- Table of Contents
-
- 06-Layer 3 - IP Routing Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-IP routing basics
- 02-Static routing configuration
- 03-RIP configuration
- 04-OSPF configuration
- 05-IS-IS configuration
- 06-BGP configuration
- 07-Policy-based routing configuration
- 08-IPv6 static routing configuration
- 09-RIPng configuration
- 10-OSPFv3 configuration
- 11-IPv6 IS-IS configuration
- 12-IPv6 policy-based routing configuration
- 13-Routing policy configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 12-IPv6 policy-based routing configuration | 129.46 KB |
Contents
IPv6 PBR configuration task list
Configuring match criteria for an IPv6 node
Configuring actions for an IPv6 node
The switch operates in IRF or standalone (the default) mode. For more information about IRF, see IRF Configuration Guide.
Introduction to IPv6 PBR
Policy-based routing (PBR) uses user-defined policies to route packets. A policy can specify the next hop and other parameters for packets that match specific criteria such as ACLs.
A device uses PBR to forward matching packets and uses the routing table to forward non-matching packets. If PBR is not configured, the device uses the routing table to forward packets.
The device supports only interface PBR, which guides the forwarding of packets received on an interface only.
Policy
An IPv6 policy includes match criteria and actions to be taken on the matching packets. A policy can have one or multiple nodes as follows:
· Each node is identified by a node number. A smaller node number has a higher priority.
· A node comprises if-match and apply clauses. An if-match clause specifies a match criterion, and an apply clause specifies an action.
· A node has a match mode of permit or deny.
An IPv6 policy matches nodes in priority order against packets. If a packet satisfies the match criteria on a node, it is processed by the action on the node. Otherwise, it goes to the next node for a match. If the packet does not match the criteria on any node, it is forwarded according to the routing table.
if-match clause
IPv6 PBR supports only the if-match acl clause, which sets an ACL match criterion.
You can specify only one if-match clause of each type for a node.
apply clause
IPv6 PBR supports only the apply next-hop clause, which sets the next hop for packets.
Relationship between the match mode and clauses on the node
|
Match mode |
||
|
In permit mode |
In deny mode |
|
|
Yes |
· If the node is configured with an apply clause, IPv6 PBR executes the apply clause on the node. · If the node is configured with no apply clause, the packet is forwarded according to the routing table. |
The packet is forwarded according to the routing table. |
|
No |
IPv6 PBR matches the packet against the next node. |
IPv6 PBR matches the packet against the next node. |
A node that has no if-match clause matches any packet.
PBR and track
PBR can work with the Track feature to dynamically adapt the availability status of a node configured with an apply clause to the link status of a tracked next hop.
When the track entry associated with the node changes to negative because the next hop is detected to be unavailable, the node cannot be used for forwarding. When the track entry changes to positive or NotReady because the next hop is detected to be available, the node can be used for forwarding.
For more information about track-PBR collaboration, see High Availability Configuration Guide.
IPv6 PBR configuration task list
|
Tasks at a glance |
|
(Required.) Configuring an IPv6 policy: |
|
(Required.) Configuring IPv6 PBR |
Configuring an IPv6 policy
Creating an IPv6 node
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Create an IPv6 policy or policy node, and enter IPv6 policy node view. |
ipv6 policy-based-route policy-name [ deny | permit ] node node-number |
By default, no IPv6 policy node is created. |
Configuring match criteria for an IPv6 node
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter IPv6 policy node view. |
ipv6 policy-based-route policy-name [ deny | permit ] node node-number |
N/A |
|
3. Configure an ACL match criterion. |
if-match acl acl-number |
By default, no ACL match criterion is configured. |
|
|
NOTE: If an ACL match criterion is defined, packets are matched against the ACL rules, and the permit or deny action of the specified ACL is ignored. If the specified ACL does not exist, no packet is matched. |
Configuring actions for an IPv6 node
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter IPv6 policy node view. |
ipv6 policy-based-route policy-name [ deny | permit ] node node-number |
N/A |
|
3. Set next hops for permitted IPv6 packets. |
apply next-hop [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] { ipv6-address [ direct ] [ track track-entry-number ] }&<1-2> |
By default, no next hop is specified. You can specify at most two next hops for backup. The first next hop configured is the active next hop and the second is the standby next hop. |
To configure two next hops for a policy node, you can enter two next hops in one command line or execute the command twice. When neither next hop is available, packets are forwarded according to the routing table.
