- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-text | 1.71 MB |
Contents
Configuring BIOS to boot from CD-ROM and enabling CPU virtualization features
Configuring network parameters
Setting the date, time, and time zone
Selecting the components to install
Changing network parameters after installation of CAS
Setting the system time for each server
Configuring link aggregation for the management network
Configuring dynamic link aggregation
Configuring static link aggregation
Appendix Building a bootable USB drive
Using Linux DD mode to build a USB bootable flash drive
Using Rufus to build a USB bootable flash drive
About CAS
H3C Cloud Automation System (CAS) is a resources management platform for constructing a cloud computing infrastructure. It provides industry-leading virtualization management solutions for the cloud computing infrastructure in the data center, and implements centralized management and control over cloud computing. It offers a unified user-friendly management interface for all hosts and virtual machines (VMs) in the data center, not only improving management efficiency and simplifying routine work, but also reducing IT maintenance complexity and management costs.
Features and functionalities
CAS is the software suite for constructing H3Cloud solutions. It delivers the following features and functionalities:
· Server infrastructure consolidation
· Centralized and unified management on computing, network, and storage resources
· High availability and dynamic resource scheduling features to ensure data center service continuity
· Rapid migration and backup of VMs
· Multi-tenant isolation
· User self-service portal
· Cloud business workflows
· Open API interfaces to ensure interoperability between clouds
Components
CAS contains the following components:
· Cloud Virtualization Kernel—CVK is the kernel that runs between the network infrastructure and the customer operating system. It helps eliminate the difference between the underlying heterogeneous hardware and the dependence of the operating system on the hardware devices and drivers. CVK enhances the performance of CAS in hardware compatibility, high reliability, availability, scalability, and performance optimization.
· Cloud Virtualization Manager—CVM provides virtualization management on computing, network, and storage resources in the data center as well as automated services for upper layer applications. CVM provides the following services:
¡ Virtual computing, networks, and storage
¡ High availability
¡ Dynamic resource scheduling (DRS)
¡ VM backup and disaster recovery
¡ VM template management
¡ Cluster file system
¡ Virtual switch (vSwitch) policies
Preparing for installation
Server compatibility with CAS
H3C CAS is a hardware-assisted virtualization system. To run H3C CAS, the server must support the Intel-VT or AMD-V technology. ARM servers must support ARM VHE. For server compatibility with H3C CAS, see Hardware and Software Compatibility with H3C CAS.
Server requirements
Management server
|
IMPORTANT: · To deploy CVM on a CAS VM, make sure the operating system of the VM is CAS/CVM OS (64-bit). · To deploy CVM on a VM of other hypervisors, make sure the operating system of the VM is CentOS 7 (64-bit) and the VM is enabled with port monitoring. |
A management server in the data center performs centralized management on hosts. You must install the CAS CVK and CVM components on the management server.
Table 1 describes the hardware requirements for a management server. If you are not to assign the management server to a host pool or create and run VMs on the management server, the management server can have much less hardware resources than a virtualization server and the CPUs on the sever are not required to support virtualization.
Table 1 Management server hardware requirements
|
Quantity of servers and VMs to manage |
CPUs |
Memory |
Storage |
Remarks |
|
Server: < 20 VM: < 200 |
≥ 4 |
≥ 8 GB |
300 GB |
Can be deployed on servers (recommended) or VMs. |
|
Server: 20 to 50 VM: 200 to 1000 |
≥ 4 |
≥ 16 GB |
600 GB |
Can be deployed on servers (recommended) or VMs. |
|
Server: 50 to 100 VM: 1000 to 3000 |
≥ 8 |
≥ 32 GB |
2 × SASs (300G) in RAID1 |
Must be deployed on servers. |
|
Server: 100 to 256 VM: 3000 to 5000 |
≥ 12 |
≥ 64 GB |
2 × SSDs (960G) in RAID1 |
Must be deployed on servers. |
|
Server: 256 to 512 VM: > 5000 |
≥ 16 |
≥ 128 GB |
2 × SSDs (960G) in RAID1 |
Must be deployed on servers. |
Virtualization server
A virtualization server is a physical host that has VMs running on it. You only need to install CAS component CVK on the virtualization server. Table 2 describes the recommended hardware requirements for a virtualization server.
Table 2 Virtualization server hardware requirements
|
Item |
Specification |
|||
|
CPU (above 2 GHz as a best practice) |
Two CPUs, four cores per CPU |
Four CPUs, two or four cores per CPU |
Eight CPUs, two, four, or more cores per CPU |
|
|
Memory |
≥ 16 GB |
≥ 32 GB |
≥ 64 GB |
|
|
GE/10-GE NIC |
Without using external storage |
≥ 4 |
≥ 4 |
≥ 4 |
|
Using FC storage |
≥ 4 |
≥ 4 |
≥ 4 |
|
|
Using IP storage |
≥ 6 |
≥ 6 |
≥ 6 |
|
|
Built-in drive (using an external drive array) |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
|
CD/DVD ROM |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
Power supply |
1+1 redundancy |
1+1 redundancy |
1+1 redundancy |
|
Required information
Before installing CAS, collect the following information:
· Server name
· Management network interface and its IP address
· Whether to install CVM
· Root password
· Disk partitioning method
Installing CAS
H3C CAS has two components CVK and CVM. On a management server, you must install all these two CAS components. On a virtualization server, you need to install only the CVK component.
Configuring BIOS to boot from CD-ROM and enabling CPU virtualization features
For information about BIOS settings, see the user manual that comes with the server.
To configure BIOS to boot from CD-ROM and enable CPU virtualization features:
1. Start the server and enter the BIOS setup utility.
2. Enable CPU virtualization features and configure CD-ROM as the first boot option.
3. Save the BIOS settings and quit the BIOS setup utility.
4. Restart the server.
Installing CAS
Installation task list
|
Tasks at a glance |
|
(Required.) Starting the installation |
|
(Optional.) Configuring network parameters To configure IPv6 addresses, this step is required. |
|
(Required.) Selecting the system disk |
|
(Required.) Partitioning the disk Choose one of the following methods: |
|
(Required.) Setting the date, time, and time zone |
|
(Required.) Selecting the components to install |
|
(Required.) Selecting the components to install |
|
(Required.) Finishing the installation |
|
(Optional.) Changing network parameters after installation of CAS |
Starting the installation
|
IMPORTANT: You can install CAS by using a CD-ROM, a bootable USB drive, or the virtual drive on the server. Be aware of the following restrictions: · To prevent access failure to the CVM server after CAS installation, do not use UltraISO to build a bootable USB drive. · You can use Linux or Rufus DD mode to build a USB bootable flash drive. Rufus has multiple versions. Some versions do not support DD mode. As a best practice, use Linux DD to build a USB bootable flash drive. For information about building a bootable USB drive, see " Building a bootable USB drive." · When you use a CD-ROM to install CAS, the installation might be unstable depending on the CD-ROM burning quality. |
To start the installation:
1. Place the CD-ROM into the optical disk drive, mount the image file onto the virtual drive, or insert the USB bootable drive into the USB port on the server.
For an ARM server, use the following procedure to mount an ISO image file onto the virtual drive:
a. Launch the BMC Web console.
b. Select Media > Virtual Media Wizard.
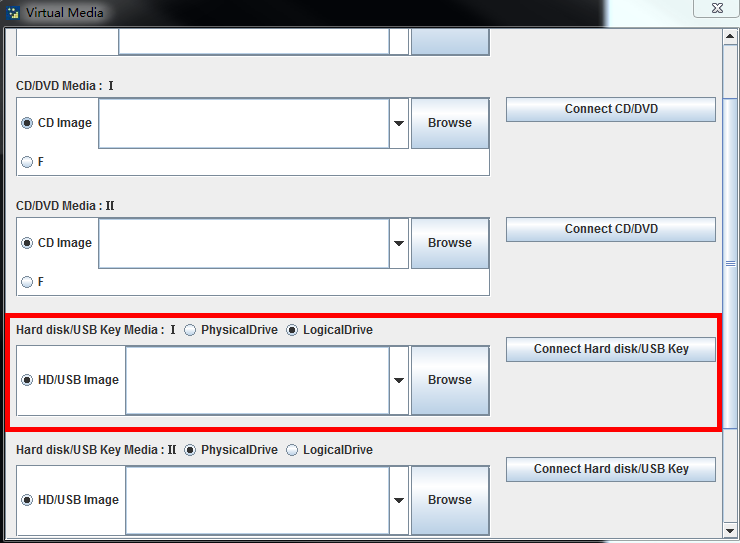
c. On the Virtual Media page, identify the Hard disk/USB Key Media : I area.
Figure 1 Identifying the Hard disk/USB Key Media : I area
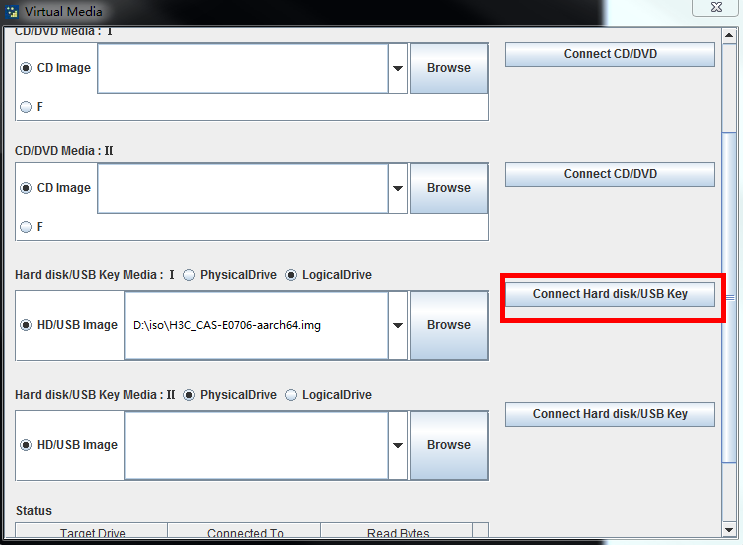
d. Click Browse and then select the ARM version of the CAS ISO image file.
e. Click Connect Hard disk/USB Key.
