- Table of Contents
-
- 03-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Security zone configuration
- 02-Security policy configuration
- 03-ASPF configuration
- 04-Session management
- 05-Object group configuration
- 06-IP source guard configuration
- 07-AAA configuration
- 08-802.1X configuration
- 09-User identification configuration
- 10-Password control configuration
- 11-Portal configuration
- 12-MAC authentication configuration
- 13-IPoE configuration
- 14-Public key management
- 15-PKI configuration
- 16-SSH configuration
- 17-SSL configuration
- 18-Connection limit configuration
- 19-Attack detection and prevention configuration
- 20-Server connection detection configuration
- 21-ARP attack protection configuration
- 22-ND attack defense configuration
- 23-uRPF configuration
- 24-IP-MAC binding configuration
- 25-APR configuration
- 26-Keychain configuration
- 27-Crypto engine configuration
- 28-MAC learning through a Layer 3 device configuration
- 29-SMS configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 28-MAC learning through a Layer 3 device configuration | 81.53 KB |
Contents
Configuring MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device
About MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device
Restrictions and guidelines: MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device configuration
MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device configuration tasks at a glance
Enabling ARP entry synchronization through SNMP
Configuring the target Layer 3 device
Setting the parameters for ARP entry synchronization
Display and maintenance commands for
MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device configuration examples
Example: Configuring MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device
Configuring MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device
About MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device
This feature enables the device to learn the MAC address of a terminal (a PC for example) when a Layer 3 device exists between the device and the terminal through SNMP for network traffic control.
Working mechanism
Figure 1 MAC address learning through a Layer device workflow
As shown in Figure 1, MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device proceeds as follows:
1. The gateway learns the IP-MAC binding of the terminal, and then generates an ARP entry.
2. The device sends SNMP requests to the gateway at the specified intervals to request the ARP entry.
3. The gateway sends a response that contains the ARP entry to the device.
4. Upon receiving the response, the device saves the ARP entry in the memory. Then it can learn the MAC address of the terminal.
Entry aging
ARP entries learned through a Layer 3 device will be automatically deleted when the aging timer expires, or can be cleared using the reset snmp-server arp-sync table command.
Restrictions and guidelines: MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device configuration
· MAC addresses learned using this feature can be used for policy packet filtering and packet information recording in the IPS logs.
· Only MAC addresses mapped from IPv4 addresses can be learned.
· Make sure no NAT devices exist between the device and the Layer 3 device.
· This feature is not applicable to a VRF network.
Prerequistes
Make sure SNMP agent has been enabled and a community name has been configured on the Layer 3 device. For information about SNMP, see SNMP configuration in Network Management and Monitoring.
MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device configuration tasks at a glance
To configure MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device, perform the following tasks:
1. Enabling ARP entry synchronization through SNMP
2. Configuring the target Layer 3 device
3. (Optional.) Setting the parameters for ARP entry synchronization
Enabling ARP entry synchronization through SNMP
About this task
With this feature enabled, the device acts as an NMS to learn all ARP entries on a Layer 3 device (agent) to obtain the MAC address of the Layer 3 device.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable ARP entry synchronization through SNMP.
snmp-server arp-sync enable
By default, ARP entry synchronization through SNMP is disabled.
Configuring the target Layer 3 device
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure the target Layer 3 device for ARP entry synchronization through SNMP.
SNMP v2c:
snmp-server arp-sync target-host address ip-address community { simple | cipher } community-name v2c
SNMP v3:
snmp-server arp-sync target-host address ip-address usm-user v3 user-name [ { simple | cipher } authentication-mode { md5 | sha } auth-password [ privacy-mode { aes128 | des56 } pri-password ] ]
By default, no target Layer 3 device is configured for ARP entry synchronization through SNMP.
Setting the parameters for ARP entry synchronization
About this task
With this feature configured, the device sends SNMP requests for ARP entry synchronization to the target Layer 3 device at the specified intervals. If the device does not receive an SNMP response before the timeout expires within the specified interval, the device re-sends SNMP requests.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the parameters for ARP entry synchronization.
snmp-server arp-sync { interval interval | timeout time } *
By default, the interval for sending SNMP requests is 5 seconds and the timeout for SNMP responses is 3 seconds.
