- Table of Contents
-
- 07-System
- 01-High availability group
- 02-VRRP
- 03-Track
- 04-BFD
- 05-NQA
- 06-Basic log settings
- 07-Email server
- 08-Session log settings
- 09-NAT log settings
- 10-AFT log settings
- 11-Sandbox log settings
- 12-Threat log settings
- 13-Application audit log settings
- 14-NetShare log settings
- 15-URL filtering log settings
- 16-Attack defense log settings
- 17-Reputation log settings
- 18-Bandwidth alarm logs
- 19-Configuration log settings
- 20-Security policy log
- 21-Terminal identification logging
- 22-Heartbeat log settings
- 23-WAF log settings
- 24-IP access logs
- 25-MAC access log
- 26-Load balancing logging
- 27-Bandwidth management logs
- 28-Context rate limit logging
- 29-Zero trust logs
- 30-Report settings
- 31-Session settings
- 32-Signature upgrade
- 33-Software upgrade
- 34-License management
- 35-IRF
- 36-IRF advanced settings
- 37-Contexts
- 38-Administrators
- 39-Date and time
- 40-MAC address learning through a Layer 3 device
- 41-SNMP
- 42-Configuration management
- 43-Reboot
- 44-About
- 45-Ping
- 46-Tracert
- 47-Packet capture
- 48-Webpage Diagnosis
- 49-Diagnostic Info
- 50-Packet trace
- 51-Load balancing test
- 52-IPsec diagnosis
- 53-Fast Internet Access
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-High availability group | 312.33 KB |
This help contains the following topics:
¡ Basic concepts in HA group configuration
¡ Operating modes of the HA group
¡ Configuration consistency check
¡ HA group in collaboration with VRRP
¡ HA group in collaboration with routing protocols
¡ Transparent in-path deployment of the HA group
Introduction
The high availability (HA) group is a device-level HA solution. It enables two devices to back up each other dynamically to ensure user service continuity upon failure of one of the devices.
The HA group works with Remote Backup Management to manage multiple VRRP groups on two devices to ensure that they have the same VRRP master and backup. The HA group can synchronize important configuration and service entries between the master and the backup devices in VRRP groups to ensure service continuity. Two devices must have the same software and hardware environments to join the HA group.