Figure 2 Connecting the hard disk or USB key
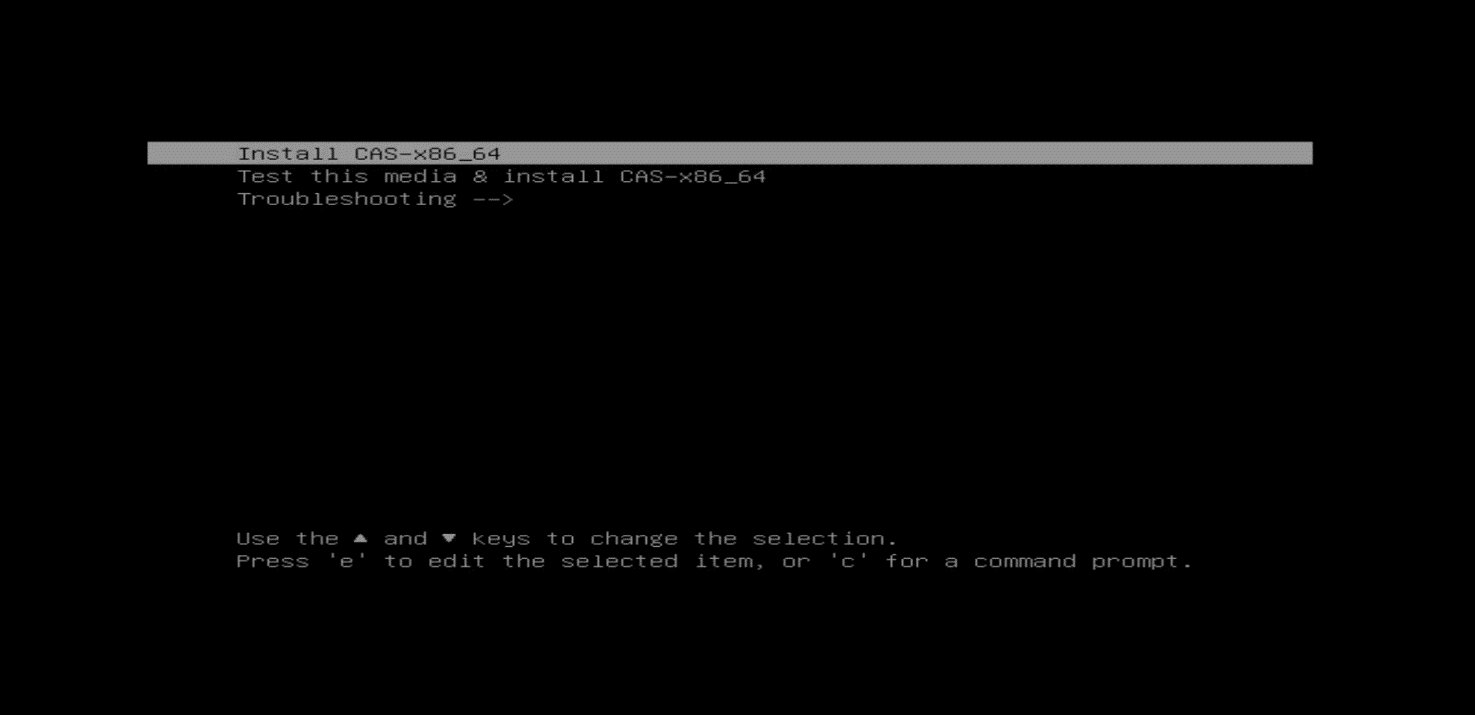
2. Start the server. Then, select to boot up from the CD-ROM or USB bootable drive. The CAS installation start page is displayed.
Figure 3 CAS installation start page
3. On the CAS installation start page, perform either of the following tasks:
a. For a server that is not Huawei 2488H V5 or 2288H V5 server, select install cas-X86_64 and then press Enter, or wait for the system to start installation automatically.
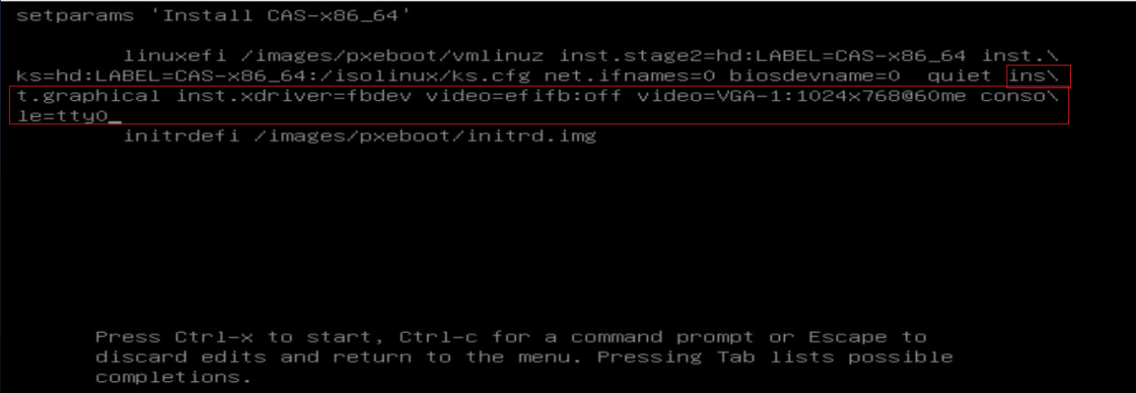
¡ For a Huawei 2488H V5 or 2288H V5 server, modify the installation parameters as follows and then press CTRL+X to start installation.
|
IMPORTANT: When installing CAS on a Huawei 2488H V5 or 2288H V5 server, a black screen might occur if you do not modify the installation parameters. If the same black screen error occurs on other server models, use the same procedure to fix it. |
# Press E to enter edit mode.
# At the end of the line starting with linuxefi or linux, add inst.graphical inst.xdriver=fbdev video=efifb:off video=VGA-1:1024x768-32@60me ro console=tty0.
Figure 4 Adding parameters
Configuring network parameters
You can choose to configure the network parameters manually or not configure the network parameters during the installation process. If you do not configure network parameters during the installation process, DHCP is used by default and you must change the network parameters to static settings after installation. For more information, see "Changing network parameters after installation of CAS."
|
IMPORTANT: To use Disaster Recovery Management (DRM) or heterogeneous migration on CAS, plan the IP address for the management network interface in advance and configure it manually. |
To configure network parameters manually:
