Advanced Power Management Configuration, and then press Enter, as shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7 Advanced Power Management Configuration submenu screen
Selecting a workload profile
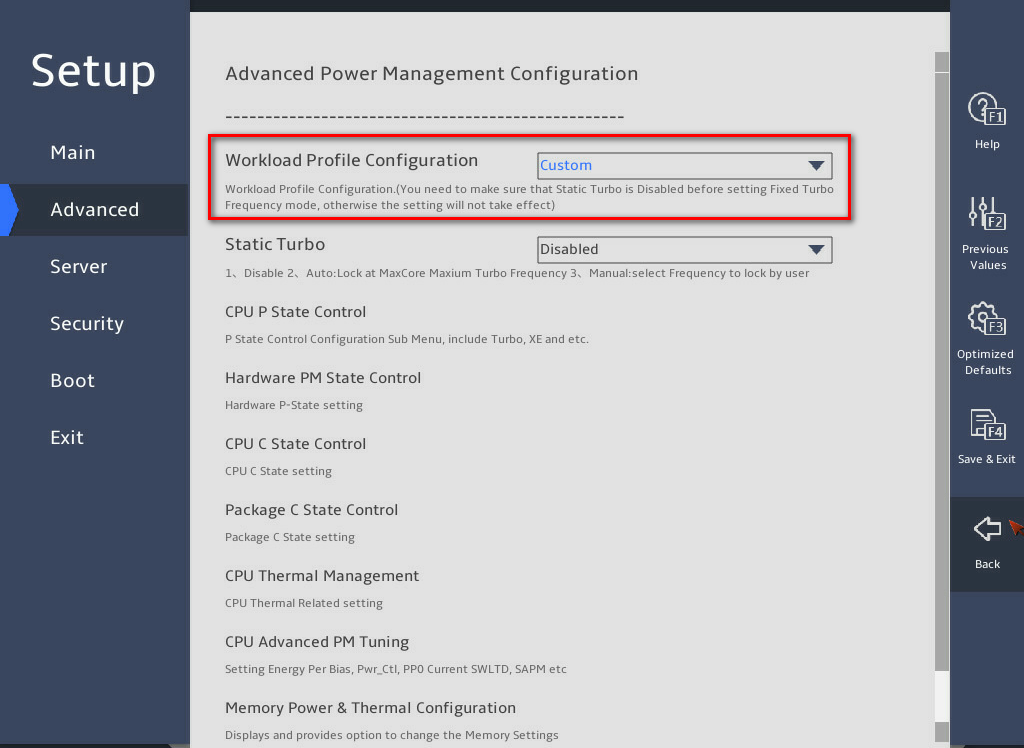
As shown in Figure 8, select a workload profile from the Workload Profile Configuration drop-down list.
Figure 8 Selecting a workload profile
Restarting the server
After the configuration, press F4. In the dialog box that opens, select Ok to save the configuration and exit the BIOS. The configuration will take effect after the server restarts.