| Title | Size | Downloads |
|---|---|---|
| 13-VLAN Mapping Configuration.pdf | 231.24 KB |
- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 13-VLAN Mapping Configuration | 231.24 KB |
Table of Contents
One-to-One VLAN Mapping and Many-to-One VLAN Mapping
Basic Concepts of VLAN Mapping
How VLAN Mapping Is Implemented
VLAN Mapping Configuration Task List
Configuring One-to-One VLAN Mapping
Configuring One-to-One VLAN Mapping
Configuring Many-to-One VLAN Mapping
Configuring Many-to-One VLAN mapping (Approach 1)
VLAN Mapping Configuration Examples
One-to-One/Many-to-One VLAN Mapping Configuration Example
When configuring VLAN mapping, go to these sections for information you are interested in:
l VLAN Mapping Configuration Task List
l Configuring One-to-One VLAN Mapping
l Configuring Many-to-One VLAN Mapping
l VLAN Mapping Configuration Examples
VLAN Mapping Overview
VLAN mapping maps the customer VLANs (CVLANs) to service-provider VLANs (SVLANs). Types of VLAN mapping include:
l One-to-one VLAN mapping that maps the CVLAN ID in the VLAN tag to the SVLAN ID.
l Many-to-one VLAN mapping that maps the CVLAN IDs in the VLAN tags of traffic of more than two VLANs to the same SVLAN ID.
The two mapping types are the same in the basic implementation except in the number of CVLANs. One-to-one VLAN mapping is many-to-one VLAN mapping with the number of CVLANs being 1.
The following sections present the scenario to which these VLAN mapping types apply.
One-to-One VLAN Mapping and Many-to-One VLAN Mapping
One-to-one VLAN mapping and many-to-one VLAN mapping are mainly applied in campus networks as shown in Figure 1-1.
Figure 1-1 Scenario for one-to-one/multiple-to-one VLAN mapping
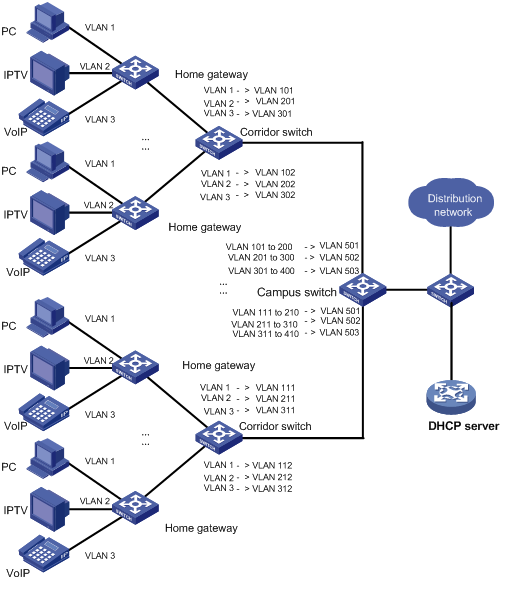
In such a network, different VLANs are used for transmitting different services (PC, IPTV, and VoIP for example) of a home user. Furthermore, to differentiate home users that are using the same service, you need to perform one-to-one VLAN mapping to map the service traffic to different VLANs by user on the corridor switches. However, an access device on the distribution layer is likely unable to support the number of VLANs required for this type of VLAN mapping.
To reduce the number of VLANs required on the edge device at the distribution layer, you can adopt many-to-one VLAN mapping. This type of VLAN mapping maps the VLANs carrying the same service of different users to the same VLAN while isolating the service traffic of different users.
Basic Concepts of VLAN Mapping
Before you configure VLAN mappings, be aware of the following concepts, which will be used throughout this document.
l Uplink traffic: Traffic transmitted from a home user network to a distribution network or from a user network to an SP network.
l Downlink traffic: Traffic transmitted from a distribution network to a home user network or from an SP network to a user network.
l Uplink port: A port transmitting uplink traffic and receiving downlink traffic.
l Downlink port: A port transmitting downlink traffic and receiving uplink traffic.
l Uplink policy: A QoS policy containing VLAN mappings for uplink traffic.
l Downlink policy: A QoS policy containing VLAN mappings for downlink traffic.
How VLAN Mapping Is Implemented
This section describes how VLAN mapping is implemented on your device.