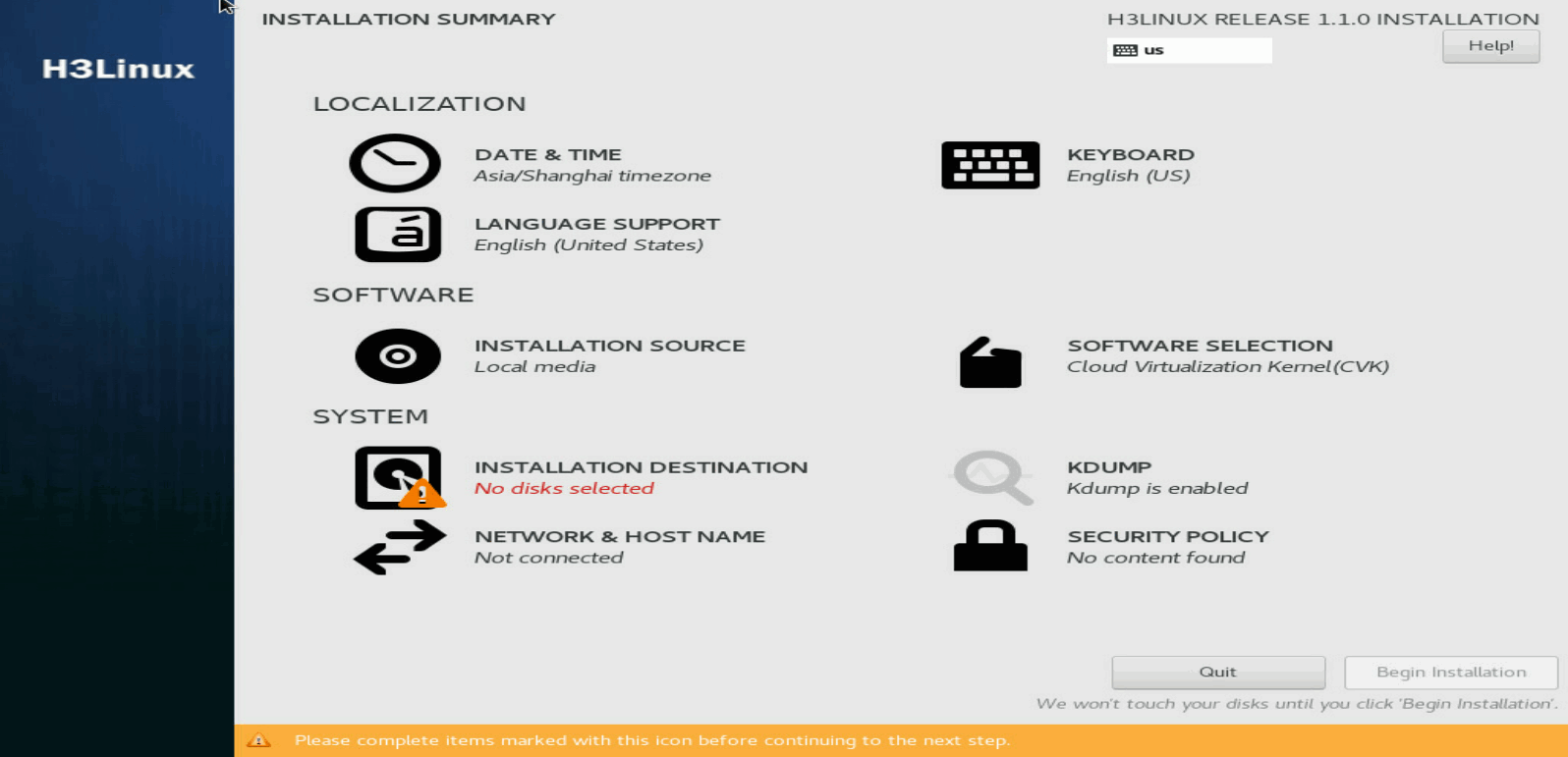
1. On the INSTALLATION SUMMARY page, click NETWORK & HOST NAME in the SYSTEM area.
Figure 5 INSTALLATION SUMMARY page
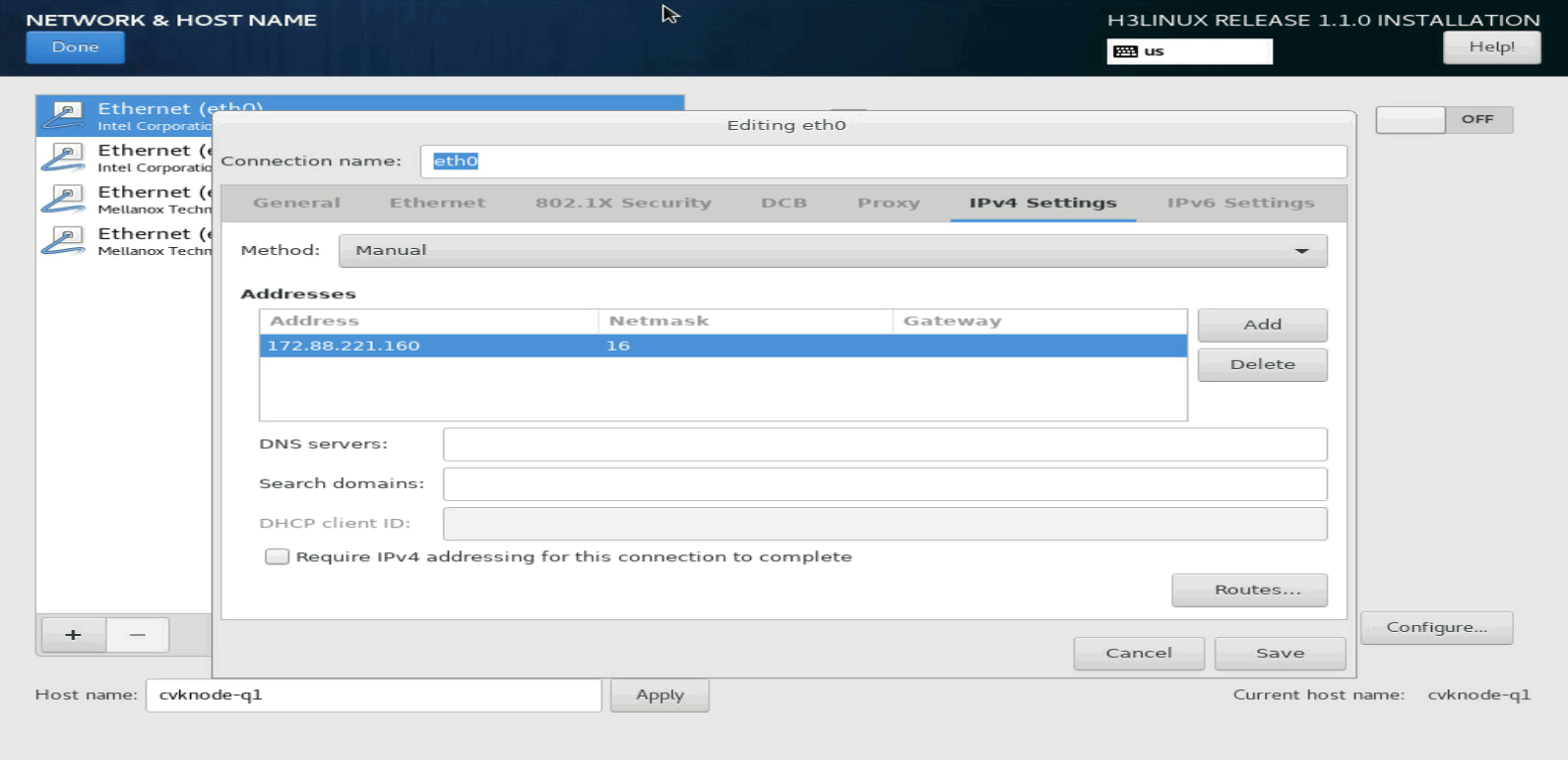
2. Select a NIC and click Configure in the bottom right corner. Then, select the manual method and configure the parameters, including the IP address, subnet mask, gateway IP address, DNS server IP address, and domain name.
