- Table of Contents
-
- 02-Configuration Examples
- 01-H3C_AAA_Configuration_Examples
- 02-H3C_ACL_Configuration_Examples
- 03-H3C_ATM_Configuration_Examples
- 04-H3C_IGMP_Configuration_Examples
- 05-H3C_IP_Source_Guard_Configuration_Examples
- 06-H3C_Ethernet_OAM_Configuration_Examples
- 07-H3C_NQA_Configuration_Examples
- 08-H3C_QinQ_Configuration_Examples
- 09-H3C_OSPF_Configuration_Examples
- 10-H3C_MPLS_TE_Configuration_Examples
- 11-H3C_OpenFlow_Configuration_Examples
- 12-H3C_NAT_Configuration_Examples
- 13-H3C_RBAC_Configuration_Examples
- 14-H3C_IRF_Configuration_Examples
- 15-H3C_POS_Interface_Configuration_Examples
- 16-H3C_CPOS_Interface_Configuration_Examples
- 17-H3C_DHCP_Relay_Redundancy_Configuration_Examples
- 18-H3C_DLDP_Configuration_Examples
- 19-H3C_IS-IS_Configuration_Examples
- 20-H3C_MPLS_L3VPN_Configuration_Examples
- 21-H3C_SSH_Configuration_Examples
- 22-H3C_Login_Management_Configuration_Examples
- 23-H3C_SNMP_Configuration_Examples
- 24-H3C_Priority_Marking_and_Queue_Scheduling_Configuration_Examples
- 25-H3C_Multicast_VPN_Configuration_Examples
- 26-H3C_BGP_Configuration_Examples
- 27-H3C_HoVPN_Configuration_Examples
- 28-H3C_L2TP_Configuration_Examples
- 29-H3C_VRRP_Configuration_Examples
- 30-H3C_Traffic_Filtering_Configuration_Examples
- 31-H3C_Samplers_and_IPv4_NetStream_Configuration_Examples
- 32-H3C_Software_Upgrade_Examples
- 33-H3C_MPLS_L2VPN_Configuration_Examples
- 34-H3C_NetStream_Configuration_Examples
- 35-H3C_Policy-Based_Routing_Configuration_Examples
- 36-H3C_Traffic_Policing_Configuration_Examples
- 37-H3C_BFD_Configuration_Examples
- 38-H3C_OSPFv3_Configuration_Examples
- 39-H3C_VPLS_Configuration_Examples
- 40-H3C_GTS_and_Rate_Limiting_Configuration_Examples
- 41-H3C_IPv6_IS-IS_Configuration_Examples
- 42-H3C_MPLS OAM_Configuration_Examples
- 43-H3C_BGP_Route_Selection_Configuration_Examples
- 44-H3C_IS-IS_Route_Summarization_Configuration_Examples
- 45-H3C_SRv6 Configuration Examples
- 46-H3C_Attack_Protection_Configuration_Examples
- 47-H3C_OSPF_Multi-Process_Configuration_Examples
- 48-H3C_OSPF_with_Multi-Instance_Configuration_Examples
- 49-H3C_ARP_Attack_Protection_Configuration_Examples
- 50-H3C_DHCPv6_Server_and_DHCPv6_Prefix_Client_Configuration_Examples
- 51-CE1 Interface Connection Configuration Examples
- 52-GRE Tunnel Establishment Using OSPF Configuration Examples
- 53-GRE Tunnel Establishment Using Static Routes Configuration Examples
- 54-OSPF over IPsec for Overseas Branch Access Configuration Examples
- 55-General QoS Configuration Examples
- 56-QoS Configuration Examples for the Financial Industry
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 54-OSPF over IPsec for Overseas Branch Access Configuration Examples | 199.74 KB |
Using encrypted tunnels for overseas branch access in international financial enterprises (OSPF over IPsec)
Introduction
Enterprises with international businesses usually require transnational office networks. To ensure data security and confidentiality, it is necessary to build secure office networks over the insecure international Internet. OSPF over IPsec can safeguard service packets and routing protocol packets. It encrypts and protects data transmission through IPsec tunnels, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality, and preventing network eavesdropping and tampering. In this way, international enterprises can establish secure office networks over the international Internet and achieve efficient data transmission.
Example: Using encrypted tunnels for overseas branch access in international financial enterprises (OSPF over IPsec)
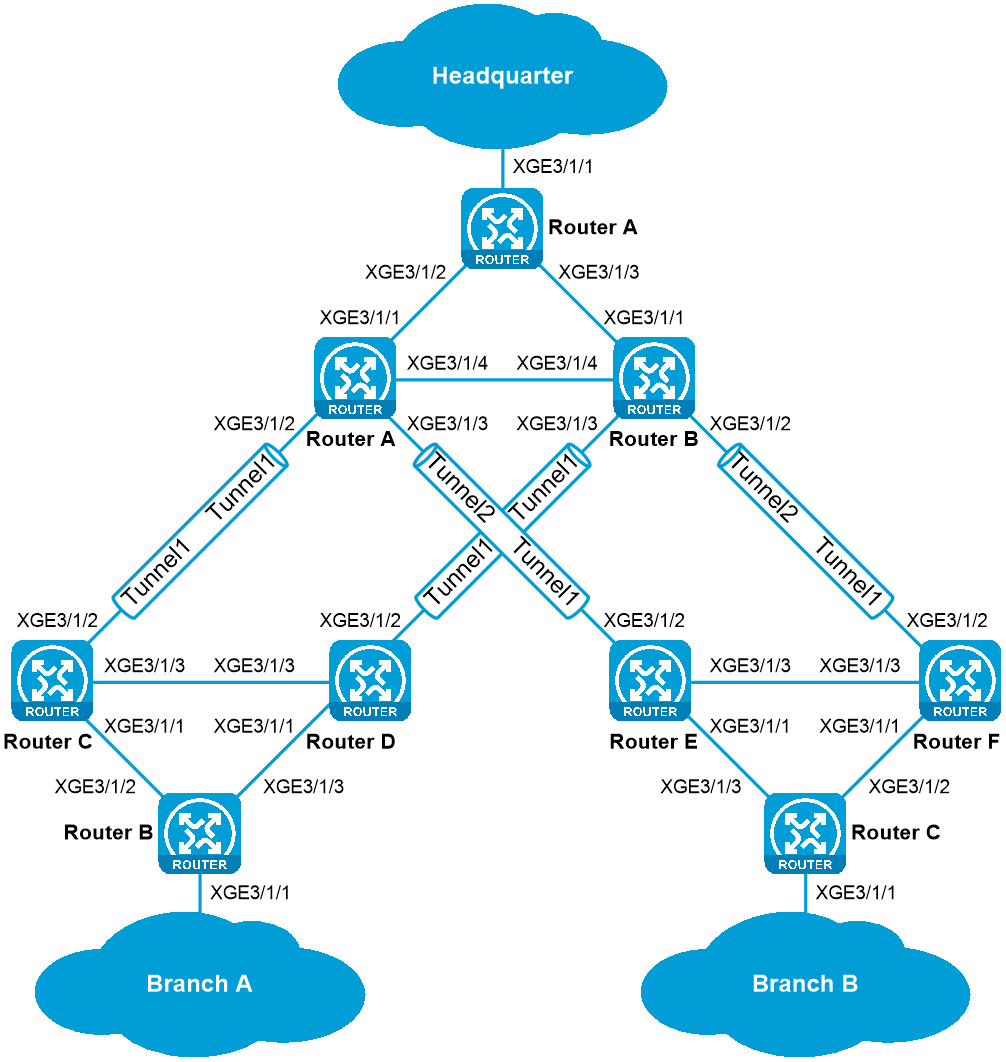
Network configuration
· Connect the headquarter to Branch A and Branch B. Establish IPsec tunnels to transmit OSPF packets and service packets, thus protecting data against network eavesdropping and tampering.