One-to-one VLAN mapping
1) Approach 1
|
On the downlink port |
On the uplink port |
||
|
For uplink traffic |
For downlink traffic |
||
|
Do… |
Based on… |
Do… |
Based on… |
|
Replace the customer VLAN (CVLAN) with the service provider VLAN (SVLAN) |
Uplink policy in the inbound direction |
Replace the SVLAN with the original CVLAN |
DHCP snooping address table, which contains mappings of the SVLAN, IP address, MAC address, and CVLAN for DHCP clients |
![]()
l For information about DHCP snooping, refer to DHCP Configuration.
l For information about QoS policies, refer to QoS Configuration
Many-to-one VLAN mapping
|
On the downlink port |
On the uplink port |
||
|
For uplink traffic |
For downlink traffic |
||
|
Do... |
Based on… |
Do... |
Based on… |
|
Map all specified customer VLANs (CVLANs) to one service provider VLAN (SVLAN) |
Uplink policy in the inbound direction |
Replace the SVLAN with the original CVLAN |
DHCP snooping address table, which contains mappings of the SVLAN, IP address, MAC address, and CVLAN for DHCP clients |
![]()
l For information about DHCP snooping, refer to DHCP Configuration.
l For information about QoS policies, refer to QoS Configuration.
VLAN Mapping Configuration Task List
You need to configure VLAN mapping on your device depending on its position in the network.
Complete the following tasks to configure VLAN mapping:
|
Task |
Remarks |
|
Optional Perform this configuration on the corridor switches shown in Figure 1-1 |
|
|
Optional Perform this configuration on the campus switches shown in Figure 1-1 |
For VLAN mapping to work, you are required to do the following in addition to configuring QoS policies:
l Enable ARP detection to send ARP packets to the CPU to allow modification of the VLAN attributes carried in the packets, which is impossible with the normal ARP packet processing procedure. For information about ARP detection, refer to ARP Configuration.
l Enable the dynamic address binding support of IP Source Guard to filter packets received on a port based on the source IP address and MAC address bindings created dynamically to prevent illegal packets from passing through the port. For information about this feature, refer to IP Source Guard Configuration.
l To save system resources, disable user bindings recording on the DHCP snooping trusted ports that forward DHCP packets. For information about this feature, refer to DHCP Configuration
Configuring One-to-One VLAN Mapping
Perform one-to-one VLAN mapping on the corridor switches shown in Figure 1-1 to use VLANs to isolate different services of different users.
Configuring One-to-One VLAN Mapping
Configuration prerequisites
l All service terminals of home users are using DHCP for obtaining an IP address. For how to get an IP address through DHCP, refer to DHCP Configuration in the IP Services Volume.
l The CVLAN-to-SVLAN mappings have been planned.
Configuration procedure
Follow these steps to configure a one-to-one VLAN mapping:
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Enable DHCP snooping |
dhcp-snooping |
Required Disabled by default. |
|
|
Enable ARP detection on the CVLAN and the SVLAN for the VLAN mapping |
Create a VLAN and enter VLAN view |
vlan vlan-id |
Required Disabled by default. Repeat this step for all CVLANs and SVLANs that the VLAN mapping involves. |
|
Enable ARP detection |
arp detection enable |
||
|
Exit to system view |
quit |
||
|
Configure an uplink policy to map the CVLAN to the SVLAN |
Refer to Table 1-1. |
Required Repeat this step to create multiple CVLAN-to-SVLAN mappings. |
|
|
Enter the interface view of the downlink port |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
|
Set the link type of the downlink port to trunk |
port link-type trunk |
Required |
|
|
Configure the downlink port to permit the CVLAN to pass through |
port trunk permit vlan { vlan-id-list | all } |
Required By default, a trunk port permits only VLAN 1 to pass through. |
|
|
Enable the dynamic address binding function of IP Source Guard |
ip check source ip-address mac-address |
Required |
|
|
Apply the uplink policy to the downlink port |
qos apply policy policy-name inbound |
Required |
|
|
Exit to system view |
quit |
— |
|
|
Enter the interface view of the uplink port |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
|
Configure the uplink port as a DHCP snooping trusted port |
dhcp-snooping trust |
Required By default, all ports with DHCP snooping enabled are DHCP snooping untrusted ports. |
|
|
Configure the uplink port as an ARP trusted port |
arp detection trust |
Required By default, all ports are ARP untrusted ports. |
|
|
Set the link type of the uplink port to trunk |
port link-type trunk |
Required |
|
|
Configure the uplink port to permit the specified SVLANs to pass through |
port trunk permit vlan { vlan-id-list | all } |
Required By default, a trunk port permits only VLAN 1 to pass through. |
|
Table 1-1 Configure an uplink policy
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Create a class and enter class view |
traffic classifier tcl-name operator or |
Required |
|
Specify the CVLAN for the VLAN mapping |
if-match customer-vlan-id vlan-id-value |
Required |
|
Exit to system view |
quit |
— |
|
Create a traffic behavior and enter traffic behavior view |
traffic behavior behavior-name |
Required |
|
Specify the SVLAN for the VLAN mapping |
remark service-vlan-id vlan-id-value |
Required |
|
Exit to system view |
quit |
— |
|
Create a QoS policy and enter QoS policy view |
qos policy policy-name |
Required |
|
Map the CVLAN to the SVLAN by associating the traffic class with the traffic behavior |
classifier tcl-name behavior behavior-name mode dot1q-tag-manipulation |
Required |
|
Exit to system view |
quit |
— |
![]()
l The VLAN mapping configuration above takes effect when the user goes online the next time.
