| Title | Size | Downloads |
|---|---|---|
| H3C WLAN Products Radio and Roaming Optimization Guide-6W100-book.pdf | 163.01 KB |
- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
|
|
|
H3C WLAN Products Radio and Roaming Optimization Guide |
Copyright © 2022 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
About radio and roaming optimization
In the rapid development era of information technologies, the demand for massive connections between people and things, and things and things in scenarios such as mobile office, smart education, smart healthcare, and mobile payment brings unprecedented challenges to wireless network capacities. Wi-Fi6 technologies that feature low power consumption, high bandwidth, and low latency have become the first choice of increasing enterprises for campus network access.
Besides continuous product innovation, H3C also focuses on experience optimization and developed the iRadio, iStation, iEdge, and iHeal technologies to optimize WLANs from radio performance, roaming access, application guarantee, and network automation.
Optimization principles
Considering limited band resources, ubiquitous interferences, and various scenarios, clients, as well as network services, H3C optimizes WLANs from the following aspects:
· AP selection and deployment
¡ Select AP types (for example, high-density AP, panel AP, and outdoor AP) based on the scenario.
¡ Adjust AP spacing according to user density.
¡ Leave a proper distance between an AP and an interfering device (a minimum of 3 m or 9.84 ft as a best practice).
¡ Make sure the minimum signal strength and signal-to-noise ratio are as follows:
- Minimum signal strength: ≥ –65 dBm indoor or ≥ –70 dBm outdoor.
- SNR: ≥ 25 dB indoor or ≥ 20 dB outdoor.
¡ Use DFS with caution. In low-density deployment, disable DFS as a best practice. In high-density deployment or 40M bandwidth, configure DFS as needed.
· Radio performance
¡ Use iRadio to adjust AP channel, bandwidth, and transmit power.
¡ Configure broadcast and multicast suppression.
¡ Configure fair scheduling for clients to share radio resources equally when the network is not busy.
· Client access
Use iStation to ensure that each client can access the optimal AP.
· Client roaming
Use iStation together with 802.11k, 802.11v, and 802.11r to guide clients to fast access the optimal AP.
Optimization recommendations
Radio optimization
Radio optimization is performed from the following aspects:
· Select the optimal channel and bandwidth, and set a proper transmit power.
· Adjust the transmit rate to balance coverage and roaming performance.
· Control multicast and broadcast to reduce radio resources used by unnecessary packets.
· Use load balancing and fair scheduling to improve efficiency.
Wireless transmission is vulnerable to environment changes and problems such as multipath can cause complicated signal attenuation in various directions. Therefore, the implementation of WLAN often requires a series of activities, such as thorough network planning, detailed onsite engineering surveys, and continuous optimization after deployment. Continuous optimization can be time-consuming and expensive if performed manually.
RRM is developed to provide dynamic radio adjustment. It automatically collects and analyzes wireless environment statistics, and then adjusts the following radio parameters as needed to maintain the best Internet experience:
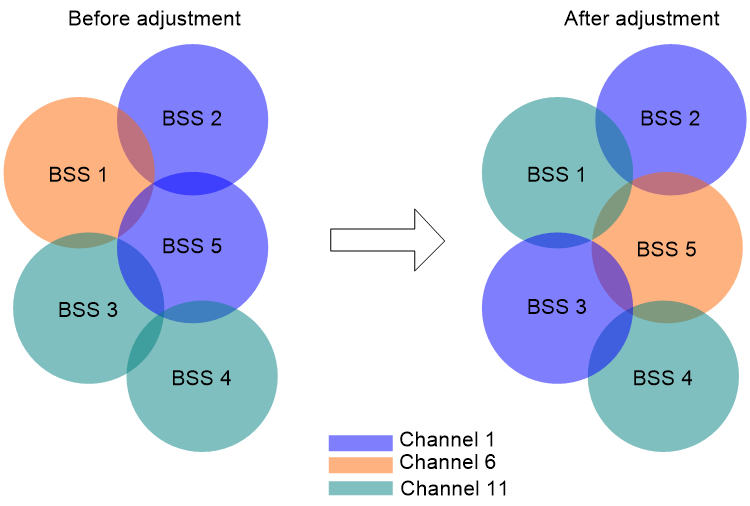
· Channel
A radio can operate in limited channels and interference might increase as the environment changes. RRM can automatically adjust the working channel of a radio to reduce interference.