· At the headquarter, configure smaller OSPF cost values for IPsec tunnels on Router B than those on Router C to make sure service packets are transmitted preferentially through Router B, with Router C as a backup.
· At Branch A, configure smaller OSPF cost values for IPsec tunnels on Router E than those on Router F to make sure service packets are transmitted preferentially through Router E, with Router F as a backup.
· At Branch B, configure smaller OSPF cost values for IPsec tunnels on Router H than those on Router I to make sure service packets are transmitted preferentially through Router H, with Router I as a backup.
Table 1 Network diagram
|
Device |
Interface |
IP address |
|
Router A |
XGE3/1/1 |
192.168.0.1/24 |
|
XGE3/1/2 |
1.2.1.1/24 |
|
|
XGE3/1/3 |
1.3.1.1/24 |
|
|
Loopback0 |
1.1.1.1/32 |
|
|
Router B |
XGE3/1/1 |
1.2.1.2/24 |
|
XGE3/1/2 |
2.5.1.1/24 |
|
|
XGE3/1/3 |
2.8.1.1/24 |
|
|
XGE3/1/4 |
2.3.1.1/24 |
|
|
Loopback0 |
2.2.2.2/32 |
|
|
Tunnel1 |
10.2.5.1/24 |
|
|
Tunnel2 |
10.2.8.1/24 |
|
|
Router C |
XGE3/1/1 |
1.3.1.2/24 |
|
XGE3/1/2 |
3.9.1.1/24 |
|
|
XGE3/1/3 |
3.6.1.1/24 |
|
|
XGE3/1/4 |
2.3.1.2/24 |
|
|
Loopback0 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
|
|
Tunnel1 |
10.3.6.1/24 |
|
|
Tunnel2 |
10.3.9.1/24 |
|
|
Router D |
XGE3/1/1 |
192.168.1.1/24 |
|
XGE3/1/2 |
4.5.1.1/24 |
|
|
XGE3/1/3 |
4.6.1.1/24 |
|
|
Loopback0 |
4.4.4.4/32 |
|
|
Router E |
XGE3/1/1 |
4.5.1.2/24 |
|
XGE3/1/2 |
2.5.1.2/24 |
|
|
XGE3/1/3 |
5.6.1.1/24 |
|
|
Loopback0 |
5.5.5.5/32 |
|
|
Tunnel1 |
10.2.5.2/24 |
|
|
Router F |
XGE3/1/1 |
4.6.1.2/24 |
|
XGE3/1/2 |
3.6.1.2/24 |
|
|
XGE3/1/3 |
5.6.1.2/24 |
|
|
Loopback0 |
6.6.6.6/32 |
|
|
Tunnel1 |
10.3.6.2/24 |
|
|
Router G |
XGE3/1/1 |
192.168.2.1/24 |
|
XGE3/1/2 |
7.9.1.1/24 |
|
|
XGE3/1/3 |
7.8.1.1/24 |
|
|
Loopback0 |
7.7.7.7/32 |
|
|
Router H |
XGE3/1/1 |
7.8.1.2/24 |
|
XGE3/1/2 |
2.8.1.2/24 |
|
|
XGE3/1/3 |
8.9.1.1/24 |
|
|
Loopback0 |
8.8.8.8/32 |
|
|
Tunnel1 |
10.2.8.2/24 |
|
|
Router I |
XGE3/1/1 |
7.9.1.2/24 |
|
XGE3/1/2 |
3.9.1.2/24 |
|
|
XGE3/1/3 |
8.9.1.2/24 |
|
|
Loopback0 |
9.9.9.9/24 |
|
|
Tunnel1 |
10.3.9.2/24 |
Procedures
Configuring Router A
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces:
# Assign IP addresses to interfaces according to the network diagram.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] ip address 192.168.0.1 24
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
[RouterA] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] ip address 1.2.1.1 24
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] quit
[RouterA] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/3
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] ip address 1.3.1.1 24
[RouterA-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] quit
[RouterA] interface loopback 0
[RouterA-LoopBack0] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[RouterA-LoopBack0] quit