l To change a VLAN mapping, you must first use the reset dhcp-snooping command to clear the corresponding DHCP snooping address binding entry (refer to DHCP Commands in the IP Services Volume) or disable the dynamic address binding function of IP Source Guard on the downlink port and then enable dynamic address binding (refer to IP Source Guard Commands in the Security Volume).
Configuring Many-to-One VLAN Mapping
Perform many-to-one VLAN mapping on the campus switches shown in Figure 1-1 to carry the same service of different users using the same VLAN on the service provider’s network.
Configuring Many-to-One VLAN mapping (Approach 1)
Configuration prerequisites
The CVLAN-to-SVLAN mappings have been planned.
Configuration procedure
Follow these steps to configure a many-to-one VLAN mapping:
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Enable DHCP snooping |
dhcp-snooping |
Required Disabled by default. |
|
|
Enable ARP detection on the CVLANs and the SVLAN for the VLAN mapping |
Create a VLAN and enter VLAN view |
vlan vlan-id |
Required Disabled by default. Repeat these steps for all CVLANs and the SVLAN that the VLAN mapping involves. |
|
Enable ARP detection |
arp detection enable |
||
|
Exit to system view |
quit |
||
|
Configure an uplink policy to map the CVLANs to the same SVLAN |
Refer to Table 1-2 |
Required |
|
|
Enter the interface view of the downlink port |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
|
Set the link type of the downlink port to trunk |
port link-type trunk |
Required |
|
|
Configure the downlink port to permit the specified CVLANs to pass through |
port trunk permit vlan { vlan-id-list | all } |
Required By default, a trunk port permits only VLAN 1 to pass through. |
|
|
Enable the dynamic address binding function of IP Source Guard |
ip check source ip-address mac-address |
Required |
|
|
Apply the uplink policy to the downlink port in the inbound direction |
qos apply policy policy-name inbound |
Required |
|
|
Exit to system view |
quit |
— |
|
|
Enter the interface view of the uplink port |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
|
Configure the uplink port as a DHCP snooping trusted port |
dhcp-snooping trust |
Required By default, all ports with DHCP snooping enabled are DHCP snooping untrusted ports. |
|
|
Configure the uplink port as an ARP trusted port |
arp detection trust |
Required By default, all ports are ARP untrusted ports. |
|
|
Set the link type of the uplink port to trunk |
port link-type trunk |
Required |
|
|
Configure the uplink port to permit the specified SVLANs to pass through |
port trunk permit vlan { vlan-id-list | all } |
Required By default, a trunk port permits only VLAN 1 to pass through. |
|
Table 1-2 Configure an uplink policy
|
To do... |
Use the command... |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Create a class and enter class view |
traffic classifier tcl-name operator or |
Required |
|
Specify the CVLANs for the VLAN mapping |
if-match customer-vlan-id { vlan-id-list | vlan-id1 to vlan-id2 } |
Required |
|
Exit to system view |
quit |
— |
|
Create a traffic behavior and enter traffic behavior view |
traffic behavior behavior-name |
Required |
|
Specify the SVLAN for the VLAN mapping |
remark service-vlan-id vlan-id-value |
Required |
|
Exit to system view |
quit |
— |
|
Create a QoS policy and enter QoS policy view |
qos policy policy-name |
Required |
|
Map the CVLANs to the SVLAN by associating the traffic class with the traffic behavior |
classifier tcl-name behavior behavior-name mode dot1q-tag-manipulation |
Required |
|
Exit to system view |
quit |
— |
![]()
To change a VLAN mapping, you must first use the reset dhcp-snooping command to clear the DHCP snooping entries (refer to DHCP Commands in the IP Services Volume) or disable the dynamic address binding function of IP Source Guard on the downlink port and then enable dynamic address binding (refer to IP Source Guard Commands in the Security Volume).
