- Table of Contents
-
- 04-DPI Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-DPI overview
- 02-DPI engine configuration
- 03-IPS configuration
- 04-URL filtering configuration
- 05-Data filtering configuration
- 06-File filtering configuration
- 07-Anti-virus configuration
- 08-Data analysis center configuration
- 09-Proxy policy configuration
- 10-WAF configuration
- 11-APT defense configuration
- 12-IP reputation configuration
- 13-Domain reputation configuration
- 14-DGA detection configuration
- 15-Intelligent service platform configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 14-DGA detection configuration | 362.91 KB |
Restrictions and guidelines: DGA detection
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with DGA detection
DGA detection tasks at a glance
Activating configurations for DPI service modules
Configuring fast log output for DGA detection logs
Enabling DGA detection logging
Display and maintenance commands for DGA detection
DGA detection configuration examples
Example: Configuring DGA detection
Configuring DGA detection
Based on deep learning algorithms, Domain Generation Algorithm (DGA) detection can effectively detect the DGA domain names that may be contained in DNS request packets, and block the communication traffic between the intranet botnet hosts and the Command and Control Servers (C&C servers, servers that issue attack instructions to malware). The DGA detection logs can be output to the data analysis center for generating botnet network analysis reports after comprehensive processing. You can view the generated reports to accurately locate the intranet botnet hosts. For more information about the data analysis center, see "Configuring the data analysis center".
About DGA detection
Background
After infecting the intranet hosts, some malware need to communicate regularly with the extranet C&C servers so as to receive instructions and send host private data.
In general, the malware communicate with the C&C servers in the following methods:
· Fixed IP—A malware communicates directly with the fixed IP address of a C&C server.
· Static domain name—A malware communicates with a C&C server through a fixed domain name.
· Static domain name list—A malware selects a domain name in the fixed domain name list to communicate with a C&C server.
· DGA domain name—A malware communicates with a C&C server through domain names dynamically generated by DGA algorithms.
If a malware communicates the C&C server through a fixed IP, static domain name, or static domain name list, the traffic can be easily blocked by IP address allowlist and domain name denylist. The unpredictability of DGA algorithms makes it easy for the malware to use DGA domain names to communicate with the C&C server. In this way, the malware can bypass traditional denylist-based defenses.
DGA algorithm
A DGA algorithm is a pseudo-random algorithm that inputs specific random seeds (for example, the current date of the system) and outputs a series of domain name strings with the following features:
· Randomness—Domain name strings generated by different random seeds have large differences in text feature.
· Unidirectionality—Malware controllers can restore the domain names that a malware will use to communicate with the C&C server through specific random seeds. Other people cannot know the DGA algorithms or obtain the random seeds from the domain name strings.
The controller of the malware uses the same DGA algorithm for the C&C server and the malware targeted to infect the intranet. The controller can generate a large number of domain names in advance through a specific random seed. As the malware can continually try resolving and connecting to each domain name, only a small number of domain names need to be registered on the domain name system before the agreed communication time. In this way, the C&C server can successfully communicate with the intranet malware.
DGA detection system
|
|
NOTE: The hardware appearance varies by device model. The hardware in the following figure is for illustration only. |
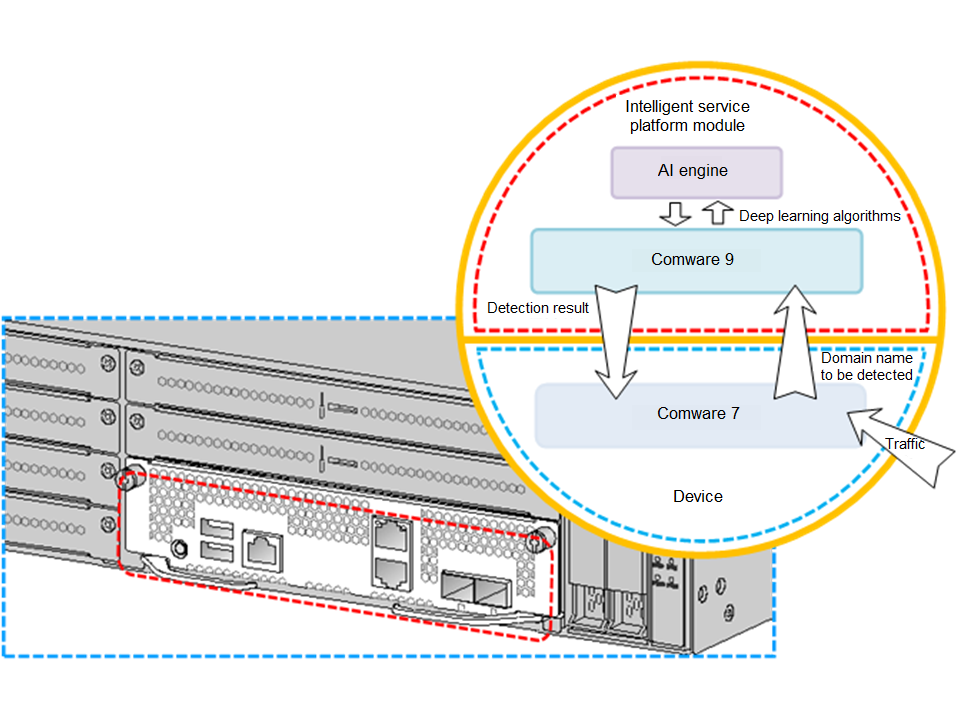
Figure 1 shows the system architecture of DGA detection. To use the DGA detection feature, install the intelligent service platform module on the device. On the AI engine of the module, you can deploy the DGA domain name feature model generated by using deep learning technologies and related detection algorithms. For more information about the intelligent service platform module, see "Configuring the intelligent service platform."