|
IMPORTANT: To configure an IPv6 address, first disable the IPv4 address. |
Figure 6 Network settings
3. Set a host name for the server in the bottom left corner and then click Done.
Selecting the system disk
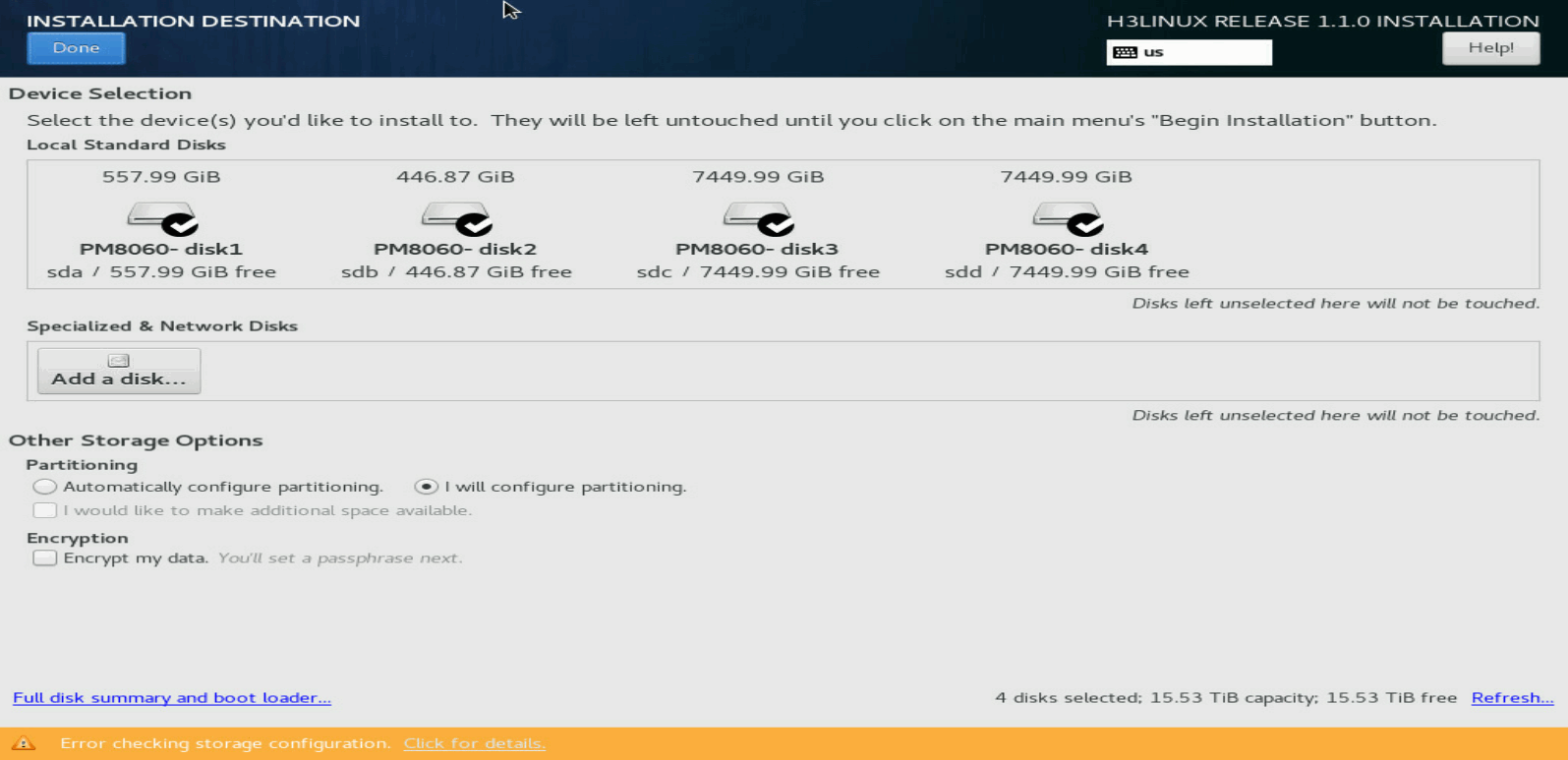
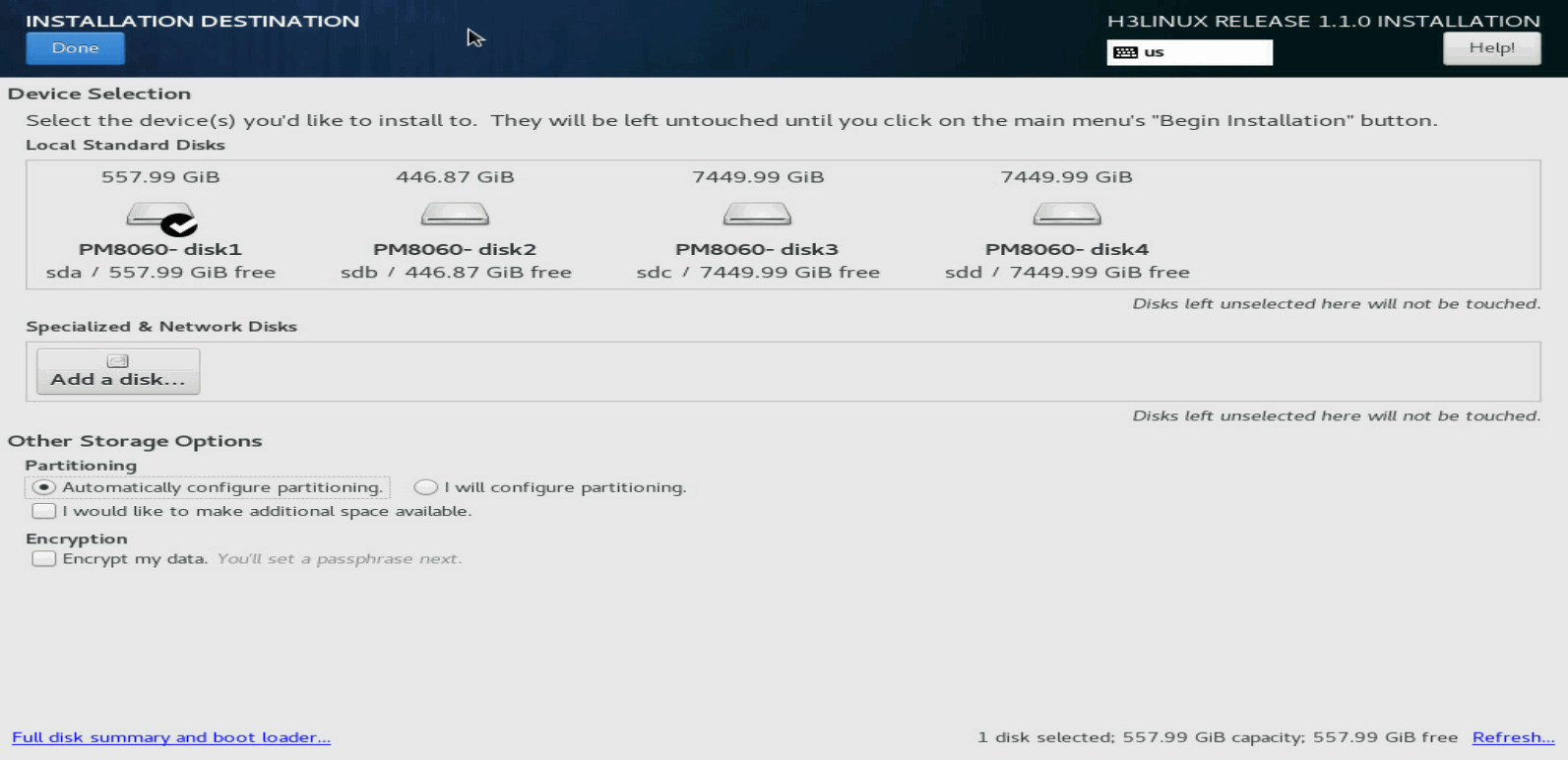
1. On the INSTALLATION SUMMARY page, click INSTALLATION DESTINATION in the SYSTEM area.
Figure 7 INSTALLATION DESTINATION page
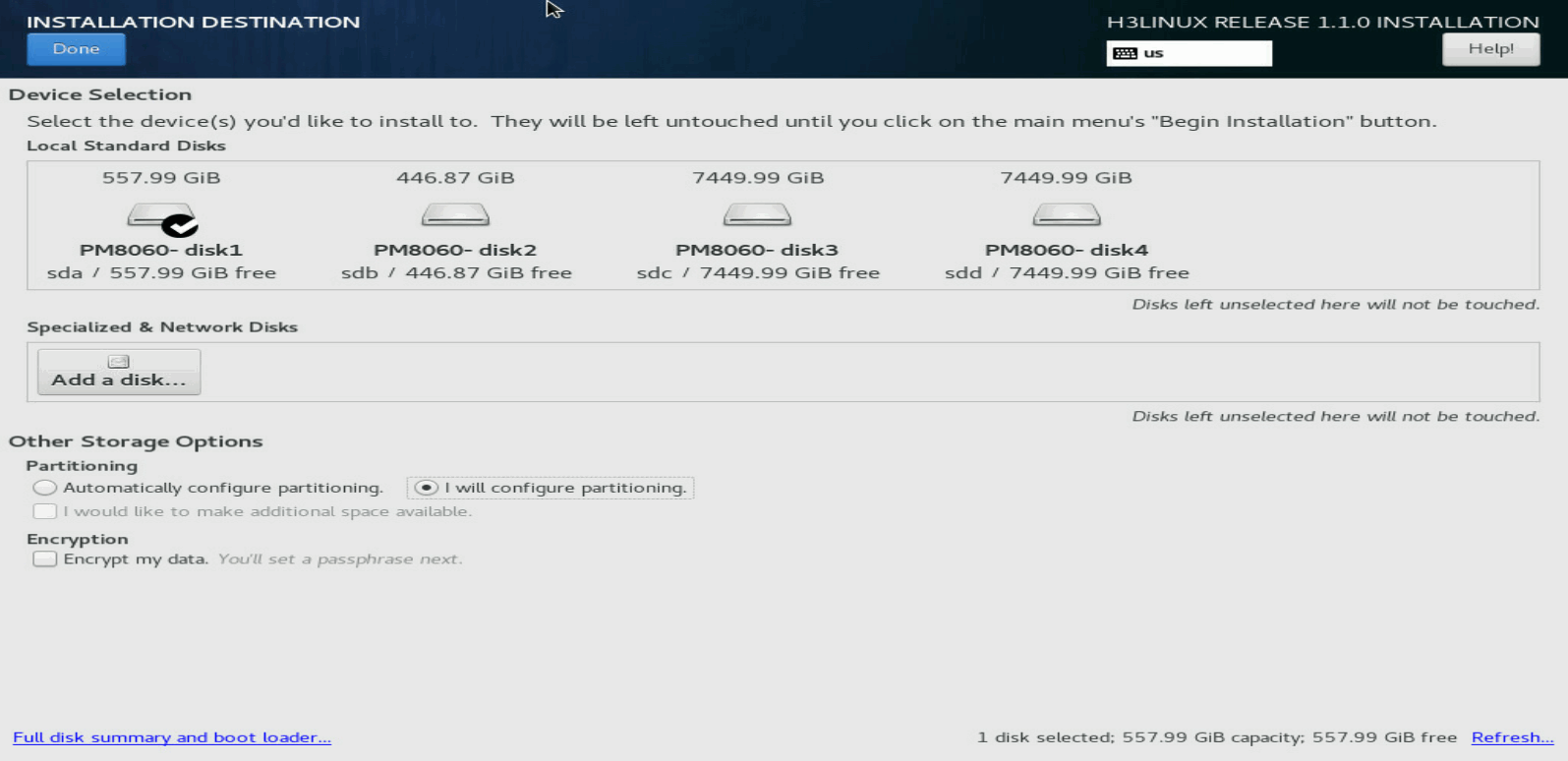
2. In the Local Standard Disks area, clear the disks on which you are not to install the system. Leave one disk selected to install the system.
Figure 8 Selecting the disk to install the system
Partitioning the disk
The disk to install CAS can be partitioned automatically or manually. As a best practice, partition the disk manually.
|
IMPORTANT: · To partition the disk automatically, make sure the disk space is larger than or equal to 120 GiB. · If a system has been installed on the disk, select manual partitioning and then delete the system before partitioning the disk. |
Automatic disk partitioning
1. On the INSTALLATION DESTINATION page, select Automatically configure partitioning in the Partitioning area.
Figure 9 Selecting automatic disk partitioning
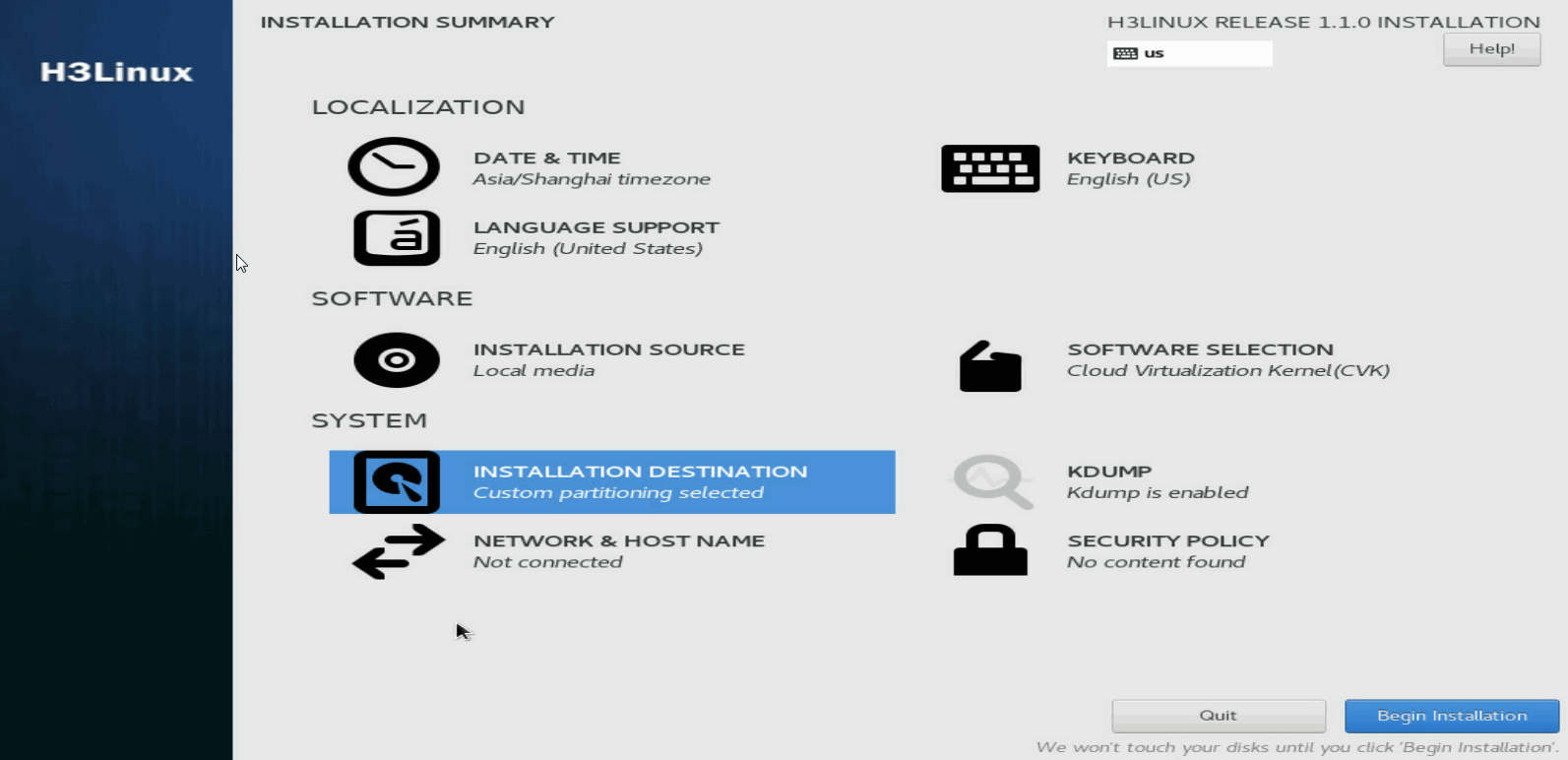
2. Click Done in the top left corner.
The system returns to the INSTALLATION SUMMARY page when the partitioning is complete.
Figure 10 Returning to the INSTALLATION SUMMARY page
Manual disk partitioning
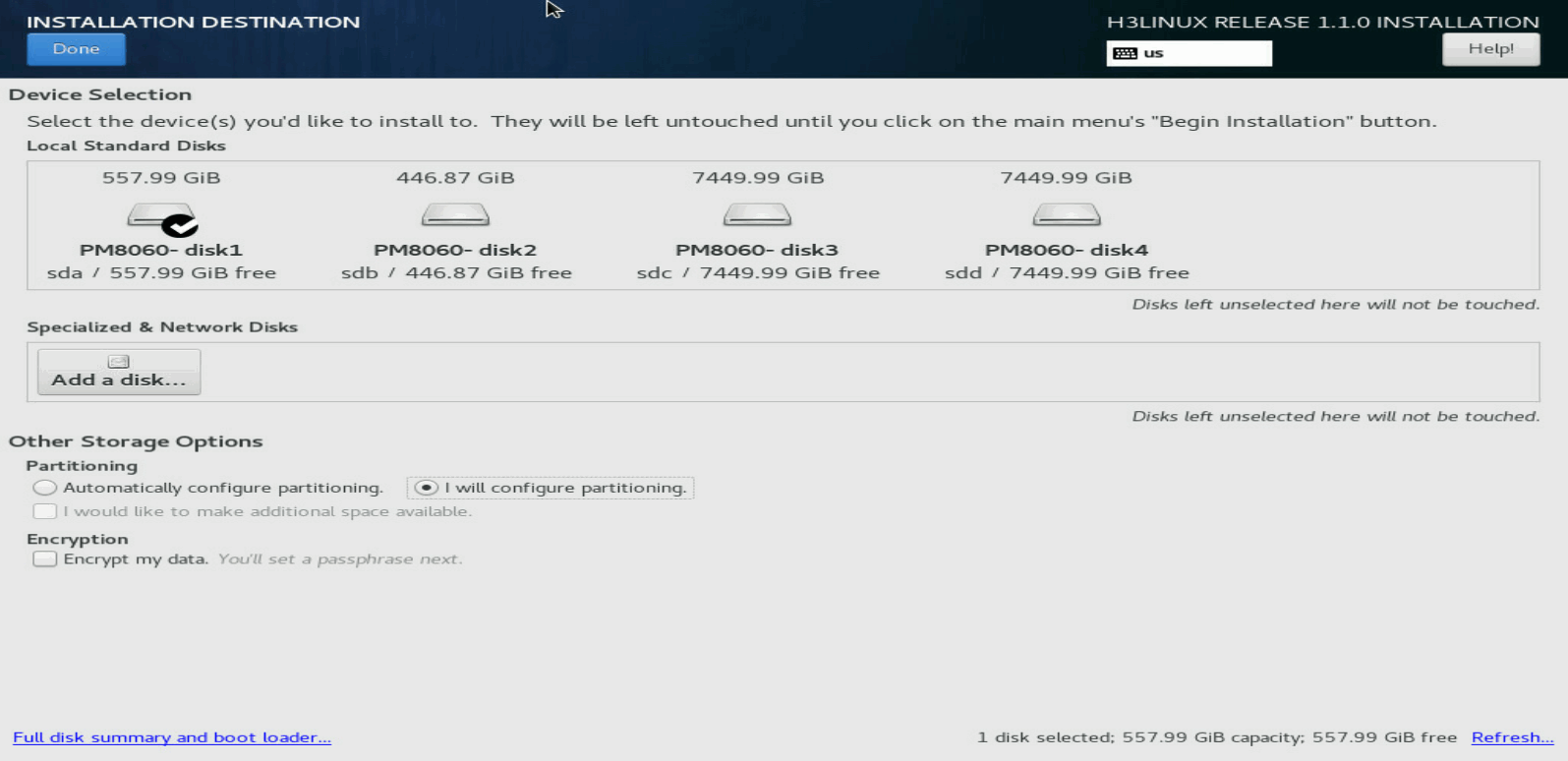
1. On the INSTALLATION DESTINATION page, select I will configure partitioning in the Partitioning area. Then click Done in the top left corner.