VLAN Mapping Configuration Examples
One-to-One/Many-to-One VLAN Mapping Configuration Example
Network requirements
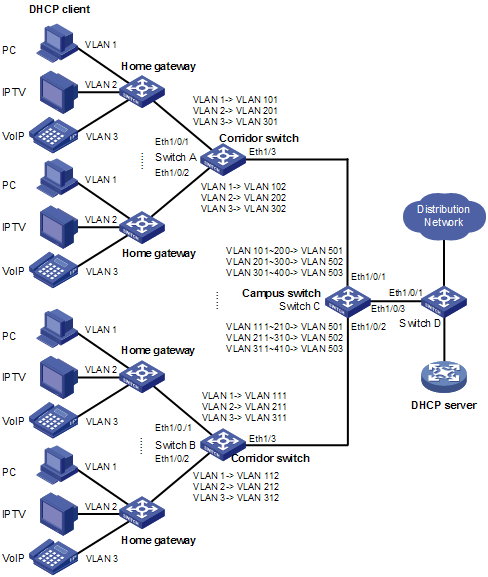
In the scenario presented in Figure 1-2, to save VLAN resources, use one VLAN to carry a type of service traffic from Switch C at the campus network edge while isolating the traffic of different home users in the VLAN.
Use VLAN 501 for PC traffic, VLAN 502 for IPTV traffic, and VLAN 503 for VoIP traffic.
Network diagram
Figure 1-2 Network diagram for one-to-one/many-to-one VLAN mapping configuration
Configuration procedure
1) Configuration on Switch A
# Enter system view.
<SwitchA> system-view
# Enable DHCP snooping.
[SwitchA] dhcp-snooping
# Enable ARP detection on each VLAN involved in VLAN mapping.
[SwitchA] vlan 1
[SwitchA-vlan1] arp detection enable
[SwitchA-vlan1] vlan 2
[SwitchA-vlan2] arp detection enable
[SwitchA-vlan2] vlan 3
[SwitchA-vlan3] arp detection enable
[SwitchA-vlan3] vlan 101
[SwitchA-vlan101] arp detection enable
[SwitchA-vlan101] vlan 201
[SwitchA-vlan201] arp detection enable
[SwitchA-vlan201] vlan 301
[SwitchA-vlan301] arp detection enable
[SwitchA-vlan301] vlan 102
[SwitchA-vlan102] arp detection enable
[SwitchA-vlan102] vlan 202
[SwitchA-vlan202] arp detection enable
[SwitchA-vlan202] vlan 302
[SwitchA-vlan302] arp detection enable
[SwitchA-vlan302] quit
# Configure uplink policies to map the CVLANs to the SVLANs.
[SwitchA] traffic classifier c1
[SwitchA-classifier-c1] if-match customer-vlan-id 1
[SwitchA-classifier-c1] traffic classifier c2
[SwitchA-classifier-c2] if-match customer-vlan-id 2
[SwitchA-classifier-c2] traffic classifier c3
[SwitchA-classifier-c3] if-match customer-vlan-id 3
[SwitchA-classifier-c3] quit
[SwitchA] traffic behavior b1
[SwitchA-behavior-b1] remark service-vlan-id 101
[SwitchA-behavior-b1] traffic behavior b2
[SwitchA-behavior-b2] remark service-vlan-id 201
[SwitchA-behavior-b2] traffic behavior b3
[SwitchA-behavior-b3] remark service-vlan-id 301
[SwitchA-behavior-b3] traffic behavior b4
[SwitchA-behavior-b4] remark service-vlan-id 102
[SwitchA-behavior-b4] traffic behavior b5
[SwitchA-behavior-b5] remark service-vlan-id 202
[SwitchA-behavior-b5] traffic behavior b6
[SwitchA-behavior-b6] remark service-vlan-id 302
[SwitchA-behavior-b6] quit
[SwitchA] qos policy p1
[SwitchA-policy-p1] classifier c1 behavior b1 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation
[SwitchA-policy-p1] classifier c2 behavior b2 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation
[SwitchA-policy-p1] classifier c3 behavior b3 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation
[SwitchA-policy-p1] quit
[SwitchA] qos policy p2
[SwitchA-policy-p2] classifier c1 behavior b4 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation
[SwitchA-policy-p2] classifier c2 behavior b5 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation
[SwitchA-policy-p2] classifier c3 behavior b6 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation
[SwitchA-policy-p2] quit
# Configure Ethernet 1/0/1 to permit frames of the specified CVLANs to pass through.
[SwitchA] interface ethernet 1/0/1
[SwitchA-Ethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[SwitchA-Ethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 2 3
# Apply the uplink policy p1 to the inbound direction of Ethernet 1/0/1.
[SwitchA-Ethernet1/0/1] qos apply policy p1 inbound
# Enable the dynamic address binding support of IP Source Guard on Ethernet 1/0/1.
[SwitchA-Ethernet1/0/1] ip check source ip-address mac-address
[SwitchA-Ethernet1/0/1] quit
# Configure Ethernet 1/0/2 to permit frames of the specified CVLANs to pass through.
[SwitchA] interface ethernet 1/0/2
[SwitchA-Ethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[SwitchA-Ethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 2 3
# Apply the uplink policy p2 to the inbound direction of Ethernet 1/0/2.
[SwitchA-Ethernet1/0/2] qos apply policy p2 inbound
# Enable the dynamic address binding support of IP Source Guard on Ethernet 1/0/2.
[SwitchA-Ethernet1/0/2] ip check source ip-address mac-address
[SwitchA-Ethernet1/0/2] quit
# Configure Ethernet 1/0/3 to permit frames of the specified SVLANs to pass through.
[SwitchA] interface ethernet 1/0/3
[SwitchA-Ethernet1/0/3] port link-type trunk
[SwitchA-Ethernet1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 101 201 301 102 202 302