Basic concepts in HA group configuration
Basic concepts in HA group configuration are as follows:
· Primary and secondary roles—Control the direction of configuration synchronization between devices. The primary and secondary roles are assigned to the two devices in an HA group, respectively. The primary device synchronizes its configuration to the secondary device, and the configuration on the secondary device is overwritten.
· VRRP master and backup roles—Determine which device forwards and processes traffic in a VRRP group. The master and backup roles are assigned to the primary and secondary devices in an HA group, respectively. In a VRRP group, the master forwards traffic of services and backs up service entries to the backup in real time. When the master fails, the backup takes over the master role to ensure service continuity.
· VRRP active and standby groups—Associate the HA group with VRRP for the HA group to centrally manage the status of multiple VRRP groups.
· HA channels—Transmit status information, important configuration, and service entries between the HA group members.
· HA group modes—Include active/standby mode and dual-active mode. In active/standby mode, the primary device processes all services. In dual-active mode, both devices process services to increase the capability of the HA group and load share traffic.
· HA packets—Transmitted through TCP over the HA channel between the HA group members.
Operating modes of the HA group
The HA group supports the active/standby and dual-active modes.
Active/standby mode
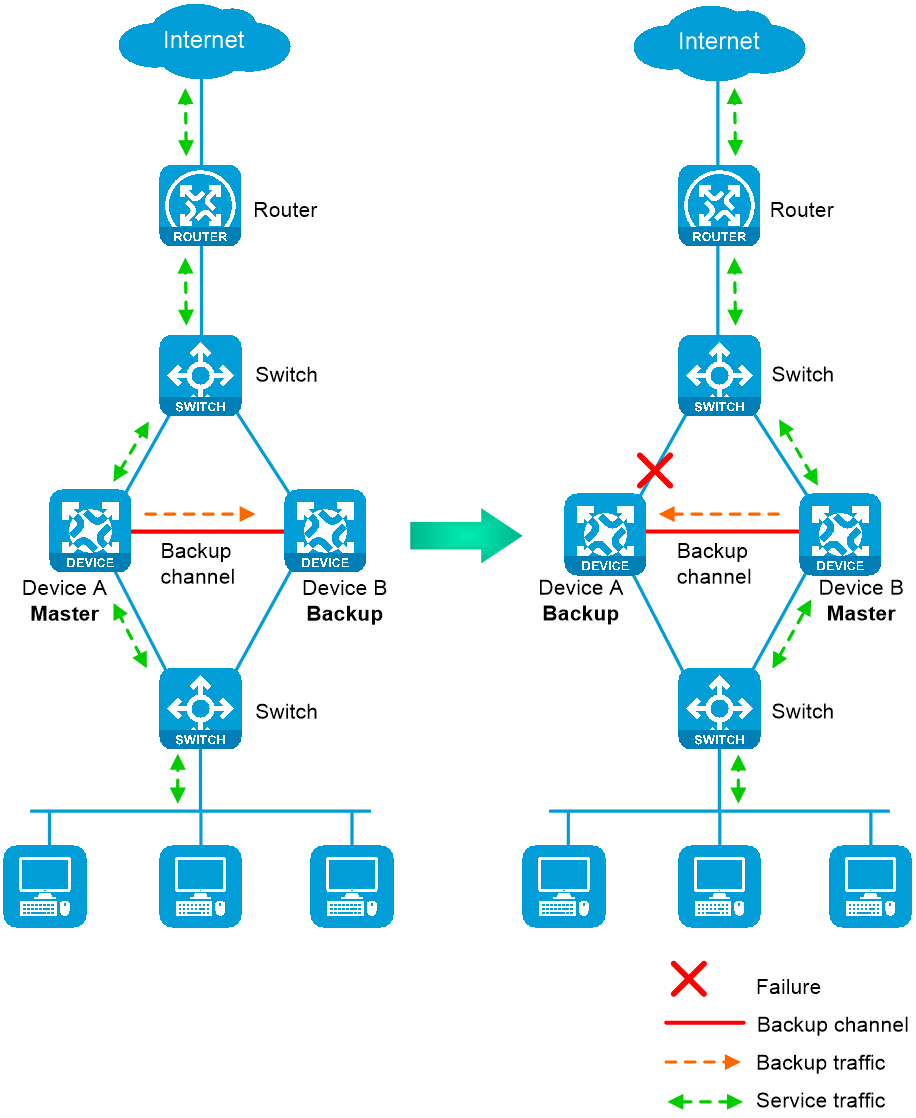
In active/standby mode, one device acts as the master to process services, and the other device stands by as a backup, as shown in Figure 1. When an interface or link on the master fails or when the master fails, the backup takes over the master role to process services.
Figure 1 Active/standby mode of the HA group
Dual-active mode
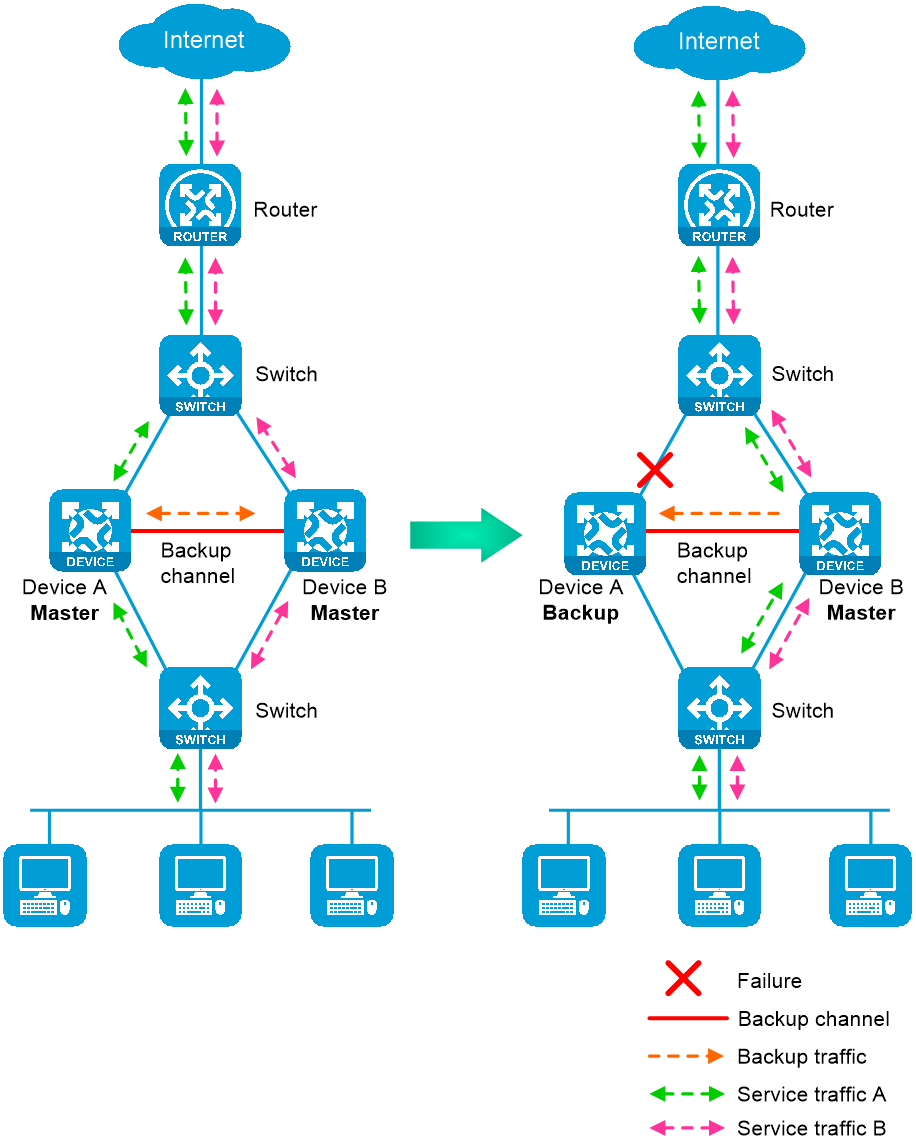
In dual-active mode, both devices process services to increase capability of the HA group, as shown in Figure 2. When one device fails, its traffic is switched to the other device for forwarding.