Figure 11 Selecting manual disk partitioning
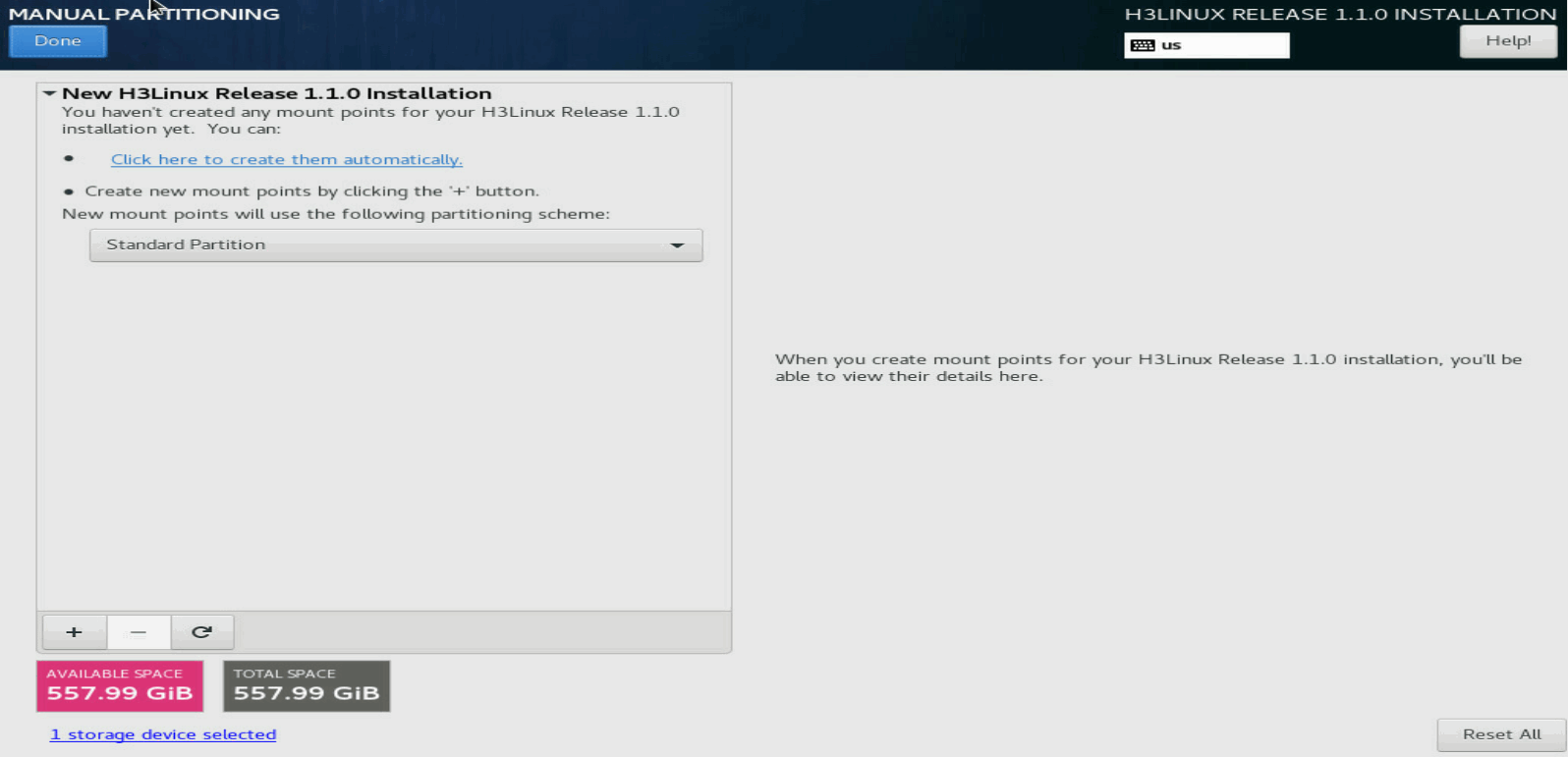
2. On the MANUAL PARTITIONING page, click the ![]() button.
button.
Figure 12 MANUAL PARTITIONING page
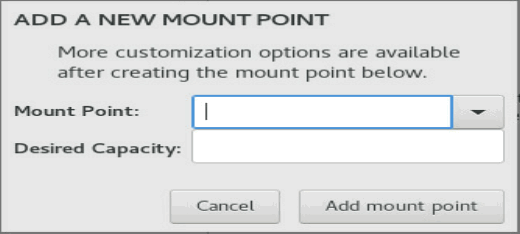
3. In the dialog box that opens, select a partition from the Mount Point list and set a capacity for it. Then click Add mount point.
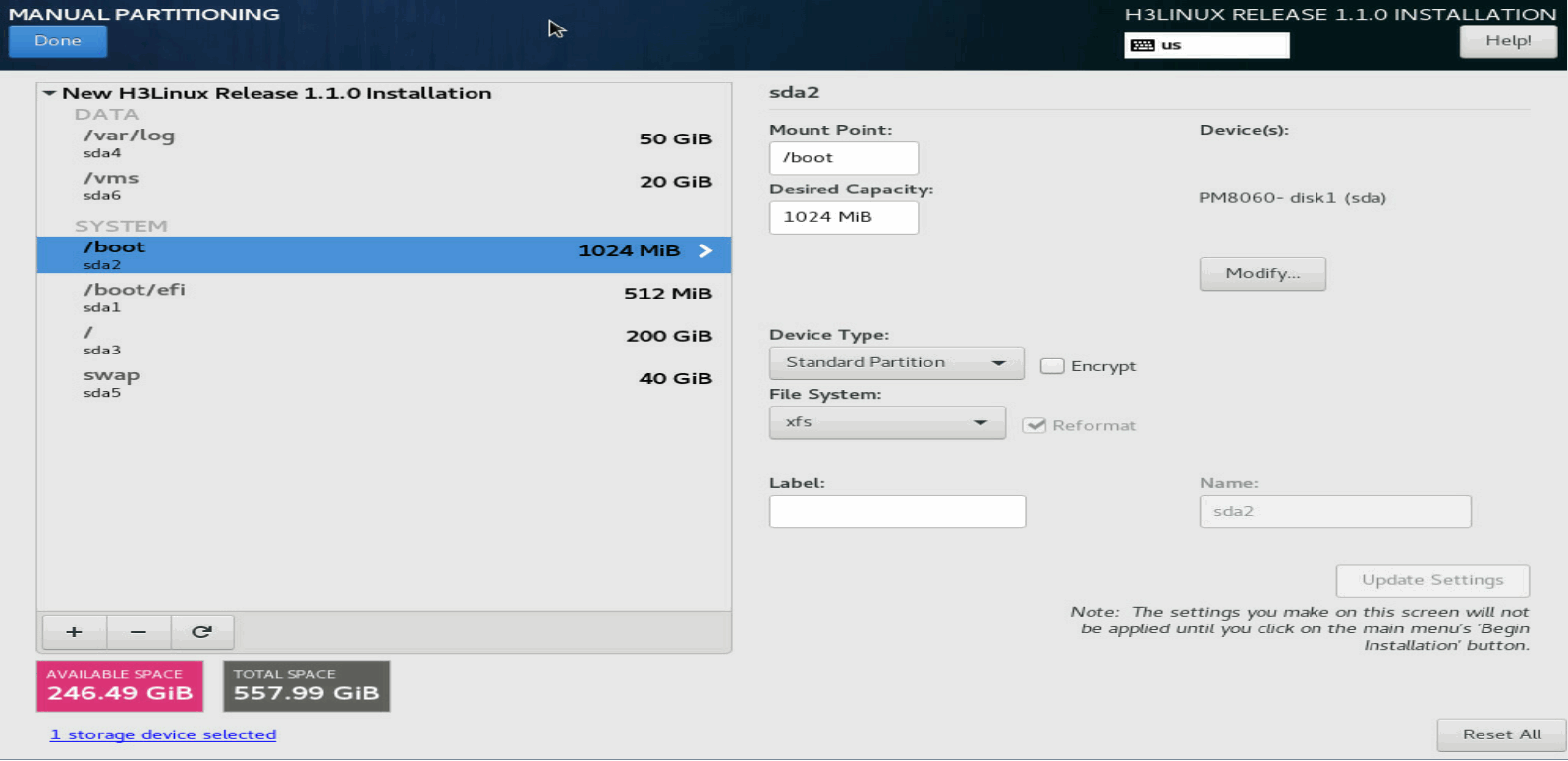
¡ If the server has booted in UEFI boot mode, add /, /boot/efi, /boot, /vms, swap, and /var/log partitions in turn. See Table 3 for the partition specifications.
¡ If the server has booted in Legacy boot mode, add /, /boot, /var/log, swap, and /vms partitions in turn. See Table 3 for the partition specifications.
Figure 13 Adding a new mount point
Figure 15 shows sample partitioning information when the partitioning is complete.
