- Table of Contents
-
- 04-Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-ARP configuration
- 02-IP addressing configuration
- 03-DHCP configuration
- 04-DNS configuration
- 05-mDNS relay configuration
- 06-IP forwarding basics configuration
- 07-Fast forwarding configuration
- 08-IRDP configuration
- 09-IP performance optimization configuration
- 10-Adjacency table configuration
- 11-UDP helper configuration
- 12-IPv6 basics configuration
- 13-DHCPv6 configuration
- 14-IPv6 fast forwarding configuration
- 15-GRE configuration
- 16-HTTP redirect configuration
- 17-Tunneling configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 05-mDNS relay configuration | 156.00 KB |
Contents
Relaying mDNS service advertisements
Specifying the mDNS gateway address
Restrictions and guidelines for enabling mDNS relay
Enabling mDNS relay for a VLAN
Specifying the source IP address for mDNS packets
About specifying source IP address for mDNS packets
Restrictions and guidelines for specifying the source IP address for mDNS packets
Specifying the source IP address for mDNS packets in a VLAN
Specifying the source IP address for mDNS packets in a VSI
Enabling mDNS relay periodic probing
About mDNS relay periodic probing
Enabling mDNS relay periodic probing in a VLAN
Enabling mDNS relay periodic probing in a VSI
Display and maintenance commands for mDNS relay
mDNS relay configuration examples
Example: Configuring mDNS relay
Configuring mDNS relay
About mDNS relay
The multicast Domain Name Service (mDNS) protocol is a zero configuration networking protocol for mDNS service discovery. In a LAN network, endpoint devices can automatically discover available services advertised by mDNS service providers without knowing these service providers.
The mDNS relay supports mDNS packet transmission across subnets and expands the use of the mDNS protocol to large-scale networks. Without the mDNS relay, mDNS packets can only be transmitted within a subnet.
mDNS network device types
An mDNS network contains the following device types:
· mDNS endpoint device—Obtains services from mDNS service providers. Examples are iPhones and iPads.
· mDNS service provider—Provides services for mDNS endpoint devices. Examples are printers and video servers.
· mDNS gateway—Records available services advertised by mDNS service providers and responds to queries from mDNS endpoint devices. The mDNS gateway is also knowns as Bonjour gateway. For more information about the mDNS gateway, see Bonjour gateway configuration in WLAN Configuration Guide.
· mDNS relay—Ensures successful mDNS communication when mDNS endpoint devices and mDNS service providers are in different subnets. The mDNS relay supports periodically probing mDNS service providers in the network.
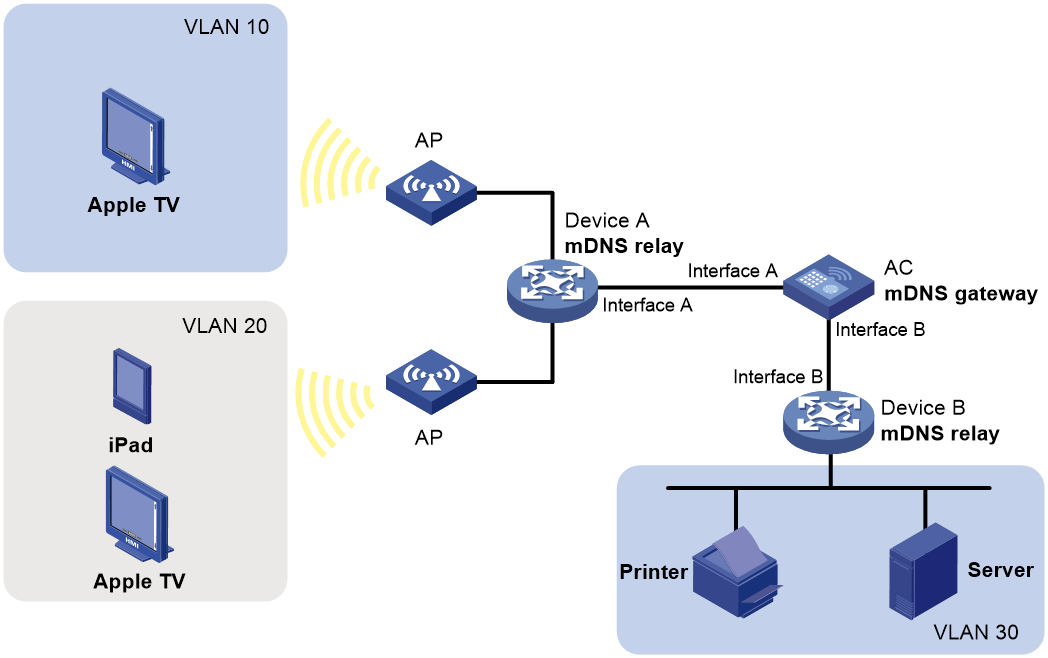
mDNS network model
As shown in Figure 1, mDNS endpoint devices (Apple TVs and iPad) and mDNS service providers (printer and server) are in different VLANs. APs and the AC require inter-subnet Layer 3 communication. The AC acts as the mDNS gateway and cannot receive multicast mDNS packets sent from the endpoint devices and service providers.