Figure 2 Dual-active mode of the HA group
HA channels
Overview
The HA group members transmit HA group status, important configuration, and service entries over the following channels:
· Control channel—Transmits data by using packets, including HA group status packets, configuration consistency check packets, backup packets for service entries, data packets that require transparent transmission, and configuration synchronization packets.
· Data channel—Transmits only backup packets and packets that require transparent transmission. The data channel uses the hardware driver for data transmission and supports only Layer 2 forwarding.
Establishment and keepalive mechanism of the control channel
The control channel uses the keepalive mechanism of TCP for reachability detection. The control channel is established through TCP. In the HA group, the device with the higher IP address acts as the server, and the other device acts as the client to initiate the TCP connection.
Each member device periodically sends HA keepalive packets to the HA peer over the HA control channel. If a device has not received any responses from the peer when the maximum number of HA keepalive attempts is reached, the HA control channel is disconnected.
Service entry backup
Overview
The HA group backs up the service entries generated on the primary device to the secondary device to prevent service interruption when a primary/secondary member switchover occurs.
Security devices like firewalls generate a session entry for each dynamic connection. In the HA group, only the primary device processes traffic and generates session entries. To ensure service continuity, the primary device backs up its session entries to the secondary device in real time. After a primary/secondary member switchover, the new primary device can forward the packets of the existing services based on the session entries without interruption.
Supported services
The HA group can perform hot backup for the following service entries:
· Session entries.
· Session relation entries.
· NAT port blocks.
· AFT port blocks.
· Entries generated by security service modules.
Support for these entries depends on the device model.
Configuration backup
Overview
The HA group backs up important configuration from the primary device to the secondary device to prevent service interruption when a primary/secondary member switchover occurs. The configuration on the secondary device is overwritten. The unidirectional backup mechanism avoids configuration conflicts, especially in dual-active mode. The HA roles can only be manually assigned to devices. As a best practice to ensure correct operation of the HA group, enable configuration backup on the primary device.
Backup type
The HA group supports both automatic backup and manual backup.
Supported services
The HA group can perform configuration backup for the following services:
· Resources: VPN instance, ACL, object group, time range, security zone, session management, APR, AAA.
· DPI: Application layer inspection engine, IPS, URL filter, data filter, file filter, anti-virus, data analysis center, WAF.
· Policies: Object policy, security policy, ASPF, attack detection and prevention, connection limit, NAT, AFT, load balancing, bandwidth management, application auditing and management, shared network access management, proxy policy.
· Logs: Fast log output, flow log.
· SSL VPN.
· VLAN.
· Information center.
Support for these services depends on the device model.
Configuration consistency check
The HA group verifies configuration consistency between the HA group members by using configuration consistency check packets. If a device detects configuration inconsistency, it generates a log for you to manually synchronize configuration.
HA group in collaboration with VRRP
Overview
You can use the HA group and VRRP in combination to control master/backup switchover for device role consistency (master or backup) in multiple VRRP groups. This ensures that both inbound and outbound traffic can be switched to the new master for symmetric forwarding upon device failure.