Figure 14 Partitioning information
Table 3 Partition descriptions and specifications
|
Partition |
Description |
File system |
Min. size (MiB) |
Recommended size (MiB) |
|
/boot/efi (bootstrap partition) |
Stores boot files of the system. |
EFI System Partition |
200 |
200 |
|
/boot (boot partition) |
Stores the files for booting the system kernel. |
ext4 (recommended) |
1024 |
1024 |
|
/ (root partition) |
Stores all directories of the system. Users can access all directories from this partition. |
ext4 (recommended) |
102400 |
204800 |
|
/var/log (log partition) |
Stores log files about system operations. |
ext4 (recommended) |
10240 |
40960 |
|
swap (swap partition) |
Stores temporary data when the system memory is insufficient. After a period of time, the system will transfer the temporary data into the memory for execution. This partition can be accessed only by the system. |
swap |
30GiB |
30GiB |
|
/vms (VM data partition) |
Stores all data files of VMs. |
ext4 |
· Standalone:1024 · Stateful failover: 30GiB |
No limited. As a best practice, allocate a largest possible space to the /vms partition while ensuring sufficient space for other partitions. |
|
IMPORTANT: The database partition for stateful failover is created in the /vms partition and the /vms partition itself requires a size of space. As a best practice, allocate a largest possible space to the /vms partition while ensuring sufficient space for other partitions. Use this formula to estimate the minimum size for the /vms partition: database partition size (number of hosts*10 MB + number of VMs*15 MB)*15/1024 MB + 10GB. If the estimated value is smaller than 30 GB, allocate a minimum of 30 GB to the partition. If the estimated value is larger than 30 GB, allocate a size equal to or larger than the estimated size to the partition. |
4. Click Done in the top left corner.
5. In the dialog box that opens, click Accept Changes to confirm the partitioning.
Figure 15 Confirming the partitioning
Setting the date, time, and time zone
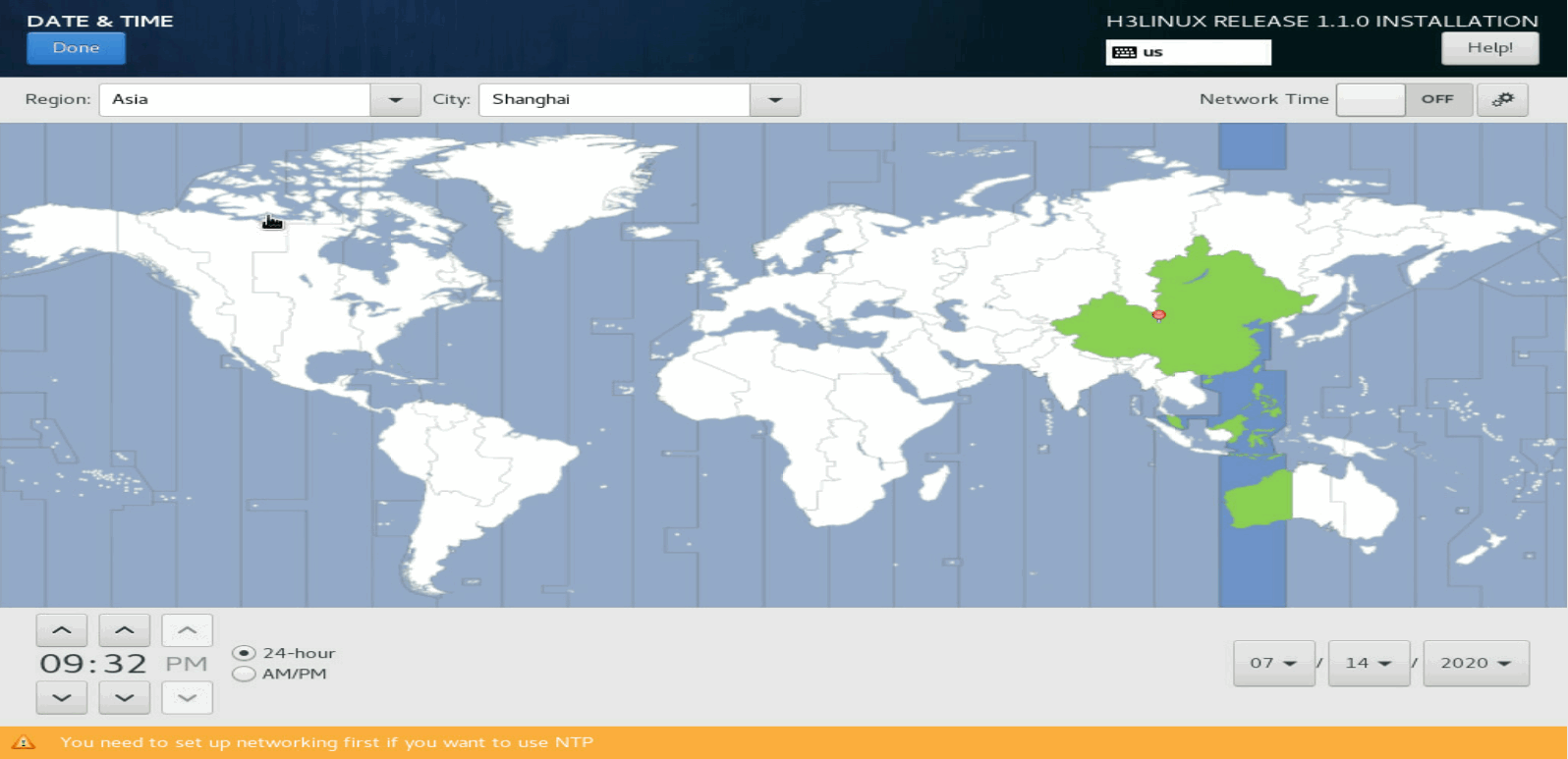
On the INSTALLATION SUMMARY page, click DATE & TIME. Then set a correct date, time, and time zone for the system.
Figure 16 Setting the date, time, and time zone
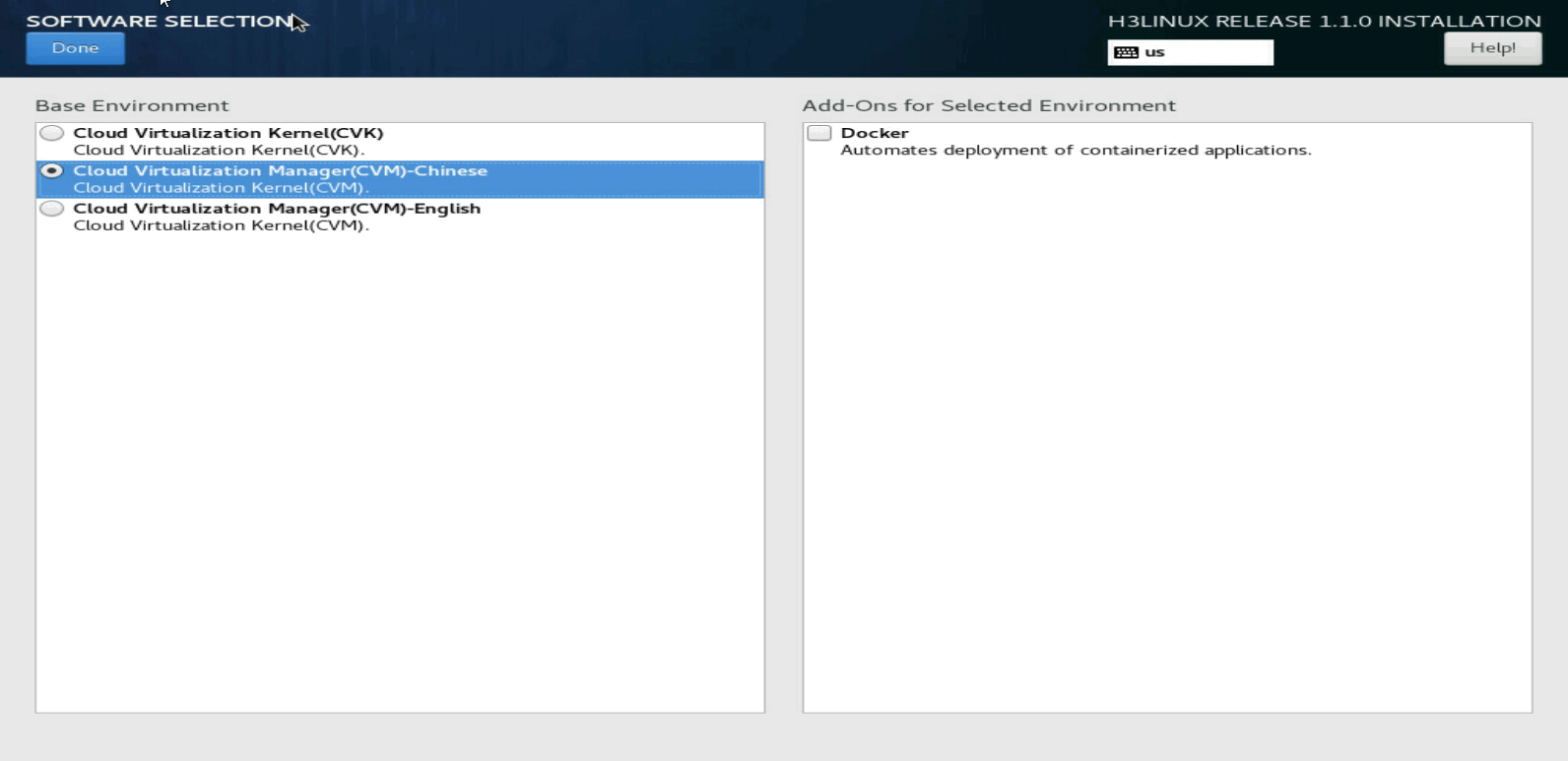
Selecting the components to install
On the SOFTWARE SELECTION page, select the components to install:
· For a management server, select CVM-English.
· For a virtualization server, select CVK.
Docker is a component in the H3Linux installation package. It does not affect installation of CAS. By default, Docker is not installed.