To resolve this problem, enable mDNS relay on Device A and Device B and specify the mDNS gateway address on them. After receiving an mDNS packet from an endpoint device, Device A changes the packet destination IP address to the mDNS gateway address and unicasts it to the gateway. After receiving an mDNS packet from an mDNS service provider, Device B changes the packet destination IP address to the mDNS gateway address and unicasts it to the gateway.
Figure 1 mDNS network model
mDNS relay functionalities
The mDNS relay provides the following functionalities:
· Relaying mDNS service advertisements—After receiving advertisements from an mDNS service provider, the relay changes the packet destination IP address to the mDNS gateway address and unicasts them to the gateway.
· Relaying mDNS queries—After receiving mDNS queries from endpoint devices, the relay changes the query destination IP address to the mDNS gateway address and unicasts them to the gateway.
· Periodic probing—The mDNS relay supports periodically sending mDNS queries to probe mDNS service providers in a subnet and forwarding the responses to the mDNS gateway for service update.
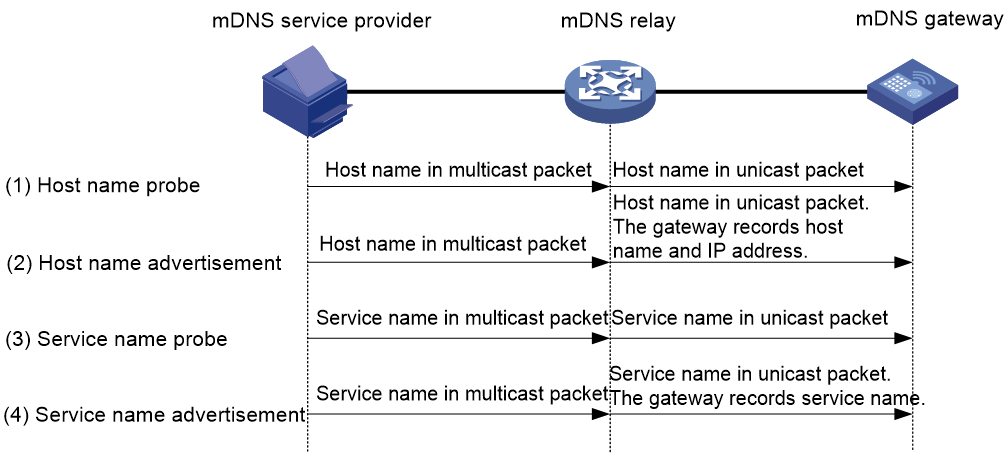
Relaying mDNS service advertisements
As shown in Figure 2, an mDNS service provider probes and advertises the host name and service name in the following workflow:
1. Host name probe.
a. The mDNS service provider automatically generates a host name after it is attached to the network. To detect the uniqueness of the host name, the service provider sends an mDNS query with multicast destination address 224.0.0.251 and starts the probe timer.
b. After receiving the query, the mDNS relay replaces the destination IP address with the mDNS gateway address and unicasts it to the mDNS gateway.
c. The mDNS gateway examines whether the host name conflicts with host names of existing mDNS service entries. If a conflict exists, the mDNS gateway sends the mDNS relay an mDNS response to announce the conflict. The mDNS relay changes the destination IP address of the response to multicast address 224.0.0.251 and forwards it to the mDNS service provider.
d. After receiving the conflict announcement, the mDNS service provider generates another host name and starts probing again.