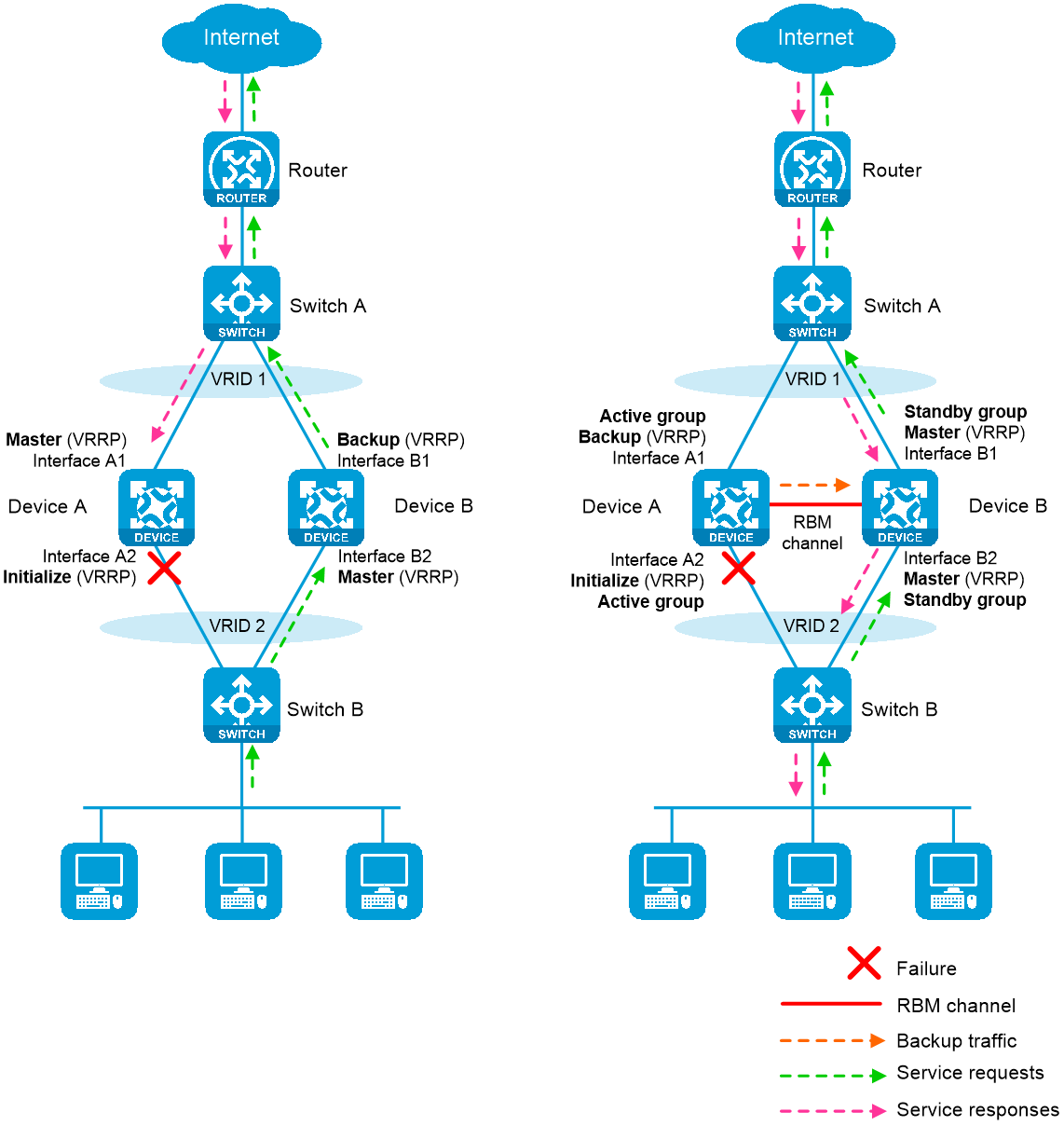
Figure 3 illustrates VRRP association with the HA group in active/standby mode.
· As shown in the left, VRRP cannot ensure symmetric forwarding upon failure on a device, which causes traffic interruption.
· As shown in the right, after the HA control channel is established, the HA group determines the roles of the devices in all VRRP groups. The master election mechanism of VRRP no longer takes effect. If the HA control channel is disconnected, the master election mechanism of VRRP takes effect again.
Figure 3 HA group in collaboration with VRRP
VRRP active/standby group
The HA group is associated with VRRP by VRRP active and standby groups.
A VRRP active/standby group can be in master or backup state, which determines the state of devices in the associated VRRP groups. For example, if a VRRP active group is in master state, all devices in the associated VRRP groups are masters.
The initial state of a VRRP active/standby group is as follows:
· Active/Standby mode—On the primary device, the initial state is master for the VRRP active and standby groups. On the secondary device, the initial state is backup for the VRRP active and standby groups.
· Dual-active mode—The state of a VRRP active/standby group is not affected by the HA roles. The initial state is master for the VRRP active group and is backup for the VRRP standby group.
VRRP master election in the HA group environment
After the HA group is associated with VRRP, the HA group determines the roles of the devices in the VRRP groups. As shown in Figure 3, Device A is the master in VRRP group 1 and VRRP group 2, and Device B is the backup in VRRP group 1 and VRRP group 2. When Interface A2 on Device A fails, the following events occur:
1. The HA group receives an interface failure event and sends the status change information of the VRRP active and standby groups to Device B.
2. Device B sets its role to master in the VRRP standby group and then becomes the master in VRRP group 1 and VRRP group 2.
3. Device B sends a response to Device A after the master/backup switchover.
4. Device A sets its role to backup in the VRRP active group and then becomes the backup in VRRP group 1 and VRRP group 2.
5. When Interface A2 recovers, the HA group performs another master/backup switchover following the same procedure. Traffic is switched back to Device A after the switchover.