# Set Ethernet 1/0/3 as a DHCP snooping trusted port.
[SwitchA-Ethernet1/0/3] dhcp-snooping trust
# Set Ethernet 1/0/3 as an ARP trusted port.
[SwitchA-Ethernet1/0/3] arp detection trust
2) Configuration on Switch B
<SwitchB> system-view
# Enable DHCP snooping.
[SwitchB] dhcp-snooping
# Enable ARP detection on each VLAN involved in VLAN mapping.
[SwitchB] vlan 1
[SwitchB-vlan1] arp detection enable
[SwitchB-vlan1] vlan 2
[SwitchB-vlan2] arp detection enable
[SwitchB-vlan2] vlan 3
[SwitchB-vlan3] arp detection enable
[SwitchB-vlan3] vlan 111
[SwitchB-vlan111] arp detection enable
[SwitchB-vlan111] vlan 211
[SwitchB-vlan211] arp detection enable
[SwitchB-vlan211] vlan 311
[SwitchB-vlan311] arp detection enable
[SwitchB-vlan311] vlan 112
[SwitchB-vlan112] arp detection enable
[SwitchB-vlan112] vlan 212
[SwitchB-vlan212] arp detection enable
[SwitchB-vlan212] vlan 312
[SwitchB-vlan312] arp detection enable
[SwitchB-vlan312] quit
# Configure uplink policies to map CVLANs of different users to different SVLANs.
[SwitchB] traffic classifier c1
[SwitchB-classifier-c1] if-match customer-vlan-id 1
[SwitchB-classifier-c1] traffic classifier c2
[SwitchB-classifier-c2] if-match customer-vlan-id 2
[SwitchB-classifier-c2] traffic classifier c3
[SwitchB-classifier-c3] if-match customer-vlan-id 3
[SwitchB-classifier-c3] quit
[SwitchB] traffic behavior b1
[SwitchB-behavior-b1] remark service-vlan-id 111
[SwitchB-behavior-b1] traffic behavior b2
[SwitchB-behavior-b2] remark service-vlan-id 211
[SwitchB-behavior-b2] traffic behavior b3
[SwitchB-behavior-b3] remark service-vlan-id 311
[SwitchB-behavior-b3] traffic behavior b4
[SwitchB-behavior-b4] remark service-vlan-id 112
[SwitchB-behavior-b4] traffic behavior b5
[SwitchB-behavior-b5] remark service-vlan-id 212
[SwitchB-behavior-b5] traffic behavior b6
[SwitchB-behavior-b6] remark service-vlan-id 312
[SwitchB-behavior-b6] quit
[SwitchB] qos policy p1
[SwitchB-policy-p1] classifier c1 behavior b1 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation
[SwitchB-policy-p1] classifier c2 behavior b2 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation
[SwitchB-policy-p1] classifier c3 behavior b3 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation
[SwitchB-policy-p1] quit
[SwitchB] qos policy p2
[SwitchB-policy-p2] classifier c1 behavior b4 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation
[SwitchB-policy-p2] classifier c2 behavior b5 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation
[SwitchB-policy-p2] classifier c3 behavior b6 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation
[SwitchB-policy-p2] quit
# Configure Ethernet 1/0/1 to permit frames of the specified CVLANs to pass through.
[SwitchB] interface ethernet 1/0/1
[SwitchB-Ethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[SwitchB-Ethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 2 3
# Apply the uplink policy p1 to the inbound direction of Ethernet 1/0/1.
[SwitchB-Ethernet1/0/1] qos apply policy p1 inbound
# Enable the dynamic address binding function of IP Source Guard on Ethernet 1/0/1.
[SwitchB-Ethernet1/0/1] ip check source ip-address mac-address
[SwitchB-Ethernet1/0/1] quit
# Configure Ethernet 1/0/2 to permit frames of the specified CVLANs to pass through.
[SwitchB] interface ethernet 1/0/2
[SwitchB-Ethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[SwitchB-Ethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 2 3
# Apply the uplink policy p2 to the inbound direction of Ethernet 1/0/2.
[SwitchB-Ethernet1/0/2] qos apply policy p2 inbound
# Enable the dynamic address binding function of IP Source Guard on Ethernet 1/0/2.
[SwitchB-Ethernet1/0/2] ip check source ip-address mac-address
[SwitchB-Ethernet1/0/2] quit
# Configure Ethernet 1/0/3 to permit frames of the specified SVLANs to pass through.
[SwitchB] interface ethernet 1/0/3
[SwitchB-Ethernet1/0/3] port link-type trunk
[SwitchB-Ethernet1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 111 211 311 112 212 312