Figure 1 DGA detection system architecture
After the device sends a domain name to the intelligent service platform module for detection, the module calls the AI engine deployed with the DGA domain name feature model to examine the domain name. It uses deep learning algorithms to determine whether the domain name is a DGA domain name. Then the module sends the detection result to the device, which drops or permits the DNS request packets requesting DGA domain name resolution to pass according to the configured processing actions.
DGA detection mechanism
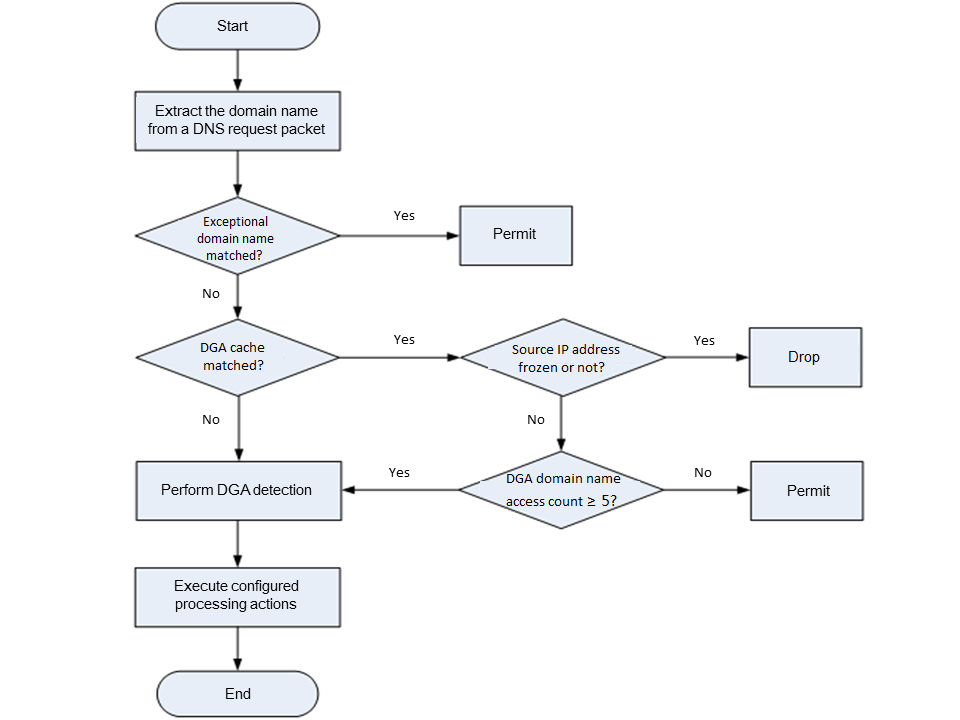
Figure 2 shows the process of DGA detection for received DNS request packets by the device.
Figure 2 DGA detection process
Upon receiving a DNS request packet, the DGA detection device performs the following operations:
1. Domain name extraction—The device extracts the requested domain name from a DNS request packet as the domain name to be detected.
2. Exceptional domain name match examination—The device examines whether the domain name to be detected matches a configured exceptional domain name. The device takes different actions depending on the matching result:
¡ If the domain name to be detected matches an exceptional domain name, the device does not perform DGA detection on the domain name, and allow the matching packet to pass.
¡ If the domain name to be detected does not match an exceptional domain name, the device proceeds to step 3.
3. DGA cache match examination—The DGA cache maintains the history of DGA domain name resolution requests initiated by each IP address over a period of time. The DGA cache include the following items:
Table 1 DGA cache information
|
Item |
Description |
|
Source IP address |
Source IP address of the DNS request packet. |
|
DGA domain name access count |
The total number of times a source IP address requested to resolve the DGA domain name (sending a DNS request packet requesting to resolve the DGA domain name is counted as one). |
|
Source IP address state |
State of the source IP address: · Frozen. · Unfrozen. |
|
Remaining frozen time |
Remaining frozen time of the source IP address in frozen state. |
The device takes different actions depending on the matching result:
¡ If the source IP address of the DNS request packet exists in the DGA cache, it indicates that the source IP address has accessed the DGA domain name. According to the source IP address state in the DGA cache, the device may take one of the following actions:
- If the IP address is frozen, the device drops the matching packet.