ARP and MAC learning in VRRP
When the members of a VRRP group receive an ARP request for the group's virtual IP address, the master replies with the group's virtual MAC address. This allows the upstream and downstream Layer 2 devices and hosts to learn the virtual MAC address.
HA group in collaboration with routing protocols
Overview
You can use the HA group to enable the routing protocols on the secondary device to advertise modified link cost. The feature ensures that both inbound and outbound traffic can be switched to the new master for symmetric forwarding.
To use the HA group with routing protocols, you must use track entries to monitor the status of uplink and downlink interfaces for the HA group to perform a primary/secondary member switchover when link or interface failure occurs.
The following information uses OSPF on the HA group in active/standby mode to describe how the HA group collaborates with dynamic routing protocols:
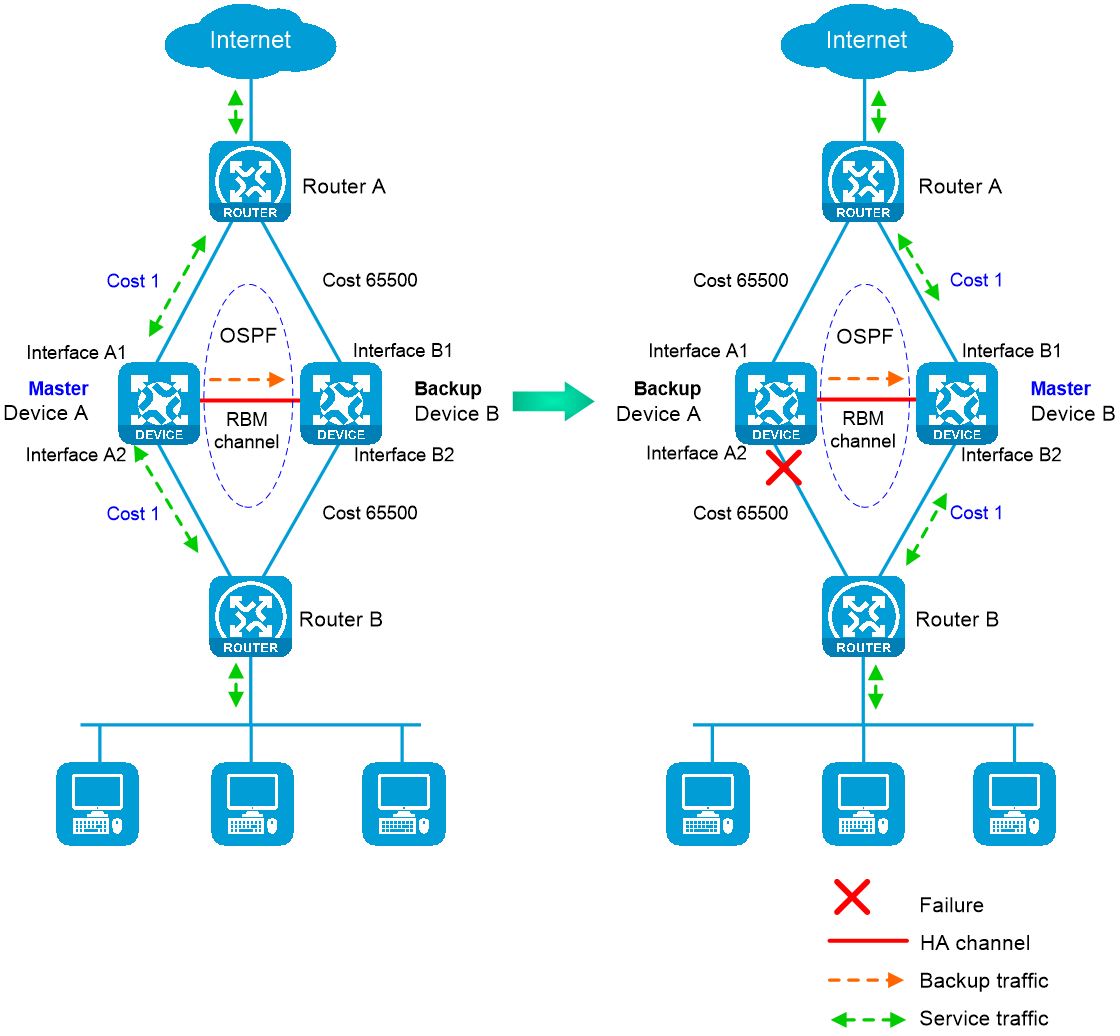
· As shown in Figure 4, when both Device A (primary) and Device B (secondary) are operating correctly, Device A advertises the original link cost 1, and Device B advertises the link cost 65500, which has been adjusted by the HA group. As a result, Device A forwards all traffic that traverses the HA group.