Display and maintenance commands for
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display the ARP entries synchronized through SNMP. |
display snmp-server arp-sync table |
|
Clear the ARP entries synchronized through SNMP. |
reset snmp-server arp-sync table |
MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device configuration examples
Example: Configuring MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device
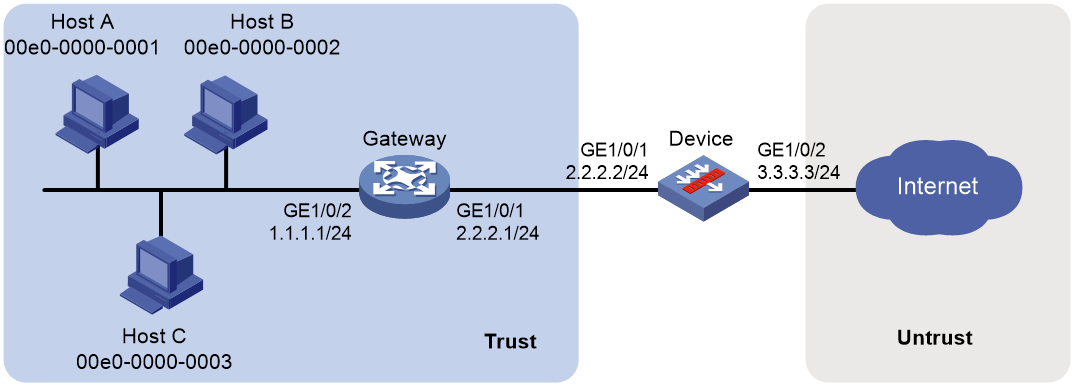
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, hosts in an internal network are connected to the device through a Layer 3 gateway and the device is connected to the Internet.
· Configure MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device to ensure that the device can learn the MAC addresses of the hosts through the gateway.
· Configure security policies by using the learned MAC addresses to allow only Host A and Host B to access the Internet.
Procedure
1. Configure the gateway:
# Specify an IP address for each interface and configure routing features to ensure network reachability. (Details not shown.)
# Configure SNMPv2c, and create the read-only community with the plaintext form name public.
<Gateway> system-view
[Gateway] snmp-agent sys-info version v2c
[Gateway] snmp-agent community read simple public
2. Configure the device:
a. Assign IP addresses to interfaces:
# Assign an IP address to interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to other interfaces in the same way. (Details not shown.)
b. Configure settings for routing.
This example configures static routes, and the next hop in the route to the Internet is 3.3.3.1.
[Device] ip route-static 1.1.1.0 24 2.2.2.1
[Device] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 3.3.3.1
c. Add interfaces to security zones.
[Device] security-zone name trust
[Device-security-zone-Trust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-security-zone-Trust] quit
[Device] security-zone name untrust
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-security-zone-Untrust] quit
d. Configure a security policy.
# Configure a rule named rule1 to allow the device to access the gateway.
[Device] security-policy ip
[Device-security-policy-ip] rule name rule1
[Device-security-policy-ip-0-rule1] source-zone local
[Device-security-policy-ip-0-rule1] destination-zone trust
[Device-security-policy-ip-0-rule1] source-ip-host 2.2.2.2
[Device-security-policy-ip-0-rule1] destination-ip-host 2.2.2.1
[Device-security-policy-ip-0-rule1] action pass
[Device-security-policy-ip-0-rule1] quit
# Configure a rule named rule2 to permit traffic only from MAC object group groupmac to the Internet.
[Device-security-policy-ip] rule name rule2
[Device-security-policy-ip-1-rule2] source-zone trust
[Device-security-policy-ip-1-rule2] destination-zone untrust
[Device-security-policy-ip-1-rule2] source-mac groupmac
[Device-security-policy-ip-1-rule2] action pass
[Device-security-policy-ip-1-rule2] quit
# Activate rule matching acceleration.
[Device-security-policy-ip] accelerate enhanced enable
[Device-security-policy-ip] quit
e. Configure MAC address learning through the gateway.
Enable ARP entry synchronization through SNMP. Configure the device to synchronize ARP entries from the gateway.
[Device] snmp-server arp-sync enable
[Device] snmp-server arp-sync target-host address 2.2.2.1 community simple public v2c
[Device] snmp-server arp-sync interval 10 timeout 4
f. Create a MAC object group named groupmac. Add Host A's MAC address 00e0-0000-0001 and Host B's MAC address 00e0-0000-0002 to the group.
[Device] object-group mac-address groupmac
[Device-obj-grp-mac-groupmac] mac 00e0-0000-0001
[Device-obj-grp-mac-groupmac] mac 00e0-0000-0002
[Device-obj-grp-mac-groupmac] quit
Verifying the configuration
1. Verify that ARP entries have been synchronized to the device.
[Device] display snmp-server arp-sync table
IP Address MAC Address Aging(M)
1.1.1.1 00e0-0000-0001 1
1.1.1.2 00e0-0000-0002 1
1.1.1.3 00e0-0000-0003 1
Total:3
2. Verify that Host A and Host B can access the external network but Host C cannot.