Figure 17 Selecting the components to install
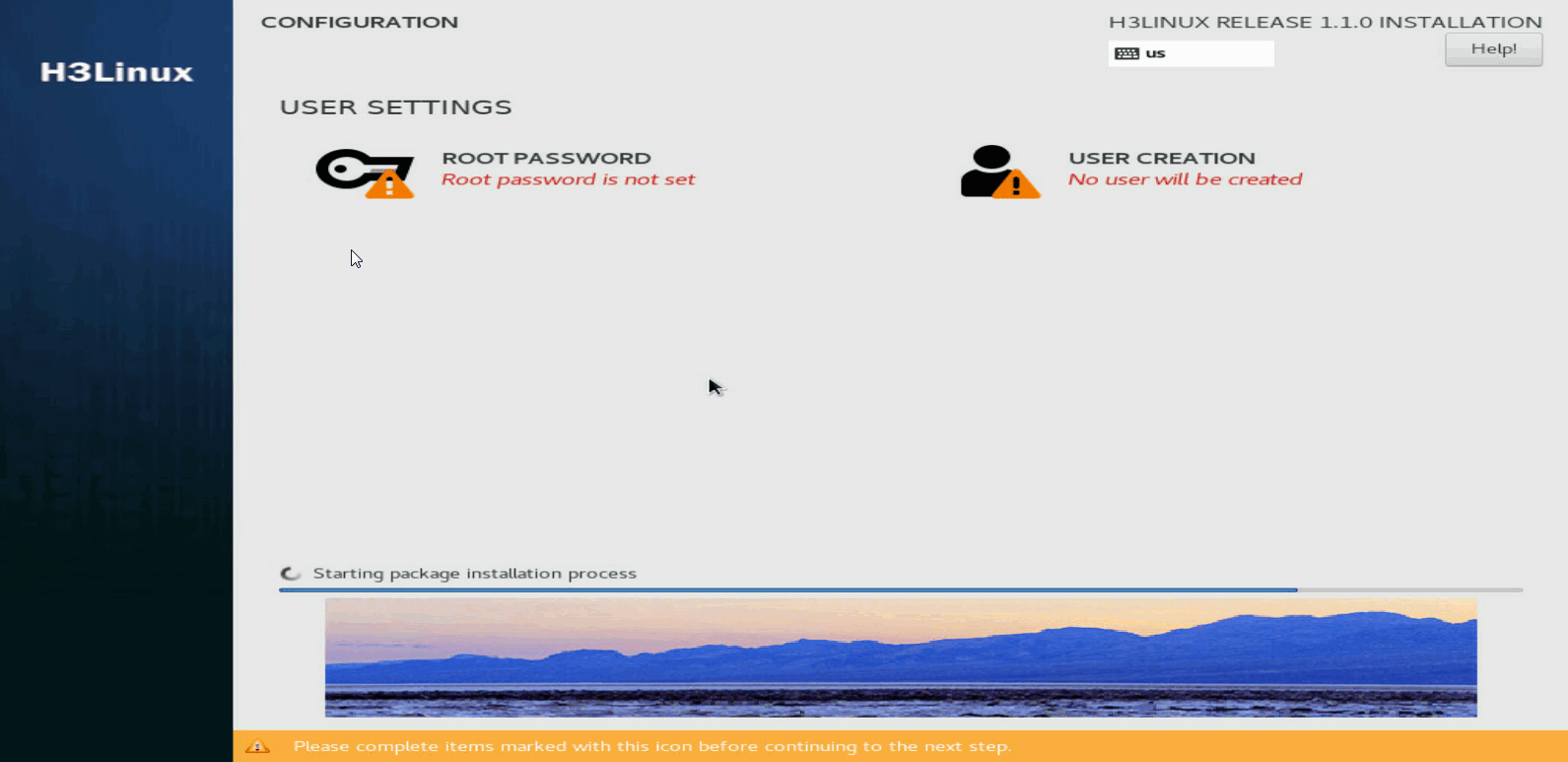
Finishing the installation
1. On the INSTALLATION SUMMARY page, click Begin installation.
2. Set a root password when prompted.
Figure 18 Setting a root password
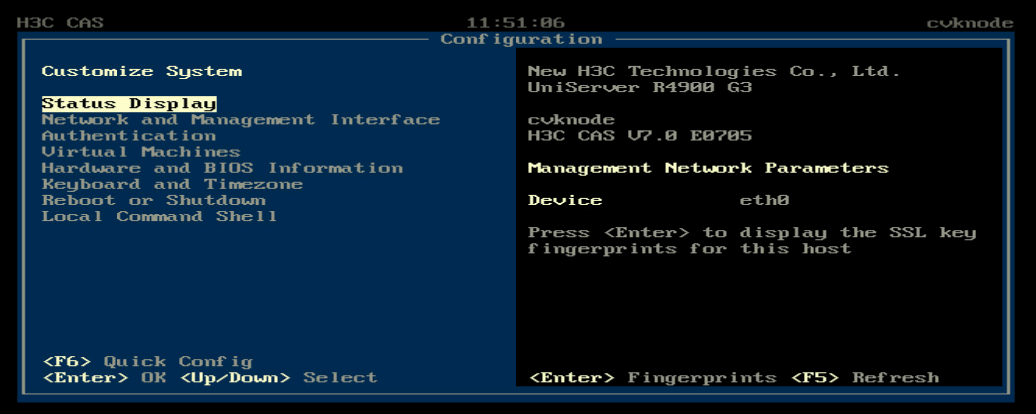
After the installation is complete, the host restarts automatically and opens the Configuration screen.
Before the reboot is completed, eject the CD-ROM, disconnect the virtual drive, or unplug the USB flash drive.
|
CAUTION: As a best practice, unplug the USB flash drive before the system is started. If the server is started with a USB flash drive installed, check the system disk name. If the system disk name is /sdb (the system disk name is /sda in normal conditions), unplug the USB flash drive and then restart the server. This prevents CVM from recording an incorrect system disk name in the stateful failover configuration file during the stateful failover setup process. |
Figure 19 Host configuration screen
|
|
NOTE: The network parameter settings, if not configured manually during the installation process, depend on whether a DHCP server is available: · If a DHCP server exists in the management network, the host obtains an IP address from the DHCP server automatically. · If no DHCP server exists in the management network, all management network parameters on the Configuration screen are empty. |
Changing network parameters after installation of CAS
To change network parameters configured during the installation process, access the server console for the change after installation.
|
IMPORTANT: You can choose to configure the network parameters manually or not configure the network parameters during the installation process. If you do not configure network parameters during the installation process, DHCP is used by default and you must change the network parameters to static settings after installation. |
To change network parameters after installation of CAS:
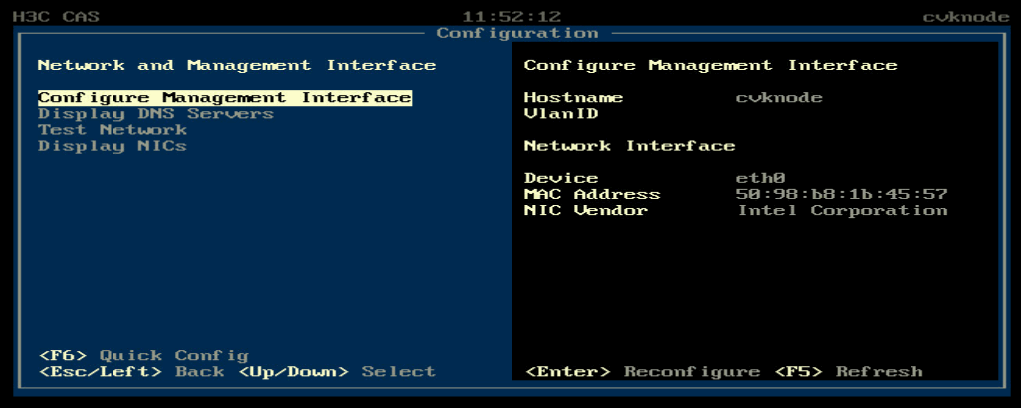
1. Access the console of the server and then access the Configuration screen.
Figure 20 Configuration screen
2. Select Network and Management Interface > Configure Management Interface.
Figure 21 Configure Management Interface screen
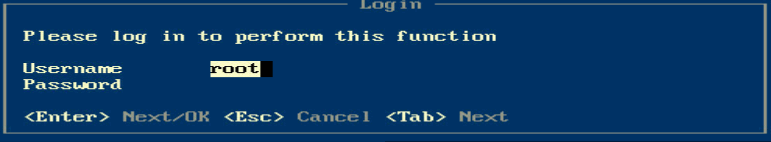
3. Enter the password of the root user. By default, the password is root.
Figure 22 Login screen
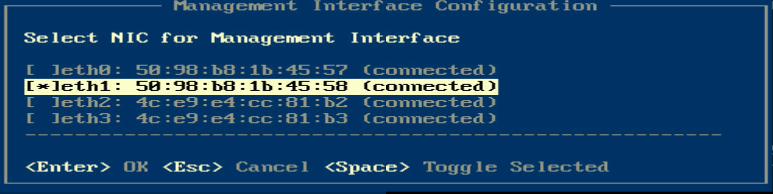
4. Select a management network interface and then press Enter.
|
IMPORTANT: Select two NICs if link aggregation has been configured for the management network. |
Figure 23 Selecting a NIC
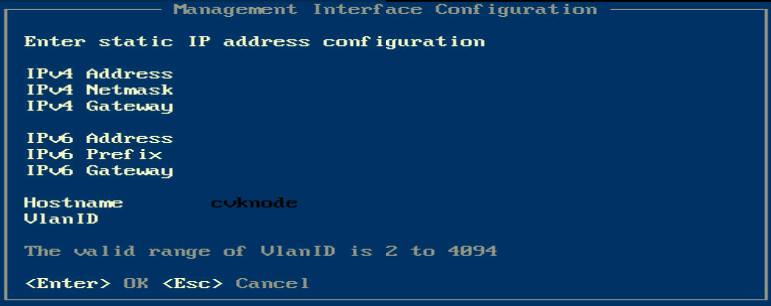
5. Enter the IP address, subnet mask, gateway address, hostname, and VLAN ID for the management interface as needed, and then press Enter.
Figure 24 Configuring management interface parameters
Setting the system time for each server
After CAS is installed on a server, the server will restart and automatically enter the CAS console. Set the system time for each server at the console to ensure consistent time among all servers.
Table 4 describes the commands for setting the system time.
Table 4 Commands for setting the system time
|
Command |
Description |
|
date xxxxxxxxxx |
Set the system time in the MMDDHHMMYY format. For example, to set the time to 14: 29, September 30th, 2012, enter date 0930142912. |
|
hwclock -w |
Write the time to the BIOS. |
Configuring link aggregation for the management network
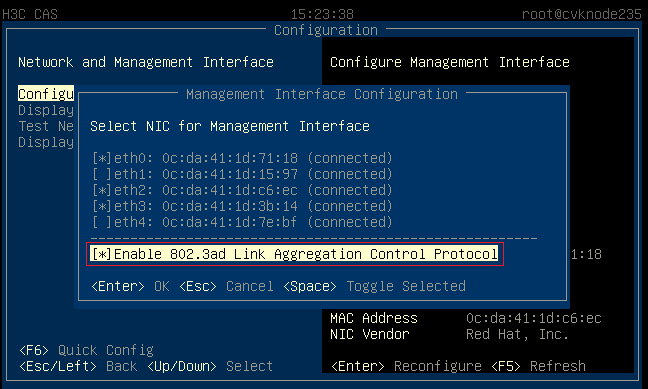
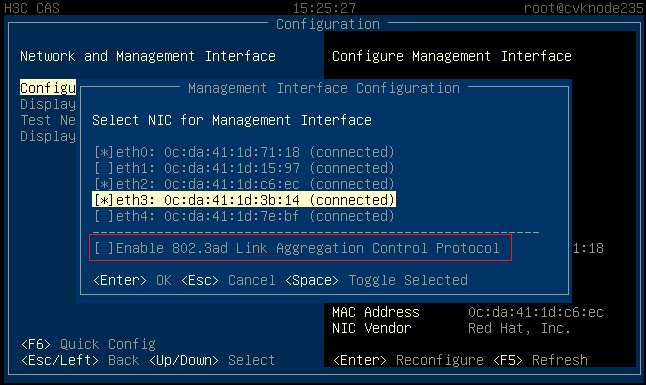
After CAS installation, you can configure link aggregation for the management network on the xsconsole page. To configure link aggregation, you must select multiple physical NICs (interfaces) for the host.