· As shown in Figure 4, when downlink Interface A2 of Device A fails, Device A and Device B switch their roles. Then, Device B (primary) advertises the original link cost 1, and Device A (secondary) advertises the adjusted link cost 65500. As a result, Device B forwards all traffic that traverses the HA group.
Figure 4 HA group in collaboration with routing protocols
Mechanism
The HA group adjusts the link costs advertised by dynamic routing protocols by using one of the following methods:
· Replacing the original link cost with the absolute link cost that you configure.
· Adding an increment value to the original link cost.
The link cost changes do not affect the HA roles of devices, and you must configure the same link cost adjustment settings on the primary and secondary member devices.
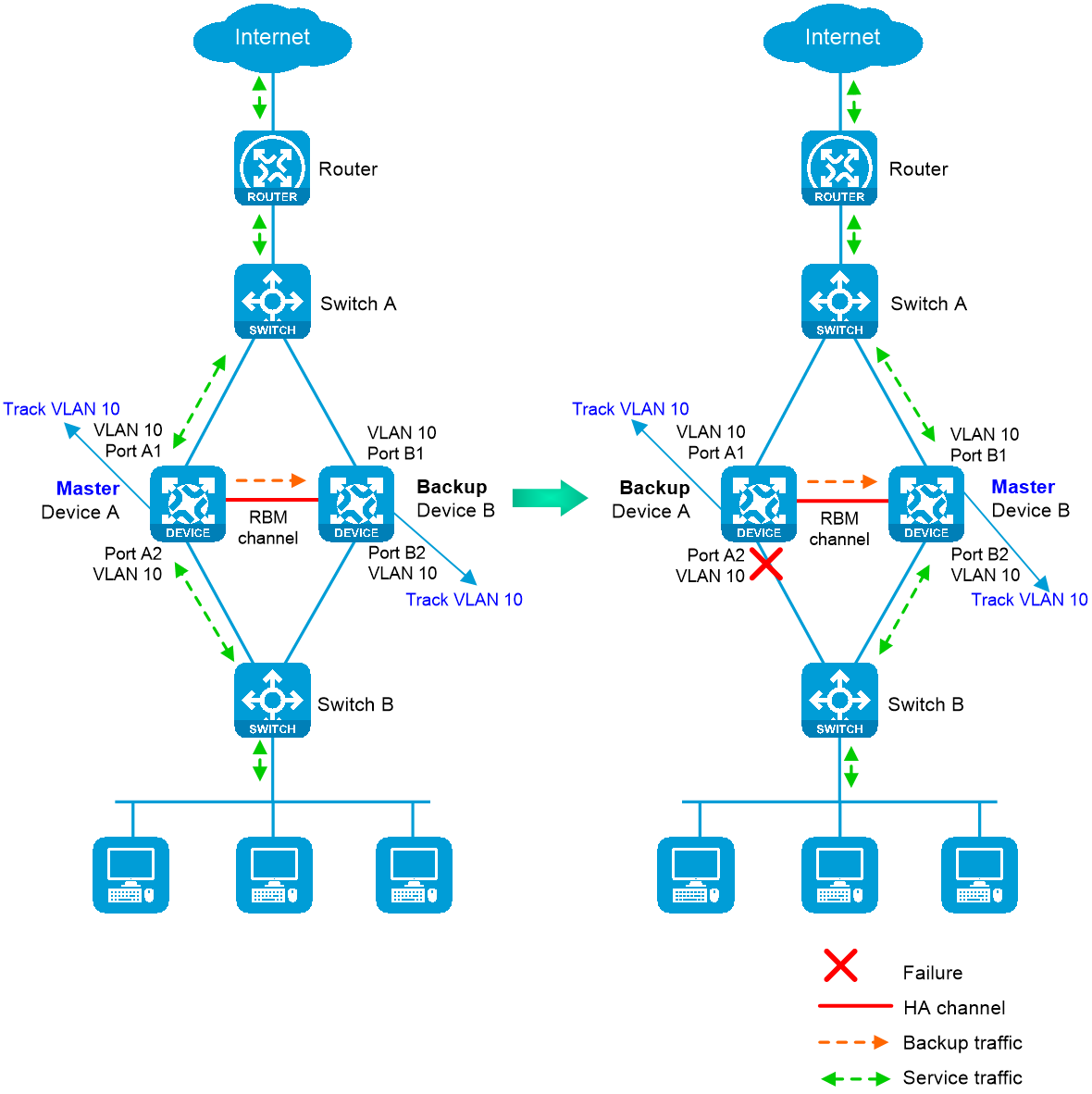
Transparent in-path deployment of the HA group
When you use this networking scheme, you can configure the HA group to monitor interfaces or VLANs to enable collaboration between uplink and downlink interfaces. The monitoring configuration ensures that a group of interfaces have the same status, and uplink and downlink traffic can be switched simultaneously between the member devices.
