- Table of Contents
-
- 02-Configuration Examples
- 01-H3C_AAA_Configuration_Examples
- 02-H3C_ACL_Configuration_Examples
- 03-H3C_ATM_Configuration_Examples
- 04-H3C_IGMP_Configuration_Examples
- 05-H3C_IP_Source_Guard_Configuration_Examples
- 06-H3C_Ethernet_OAM_Configuration_Examples
- 07-H3C_NQA_Configuration_Examples
- 08-H3C_QinQ_Configuration_Examples
- 09-H3C_OSPF_Configuration_Examples
- 10-H3C_MPLS_TE_Configuration_Examples
- 11-H3C_OpenFlow_Configuration_Examples
- 12-H3C_NAT_Configuration_Examples
- 13-H3C_RBAC_Configuration_Examples
- 14-H3C_IRF_Configuration_Examples
- 15-H3C_POS_Interface_Configuration_Examples
- 16-H3C_CPOS_Interface_Configuration_Examples
- 17-H3C_DHCP_Relay_Redundancy_Configuration_Examples
- 18-H3C_DLDP_Configuration_Examples
- 19-H3C_IS-IS_Configuration_Examples
- 20-H3C_MPLS_L3VPN_Configuration_Examples
- 21-H3C_SSH_Configuration_Examples
- 22-H3C_Login_Management_Configuration_Examples
- 23-H3C_SNMP_Configuration_Examples
- 24-H3C_Priority_Marking_and_Queue_Scheduling_Configuration_Examples
- 25-H3C_Multicast_VPN_Configuration_Examples
- 26-H3C_BGP_Configuration_Examples
- 27-H3C_HoVPN_Configuration_Examples
- 28-H3C_L2TP_Configuration_Examples
- 29-H3C_VRRP_Configuration_Examples
- 30-H3C_Traffic_Filtering_Configuration_Examples
- 31-H3C_Samplers_and_IPv4_NetStream_Configuration_Examples
- 32-H3C_Software_Upgrade_Examples
- 33-H3C_MPLS_L2VPN_Configuration_Examples
- 34-H3C_NetStream_Configuration_Examples
- 35-H3C_Policy-Based_Routing_Configuration_Examples
- 36-H3C_Traffic_Policing_Configuration_Examples
- 37-H3C_BFD_Configuration_Examples
- 38-H3C_OSPFv3_Configuration_Examples
- 39-H3C_VPLS_Configuration_Examples
- 40-H3C_GTS_and_Rate_Limiting_Configuration_Examples
- 41-H3C_IPv6_IS-IS_Configuration_Examples
- 42-H3C_MPLS OAM_Configuration_Examples
- 43-H3C_BGP_Route_Selection_Configuration_Examples
- 44-H3C_IS-IS_Route_Summarization_Configuration_Examples
- 45-H3C_SRv6 Configuration Examples
- 46-H3C_Attack_Protection_Configuration_Examples
- 47-H3C_OSPF_Multi-Process_Configuration_Examples
- 48-H3C_OSPF_with_Multi-Instance_Configuration_Examples
- 49-H3C_ARP_Attack_Protection_Configuration_Examples
- 50-H3C_DHCPv6_Server_and_DHCPv6_Prefix_Client_Configuration_Examples
- 51-CE1 Interface Connection Configuration Examples
- 52-GRE Tunnel Establishment Using OSPF Configuration Examples
- 53-GRE Tunnel Establishment Using Static Routes Configuration Examples
- 54-OSPF over IPsec for Overseas Branch Access Configuration Examples
- 55-General QoS Configuration Examples
- 56-QoS Configuration Examples for the Financial Industry
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 49-H3C_ARP_Attack_Protection_Configuration_Examples | 96.27 KB |
Example: Configuring ARP attack protection
Disabling gratuitous ARP packet learning
Source MAC-based ARP attack detection
Configuring VLANs and interface IP addresses
Enabling ARP blackhole routing
Enabling ARP active acknowledgment in strict mode
Disabling gratuitous ARP packet learning
Setting dynamic ARP learning limits for interfaces
Enabling ARP packet rate limit and setting the limit rate
Configuring ARP source suppression
Configuring source MAC-based ARP attack detection
Example: Configuring ARP attack protection
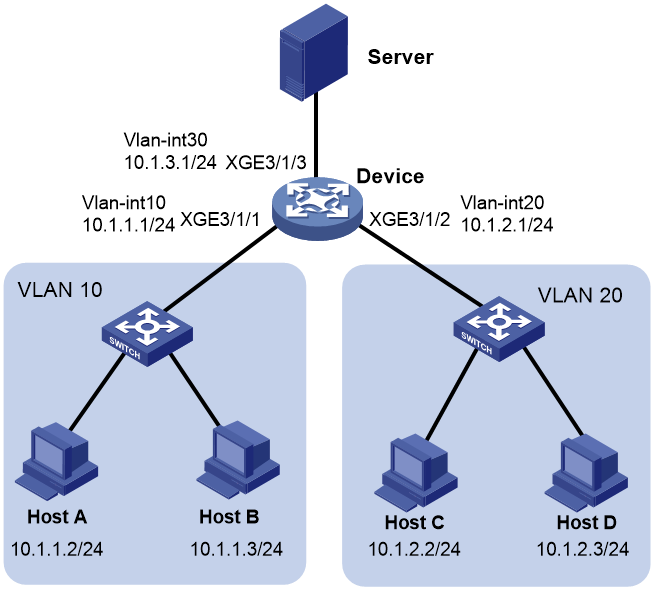
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 1, the device connects to the server through XGE3/1/3 as a gateway and connects to Host A and Host B in VLAN 10, and Host C and Host D in VLAN 20 through XGE3/1/1 and XGE3/1/2, respectively.