Figure 1 Channel adjustment
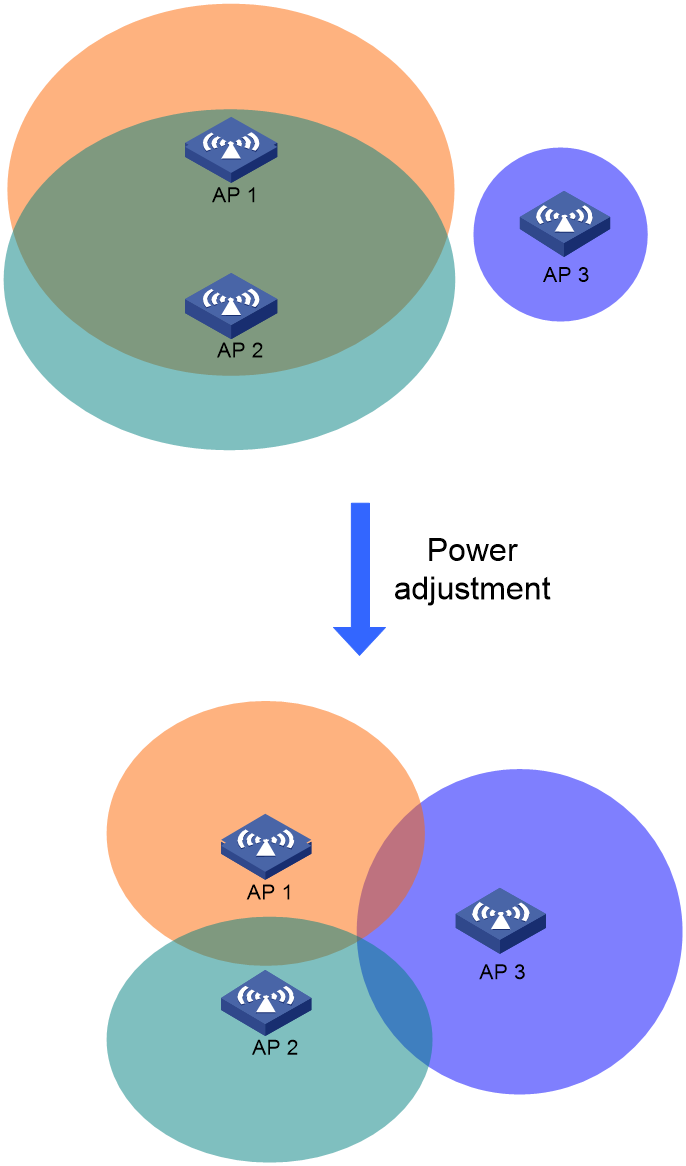
· Power
Using fixed transmit power cannot provided balanced coverage and interference performance, and can also cause client sticky or weak-signal access.
RRM can adjust the transmit power of each radio to balance coverage and roaming while minimizing inter-device interferences. You can also deploy APs at proper spacing and specify proper transmit power for the APs to ensure coverage and throughput and reduce inter-device interference.
Figure 2 Power adjustment
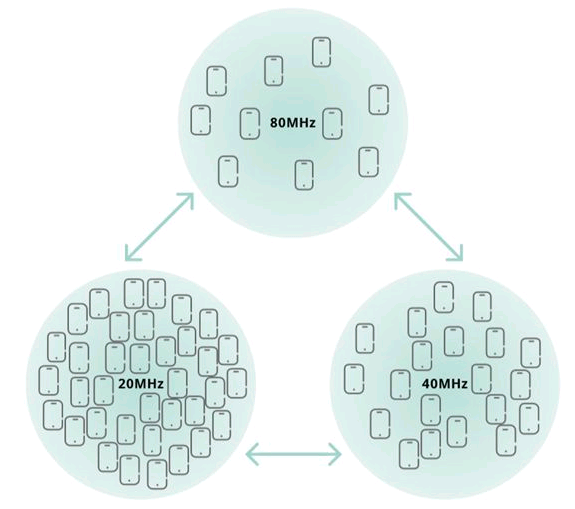
· Bandwidth
Large bandwidth increases the negotiated speed of APs and clients, but leads to strong interference if adjacent APs using the same channel.