The following information uses VLAN monitoring as an example to describe how interfaces collaborate:
· As shown in Figure 5, when both Device A (primary) and Device B (secondary) are operating correctly, tracked VLAN 10 is in active state on Device A and in inactive state on Device B. As a result, Device A forwards all traffic that traverses the HA group.
· As shown in Figure 5, when downlink Port A2 of Device A fails, Device A and Device B switch their roles. Then, the HA group places VLAN 10 in inactive state on Device A (secondary) and in active state on Device B (primary). As a result, Device B forwards all traffic that traverses the HA group.
Figure 5 Transparent in-path deployment of the HA group
Restrictions and guidelines
You can use the HA group only with VRRP master/backup mode. VRRP load sharing mode does not support the HA group.
You can configure the HA group to monitor track entries, VLANs, or interfaces, but you cannot configure VLAN monitoring in combination with track entry monitoring or interface monitoring. When you configure the HA group to monitor both track entries and interfaces, make sure the track entries are not associated with the monitored interfaces.
Configure the HA group
Prerequisites
Before you configure the HA group, verify that the following hardware and software settings are the same on the devices to be assigned to the HA group:
· Device model.
· Software version.
· Interface numbers.
· Interface for setting up the control channel.
· Interface for setting up the data channel.
· Security zone configuration on the interfaces with the same interface number.
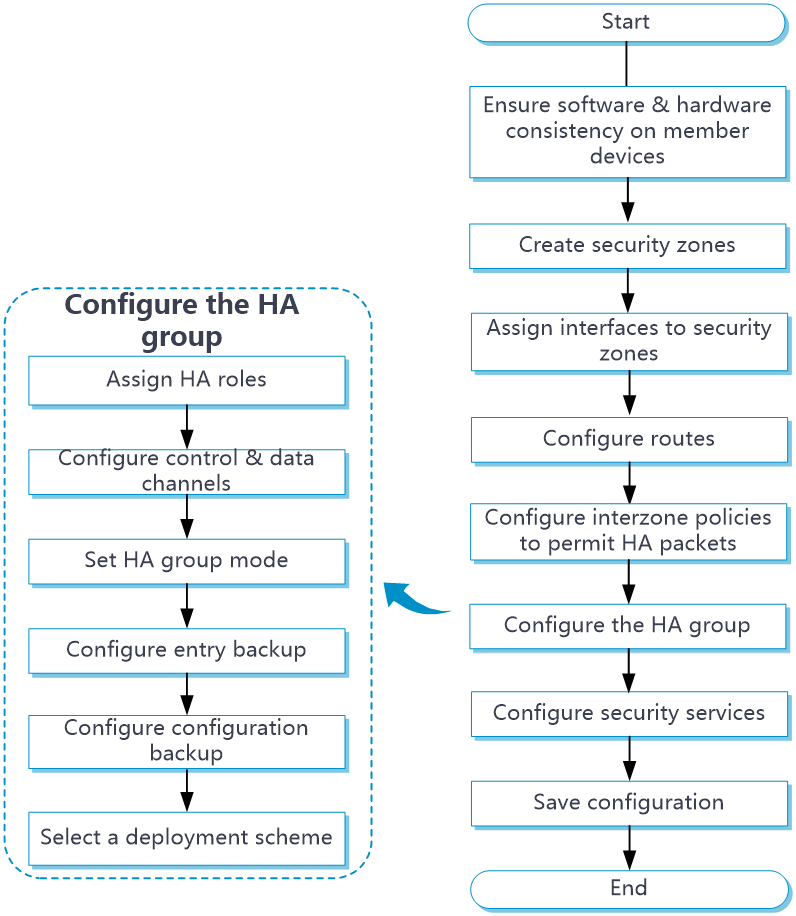
HA group configuration flow
Figure 6 HA group configuration flow chart
Configure the HA group
1. Click the System tab.
2. In the navigation pane, select High Availability > HA Group.
The HA Group page opens.
3. Click Configure.
The Configure HA Group page opens.