Configure ARP attack protection on the device to prevent the following ARP threats:
· Host A sends forged ARP packets and forged gratuitous ARP packets to the device to edit the ARP entries on the device maliciously. As a result, other users cannot receive data packets normally.
· Host C sends a large number of unresolvable IP packets to attack the device, causing the following results:
¡ The device CPU is busy, affecting normal service processing.
¡ The device sends a large number of ARP requests, overloading the target subnets.
· Host D launches ARP flood attacks by sending a large number of ARP packets with different source IP addresses but fixed MAC address. Such attacks run out the ARP table resources on the device and cause a busy CPU, affecting normal service processing.
Besides, Host B might send a large number of ARP packets to the device. This is normal ARP behavior required by services. Do not filter out packets sent from Host B when you configure ARP attack protection.
Analysis
To meet the network requirements, configure the device as follows:
· To prevent forged ARP packets sent by Host A from updating the ARP entries on the device, configure ARP blackhole routing and ARP active acknowledgement in strict mode.
· To prevent the forged gratuitous ARP packets sent by Host A from updating the ARP entries on the device, disable gratuitous ARP packet learning.
· To avoid unresolvable packets sent by Host C, enable ARP source suppression and set the maximum number of unresolvable packets that the device can process per source IP address within 5 seconds.
· To avoid ARP flood attacks caused by ARP packets with the same IP address, enable ARP packet rate limit and set the limit rate. When Host C launches ARP flood attacks on the device by sending a large number of ARP packets with the same source IP address, the device discards the packets that exceed the limit rate to avoid a busy CPU.
· To prevent users on interfaces from consuming too many ARP resources, set dynamic ARP learning limits on interfaces.
· To avoid ARP flood attacks caused by ARP packets with different IP addresses but fixed MAC address sent by Host D, configure source MAC-based ARP attack detection. If you fail to configure this feature, the ARP table resources run out and the CPU is busy. To avoid filtering out packets sent by Host B, exclude the MAC address of Host B from this detection.
Restrictions and guidelines
ARP active acknowledgement
When you configure ARP active acknowledgement in strict mode, make sure ARP blackhole routing is enabled.
Disabling gratuitous ARP packet learning
After you disable gratuitous ARP packet learning, the device does not create ARP entries when receiving gratuitous ARP packets, but updates the existing corresponding ARP entries. If you do not want the device to create ARP entries for gratuitous ARP packets, disable gratuitous ARP packet learning to save ARP entry resources.
Source MAC-based ARP attack detection
· If attacks occur frequently in your network, set a short check interval for source MAC-based ARP attack detection so that source MAC-based ARP attacks can be detected in a timely manner. If attacks seldom occur, you can set a long check interval.
· If you set the check interval for source MAC-based ARP attack detection multiple times, the most recent configuration takes effect.
Procedures
Configuring VLANs and interface IP addresses
# Configure the operating mode of XGE3/1/1, XGE3/1/2, and XGE3/1/3 as Layer 2.
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[Device-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1]port link-mode bridge
[Device-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
[Device] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[Device-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2]port link-mode bridge
[Device-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] quit
[Device] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/3
[Device-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3]port link-mode bridge
[Device-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3] quit
# Create VLAN 10, and assign XGE3/1/1 to the VLAN.
[Device] vlan 10
[Device-vlan10] port ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[Device-vlan10] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 10, and assign IP address 10.1.1.1/24 to it.
[Device] interface vlan-interface 10
[Device-Vlan-interface10] ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
[Device-Vlan-interface10] quit
# Create VLAN 20, and assign XGE3/1/2 to the VLAN.
[Device] vlan 20
[Device-vlan20] port ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[Device-vlan20] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 20, and assign IP address 10.1.2.1/24 to it.