- If the IP address is unfrozen, the device judges whether the DGA domain name access count of this IP address in the DGA cache is greater than or equal to five. If yes, the device proceeds to step 4. Otherwise, the device permits the matching packet to pass.
¡ If the source IP address of the DNS request packet does not exist in the DGA cache, the device proceeds to step 4.
4. DGA detection—The device sends the domain name to be detected to the intelligent service platform module through the internal Ethernet interface. Upon receiving the domain name, the intelligent service platform module calls the AI engine to detect the domain name. After detection, the module returns the detection result to the device.
5. Execute configured processing actions—The device judges whether the domain name to be detected is a non-DGA domain name.
¡ If yes, the device permits the DNS request packet to pass.
¡ If no, the device judges whether the DGA domain name access count (including this time) of the source IP address in the DGA cache is greater than or equal to five.
- If yes, the device drops or permits the DNS request packet to pass according to the configured processing actions, and generate a DGA detection log.
The source IP address of the dropped DNS request packet will become frozen in the DGA cache. In the remaining frozen time, all domain name resolution requests initiated by the IP address will be dropped by the device.
- If no, the device permits the DNS request packet to pass.
If no record of the IP address exists in the DGA cache, the device creates a record for the IP address with the DGA domain name access count of one and state of unfrozen.
DGA detection log
The DGA detection log is used to record DGA domain name information detected by the device from DNS request packets. A log records the packet source/destination IP address, source/destination port, source VPN, source/destination security zone, processing actions on the packet, DGA domain name access count, and DGA domain name.
Once the domain name is determined as a DGA domain name by the intelligent service platform module and the configured processing actions include logging, the device generates a DGA detection log:
· The device aggregates DGA detection information with the same source IP address into a DGA detection log for output. DGA detection logs can be output to the information center or to the log hosts in fast logs (with fast log output enabled and relevant parameters configured). For more information about the information center, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide. For more information about fast log output, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
· With DGA detection logging enabled, the DGA detection logs generated by the device are processed by the data analysis center. Then the data analysis center generates botnet network analysis reports and displays them on the device's Web interface. You can accurately locate intranet botnet hosts based on the reports.
Restrictions and guidelines: DGA detection
DGA detection only supports detecting standard English domain names up to 128 characters (containing letters, digits, dots (.), hyphens(-), and underscores (_)). Detection of domain names in other languages, including their corresponding international domain name codes (Punycode), is not supported.
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with DGA detection
|
Series |
Models |
DGA detection compatibility |
|
F5000 series |
F5000-AI-40, F5000-AI-20, F5000-AI-15 |
Yes |
|
F5000-AI160, F5000-CN160, F5000-CN-G85, F5000-CN-G65, F5000-CN-G55 |
No |
|
|
F1000 series |
F1000-AI-25 |
Yes |
DGA detection tasks at a glance
To configure DGA detection, perform the following tasks:
1. Configuring the intelligent service platform module
Activating configurations for DPI service modules
2. Configuring the device
¡ (Optional.) Configuring fast log output for DGA detection logs
¡ (Optional.) Enabling DGA detection logging
Activating configurations for DPI service modules
About this task
The DGA detection feature requires the device to use the intelligent service platform module installed on it. After the configurations for DPI service modules are activated, the intelligent service platform can receive the domain names submitted by the device for DGA detection.
Prerequisites
Before you activate configurations for DPI service modules, install the intelligent service platform module on the device and complete the initialization configurations. For more information about the installation and configuration methods, see Intelligent Service Platform Module Deployment Manual.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Activate configurations for DPI service modules.
inspect activate
By default, the configurations for DPI service modules are not activated.
|
CAUTION: This command causes transient DPI service interruption. DPI-based services might also be interrupted. For example, security policies cannot control access to applications. |
For more information about this command, see DPI engine commands in DPI Command Reference.
Configuring DGA detection
Restrictions and guidelines
The IP address of the internal Ethernet interface on the intelligent service platform module is the IP address of the platform.
If the configured processing action is changed from permit to drop, the state of the source IP address with DGA domain name access count reaching five will become frozen.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify the IP address of the intelligent service platform.
intelligent-inspect ip ip-address
By default, the IP address of the intelligent service platform is not specified.
For more information about this command, see intelligent service platform commands in DPI Command Reference.