2. Host name advertisement.
a. The mDNS service provider advertises its host name if it does not receive any host name conflict announcement within the probe period. The destination of the advertisement packet is 224.0.0.251.
b. After receiving the packet, the mDNS relay changes the packet destination IP address to the mDNS gateway address and unicasts it to the mDNS gateway.
c. The mDNS gateway records the host name and IP address in the received packet.
3. Service name probe.
a. The mDNS service provider sends an mDNS query with destination address 224.0.0.251 to detect the uniqueness of the service name and starts the probe timer.
b. After receiving the query, the mDNS relay replaces the destination IP address with the mDNS gateway address and unicasts it to the mDNS gateway.
c. The mDNS gateway examines whether the service name conflicts with service names of existing mDNS service entries. If a conflict exists, the mDNS gateway sends the mDNS relay an mDNS response to announce the conflict. The mDNS relay changes the destination IP address of the response to multicast address 224.0.0.251 and forwards it to the mDNS service provider.
d. After receiving the conflict announcement, the mDNS service provider generates another service name and starts probing again.
4. Service name advertisement.
a. The mDNS service provider advertises its service name if it does not receive any service name conflict announcement within the probe period. The destination of the advertisement packet is 224.0.0.251.
b. After receiving the packet, the mDNS relay changes the packet destination IP address to the mDNS gateway address and unicasts it to the mDNS gateway.
c. The mDNS gateway records the service name information in the received packet.
Figure 2 Relaying mDNS service advertisements
Relaying mDNS queries
As shown in Figure 3, an mDNS query originated from the mDNS endpoint device is relayed as follows:
1. Before accessing a service, the mDNS endpoint device first sends an mDNS query with multicast address 224.0.0.251 to detect whether this service is available.
2. Upon receiving the query, the mDNS relay changes the query destination IP address to the mDNS gateway address and unicasts the query to the gateway.
3. The mDNS gateway looks for a matching service after receiving the query. If the matching service exists, the mDNS gateway encapsulates the host name and IP address of the service provider into the response and unicasts it to the mDNS relay.
4. The mDNS relay changes the response destination IP address to 224.0.0.251 and multicasts the response.
5. After receiving the response, the mDSN endpoint device can access the service provider based on the IP address in the response. Other mDNS endpoints that receive the response will also record information about the service provider for future use.
Figure 3 Relaying mDNS queries
Periodic probing
When an mDNS service provider connects to the network, it unsolicitly sends an advertisement to the mDNS gateway. The mDNS gateway creates a service entry based on the advertisement information. When a new mDNS gateway joins the network where the mDNS service providers already exist, the mDNS service providers do not send advertisements. Therefore, the new mDNS gateway does not know existing mDNS services in the network.
The mDNS gateway creates and maintains service entries for mDNS services. If the mDNS gateway receives an update message for a service before the service entry ages out, the mDNS gateway resets the service entry timer. If the mDNS gateway does not receives any update message for a service before the service entry ages out, the mDNS gateway deletes the entry. In a large-sized network where mDNS service providers exists in many VLANs or VSIs, the mDNS gateway cannot receive update messages timely and might delete service entries mistakenly.
To resolve these issues, enable periodic probing on the mDNS relay and set a probe interval. The mDNS relay sends mDNS queries at intervals to VLANs and VSIs where mDNS relay is enabled. Each mDNS service provider that receives the query sends back an mDNS response. The mDNS relay then unicasts the response to the mDNS gateway, so that the mDNS gateway can quickly learn the latest services provided by all mDNS service providers.