[Device] interface vlan-interface 20
[Device-Vlan-interface20] ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0
[Device-Vlan-interface20] quit
# Create VLAN 30, and assign XGE3/1/3 to the VLAN.
[Device] vlan 30
[Device-vlan30] port ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/3
[Device-vlan30] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 30, and assign IP address 10.1.3.1/24 to it.
[Device] interface vlan-interface 30
[Device-Vlan-interface30] ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0
Enabling ARP blackhole routing
<Device> system-view
[Device] arp resolving-route enable
Enabling ARP active acknowledgment in strict mode
<Device> system-view
[Device] arp active-ack strict enable
Disabling gratuitous ARP packet learning
<Device> system-view
[Device] undo gratuitous-arp-learning enable
Setting dynamic ARP learning limits for interfaces
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[Device-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] arp max-learning-num 20
[Device-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
[Device] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[Device-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] arp max-learning-num 20
Enabling ARP packet rate limit and setting the limit rate
[Device] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/1
[Device-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] arp rate-limit 50
[Device-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1] quit
[Device] interface ten-gigabitethernet 3/1/2
[Device-Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2] arp rate-limit 50
Configuring ARP source suppression
<Device> system-view
[Device] arp source-suppression enable
[Device] arp source-suppression limit 40
Configuring source MAC-based ARP attack detection
# Enable source MAC-based ARP attack detection, and specify the handling method as filter.
<Device> system-view
[Device] arp source-mac filter
# Set the check interval for source MAC-based ARP attack detection to 10 seconds.
[Device] arp source-mac check-interval 10
# Set the threshold to 30.
[Device] arp source-mac threshold 30
# Set the lifetime for ARP attack entries to 60 seconds.
[Device] arp source-mac aging-time 60
# Exclude MAC address 0c68-d691-0606 from this detection.
[Device] arp source-mac exclude-mac 0c68-d691-0606
Verifying the configuration
# Display the current configuration information about ARP source suppression. ARP source suppression is enabled and the maximum number of unresolvable packets that can be processed per source IP address within 5 seconds is 40.
<Device> display arp source-suppression
ARP source suppression is enable
Current suppression limit: 40
# Display the ARP attack entries for Host D when Host D sends more than 30 ARP requests to the device within 5 seconds. The command output shows that an ARP attack entry has been generated for Host D. With this ARP attack entry, the device cannot create ARP entries for Host D.
<Device> display arp source-mac
Source-MAC VLAN ID Interface Aging time (sec) Packets dropped
0c68-be82-0206 20 XGE3/1/2 10 244
<Device> display arp
Type: S-Static D-Dynamic O-Openflow R-Rule M-Multiport I-Invalid
IP address MAC address VLAN/VSI name Interface Aging Type
# Display the ARP attack entries when Host B sends more than 30 ARP requests to the device within 5 seconds. No ARP attack entries for Host B exist, so the device can create ARP entries for Host B.
<Device> display arp source-mac
Source-MAC VLAN ID Interface Aging time (sec) Packets dropped
<Device> display arp
Type: S-Static D-Dynamic O-Openflow R-Rule M-Multiport I-Invalid
IP address MAC address VLAN/VSI name Interface Aging Type
10.1.1.3 0c68-d691-0606 10 XGE3/1/1 1197 D
# Stop sending ARP packets from Host D to the device and wait the lifetime of the ARP attack entry for Host D expires. Then, configure Host D to send ARP packets to the device. Use the following command to display ARP entries on the device. The output shows that the device has created ARP entries for Host D.
<Device> display arp
Type: S-Static D-Dynamic O-Openflow R-Rule M-Multiport I-Invalid
IP address MAC address VLAN/VSI name Interface Aging Type
10.1.1.3 0c68-d691-0606 10 XGE3/1/1 944 D
10.1.2.3 0c68-be82-0206 10 XGE3/1/2 1195 D
Configuration files
#
vlan 1
#
vlan 10
#
vlan 20
#
vlan 30
#
interface Vlan-interface10
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vlan-interface20
ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vlan-interface30
ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 10
combo enable copper
arp max-learning-num 20
arp rate-limit 50
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 20
combo enable copper
arp max-learning-num 20
arp rate-limit 50
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet3/1/3
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 30
combo enable copper
#
undo gratuitous-arp-learning enable
arp source-mac filter
arp source-mac aging-time 60
arp source-mac exclude-mac 0c68-d691-0606
arp source-mac check-interval 10
arp active-ack strict enable
arp source-suppression enable
arp source-suppression limit 40