2. Configure a routing policy:
# Create IPv4 prefix list 1 to permit only routes destined for network 192.168.0.1/24.
[RouterA] ip prefix-list 1 permit 192.168.0.1 24
# Create routing policy 1 and associate node 1 of routing policy 1 with IPv4 prefix list 1.
[RouterA] route-policy 1 permit node 1
[RouterA-route-policy-1-1] if-match ip address prefix-list 1
[RouterA-route-policy-1-1] quit
3. Configure OSPF:
# Configure OSPF process 1 to advertise public network routes.
[RouterA] ospf 1
[RouterA-ospf-1] area 0
[RouterA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
[RouterA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.2.1.1 0.0.0.255
[RouterA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.3.1.1 0.0.0.255
[RouterA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[RouterA-ospf-1] import-route direct route-policy 1
[RouterA-ospf-1] quit
Configuring Router B
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces:
# Assign IP addresses to interfaces according to the network diagram.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[RouterB-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] ip address 1.2.1.2 24
[RouterB-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
[RouterB] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[RouterB-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] ip address 2.5.1.1 24
[RouterB-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] quit
[RouterB] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/3
[RouterB-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] ip address 2.8.1.1 24
[RouterB-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] quit
[RouterB] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/4
[RouterB-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/4] ip address 2.3.1.1 24
[RouterB-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/4] quit
[RouterB] interface loopback 0
[RouterB-LoopBack0] ip address 2.2.2.2 32
[RouterB-LoopBack0] quit
2. Configure an IPsec profile:
# Create IPsec transform set abc and enter its view.
[RouterB] ipsec transform-set abc
# Specify the AES algorithm in CBC mode as the encryption algorithm for ESP, which uses a 128-bit key.
[RouterB-ipsec-transform-set-abc] esp encryption-algorithm aes-cbc-128
# Specify the HMAC-SHA1 algorithm as the authentication algorithm for ESP, which uses a 160-bit key.
[RouterB-ipsec-transform-set-abc] esp authentication-algorithm sha1
[RouterB-ipsec-transform-set-abc] quit
# Create IKE keychain abc, and enter its view.
[RouterB] ike keychain abc
# Specify admin@123 in plain text as the pre-shared key used for IKE negotiation with peer 2.5.1.2.
[RouterB-ike-keychain-abc] pre-shared-key address 2.5.1.2 24 key simple admin@123
# Specify admin@123 in plain text as the pre-shared key used for IKE negotiation with peer 2.8.1.2.
[RouterB-ike-keychain-abc] pre-shared-key address 2.8.1.2 24 key simple admin@123
[RouterB-ike-keychain-abc] quit
# Create IKE profile abc and enter its view.
[RouterB] ike profile abc
# Specify IKE keychain abc for IKE profile abc.
[RouterB-ike-profile-abc] keychain abc
# Specify peer address 2.5.1.2 as the peer ID for IKE profile matching.
[RouterB-ike-profile-abc] match remote identity address 2.5.1.2 24
# Specify peer address 2.8.1.2 as the peer ID for IKE profile matching.
[RouterB-ike-profile-abc] match remote identity address 2.8.1.2 24
[RouterB-ike-profile-abc] quit
# Create IPsec profile abc with the IPsec SA setup mode as IKE.
[RouterB] ipsec profile abc isakmp
# Specify IPsec transform set abc for the IPsec profile.
[RouterB-ipsec-profile-isakmp-abc] transform-set abc
# Specify IKE profile abc for the IPsec profile.
[RouterB-ipsec-profile-isakmp-abc] ike-profile abc
[RouterB-ipsec-profile-isakmp-abc] quit
3. Configure IPsec tunnel interfaces:
# Create IPsec/IPv4 tunnel interface Tunnel 1 and enter its view.
[RouterB] interface tunnel 1 mode ipsec
# Configure an IP address for Tunnel 1.
[RouterB-Tunnel1] ip address 10.2.5.1 24
# Configure the IP address of XGE3/1/2 as the source address for Tunnel 1.
[RouterB-Tunnel1] source 2.5.1.1
Configure the IP address of XGE3/1/2 on Router E as the destination address for Tunnel 1.
[RouterB-Tunnel1] destination 2.5.1.2
# Set the OSPF cost for Tunnel 1 to 900.
[RouterB-Tunnel1] ospf cost 900
# Apply IPsec profile abc to the tunnel interface.
[RouterB-Tunnel1] tunnel protection ipsec profile abc
[RouterB-Tunnel1] quit
# Create IPsec/IPv4 tunnel interface Tunnel 2 and enter its view.
[RouterB] interface tunnel 2 mode ipsec
# Configure an IP address for Tunnel 2.
[RouterB-Tunnel2] ip address 10.2.8.1 24
# Configure the IP address of XGE3/1/3 as the source address for Tunnel 2.
[RouterB-Tunnel2] source 2.8.1.1
Configure the IP address of XGE3/1/2 on Router H as the destination address for Tunnel 2.
[RouterB-Tunnel2] destination 2.8.1.2
# Set the OSPF cost for Tunnel 2 to 900.
[RouterB-Tunnel2] ospf cost 900
# Apply IPsec profile abc to the tunnel interface.
[RouterB-Tunnel2] tunnel protection ipsec profile abc
[RouterB-Tunnel2] quit
4. Configure OSPF:
# Configure OSPF process 1 to advertise public network routes.
[RouterB] ospf 1
[RouterB-ospf-1] area 0
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.2.1.2 0.0.0.255
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.3.1.1 0.0.0.255
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[RouterB-ospf-1] area 1
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] network 10.2.5.1 0.0.0.255
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] quit
[RouterB-ospf-1] area 2
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2] network 10.2.8.1 0.0.0.255
[RouterB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2] quit
[RouterB-ospf-1] quit
Configuring Router C
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces:
# Assign IP addresses to interfaces according to the network diagram.
<RouterC> system-view
[RouterC] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[RouterC-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] ip address 1.3.1.2 24
[RouterC-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
[RouterC] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[RouterC-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] ip address 3.9.1.1 24
[RouterC-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] quit
[RouterC] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/3
[RouterC-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] ip address 3.6.1.1 24
[RouterC-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] quit
[RouterC] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/4
[RouterC-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/4] ip address 2.3.1.2 24
[RouterC-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/4] quit
[RouterC] interface loopback 0
[RouterC-LoopBack0] ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[RouterC-LoopBack0] quit