4. Configure the HA group. For more information about the related parameters, see Table 1.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
HA group |
Set the status of the HA group feature. |
|
Operating mode |
Set the operating mode of the HA group. · Active/standby—The primary device processes services, and the secondary device stands by. · Dual-active—Both the primary and secondary devices process services. |
|
Device role |
Assign HA roles to the member devices in the HA group. |
|
Local IP |
Enter a local IP address to set up the control channel. The server end listens for TCP connection requests at this IP address. You can enter an IPv4 or IPv6 address, but not both. |
|
Peer IP |
Enter the peer IP address used for setting up the control channel. You can enter an IPv4 or IPv6 address, but not both. |
|
Peer port |
Enter the port number for the control channel. The primary and secondary devices must have the same port number. |
|
Data channel |
Select an interface to set up the data channel which transmits backup packets and the packets that require transparent transmission. |
|
Keepalive interval |
Set the interval for the device to periodically send keepalive packets to the peer device. |
|
Max keepalive retries |
Set the maximum number of keepalive retries. If this limit is reached before the device receives any responses from the peer device, the device disconnects the HA channels to the peer device. |
|
Fallback |
Enable this feature for traffic to be switched back to the original primary device upon its recovery. |
|
Traffic reversion delay |
Set the delay that the primary and secondary devices must wait before a switchback. This delay allows the devices to finish service entry backup to prevent traffic loss. |
|
Back up sessions |
Set the status of session backup. If you enable this feature, the primary device backs up service module entries to the secondary device in real time. When the primary device fails, the secondary device can take over without service interruption. |
|
Back up HTTP Back up DNS |
Backs up the session entries created for received DNS and HTTP protocol packets. The HA group backs up the sessions created for other application protocols as long as service entry backup is enabled. Enable HTTP and DNS backup if asymmetric-path traffic traverses the HA group. HTTP and DNS backup ensures that a flow and its return traffic are processed correctly on the HA group members. If HA active/standby mode is used or only symmetric-path traffic traverses the HA group, disabling HTTP and DNS backup can improve performance of the HA group members at the expense of delayed data synchronization. When you disable HTTP and DNS backup, make sure you are fully aware of the impact on the network. A device removes a DNS or HTTP connection if packet exchange is inactive. When a switchover interrupts a connection, the DNS or HTTP client re-initiates the connection immediately, which has little impact on user services. |
|
Configuration consistency check |
Set the status of the configuration consistency check feature. |
|
Automatic configuration synchronization |
Set the status of the automatic configuration synchronization feature. After you enable this feature, the primary device backs up its configuration to the secondary device in bulk. When the configuration on the primary device changes, the primary device backs up the new configuration to the secondary device in real time. If the amount of configuration to be synchronized is large, bulk synchronization might take one to two hours. As a best practice to reduce the bulk synchronization duration, enable this feature when you configure the HA group. |
5. Configure Track settings. For more information about the related parameters, see Table 2.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Track entry association |
Select the track entries to be monitored by the HA group. If one of the monitored track entries becomes Negative, the HA group performs a primary/secondary member switchover and switches traffic to the new primary device to ensure service continuity. |
6. Click OK.
7. Click Check or Synchronize configuration to check configuration consistency or synchronize configuration on the HA Group page.
Table 3 Configuration consistency check and configuration synchronization parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Check |
Perform configuration consistency check manually. |
|
Synchronize configuration |
Manually synchronize the configuration of the primary device to the secondary device. |
8. Click Switch states on the HA Group page to switch the HA roles of the devices in the HA group.
Table 4 HA role switchover parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Switch states |
Manually switch the HA roles of the devices in the HA group. You can perform this task when the hardware of the primary device requires replacement. You can perform this task only on the primary member device when the HA group is operating in active/standby mode. Transient VRRP virtual IP conflicts might occur after you perform this task if VRRP is used with the HA group. The conflicts do not affect services. |
Configure VRRP collaboration
Associate the HA group with VRRP on the VRRP page. For more information about the configuration procedure, see VRRP help.
Configure the HA group to collaborate with a routing protocol
1. Click the System tab.
2. In the navigation pane, select High Availability > HA Group.
The HA Group page opens.
3. Click Configure.
The Configure HA Group page opens.
4. Configure routing collaboration parameters. For more information about the related parameters, see Table 5.
Table 5 Routing collaboration parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
OSPF |
Adjust the link costs advertised by OSPF. |
|
IS-IS |
Adjust the link costs advertised by IS-IS. |
|
BGP |
Adjust the link costs advertised by BGP. |
|
OSPFv3 |
Adjust the link costs advertised by OSPFv3. |
|
Set absolute cost |
Enter an absolute link cost. The HA group will use this value to replace the link costs to be advertised. |
|
Set increment cost |
Enter an increment value. The HA group will add this value to the link costs to be advertised. |
5. Click OK.
Configure transparent in-path deployment
1. Click the System tab.
2. In the navigation pane, select High Availability > HA Group.
The HA Group page opens.
3. Click Configure.
The Configure HA Group page opens.
4. Configure monitoring parameters. For more information about the related parameters, see Table 6.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Interface |
Select the interfaces to be monitored by the HA group. You cannot configure the HA group to monitor aggregation member ports. The HA group monitors the status of the monitored interfaces to ensure interface status consistency. A monitored interface can forward traffic only when all monitored interfaces are up. |
|
VLAN |
Select the VLANs to be monitored by the HA group. The HA group monitors the member ports of a monitored VLAN to ensure member port status consistency. A port in a monitored VLAN can forward traffic only when all ports in the VLAN are up. You cannot configure the HA group to monitor VLAN 1. All access ports belong to VLAN 1 by default. If you configure the HA group to monitor VLAN 1, traffic forwarding will be affected on ports in use when an unused port is placed in down state in VLAN 1. |
5. Click OK.