RRM can adjust the bandwidth of each radio based on AP density, AP model, and supported channels of each radio, ensuring that APs and clients can negotiate a proper speed.
Figure 3 Bandwidth adjustment
Use Table 1 through Table 6 to identify detailed radio optimization recommendations.
Table 1 iRadio optimization recommendations
|
Item |
Default |
Recommended setting |
Remarks |
|
Transmit power |
Max-power |
Auto TPC |
N/A |
|
Channel and bandwidth |
11ac/ax: 80M · 11an: 40M · 11gn: 20M |
11ac/ax: · 20M for high density · 40M for medium density |
Use 20M for APs with three radios. |
|
Dynamic frequency adjustment (DFS) |
· Low- to medium-end ACs: Enable · High-end ACs: Disable |
Enable |
N/A |
|
Transmit power control (TPC) |
· Low- to medium-end ACs: Enable · High-end ACs: Disable |
Enable |
N/A |
|
Bandwidth adjustment |
Disabled |
· Without professional maintenance staff: Enable · With professional maintenance staff: Disable |
N/A |
|
Channel usage threshold |
60% |
60% |
If the AP suffers severe interferences but the channel usage threshold is not reached, lower the threshold. If the threshold is reached but interferences are not severe enough to affect client services, increase the threshold. |
|
Power adjustment threshold |
65 |
65 |
If signal coverage is insufficient or client signals are weak, increase the power adjustment threshold. If clients rarely roam and inter-AP interferences are severe, lower the power adjustment threshold. As a best practice, increase or lower the threshold at a step size of 3. |
|
Min transmit power |
· 2.4 GHz: 6 dBm · 5 GHz: 11 dBm |
· 2.4 GHz: 6 dBm · 5 GHz: 11 dBm |
If the radios are already using the minimum transmit power, but the difficult roaming and severe interference issues still exist, lower the minimum transmit power. You can also increase the minimum transmit power if required. |
Table 2 Transmit power optimization
|
Item |
Default |
Recommended setting |
Remarks |
|
Basic rate sets |
· 802.11a: ¡ Mandatory: 6, 12, 24 ¡ Supported: 9, 18, 36, 48, 54 · 802.11g ¡ Mandatory: 1, 2, 5.5, 11 ¡ Supported: 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54 |
High density: · 802.11a/g: ¡ Mandatory: 24 ¡ Supported: 36, 48, 54 Medium- to high-density: · 802.11a: ¡ Mandatory: 12, 24 ¡ Supported: 18, 36, 48, 54 · 802.11g: ¡ Mandatory: 11, 24 ¡ Supported: 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54 |
If over five SSIDs exist in a low-density scenario, refer to the recommendations for medium- to high-density deployment as a best practice. |
|
Max probe response transmission attempts |
3 |
3 |
Set the value to 2 if a large number of clients exist in a single BSS (for example, client production line). |
|
Multicast rate optimization |
Disabled |
Enable Configure rate settings for multicast packets separately. |
Use a high rate to transmit multicast packets as much as possible to save radio resources. |
Table 3 Broadcast and multicast optimization
|
Item |
Default |
Recommended setting |
Remarks |
|
User isolation |
Disabled |
Enable |
This feature isolates client broadcast packets completely and forbids wireless clients from directly reaching each other, which affects wireless printers and applications using Layer 2 broadcast discovery. As a best practice, use broadcast suppression instead if such services exist. |
|
Broadcast suppression |
Enabled |
Enable |
N/A |
|
Multicast optimization |
Disabled |
N/A |
This feature converts multicast packets to unicast packets to improve efficiency. |
|
Multicast rate optimization |
Disabled |
Enable |
Use a high rate to transmit multicast packets as much as possible to save radio resources. |
Table 4 Load balancing
|
Item |
Default |
Recommended setting |
Remarks |
|
Load balancing between 5GHz radios on the same AP |
Enabled |
Enable |
Available only for tri-radio devices with two 5GHz radios |
|
Load balancing between APs |
Disabled |
Enable according to AP density and online client quantity |
As a best practice, disable this feature when less than 60 clients exist. |
Table 5 Radio fair scheduling
|
Item |
Default |
Recommended setting |
Remarks |
|
Airtime-Fairness (ATF) |
Disabled and FIFO is used |
Enable according to service requirements |
Available only for Wi-Fi6 products. |
|
Client mode-based rate limit |
Disabled |
Disable |
If low-rate 802.11a/g clients exist in an 802.11ac/ax network, you can rate limit 802.11a/g clients. |
Table 6 Anti-interference optimization
|
Item |
Default |
Recommended setting |
Remarks |
|
Channel sharing |
Disable |
Enable when interferences are severe, especially on 2.4 GHz channels |
Use this feature to ignore some weak signals to improve transmission efficiency. |
Client access optimization
802.11 standards and MIMO modes supported by clients differ greatly as wireless technologies develop rapidly. If clients supporting different 802.11 standards and MIMO modes exist in the same network, advanced features such as OFDMA and MU-MIMO of 802.11ax cannot take effect to the full extent because some clients do not support these features. This affects the network transmission performance.