2. Configure an IPsec profile:
# Create IPsec transform set abc and enter its view.
[RouterC] ipsec transform-set abc
# Specify the AES algorithm in CBC mode as the encryption algorithm for ESP, which uses a 128-bit key.
[RouterC-ipsec-transform-set-abc] esp encryption-algorithm aes-cbc-128
# Specify the HMAC-SHA1 algorithm as the authentication algorithm for ESP, which uses a 160-bit key.
[RouterC-ipsec-transform-set-abc] esp authentication-algorithm sha1
[RouterC-ipsec-transform-set-abc] quit
# Create IKE keychain abc, and enter its view.
[RouterC] ike keychain abc
# Specify admin@123 in plain text as the pre-shared key used for IKE negotiation with peer 3.6.1.2.
[RouterC-ike-keychain-abc] pre-shared-key address 3.6.1.2 24 key simple admin@123
# Specify admin@123 in plain text as the pre-shared key used for IKE negotiation with peer 3.9.1.2.
[RouterC-ike-keychain-abc] pre-shared-key address 3.9.1.2 24 key simple admin@123
[RouterC-ike-keychain-abc] quit
# Create IKE profile abc and enter its view.
[RouterC] ike profile abc
# Specify IKE keychain abc for IKE profile abc.
[RouterC-ike-profile-abc] keychain abc
# Specify peer address 3.6.1.2 as the peer ID for IKE profile matching.
[RouterC-ike-profile-abc] match remote identity address 3.6.1.2 24
# Specify peer address 3.9.1.2 as the peer ID for IKE profile matching.
[RouterC-ike-profile-abc] match remote identity address 3.9.1.2 24
[RouterC-ike-profile-abc] quit
# Create IPsec profile abc with the IPsec SA setup mode as IKE.
[RouterC] ipsec profile abc isakmp
# Specify IPsec transform set abc for the IPsec profile.
[RouterC-ipsec-profile-isakmp-abc] transform-set abc
# Specify IKE profile abc for the IPsec profile.
[RouterC-ipsec-profile-isakmp-abc] ike-profile abc
[RouterC-ipsec-profile-isakmp-abc] quit
3. Configure IPsec tunnel interfaces:
# Create IPsec/IPv4 tunnel interface Tunnel 1 and enter its view.
[RouterC] interface tunnel 1 mode ipsec
# Configure an IP address for Tunnel 1.
[RouterC-Tunnel1] ip address 10.3.6.1 24
# Configure the IP address of XGE3/1/3 as the source address for Tunnel 1.
[RouterC-Tunnel1] source 3.6.1.1
# Configure the destination address for Tunnel 1 as the IP address of XGE3/1/2 on Router F.
[RouterC-Tunnel1] destination 3.6.1.2
# Set the OSPF cost for Tunnel 1 to 1000.
[RouterC-Tunnel1] ospf cost 1000
# Apply IPsec profile abc to the tunnel interface.
[RouterC-Tunnel1] tunnel protection ipsec profile abc
[RouterC-Tunnel1] quit
# Create IPsec/IPv4 tunnel interface Tunnel 2 and enter its view.
[RouterC] interface tunnel 2 mode ipsec
# Configure an IP address for Tunnel 2.
[RouterC-Tunnel2] ip address 10.3.9.1 24
# Configure the IP address of XGE3/1/2 as the source address for Tunnel 2.
[RouterC-Tunnel2] source 3.9.1.1
Configure the IP address of XGE3/1/2 on Router I as the destination address for Tunnel 2.
[RouterC-Tunnel2] destination 3.9.1.2
# Set the OSPF cost for Tunnel 2 to 1000.
[RouterC-Tunnel2] ospf cost 1000
# Apply IPsec profile abc to the tunnel interface.
[RouterC-Tunnel2] tunnel protection ipsec profile abc
[RouterC-Tunnel2] quit
4. Configure OSPF:
# Configure OSPF process 1 to advertise public network routes.
[RouterC] ospf 1
[RouterC-ospf-1] area 0
[RouterC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.3.1.2 0.0.0.255
[RouterC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.3.1.2 0.0.0.255
[RouterC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
[RouterC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[RouterC-ospf-1] area 1
[RouterC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] network 10.3.6.1 0.0.0.255
[RouterC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] quit
[RouterC-ospf-1] area 2
[RouterC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2] network 10.3.9.1 0.0.0.255
[RouterC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2] quit
[RouterC-ospf-1] quit
Configuring Router D
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces:
# Assign IP addresses to interfaces according to the network diagram.
<RouterD> system-view
[RouterD] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[RouterD-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] ip address 192.168.1.1 24
[RouterD-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
[RouterD] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[RouterD-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] ip address 4.5.1.1 24
[RouterD-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] quit
[RouterD] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/3
[RouterD-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] ip address 4.6.1.1 24
[RouterD-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] quit
[RouterD] interface loopback 0
[RouterD-LoopBack0] ip address 4.4.4.4 32
[RouterD-LoopBack0] quit
2. Configure a routing policy:
# Create IPv4 prefix list 1 to permit only routes destined for network 192.168.1.1/24.
[RouterD] ip prefix-list 1 permit 192.168.1.1 24
# Create routing policy 1 and associate node 1 of routing policy 1 with IPv4 prefix list 1.
[RouterD] route-policy 1 permit node 1
[RouterD-route-policy-1-1] if-match ip address prefix-list 1
[RouterD-route-policy-1-1] quit
3. Configure OSPF:
# Configure OSPF process 1 to advertise public network routes.
[RouterD] ospf 1
[RouterD-ospf-1] area 1
[RouterD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0
[RouterD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] network 4.5.1.1 0.0.0.255
[RouterD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] network 4.6.1.1 0.0.0.255
[RouterD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] quit
[RouterD-ospf-1] import-route direct route-policy 1
[RouterD-ospf-1] quit
Configuring Router E
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces:
# Assign IP addresses to interfaces according to the network diagram.
<RouterE> system-view
[RouterE] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[RouterE-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] ip address 4.5.1.2 24
[RouterE-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
[RouterE] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[RouterE-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] ip address 2.5.1.2 24
[RouterE-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] quit
[RouterE] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/3
[RouterE-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] ip address 5.6.1.1 24
