- Table of Contents
-
- 09-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-AAA configuration
- 02-802.1X configuration
- 03-MAC authentication configuration
- 04-Portal configuration
- 05-Port security configuration
- 06-Password control configuration
- 07-Public key management
- 08-PKI configuration
- 09-IPsec configuration
- 10-SSH configuration
- 11-SSL configuration
- 12-IP source guard configuration
- 13-ARP attack protection configuration
- 14-MFF configuration
- 15-Crypto engine configuration
- 16-FIPS configuration
- 17-User profile configuration
- 18-Attack detection and prevention configuration
- 19-ND attack defense configuration
- 20-Keychain configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 11-SSL configuration | 85.21 KB |
Configuring SSL
Overview
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a cryptographic protocol that provides communication security for TCP-based application layer protocols such as HTTP. SSL has been widely used in applications such as e-business and online banking to provide secure data transmission over the Internet.
SSL security services
SSL provides the following security services:
· Privacy—SSL uses a symmetric encryption algorithm to encrypt data and uses an asymmetric key algorithm such as RSA to encrypt the key used by the symmetric encryption algorithm. For more information about RSA, see "Managing public keys."
· Authentication—SSL uses certificate-based digital signatures to authenticate the SSL server and client. The SSL server and client obtain digital certificates through PKI. For more information about PKI and digital certificates, see "Configuring PKI."
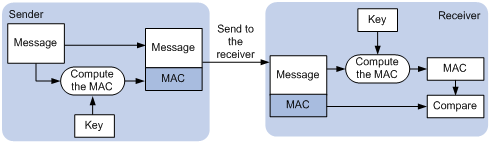
· Integrity—SSL uses the message authentication code (MAC) to verify message integrity. It uses a MAC algorithm and a key to transform a message of any length to a fixed-length message. Any change to the original message will result in a change to the calculated fixed-length message. As shown in Figure 1, the message integrity verification process is as follows:
a. The sender uses a MAC algorithm and a key to calculate a MAC value for a message. Then, it appends the MAC value to the message, and sends the message to the receiver.
b. The receiver uses the same key and MAC algorithm to calculate a MAC value for the received message, and compares it with the MAC value appended to the message.
c. If the two MAC values match, the receiver considers the message intact. Otherwise, the receiver considers that the message was tampered with and it discards the message.
Figure 1 MAC algorithm diagram
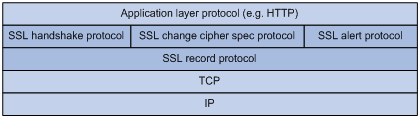
SSL protocol stack
The SSL protocol stack includes the following protocols:
· SSL record protocol at the lower layer.
· SSL handshake protocol, SSL change cipher spec protocol, and SSL alert protocol at the upper layer.
The following describes the major functions of SSL protocols:
· SSL record protocol—Fragments data received from the upper layer, computes and adds MAC to the data, and encrypts the data.
· SSL handshake protocol—Negotiates the cipher suite used for secure communication, authenticates the server and client, and securely exchanges the keys between the server and client. The cipher suite that needs to be negotiated includes the symmetric encryption algorithm, key exchange algorithm, and MAC algorithm.
· SSL change cipher spec protocol—Notifies the receiver that subsequent packets are to be protected based on the negotiated cipher suite and key.
· SSL alert protocol—Sends alert messages to the receiving party. An alert message contains the alert severity level and a description.
FIPS compliance
The device supports the FIPS mode that complies with NIST FIPS 140-2 requirements. Support for features, commands, and parameters might differ in FIPS mode (see "Configuring FIPS") and non-FIPS mode.
SSL configuration task list
|
Tasks at a glance |
Remarks |
|
Perform this configuration task on the SSL server. |
|
|
Perform this configuration task on the SSL client. |
Configuring an SSL server policy
An SSL server policy is a set of SSL parameters used by the SSL server. An SSL server policy takes effect only after it is associated with an application such as HTTPS.
SSL protocol versions include SSL 2.0, SSL 3.0, TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, and TLS 1.2. By default, the SSL server can communicate with clients running all SSL protocol versions. When the server receives an SSL 2.0 Client Hello message from a client, it notifies the client to use a later version for communication.
You can disable specific SSL protocol versions for the SSL server to enhance system security.
To configure an SSL server policy:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. (Optional.) Disable specific SSL protocol versions for the SSL server. |
·
In non-FIPS mode: ·
In FIPS mode: |
The default setting is as follows: · In non-FIPS mode, the SSL server supports SSL 3.0, TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, and TLS 1.2. · In FIPS mode, the SSL server supports TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, and TLS 1.2. |
|
3. (Optional.) Disable SSL session renegotiation for the SSL server. |
ssl renegotiation disable |
By default, SSL session renegotiation is enabled. |
|
4. Create an SSL server policy and enter its view. |
ssl server-policy policy-name |
By default, no SSL server policy exists on the device. |
|
5. (Optional.) Specify a PKI domain for the SSL server policy. |
pki-domain domain-name |
By default, no PKI domain is specified for an SSL server policy. If SSL server authentication is required, you must specify a PKI domain and request a local certificate for the SSL server in the domain. For information about how to create and configure a PKI domain, see "Configuring PKI." |
|
6. Specify the cipher suites that the SSL server supports. |
By default, the SSL server supports all cipher suites. |
|
|
7. Set the maximum number of sessions that the SSL server can cache. |
session cachesize size |
By default, an SSL server can cache a maximum of 500 sessions. |
|
8. Enable the SSL server to authenticate SSL clients through digital certificates. |
client-verify enable |
By default, SSL client authentication is disabled. |
Configuring an SSL client policy
An SSL client policy is a set of SSL parameters that the client uses to establish a connection to the server. An SSL client policy takes effect only after it is associated with an application such as DDNS.
As a best practice to enhance system security, disable SSL 3.0 on the device and specify TLS 1.0 for an SSL client policy.
To configure an SSL client policy:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. (Optional.) Disable SSL session renegotiation. |
ssl renegotiation disable |
By default, SSL session renegotiation is enabled. |
|
3. Create an SSL client policy and enter its view. |
ssl client-policy policy-name |
By default, no SSL client policy exists on the device. |
|
4. (Optional.) Specify a PKI domain for the SSL client policy. |
pki-domain domain-name |
By default, no PKI domain is specified for an SSL client policy. If SSL client authentication is required, you must specify a PKI domain and request a local certificate for the SSL client in the PKI domain. For information about how to create and configure a PKI domain, see "Configuring PKI." |
|
5. Specify the preferred cipher suite for the SSL client policy. |
·
In non-FIPS mode: ·
In FIPS mode: |
·
In non-FIPS mode: ·
In FIPS mode: |
|
6. Specify the SSL protocol version for the SSL client policy. |
·
In non-FIPS mode: ·
In FIPS mode: |
By default, an SSL client policy uses TLS 1.0. To ensure security, do not specify SSL 3.0 for the SSL client policy. |
|
7. Enable the SSL client to authenticate servers through digital certificates. |
server-verify enable |
By default, SSL server authentication is enabled. |
Displaying and maintaining SSL
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display cryptographic library version information. |
display crypto version |
|
Display SSL server policy information. |
display ssl server-policy [ policy-name ] |
|
Display SSL client policy information. |
display ssl client-policy [ policy-name ] |