To resolve the issue, H3C adopts the following methods:
· Access optimization
Client access involves three stages: scanning, probe, and association. Access optimization uses beacon/probe power limit, beacon auto hiding, probe auto rejection, and association control to guide clients to the optimal AP.
· VIP user classification
This feature allows users to classify clients into level-1 VIP, level-2 VIP, and non-VIP clients and apply different policies to control clients from multiple dimensions, including access, forwarding, rate limit, resource reservation, and cloud report. This also meets the requirement of identity-based client control.
Use Table 7, Table 8, and Table 9 to identify detailed client access optimization recommendations.
|
Item |
Default |
Recommended setting |
Remarks |
|
Responding to specific broadcast probe requests |
Disabled |
Enable RSSI threshold: · 2.4 GHz: 18 dBm |
Enable the feature for 2.4 GHz radios as a best practice. |
|
Weak-signal client rejection |
Disabled |
Enable RSSI threshold: · 2.4 GHz: 18 dBm · 5 GHz: 12 dBm |
You can adjust the threshold as needed. |
|
Band navigation |
Disabled |
Enable |
N/A |
|
Item |
Default |
Recommended setting |
Remarks |
|
VIP client |
Disabled |
Enable if some clients require resource guarantee |
N/A |
|
Item |
Default |
Recommended setting |
Remarks |
|
VIP client |
Disabled |
Enable if some clients require resource guarantee |
N/A |
|
Dot11n/ac/ax only |
Disabled |
Enable according to actual capabilities of clients |
This feature limits the access of dot11a/g/b clients. Use this feature with caution. |
|
SSID hidden |
Enabled |
Enable |
N/A |
|
Weak-signal client rejection |
Disabled |
Enable RSSI threshold: · 2.4 GHz: 18 dBm · 5 GHz: 12 dBm |
You can adjust the threshold as needed. |
|
Band navigation |
Disabled |
Enable |
N/A |
Client roaming optimization
WLAN protocols do not provide any mechanism for devices to guide or trigger client roaming and a client decides for itself when to roam and where to roam to. In actual application, how clients roam differ greatly.
Client roaming optimization classifies and labels clients by client capability, for example, support for 5G, 802.11k, and 802.11v, and allows devices to guide client roaming based on the labels.
Available optimization methods include:
· Basic optimization
¡ Adjust AP coverage
¡ Adjust radio transmit power
· Advanced optimization
See Table 10, Table 11, and Table 12.
|
Item |
Default |
Recommended setting |
Remarks |
|
802.11v |
Disabled |
Enable |
N/A |
|
Roaming navigation |
Disabled |
Enable if RRM is disabled |
Set the transmit power for beacon frames and probe responses as needed. |
|
Client anti-sticky |
Disabled |
Enable |
N/A |
|
Responding to specific broadcast probe requests |
Disabled |
Enable |
Use a high rate to transmit multicast packets as much as possible to save radio resources. |
|
Item |
Default |
Recommended setting |
Remarks |
|
802.11k |
Disabled |
Enable |
N/A |
|
802.11r |
Disabled |
Enable |
Clients of an early version may not support this feature. Use this feature with caution. |
Table 12 Forced disassociation
|
Item |
Default |
Recommended setting |
Remarks |
|
Client reassociation |
Disabled |
Enable RSSI threshold: · 2.4 GHz: 18 dBm · 5 GHz: 12 dBm |
Adjust the threshold as needed. |