[RouterE-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] quit
[RouterE] interface loopback 0
[RouterE-LoopBack0] ip address 5.5.5.5 32
[RouterE-LoopBack0] quit
2. Configure an IPsec profile:
# Create IPsec transform set abc and enter its view.
[RouterE] ipsec transform-set abc
# Specify the AES algorithm in CBC mode as the encryption algorithm for ESP, which uses a 128-bit key.
[RouterE-ipsec-transform-set-abc] esp encryption-algorithm aes-cbc-128
# Specify the HMAC-SHA1 algorithm as the authentication algorithm for ESP, which uses a 160-bit key.
[RouterE-ipsec-transform-set-abc] esp authentication-algorithm sha1
[RouterE-ipsec-transform-set-abc] quit
# Create IKE keychain abc, and enter its view.
[RouterE] ike keychain abc
# Specify admin@123 in plain text as the pre-shared key used for IKE negotiation with peer 2.5.1.1.
[RouterE-ike-keychain-abc] pre-shared-key address 2.5.1.1 24 key simple admin@123
[RouterE-ike-keychain-abc] quit
# Create IKE profile abc and enter its view.
[RouterE] ike profile abc
# Specify IKE keychain abc for IKE profile abc.
[RouterE-ike-profile-abc] keychain abc
# Specify peer address 2.5.1.1 as the peer ID for IKE profile matching.
[RouterE-ike-profile-abc] match remote identity address 2.5.1.1 24
[RouterE-ike-profile-abc] quit
# Create IPsec profile abc with the IPsec SA setup mode as IKE.
[RouterE] ipsec profile abc isakmp
# Specify IPsec transform set abc for the IPsec profile.
[RouterE-ipsec-profile-isakmp-abc] transform-set abc
# Specify IKE profile abc for the IPsec profile.
[RouterE-ipsec-profile-isakmp-abc] ike-profile abc
[RouterE-ipsec-profile-isakmp-abc] quit
3. Configure IPsec tunnel interfaces:
# Create IPsec/IPv4 tunnel interface Tunnel 1 and enter its view.
[RouterE] interface tunnel 1 mode ipsec
# Configure an IP address for Tunnel 1.
[RouterE-Tunnel1] ip address 10.2.5.2 24
# Configure the IP address of XGE3/1/2 as the source address for Tunnel 1.
[RouterE-Tunnel1] source 2.5.1.2
Configure the IP address of XGE3/1/2 on Router B as the destination address for Tunnel 1.
[RouterE-Tunnel1] destination 2.5.1.1
# Set the OSPF cost for Tunnel 1 to 900.
[RouterE-Tunnel1] ospf cost 900
# Apply IPsec profile abc to the tunnel interface.
[RouterE-Tunnel1] tunnel protection ipsec profile abc
[RouterE-Tunnel1] quit
4. Configure OSPF:
# Configure OSPF process 1 to advertise public network routes.
[RouterE] ospf 1
[RouterE-ospf-1] area 1
[RouterE-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] network 5.5.5.5 0.0.0.0
[RouterE-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] network 4.5.1.2 0.0.0.255
[RouterE-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] network 5.6.1.1 0.0.0.255
[RouterE-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] network 10.2.5.2 0.0.0.255
[RouterE-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] quit
[RouterE-ospf-1] quit
Configuring Router F
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces:
# Assign IP addresses to interfaces according to the network diagram.
<RouterF> system-view
[RouterF] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[RouterF-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] ip address 4.6.1.2 24
[RouterF-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
[RouterF] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[RouterF-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] ip address 3.6.1.2 24
[RouterF-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] quit
[RouterF] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/3
[RouterF-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] ip address 5.6.1.2 24
[RouterF-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] quit
[RouterF] interface loopback 0
[RouterF-LoopBack0] ip address 6.6.6.6 32
[RouterF-LoopBack0] quit
2. Configure an IPsec profile:
# Create IPsec transform set abc and enter its view.
[RouterF] ipsec transform-set abc
# Specify the AES algorithm in CBC mode as the encryption algorithm for ESP, which uses a 128-bit key.
[RouterF-ipsec-transform-set-abc] esp encryption-algorithm aes-cbc-128
# Specify the HMAC-SHA1 algorithm as the authentication algorithm for ESP, which uses a 160-bit key.
[RouterF-ipsec-transform-set-abc] esp authentication-algorithm sha1
[RouterF-ipsec-transform-set-abc] quit
# Create IKE keychain abc, and enter its view.
[RouterF] ike keychain abc
# Specify admin@123 in plain text as the pre-shared key used for IKE negotiation with peer 3.6.1.1.
[RouterF-ike-keychain-abc] pre-shared-key address 3.6.1.1 24 key simple admin@123
[RouterF-ike-keychain-abc] quit
# Create IKE profile abc and enter its view.
[RouterF] ike profile abc
# Specify IKE keychain abc for IKE profile abc.
[RouterF-ike-profile-abc] keychain abc
# Specify peer address 3.6.1.1 as the peer ID for IKE profile matching.
[RouterF-ike-profile-abc] match remote identity address 3.6.1.1 24
[RouterF-ike-profile-abc] quit
# Create IPsec profile abc with the IPsec SA setup mode as IKE.
[RouterF] ipsec profile abc isakmp
# Specify IPsec transform set abc for the IPsec profile.
[RouterF-ipsec-profile-isakmp-abc] transform-set abc
# Specify IKE profile abc for the IPsec profile.
[RouterF-ipsec-profile-isakmp-abc] ike-profile abc
[RouterF-ipsec-profile-isakmp-abc] quit
3. Configure IPsec tunnel interfaces:
# Create IPsec/IPv4 tunnel interface Tunnel 1 and enter its view.
[RouterF] interface tunnel 1 mode ipsec
# Configure an IP address for Tunnel 1.
[RouterF-Tunnel1] ip address 10.3.6.2 24
# Configure the IP address of XGE3/1/2 as the source address for Tunnel 1.
[RouterF-Tunnel1] source 3.6.1.2
Configure the IP address of XGE3/1/3 on Router C as the destination address for Tunnel 1.