3. (Optional.) Specify the exceptional domain names.
inspect domain-name exception domain-name
By default, no exceptional domain name is specified.
4. Enter a DGA detection view.
dga
5. Specify DGA detection processing actions for detected packets.
action { permit | drop } [ logging ]
By default, the DGA detection processing action for detected packets is permit.
6. Enable DGA detection.
service enable
By default, DGA detection is disabled.
Configuring fast log output for DGA detection logs
About this task
By default, the DGA detection logs generated by the device are output to the information center for processing. With this feature configured, the DGA detection logs will be output through only the fast log output channel, not the information center.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable fast log output.
customlog format dpi dga
By default, fast log output is disabled.
For more information about this command, see fast log output commands in Network Management and Monitoring Command Reference.
3. Configure fast log output parameters.
customlog host [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] { hostname | ipv4-address | ipv6 ipv6-address } [ port port-number ] export dpi dga
By default, no fast log output parameters are configured.
For more information about this command, see fast log output commands in Network Management and Monitoring Command Reference.
Enabling DGA detection logging
About this task
When this feature enabled, the DGA detection logs generated by the device will be processed by the data analysis center for generating botnet network analysis reports. You can view the reports on the device's Web interface.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable DGA detection logging.
dac log-collect service dpi dga enable
By default, DGA detection logging is disabled.
For more information about this command, see data analysis center commands in DPI Command Reference.
Display and maintenance commands for DGA detection
Execute the display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display exceptional domain names. |
display inspect domain-name exception |
DGA detection configuration examples
Example: Configuring DGA detection
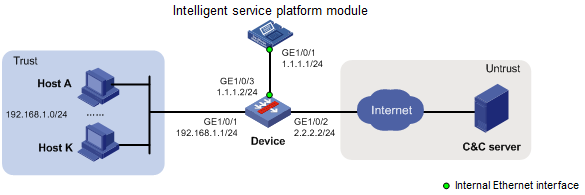
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 3, with DGA detection enabled on the enterprise security gateway device, abnormal external connection behaviors of intranet hosts can be detected in time.
Configure the device to meet the following requirements:
· Perform DGA detection on DNS request packets in the network.
· Freeze the IP addresses of suspected botnet hosts and drop all DNS request packets initiated by the IP addresses.
· Generate DGA detection logs for comprehensive analysis by the data analysis center module to accurately locate possible intranet botnet hosts.
Prerequisites
Before you configure DGA detection, install the intelligent service platform module on the device and complete the initialization configurations. For more information about the installation and configuration methods, see Intelligent Service Platform Module Deployment Manual.
Procedure
1. Configure the intelligent service platform module:
# Assign an IP address to interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<Module> system-view
[Module] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Module-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip address 1.1.1.1 24
[Module-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to other interfaces in the same way. (Details not shown.)
# Activate configurations for DPI service modules
[Module] inspect activate
2. Configure the device:
# Assign an IP address to interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip address 192.168.1.1 24
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to other interfaces in the same way. (Details not shown.)
# Assign interfaces to security zones.
[Device] security-zone name Trust
[Device-security-zone-Trust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-security-zone-Trust] quit
[Device] security-zone name Untrust
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] quit
# Configure a security policy to ensure network connectivity.
[Device] security-policy ip
[Device-security-policy-ip] rule name trust-untrust
[Device-security-policy-ip-0-trust-untrust] action pass
[Device-security-policy-ip-0-trust-untrust] source-zone Trust
[Device-security-policy-ip-0-trust-untrust] destination-zone Untrust
[Device-security-policy-ip-0-trust-untrust] source-ip-subnet 192.168.1.0 24
[Device-security-policy-ip-0-trust-untrust] quit
[Device-security-policy-ip] quit
# Configure ACL 2000 to identify packets from subnet 192.168.1.0/24 to be translated.
[Device] acl basic 2000
[Device-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] rule permit source 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
[Device-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] quit
# Enable outbound NAT with Easy IP on GigabitEthernet1/0/2 so that NAT translates the source addresses of the packets from internal hosts into the IP address of interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2.
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] nat outbound 2000
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Specify the IP address of the intelligent service platform.
[Device] intelligent-inspect ip 1.1.1.1
# Configure DGA detection.
[Device] dga
[Device-dga] action drop logging
[Device-dga] service enable
[Device-dga] quit
# Enable DGA detection logging.
[Device] dac log-collect service dpi dga enable
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the device is connected to the intelligent service platform.
[Device] display intelligent-inspect status
State: Connected.
# Verify that device can take the following actions after a network request for DGA domain name resolution appears (Details not shown.):
· Freeze the IP address of the suspected botnet host.
· Drop all DNS request packets initiated by the IP address for 30 minutes.
· Generate DGA detection logs with the prefix of DGA/4/DGA_IPV4_INTERZONE.