# Configure Ethernet 1/0/3 as a DHCP snooping trusted port.
[SwitchB-Ethernet1/0/3] dhcp-snooping trust
# Configure Ethernet 1/0/3 as an ARP trusted port.
[SwitchB-Ethernet1/0/3] arp detection trust
3) Configuration on Switch C
# Enter system view.
<SwitchC> system-view
# Enable DHCP snooping.
[SwitchC] dhcp-snooping
# Enable ARP detection on each VLAN involved in VLAN mapping.
[SwitchC] vlan 101
[SwitchC-vlan101] arp detection enable
[SwitchC-vlan101] vlan 201
[SwitchC-vlan201] arp detection enable
[SwitchC-vlan201] vlan 301
[SwitchC-vlan301] arp detection enable
[SwitchC-vlan301] vlan 102
[SwitchC-vlan102] arp detection enable
[SwitchC-vlan102] vlan 202
[SwitchC-vlan202] arp detection enable
[SwitchC-vlan202] vlan 302
[SwitchC-vlan302] arp detection enable
[SwitchC-vlan302] vlan 111
[SwitchC-vlan111] arp detection enable
[SwitchC-vlan111] vlan 211
[SwitchC-vlan211] arp detection enable
[SwitchC-vlan211] vlan 311
[SwitchC-vlan311] arp detection enable
[SwitchC-vlan311] vlan 112
[SwitchC-vlan112] arp detection enable
[SwitchC-vlan112] vlan 212
[SwitchC-vlan212] arp detection enable
[SwitchC-vlan212] vlan 312
[SwitchC-vlan312] arp detection enable
[SwitchC-vlan312] vlan 501
[SwitchC-vlan501] arp detection enable
[SwitchC-vlan501] vlan 502
[SwitchC-vlan502] arp detection enable
[SwitchC-vlan502] vlan 503
[SwitchC-vlan503] arp detection enable
[SwitchC-vlan503] quit
# Configure uplink policies to map the CVLANs that carry the same service for different users to the same SVLAN.
[SwitchC] traffic classifier c1
[SwitchC-classifier-c1] if-match customer-vlan-id 101 to 200
[SwitchC-classifier-c1] traffic classifier c2
[SwitchC-classifier-c2] if-match customer-vlan-id 201 to 300
[SwitchC-classifier-c2] traffic classifier c3
[SwitchC-classifier-c3] if-match customer-vlan-id 301 to 400
[SwitchC-classifier-c3] traffic classifier c4
[SwitchC-classifier-c4] if-match customer-vlan-id 111 to 210
[SwitchC-classifier-c4] traffic classifier c5
[SwitchC-classifier-c5] if-match customer-vlan-id 211 to 310
[SwitchC-classifier-c5] traffic classifier c6
[SwitchC-classifier-c6] if-match customer-vlan-id 311 to 410
[SwitchC-classifier-c6] quit
[SwitchC] traffic behavior b1
[SwitchC-behavior-b1] remark service-vlan-id 501
[SwitchC-behavior-b1] traffic behavior b2
[SwitchC-behavior-b2] remark service-vlan-id 502
[SwitchC-behavior-b2] traffic behavior b3
[SwitchC-behavior-b3] remark service-vlan-id 503
[SwitchC-behavior-b3] quit
[SwitchC] qos policy p1
[SwitchC-policy-p1] classifier c1 behavior b1 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation
[SwitchC-policy-p1] classifier c2 behavior b2 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation
[SwitchC-policy-p1] classifier c3 behavior b3 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation
[SwitchC-policy-p1] quit
[SwitchC] qos policy p2
[SwitchC-policy-p2] classifier c4 behavior b1 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation
[SwitchC-policy-p2] classifier c5 behavior b2 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation
[SwitchC-policy-p2] classifier c6 behavior b3 mode dot1q-tag-manipulation
[SwitchC-policy-p2] quit
# Configure Ethernet 1/0/1 to permit frames of the specified CVLANs to pass through.
[SwitchC] interface ethernet 1/0/1
[SwitchC-Ethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[SwitchC-Ethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 101 201 301 102 202 302
# Apply the uplink policy p1 to Ethernet 1/0/1.
[SwitchC-Ethernet1/0/1] qos apply policy p1 inbound
# Enable the dynamic address binding function of IP Source Guard on Ethernet 1/0/1.
[SwitchC-Ethernet1/0/1] ip check source ip-address mac-address
[SwitchC-Ethernet1/0/1] quit
# Configure Ethernet 1/0/2 to permit frames of the specified CVLANs to pass through.
[SwitchC] interface ethernet 1/0/2
[SwitchC-Ethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[SwitchC-Ethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 111 211 311 112 212 312
# Apply the uplink policy p2 to the inbound direction of Ethernet 1/0/2.
[SwitchC-Ethernet1/0/2] qos apply policy p2 inbound
# Enable the dynamic address binding function of IP Source Guard on Ethernet 1/0/2.
[SwitchC-Ethernet1/0/2] ip check source ip-address mac-address
[SwitchC-Ethernet1/0/2] quit
# Configure Ethernet 1/0/3 to permit frames of the specified SVLANs to pass through.
[SwitchC] interface ethernet 1/0/3
[SwitchC-Ethernet1/0/3] port link-type trunk
[SwitchC-Ethernet1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 501 502 503
# Configure Ethernet 1/0/3 as a DHCP snooping trusted port.
[SwitchC-Ethernet1/0/3] dhcp-snooping trust
# Configure Ethernet 1/0/3 as an ARP trusted port.
[SwitchC-Ethernet1/0/3] arp detection trust
4) Configuration on Switch D
<SwitchD> system-view
# Enable DHCP snooping.
[SwitchD] dhcp-snooping
# Configure Ethernet 1/0/1 to permit frames of the specified SVLANs to pass through.
[SwitchD] interface ethernet 1/0/1
[SwitchD-Ethernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[SwitchD-Ethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 501 502 503
# Configure Ethernet 1/0/1 as a trusted port and disable DHCP snooping to record the IP-to-MAC bindings for DHCP clients on it.
[SwitchD-Ethernet1/0/1] dhcp-snooping trust no-user-binding
![]()
On corridor switches, set the link type of the port directly connected to a PC to access or trunk. As frames sent from the PC are VLAN untagged, you need to assign the port to the SVLAN if its link type is access or configure the default VLAN on the port as the SVLAN if its link type is trunk.