[RouterF-Tunnel1] destination 3.6.1.1
# Set the OSPF cost for Tunnel 1 to 1000.
[RouterF-Tunnel1] ospf cost 1000
# Apply IPsec profile abc to the tunnel interface.
[RouterF-Tunnel1] tunnel protection ipsec profile abc
[RouterF-Tunnel1] quit
4. Configure OSPF:
# Configure OSPF process 1 to advertise public network routes.
[RouterF] ospf 1
[RouterF-ospf-1] area 1
[RouterF-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] network 6.6.6.6 0.0.0.0
[RouterF-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] network 4.6.1.2 0.0.0.255
[RouterF-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] network 5.6.1.2 0.0.0.255
[RouterF-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] network 10.3.6.2 0.0.0.255
[RouterF-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1] quit
[RouterF-ospf-1] quit
Configuring Router G
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces:
# Assign IP addresses to interfaces according to the network diagram.
<RouterG> system-view
[RouterG] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[RouterG-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] ip address 192.168.2.1 24
[RouterG-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
[RouterG] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[RouterG-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] ip address 7.9.1.1 24
[RouterG-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] quit
[RouterG] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/3
[RouterG-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] ip address 7.8.1.1 24
[RouterG-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] quit
[RouterG] interface loopback 0
[RouterG-LoopBack0] ip address 7.7.7.7 32
[RouterG-LoopBack0] quit
2. Configure a routing policy:
# Create IPv4 prefix list 1 to permit only routes destined for network 192.168.1.1/24.
[RouterG] ip prefix-list 1 permit 192.168.2.1 24
# Create routing policy 1 and associate node 1 of routing policy 1 with IPv4 prefix list 1.
[RouterG] route-policy 1 permit node 1
[RouterG-route-policy-1-1] if-match ip address prefix-list 1
[RouterG-route-policy-1-1] quit
3. Configure OSPF:
# Configure OSPF process 1 to advertise public network routes.
[RouterG] ospf 1
[RouterG-ospf-1] area 2
[RouterG-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2] network 7.7.7.7 0.0.0.0
[RouterG-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2] network 7.9.1.1 0.0.0.255
[RouterG-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2] network 7.8.1.1 0.0.0.255
[RouterG-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2] quit
[RouterG-ospf-1] import-route direct route-policy 1
[RouterG-ospf-1] quit
Configuring Router H
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces:
# Assign IP addresses to interfaces according to the network diagram.
<RouterH> system-view
[RouterH] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[RouterH-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] ip address 7.8.1.2 24
[RouterH-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
[RouterH] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[RouterH-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] ip address 2.8.1.2 24
[RouterH-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] quit
[RouterH] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/3
[RouterH-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] ip address 8.9.1.1 24
[RouterH-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] quit
[RouterH] interface loopback 0
[RouterH-LoopBack0] ip address 8.8.8.8 32
[RouterH-LoopBack0] quit
2. Configure an IPsec profile:
# Create IPsec transform set abc and enter its view.
[RouterH] ipsec transform-set abc
# Specify the AES algorithm in CBC mode as the encryption algorithm for ESP, which uses a 128-bit key.
[RouterH-ipsec-transform-set-abc] esp encryption-algorithm aes-cbc-128
# Specify the HMAC-SHA1 algorithm as the authentication algorithm for ESP, which uses a 160-bit key.
[RouterH-ipsec-transform-set-abc] esp authentication-algorithm sha1
[RouterH-ipsec-transform-set-abc] quit
# Create IKE keychain abc, and enter its view.
[RouterH] ike keychain abc
# Specify admin@123 in plain text as the pre-shared key used for IKE negotiation with peer 2.8.1.1.
[RouterH-ike-keychain-abc] pre-shared-key address 2.8.1.1 24 key simple admin@123
[RouterH-ike-keychain-abc] quit
# Create IKE profile abc and enter its view.
[RouterH] ike profile abc
# Specify IKE keychain abc for IKE profile abc.
[RouterH-ike-profile-abc] keychain abc
# Specify peer address 2.8.1.1 as the peer ID for IKE profile matching.
[RouterH-ike-profile-abc] match remote identity address 2.8.1.1 24
[RouterH-ike-profile-abc] quit
# Create IPsec profile abc with the IPsec SA setup mode as IKE.
[RouterH] ipsec profile abc isakmp
# Specify IPsec transform set abc for the IPsec profile.
[RouterH-ipsec-profile-isakmp-abc] transform-set abc
# Specify IKE profile abc for the IPsec profile.
[RouterH-ipsec-profile-isakmp-abc] ike-profile abc
[RouterH-ipsec-profile-isakmp-abc] quit
3. Configure IPsec tunnel interfaces:
# Create IPsec/IPv4 tunnel interface Tunnel 1 and enter its view.
[RouterH] interface tunnel 1 mode ipsec
# Configure an IP address for Tunnel 1.
[RouterH-Tunnel1] ip address 10.2.8.2 24
# Configure the IP address of XGE3/1/2 as the source address for Tunnel 1.
[RouterH-Tunnel1] source 2.8.1.2
Configure the IP address of XGE3/1/3 on Router B as the destination address for Tunnel 1.
[RouterH-Tunnel1] destination 2.8.1.1
# Set the OSPF cost for Tunnel 1 to 900.
[RouterH-Tunnel1] ospf cost 900
# Apply IPsec profile abc to the tunnel interface.
[RouterH-Tunnel1] tunnel protection ipsec profile abc
[RouterH-Tunnel1] quit
4. Configure OSPF:
# Configure OSPF process 1 to advertise public network routes.
[RouterH] ospf 1
[RouterH-ospf-1] area 2
[RouterH-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2] network 8.8.8.8 0.0.0.0
[RouterH-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2] network 7.8.1.2 0.0.0.255
[RouterH-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2] network 8.9.1.1 0.0.0.255
[RouterH-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2] network 10.2.8.2 0.0.0.255
[RouterH-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2] quit
[RouterH-ospf-1] quit
Configuring Router I
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces:
# Assign IP addresses to interfaces according to the network diagram.
<RouterI> system-view
[RouterI] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[RouterI-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] ip address 7.9.1.2 24
[RouterI-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
[RouterI] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[RouterI-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] ip address 3.9.1.2 24
[RouterI-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] quit
[RouterI] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/3
[RouterI-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] ip address 8.9.1.2 24