The rule you add to an ACL that has been used by a policy cannot take effect if hardware resources are insufficient or the policy does not support the rule. Such rules are marked as uncompleted in the output of the display acl { acl-number | all | name acl-name } slot slot-number command. To successfully apply the rule, you must delete the rule and reconfigure it when hardware resources are sufficient. For more information about the display acl command, see ACL and QoS Command Reference.
Configuring IPv6 PBR
Configure IPv6 PBR by applying an IPv6 policy to an interface. IPv6 PBR uses the policy to guide the forwarding of IPv6 packets received on the interface. The specified policy must exist. Otherwise, the IPv6 interface PBR configuration fails.
You can apply only one policy on an interface. Before you apply a new policy, you must first remove the current policy from the interface.
You can apply the same IPv6 policy on multiple interfaces.
To configure IPv6 interface PBR:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Apply an IPv6 policy on the interface. |
ipv6 policy-based-route policy-name |
By default, no IPv6 policy is applied on the interface. |
Displaying and maintaining IPv6 PBR
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display IPv6 PBR policy information. |
display ipv6 policy-based-route [ policy policy-name ] |
|
Display IPv6 PBR configuration. |
display ipv6 policy-based-route setup |
|
Display IPv6 interface PBR configuration and statistics (in standalone mode). |
display ipv6 policy-based-route interface interface-type interface-number [ slot slot-number ] |
|
Display IPv6 interface PBR configuration and statistics (in IRF mode). |
display ipv6 policy-based-route interface interface-type interface-number [ chassis chassis-number slot slot-number ] |
|
Clear IPv6 PBR statistics. |
reset ipv6 policy-based-route statistics [ policy policy-name ] |
Packet type-based IPv6 interface PBR configuration example
By default, Ethernet, VLAN, and aggregate interfaces are down. To configure such an interface, bring the interface up by executing the undo shutdown command.
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 1, configure IPv6 PBR on Switch A to forward all TCP packets received on VLAN-interface 11 to the next hop 1::2. Switch A forwards other IPv6 packets according to the routing table.
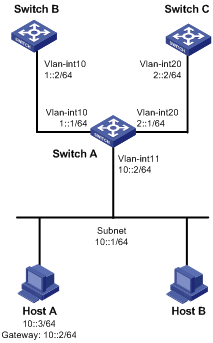
Configuration procedure
1. Configure Switch A:
# Configure RIPng.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] ripng 1
[SwitchA-ripng-1] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 10
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] ipv6 address 1::1 64
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] ripng 1 enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 20
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface20] ipv6 address 2::1 64
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface20] ripng 1 enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface20] quit
# Configure ACL 3001 to match TCP packets.
[SwitchA] acl ipv6 number 3001
[SwitchA-acl6-adv-3001] rule permit tcp
[SwitchA-acl6-adv-3001] quit
# Configure Node 5 for policy aaa to forward TCP packets to next hop 1::2.
[SwitchA] ipv6 policy-based-route aaa permit node 5
[SwitchA-pbr6-aaa-5] if-match acl 3001
[SwitchA-pbr6-aaa-5] apply next-hop 1::2
[SwitchA-pbr6-aaa-5] quit
# Configure IPv6 interface PBR by applying the policy aaa on VLAN-interface 11.
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 11
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface11] ipv6 address 10::2 64
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface11] undo ipv6 nd ra halt
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface11] ripng 1 enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface11] ipv6 policy-based-route aaa
2. Configure RIPng on Switch B.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] ripng 1
[SwitchB-ripng-1] quit
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 10
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface10] ipv6 address 1::2 64
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface10] ripng 1 enable
3. Configure RIPng on Switch C.
<SwitchC> system-view
[SwitchC] ripng 1
[SwitchC-ripng-1] quit
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 20
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface20] ipv6 address 2::2 64
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface20] ripng 1 enable
Verifying the configuration
# Enable IPv6 and configure the IPv6 address 10::3 for Host A.
C:\>ipv6 install
Installing...
Succeeded.
C:\>ipv6 adu 4/10::3
# On Host A, Telnet to Switch B that is directly connected to Router A. The operation succeeds.
# On Host A, Telnet to Switch C that is directly connected to Router A. The operation fails.
# Ping Switch C from Host A. The operation succeeds.
Telnet uses TCP, and ping uses ICMP. The preceding results show that all TCP packets arriving on VLAN-interface 11 of Switch A are forwarded to next hop 1::2, and other packets are forwarded through VLAN-interface 20. The IPv6 interface PBR configuration is effective.