Protocols and standards
RFC 6762, Multicast DNS
mDNS relay tasks at a glance
To configure the mDNS relay, perform the following tasks:
1. Specifying the mDNS gateway address
3. (Optional.) Specifying the source IP address for mDNS packets
4. (Optional.) Enabling mDNS relay periodic probing
Specifying the mDNS gateway address
About this task
After receiving an mDNS query from an mDNS endpoint device, the mDNS relay replaces the multicast destination address with the specified mDNS gateway address and unicasts the query to the mDNS gateway. When receiving the response from the gateway, the mDNS relay multicasts it in the VLAN or VSI where the requesting mDNS endpoint resides. The requesting endpoint device can then receive the response and other mDNS endpoint devices can learn and update the service information.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify the IP address of the mDNS gateway.
mdns relay gateway ip ip-address [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
By default, no mDNS gateway address is specified on the mDNS relay.
Enabling mDNS relay
Restrictions and guidelines for enabling mDNS relay
The mDNS relay feature takes effect only after you specify the mDNS gateway address on the mDNS relay.
Enabling mDNS relay for a VLAN
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter VLAN view.
vlan vlan-id
3. Enable mDNS relay.
mdns relay enable
By default, mDNS relay is disabled.
Enabling mDNS relay for a VSI
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter VSI view.
vsi vsi-name
3. Enable mDNS relay.
mdns relay enable
By default, mDNS relay is disabled.
Specifying the source IP address for mDNS packets
About specifying source IP address for mDNS packets
For responses destined for endpoint devices and probe queries sent within a VLAN or VSI, the default source IP address is the IP address of the VLAN interface or VSI interface. If no IP address is configured for the VLAN interface or VSI interface, the mDNS relay cannot send out the queries.
If the mDNS relay is connected to a large number of VLANs or VSIs, configuring an IP address to each VLAN interface or VSI interface wastes IP address resources. You can use this command to specify a specific IP address for the mDNS relay to use.
Restrictions and guidelines for specifying the source IP address for mDNS packets
Make sure the specified source address is on the relay and has a reachable route to the mDNS gateway. If these requirements are not met, the mDNS relay cannot receive responses for the queries or forwarded packets.
As a best practice, specify the interface connecting to the mDNS gateway in the mdns relay source ip command.
Specifying the source IP address for mDNS packets in a VLAN
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter VLAN view.
vlan vlan-id
3. Specify source IP address for mDNS packets.
mdns relay source ip { ip-address | interface interface-type interface-number }
By default, the mDNS relay encapsulates source IP addresses for packets as follows:
¡ For responses destined for endpoint devices and VLAN-specific probe queries, the default source IP address is the IP address of the VLAN interface.
¡ For multicast packets destined for the gateway, the default source IP address is the IP address of the packet output interface on the mDNS relay.
Specifying the source IP address for mDNS packets in a VSI
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter VSI view.
vsi vsi-name
3. Specify source IP address for mDNS packets.
mdns relay source ip { ip-address | interface interface-type interface-number }
By default, the mDNS relay encapsulates source IP addresses for packets as follows:
¡ For responses destined for endpoint devices and VSI-specific probe queries, the default source IP address is the IP address of the VSI interface.
¡ For multicast packets destined for the gateway, the default source IP address is the IP address of the packet output interface on the mDNS relay.
Enabling mDNS relay periodic probing
About mDNS relay periodic probing
This feature enables the mDNS relay to send mDNS probe queries within an mDNS relay-enabled VLAN or VSI at intervals. Each mDNS service provider sends a response to the mDNS relay after receiving the query. The mDNS relay then unicasts the responses to the mDNS gateway. The mDNS gateway can learn the latest service information of all mDNS service providers in the network in a timely manner.
Enabling mDNS relay periodic probing in a VLAN
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter VLAN view.
vlan vlan-id
3. Enable mDNS relay periodic probing.
mdns relay probe interval interval
By default, mDNS relay periodic probing is disabled.
Enabling mDNS relay periodic probing in a VSI
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter VSI view.
vsi vsi-name
3. Enable mDNS relay periodic probing.
mdns relay probe interval interval
By default, mDNS relay periodic probing is disabled.