[RouterI-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] quit
[RouterI] interface loopback 0
[RouterI-LoopBack0] ip address 9.9.9.9 24
[RouterI-LoopBack0] quit
2. Configure an IPsec profile:
# Create IPsec transform set abc and enter its view.
[RouterI] ipsec transform-set abc
# Specify the AES algorithm in CBC mode as the encryption algorithm for ESP, which uses a 128-bit key.
[RouterI-ipsec-transform-set-abc] esp encryption-algorithm aes-cbc-128
# Specify the HMAC-SHA1 algorithm as the authentication algorithm for ESP, which uses a 160-bit key.
[RouterI-ipsec-transform-set-abc] esp authentication-algorithm sha1
[RouterI-ipsec-transform-set-abc] quit
# Create IKE keychain abc, and enter its view.
[RouterI] ike keychain abc
# Specify admin@123 in plain text as the pre-shared key used for IKE negotiation with peer 3.9.1.1.
[RouterI-ike-keychain-abc] pre-shared-key address 3.9.1.1 24 key simple admin@123
[RouterI-ike-keychain-abc] quit
# Create IKE profile abc and enter its view.
[RouterI] ike profile abc
# Specify IKE keychain abc for IKE profile abc.
[RouterI-ike-profile-abc] keychain abc
# Specify peer address 3.9.1.1 as the peer ID for IKE profile matching.
[RouterI-ike-profile-abc] match remote identity address 3.9.1.1 24
[RouterI-ike-profile-abc] quit
# Create IPsec profile abc with the IPsec SA setup mode as IKE.
[RouterI] ipsec profile abc isakmp
# Specify IPsec transform set abc for the IPsec profile.
[RouterI-ipsec-profile-isakmp-abc] transform-set abc
# Specify IKE profile abc for the IPsec profile.
[RouterI-ipsec-profile-isakmp-abc] ike-profile abc
[RouterI-ipsec-profile-isakmp-abc] quit
3. Configure IPsec tunnel interfaces:
# Create IPsec/IPv4 tunnel interface Tunnel 1 and enter its view.
[RouterI] interface tunnel 1 mode ipsec
# Configure an IP address for Tunnel 1.
[RouterI-Tunnel1] ip address 10.3.9.2 24
# Configure the IP address of XGE3/1/2 as the source address for Tunnel 1.
[RouterI-Tunnel1] source 3.9.1.2
Configure the IP address of XGE3/1/2 on Router C as the destination address for Tunnel 1.
[RouterI-Tunnel1] destination 3.9.1.1
# Set the OSPF cost for Tunnel 1 to 1000.
[RouterI-Tunnel1] ospf cost 1000
# Apply IPsec profile abc to the tunnel interface.
[RouterI-Tunnel1] tunnel protection ipsec profile abc
[RouterI-Tunnel1] quit
4. Configure OSPF:
# Configure OSPF process 1 to advertise public network routes.
[RouterI] ospf 1
[RouterI-ospf-1] area 2
[RouterI-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2] network 9.9.9.9 0.0.0.0
[RouterI-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2] network 7.9.1.2 0.0.0.255
[RouterI-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2] network 8.9.1.2 0.0.0.255
[RouterI-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2] network 10.3.9.2 0.0.0.255
[RouterI-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2] quit
[RouterI-ospf-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# On Router A, use the ping command to ping the addresses of Branch A and Branch B.
[RouterA] ping -a 192.168.0.1 192.168.1.1
Ping 192.168.1.1 (192.168.1.1) from 192.168.0.1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 192.168.1.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=253 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 192.168.1.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=253 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 192.168.1.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=253 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 192.168.1.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=253 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 192.168.1.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=253 time=1.000 ms
--- Ping statistics for 192.168.1.1 ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/1.600/2.000/0.490 ms
[RouterA]%Jul 17 14:56:49:694 2023 RouterA PING/6/PING_STATISTICS: Ping statistics for 192.168.1.1: 5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss, round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/1.600/2.000/0.490 ms.
[RouterA] ping -a 192.168.0.1 192.168.2.1
Ping 192.168.2.1 (192.168.2.1) from 192.168.0.1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 192.168.2.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=253 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 192.168.2.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=253 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 192.168.2.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=253 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 192.168.2.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=253 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 192.168.2.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=253 time=1.000 ms
--- Ping statistics for 192.168.2.1 ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/1.400/2.000/0.490 ms
[RouterA]%Jul 17 14:56:54:783 2023 RouterA PING/6/PING_STATISTICS: Ping statistics for 192.168.2.1: 5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss, round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/1.400/2.000/0.490 ms.
The output shows that the headquarter can access both of the overseas branches.
# On Router A, display routes destined for 192.168.1.1/24 and 192.168.2.1/24.
[RouterA] display ip routing-table 192.168.1.1 24
Summary count : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
192.168.1.0/24 O_ASE2 150 902 1.2.1.2 XGE3/1/2
[RouterA] display ip routing-table 192.168.2.1 24
Summary count : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
192.168.2.0/24 O_ASE2 150 902 1.2.1.2 XGE3/1/2
# On Router B, display routes destined for 192.168.1.1/24 and 192.168.2.1/24.
[RouterB] display ip routing-table 192.168.1.1 24
Summary count : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
192.168.1.0/24 O_ASE2 150 901 10.2.5.2 Tun1
[RouterB] display ip routing-table 192.168.2.1 24
Summary count : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
192.168.2.0/24 O_ASE2 150 901 10.2.8.2 Tun2
The output shows that Router A's routes destined for Branch A and Branch B go through the IPsec tunnels of Router B.
# Shut down the IPsec tunnels on Router B, and then display routes destined for 192.168.1.1/24 and 192.168.2.1/24 on Router A.
[RouterA] display ip routing-table 192.168.1.1 24
Summary count : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
192.168.1.0/24 O_ASE2 150 1002 1.3.1.2 XGE3/1/3
[RouterA] display ip routing-table 192.168.2.1 24
Summary count : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
192.168.2.0/24 O_ASE2 150 1002 1.3.1.2 XGE3/1/3
# On Router C, display routes destined for 192.168.1.1/24 and 192.168.2.1/24.
[RouterC] display ip routing-table 192.168.1.1 24
Summary count : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
192.168.1.0/24 O_ASE2 150 1001 10.3.6.2 Tun1
[RouterC] display ip routing-table 192.168.2.1 24
Summary count : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
192.168.2.0/24 O_ASE2 150 1001 10.3.9.2 Tun2
The output shows that after the IPsec tunnels of Router B fail, Router C operates as a backup to forward the traffic between the headquarter and the branches.
Display routes destined for 192.168.0.1/24 on the routers connected to Branch A and Branch B in the same way as mentioned above.