· You can configure static or dynamic link aggregation for the interfaces as required. To configure dynamic link aggregation, you must enable LACP on the physical switch.
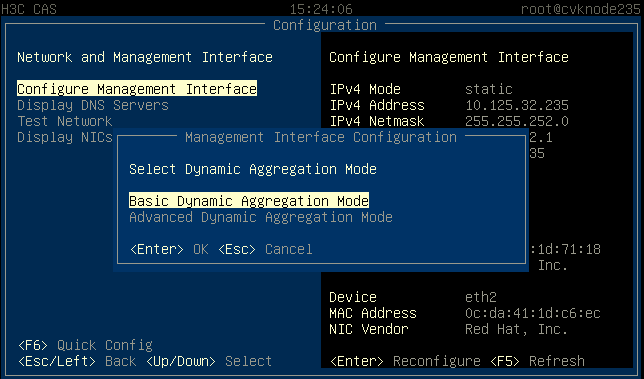
· You can configure basic, advanced, or active/standby load balancing for the interfaces as required.
¡ Advanced load balancing—Distributes traffic across the interfaces based on Ethernet type, IP protocol, source IP address, destination IP address, source port, and destination port.
¡ Basic load balancing—Distributes traffic across the interfaces based on the source MAC address and VLAN tag.
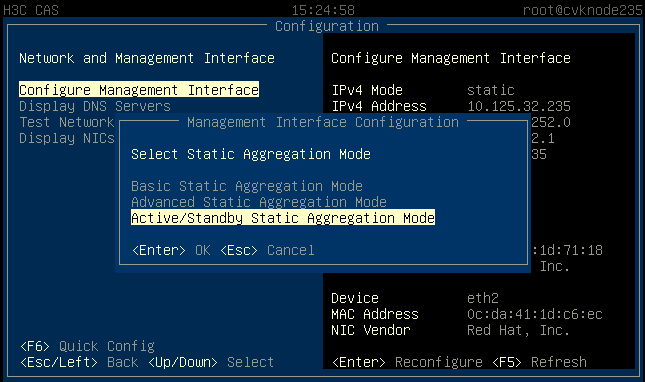
¡ Active/standby load balancing—Distributes traffic based on the primary and backup roles of the interfaces. When the primary interface fails, traffic is automatically switched to the backup interfaces. Dynamic link aggregation does not support this mode.
Configuring dynamic link aggregation
1. On the Management Interface Configuration page, select multiple NICs and enable LACP.
Figure 25 Configuring dynamic link aggregation
2. Select basic or advanced load balancing mode as required.
Figure 26 Configuring the load balancing mode
Configuring static link aggregation
1. On the Management Interface Configuration page, select multiple NICs and leave LACP unselected.
Figure 27 Configuring static link aggregation
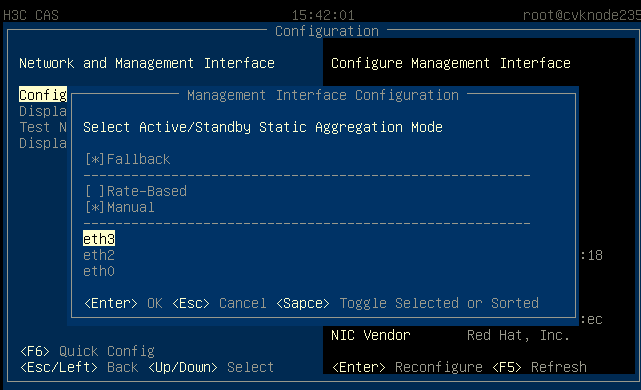
2. Select basic, advanced, or active/standby load balancing mode as required.
Figure 28 Configuring the load balancing mode
3. (Optional.) Specify the priority for the primary and backup interfaces if active/standby load balancing mode is configured.
Figure 29 Specifying the priority for the primary and backup interfaces
Accessing CVM
You can access CVM through HTTP or HTTPS.
To access CVM:
1. Launch your web browser such as Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox.
2. Enter http://server-ip:8080/cas or http://server-ip:8443/cas in the address bar of the Web browser.
The IP address must be that of the management network interface configured for the management server.
3. Enter the username and password.
Both the default username and password are admin and Cloud@1234, respectively.
|
IMPORTANT: As a best practice, change your password at the first login and keep the new password safe. |
FAQs
What browsers can I use to access CAS?
As a best practice, use browser Google Chrome 39 or later, or Mozilla Firefox 22 or later to access CAS.
Do I need to install a client for accessing CAS?
No. CAS uses the browser/server (B/S) architecture and you can access CAS directly by using a browser.
To access CAS, enter http://server-ip:8080/cas or https://server-ip:8443/cas in the address bar of a Web browser. The IP address must be that of the management interface configured for the management server.
Why do some pages look different when they are accessed from different browsers?
This is because the browsers interpret some page elements differently. This issue is normal and does not affect the functionality of the product.
What installation media can I use to install CAS?
As a best practice, use a USB drive or virtual drive to install CAS.
Appendix Building a bootable USB drive
You can build a bootable USB drive by burning an ISO image file to the USB drive, and use the bootable USB drive to install software for the server.
You can use Linux or Rufus DD mode to build a USB bootable flash drive. Rufus has multiple versions. Some versions do not support DD mode. As a best practice, use Linux DD to build a USB bootable flash drive.
Using Linux DD mode to build a USB bootable flash drive
1. Prepare for the building.
a. Insert a USB flash drive into a device running a Linux operating system.
b. Copy the ISO image file to the Linux system.
Execute the md5sum xx.iso command (xx.iso is the file name) before and after the copying operation to verify the integrity of the copied file.
c. Execute the fdisk -l command to view the name of the USB flash drive. This procedure uses name sdb as an example.
2. Execute the mount | grep sdb command.
¡ If this command displays mounting information for the USB flash drive, the drive has been automatically mounted to the Linux system. You must first unmount it and then mount it.
[root@cvknode-32 ~]# mount | grep sdb
/dev/sdb1 on /var/ftp type ext4 (rw,relatime,stripe=64,data=ordered)
[root@cvknode-32 ~]# umount /dev/sdb1
[root@cvknode-32 ~]# mount | grep sdb
¡ If no output is displayed, go to the next step.
3. Execute the dd if=kylin-image-name.iso of=/dev/USB flash drive name bs=1M command to burn the ISO image file onto the USB flash drive.
4. Execute the sync && sync command.
5. Remove the USB flash drive from the device.
Using Rufus to build a USB bootable flash drive
Rufus is a free bootable drive building tool that can be downloaded from its official website.
To build a bootable USB drive, perform steps 1 and 2 for a Ubuntu ISO image file and steps 1 to 4 for a CentOS ISO image file.
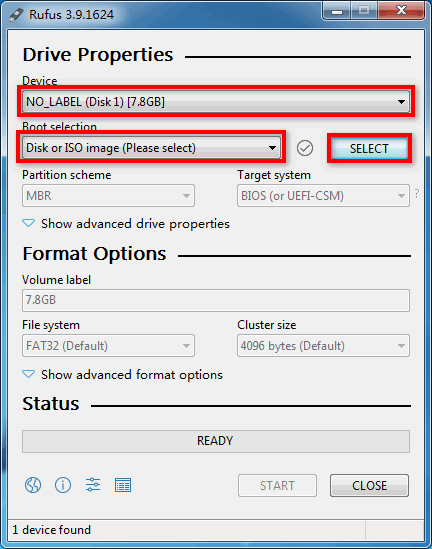
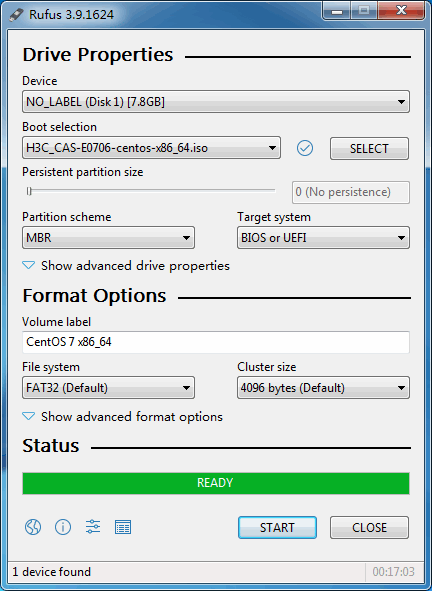
1. Double-click the Rufus tool. On the Rufus window, select the target USB drive from the Device list and Disk or ISO image (Please select) from the Boot selection list and then click SELECT.
Figure 30 Selecting the USB drive and ISO image booting
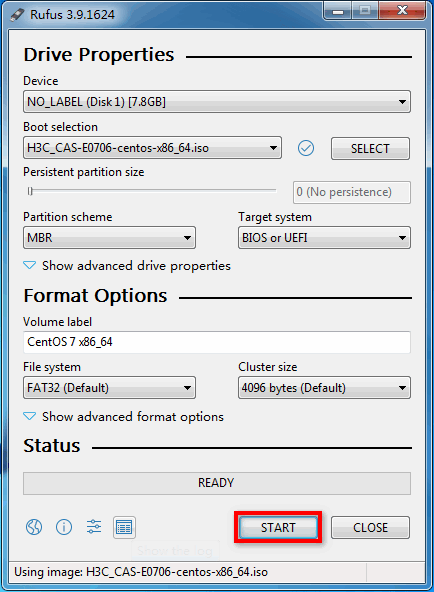
2. Select the H3C CAS ISO image file, for example, H3C_CAS-E0706-centos-x86.iso and configure the other settings as required. Then click START.
Figure 31 Starting to build the bootable USB flash drive
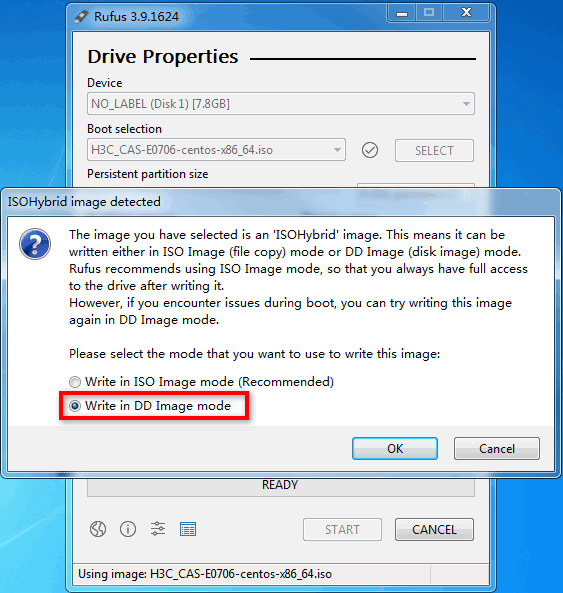
3. On the ISOHybrid image detected window, select Write in DD image mode and then click OK.
Figure 32 Selecting to write in DD image node
Figure 33 Building the bootable USB flash drive