- Table of Contents
-
- 13-Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-System Maintenance and Debugging Configuration
- 02-NQA Configuration
- 03-NTP Configuration
- 04-Clock Monitoring Configuration
- 05-IPC Configuration
- 06-SNMP Configuration
- 07-RMON Configuration
- 08-CWMP Configuration
- 09-Sampler Configuration
- 10-Mirroring Configuration
- 11-Protocol Packet Statistics Configuration
- 12-sFlow Configuration
- 13-Information Center Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 05-IPC Configuration | 83.09 KB |
Overview
Inter-Process Communication (IPC) is a reliable communication mechanism among processing units, typically CPUs. It is typically used on a distributed device or in an IRF fabric to provide reliable inter-card or inter-device transmission. The following are the basic IPC concepts.
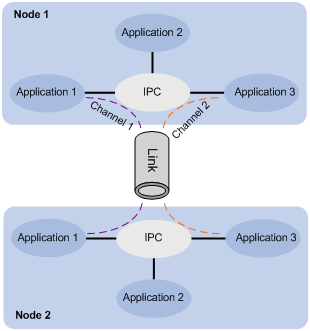
Node
An IPC node is an independent IPC-capable processing unit, typically, a CPU. Typically, distributed devices and IRF fabrics have multiple IPC nodes, because each card or device in them has at least one CPU.
Link
An IPC link is a connection between any two IPC nodes. There is one and only one link for packet sending and receiving between any two nodes. All IPC nodes are fully connected.
IPC links are created when the system is initialized. An IPC node, upon startup, sends handshake packets to other nodes. If the handshake succeeds, a connection is established.
The system uses link status to identify the link connectivity between two nodes. An IPC node can have multiple links, each having its own status.
Channel
A channel is a communication interface used by an upper layer application module of a node to communicate with an application module of a peer node. Each node assigns a locally unique channel number to each upper layer application module for identification.
Data of an upper layer application module is sent to the IPC module through a channel, and the IPC module sends the data to a peer node through the link. The relationship between a node, link and channel is as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Relationship between a node, link and channel
Packet sending modes
IPC supports three packet sending modes: unicast, multicast (including broadcast, a special multicast), and mixcast, each having a corresponding queue. The upper layer application modules can automatically select a packet sending mode as needed.
· Unicast—One node sends packets to another node.
· Multicast—One node sends packets to multiple nodes. To use multicast mode, an application module must create a multicast group that includes a set of nodes. Multicasts destined for this group are sent to all the nodes in the group. An application module can create multiple multicast groups. Creation and deletion of a multicast group and multicast group members depend on the application module.
· Mixcast—Supports both unicast and multicast.
Enabling IPC performance statistics
When IPC performance statistics is enabled, the system collects input and output statistics for a node in a specified time range (for example, in the last 10 seconds, or in the last 1 minute). When IPC performance statistics is disabled, statistics collection is stopped. If you execute the display command, the system displays the statistics collected before IPC performance statistics was disabled.
To enable IPC performance statistics:
|
Task |
Command |
Remarks |
|
Enable IPC performance statistics in user view. |
ipc performance enable { node node-id | self-node } [ channel channel-id ] |
By default, the function is disabled. |
Displaying and maintaining IPC
|
Task |
Command |
Remarks |
|
Display IPC node information. |
display ipc node [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view |
|
Display channel information for a node. |
display ipc channel { node node-id | self-node } [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view |
|
Display queue information for a node. |
display ipc queue { node node-id | self-node } [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view |
|
Display multicast group information for a node. |
display ipc multicast-group { node node-id | self-node } [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view |
|
Display packet information for a node. |
display ipc packet { node node-id | self-node } [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view |
|
Display link status information for a node. |
display ipc link { node node-id | self-node } [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view |
|
Display IPC performance statistics of a node. |
display ipc performance { node node-id | self-node } [ channel channel-id ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view |
|
Clear IPC performance statistics of a node. |
reset ipc performance [ node node-id | self-node ] [ channel channel-id ] |
Available in user view |