Display and maintenance commands for mDNS relay
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display mDNS relay configuration. |
display mdns relay |
|
Display packet statistics on the mDNS relay. |
display mdns relay statistics |
|
Clear packet statistics on the mDNS relay. |
reset mdns relay statistics |
mDNS relay configuration examples
Example: Configuring mDNS relay
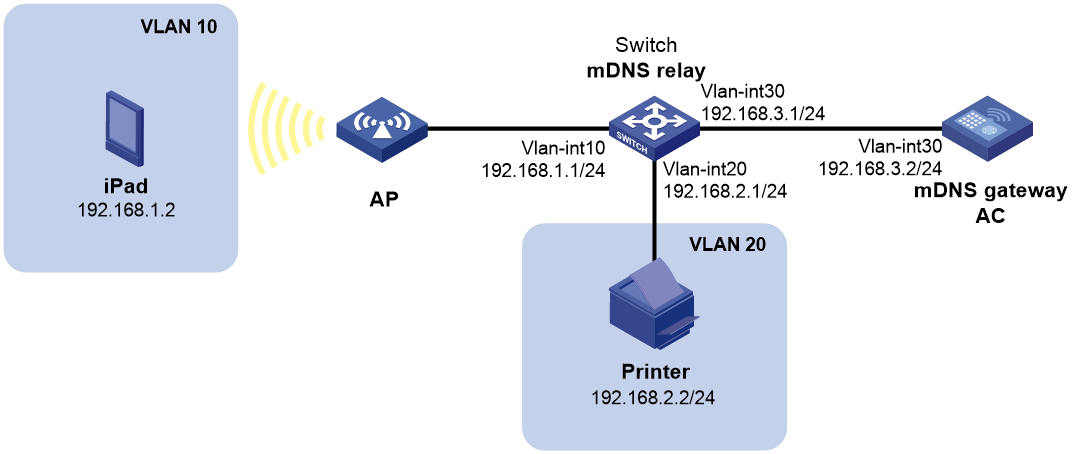
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 4, an enterprise network uses mDNS for communication. The working area is in VLAN 10 and uses subnet 192.168.1.0. The service area is in VLAN 20 and uses subnet 192.168.2.0. Subnet 192.168.3.0 runs between the mDNS relay and the mDNS gateway.
Configure mDNS relay on the switch to allow employers in the working area to access the printer in the service area.
Procedure
1. Configure the mDNS gateway and make sure route among the AP, the mDNS relay, and the mDNS gateway is reachable. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure the mDNS relay.
# Specify 192.168.3.2 as the mDNS gateway address.
<Switch> system-view
[Switch] mdns relay gateway ip 192.168.3.2
# Enable mDNS relay in VLAN 10.
[Switch] vlan 10
[Switch-vlan10] mdns relay enable
# Specify 192.168.3.1 as the source IP address for mDNS packets.
[Switch-vlan10] mdns relay source ip 192.168.3.1
[Switch-vlan10] quit
# Enable mDNS relay in VLAN 20.
[Switch] vlan 20
[Switch-vlan20] mdns relay enable
# Specify 192.168.3.1 as the source IP address for mDNS packets.
[Switch-vlan20] mdns relay source ip 192.168.3.1
[Switch-vlan20] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display mDNS relay configuration.
[Switch] display mdns relay
mDNS relay configuration:
mDNS gateway IP: 192.168.3.2
mDNS relay configuration in VLANs:
VLAN ID Source IP address Probe interval (sec)
10 192.168.3.1 --
20 192.168.3.1 --
# Verify that the user in VLAN 10 can use the iPad to access the printer in VLAN 20. (Details not shown.)
Troubleshooting mDNS relay
mDNS packet receiving failure
Symptom
The mDNS relay cannot receive mDNS packets.
Analysis
Possible reasons are:
· The mDNS relay is not enabled.
· The IP address of the mDNS gateway is not specified on the mDNS relay.
Solution
To resolve this issue:
1. Execute the display mdns relay command to view current configuration.
2. Perform one of the following tasks:
¡ If mDNS relay is not enabled, execute the mdns relay enable command to enable this feature.
¡ If the IP address of the mDNS gateway is not specified on the mDNS relay, execute the mdns relay gateway ip command to specify the mDNS gateway address.