Configuration files
Router A
#
ospf 1
import-route direct route-policy 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
network 1.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 1.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1
ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2
ip address 1.2.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3
ip address 1.3.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
route-policy 1 permit node 1
if-match ip address prefix-list 1
#
ip prefix-list 1 index 10 permit 192.168.0.0 24
#
Router B
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 1.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
network 2.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
area 0.0.0.1
network 10.2.5.0 0.0.0.255
area 0.0.0.2
network 10.2.8.0 0.0.0.255
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1
ip address 1.2.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2
ip address 2.5.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3
ip address 2.8.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/4
ip address 2.3.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Tunnel1 mode ipsec
ip address 10.2.5.1 255.255.255.0
ospf cost 900
source 2.5.1.1
destination 2.5.1.2
tunnel protection ipsec profile abc
#
interface Tunnel2 mode ipsec
ip address 10.2.8.1 255.255.255.0
ospf cost 900
source 2.8.1.1
destination 2.8.1.2
tunnel protection ipsec profile abc
#
ipsec transform-set abc
esp encryption-algorithm aes-cbc-128
esp authentication-algorithm sha1
#
ipsec profile abc isakmp
transform-set abc
ike-profile abc
#
ike profile abc
keychain abc
match remote identity address 2.5.1.2 255.255.255.0
match remote identity address 2.8.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
ike keychain abc
pre-shared-key address 2.5.1.2 255.255.255.0 key simple admin@123
pre-shared-key address 2.8.1.2 255.255.255.0 key simple admin@123
#
Router C
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 1.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 2.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
area 0.0.0.1
network 10.3.6.0 0.0.0.255
area 0.0.0.2
network 10.3.9.0 0.0.0.255
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1
ip address 1.3.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2
ip address 3.9.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3
ip address 3.6.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/4
ip address 2.3.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface Tunnel1 mode ipsec
ip address 10.3.6.1 255.255.255.0
ospf cost 1000
source 3.6.1.1
destination 3.6.1.2
tunnel protection ipsec profile abc
#
interface Tunnel2 mode ipsec
ip address 10.3.9.1 255.255.255.0
ospf cost 1000
source 3.9.1.1
destination 3.9.1.2
tunnel protection ipsec profile abc
#
ipsec transform-set abc
esp encryption-algorithm aes-cbc-128
esp authentication-algorithm sha1
#
ipsec profile abc isakmp
transform-set abc
ike-profile abc
#
ike profile abc
keychain abc
match remote identity address 3.6.1.2 255.255.255.0
match remote identity address 3.9.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
ike keychain abc
pre-shared-key address 3.6.1.2 255.255.255.0 key simple admin@123
pre-shared-key address 3.9.1.2 255.255.255.0 key simple admin@123
#
Router D
#
ospf 1
import-route direct route-policy 1
area 0.0.0.1
network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0
network 4.5.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 4.6.1.0 0.0.0.255
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2
ip address 4.5.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3
ip address 4.6.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
route-policy 1 permit node 1
if-match ip address prefix-list 1
#
ip prefix-list 1 index 10 permit 192.168.1.0 24
#
Router E
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.1
network 4.5.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 5.5.5.5 0.0.0.0
network 5.6.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 10.2.5.0 0.0.0.255
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1
ip address 4.5.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2
ip address 2.5.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3
ip address 5.6.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Tunnel1 mode ipsec
ip address 10.2.5.2 255.255.255.0
ospf cost 900
source 2.5.1.2
destination 2.5.1.1
tunnel protection ipsec profile abc
#
ipsec transform-set abc
esp encryption-algorithm aes-cbc-128
esp authentication-algorithm sha1
#
ipsec profile abc isakmp
transform-set abc
ike-profile abc
#
ike profile abc
keychain abc
match remote identity address 2.5.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
ike keychain abc
pre-shared-key address 2.5.1.1 255.255.255.0 key simple admin@123
#
Router F
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.1
network 4.6.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 5.6.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 6.6.6.6 0.0.0.0
network 10.3.6.0 0.0.0.255
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 6.6.6.6 255.255.255.255
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1
ip address 4.6.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2
ip address 3.6.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3
ip address 5.6.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface Tunnel1 mode ipsec
ip address 10.3.6.2 255.255.255.0
ospf cost 1000
source 3.6.1.2
destination 3.6.1.1
tunnel protection ipsec profile abc
#
ipsec transform-set abc
esp encryption-algorithm aes-cbc-128
esp authentication-algorithm sha1
#
ipsec profile abc isakmp
transform-set abc
ike-profile abc
#
ike profile abc
keychain abc
match remote identity address 3.6.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
ike keychain abc
pre-shared-key address 3.6.1.1 255.255.255.0 key simple admin@123
#
Router G
#
ospf 1
import-route direct route-policy 1
area 0.0.0.2
network 7.7.7.7 0.0.0.0
network 7.8.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 7.9.1.0 0.0.0.255
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 7.7.7.7 255.255.255.255
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2
ip address 7.9.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3
ip address 7.8.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
route-policy 1 permit node 1
if-match ip address prefix-list 1
#
ip prefix-list 1 index 10 permit 192.168.2.0 24
#
Router H
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.2
network 7.8.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 8.8.8.8 0.0.0.0
network 8.9.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 10.2.8.0 0.0.0.255
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 8.8.8.8 255.255.255.255
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1
ip address 7.8.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2
ip address 2.8.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3
ip address 8.9.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Tunnel1 mode ipsec
ip address 10.2.8.2 255.255.255.0
ospf cost 900
source 2.8.1.2
destination 2.8.1.1
tunnel protection ipsec profile abc
#
ipsec transform-set abc
esp encryption-algorithm aes-cbc-128
esp authentication-algorithm sha1
#
ipsec profile abc isakmp
transform-set abc
ike-profile abc
#
ike profile abc
keychain abc
match remote identity address 2.8.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
ike keychain abc
pre-shared-key address 2.8.1.1 255.255.255.0 key simple admin@123
#
Router I
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.2
network 7.9.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 8.9.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 9.9.9.9 0.0.0.0
network 10.3.9.0 0.0.0.255
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 9.9.9.9 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1
ip address 7.9.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2
ip address 3.9.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3
ip address 8.9.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface Tunnel1 mode ipsec
ip address 10.3.9.2 255.255.255.0
ospf cost 1000
source 3.9.1.2
destination 3.9.1.1
tunnel protection ipsec profile abc
#
ipsec transform-set abc
esp encryption-algorithm aes-cbc-128
esp authentication-algorithm sha1
#
ipsec profile abc isakmp
transform-set abc
ike-profile abc
#
ike profile abc
keychain abc
match remote identity address 3.9.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
ike keychain abc
pre-shared-key address 3.9.1.1 255.255.255.0 key simple admin@123
#