- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-Ethernet Link Aggregation Troubleshooting Guide | 139.71 KB |
Troubleshooting Layer 2—LAN switching
Ethernet link aggregation issues
Down aggregate interface
Symptom
When two devices are connected through link aggregation, the output from the display interface command indicates that an aggregate interface is down.
Common causes
The following are the common causes for this type of issue:
· Incorrect configuration on the aggregate interface.
· Physical link fault on the member ports.
· Failure in sending and receiving LACP protocol packets.
Troubleshooting flow
To resolve this issue:
1. Use the display link-aggregation verbose command to check whether the member ports are in selected state. If a port is in unselected state, use the display interface command to check whether the physical status of the member port is up and eliminate physical faults on the port.
2. Check the local and peer aggregate interface configurations to eliminate configuration faults.
3. Use the debugging link-aggregation lacp packet command to view the LACP interaction situation of the member ports of dynamic aggregation.
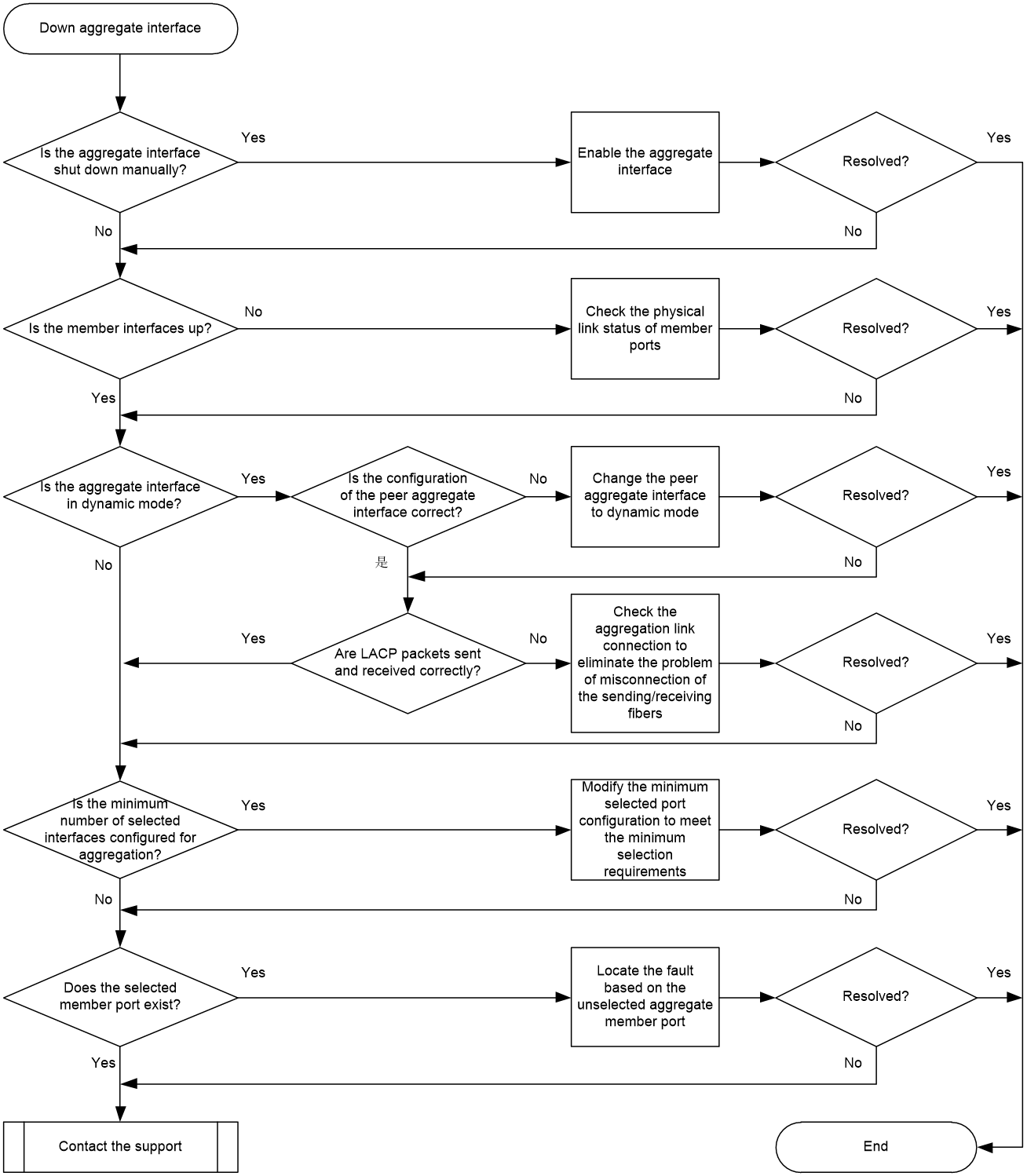
Figure 1 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 1 Flowchart for troubleshooting down aggregate interface
Solution
1. Check whether the physical connections are correct.
Verify that links are connected to the aggregate interface as planned.
If a physical connection is correct, proceed to step 2.
2. Whether the aggregate interface is shut down manually.
Execute the display interface command to check the physical state of the aggregate interface. If it displays Administratively DOWN, the aggregate interface is manually shut down. Execute the undo shutdown command to enable the aggregate interface. If the aggregate interface has not been manually shut down, proceed to step 3.
3. Check whether the member ports in the aggregation group are up.
Execute the display interface command to check if the member ports in the aggregation group are up. If not, follow the troubleshooting procedure for the down interface issue.
If the interface is up, proceed to step 4.
For example, the member port Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/6 in the Layer 2 aggregation group 1 is in unselected state. In the output from the display interface command, the physical status of Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/6 is DOWN, making the member port Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/6 unselected.
<Sysname> display link-aggregation verbose
Loadsharing Type: Shar -- Loadsharing, NonS -- Non-Loadsharing
Port Status: S -- Selected, U -- Unselected, I -- Individual
Port: A -- Auto port, M -- Management port, R -- Reference port
Flags: A -- LACP_Activity, B -- LACP_Timeout, C -- Aggregation,
D -- Synchronization, E -- Collecting, F -- Distributing,
G -- Defaulted, H -- Expired
Role: P -- Primary, S -- Secondary
Aggregate Interface: Route-Aggregation1
Aggregation Mode: Static
Loadsharing Type: Shar
Management VLANs: None
Port Status Priority Oper-Key
XGE0/0/6 U 32768 1
<Sysname> display interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/6
Current state: DOWN
Line protocol state: DOWN
IP packet frame type: Ethernet II, hardware address: 2a41-21c1-0100
Description: Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/6 Interface
Bandwidth: 1000000 kbps
Maximum transmission unit: 1500
Allow jumbo frames to pass
Broadcast max-ratio: 100%
Unknown-multicast max-ratio: 100%
Unicast max-ratio: 100%
Internet protocol processing: Disabled
IP packet frame type: Ethernet II, hardware address: 3822-d666-bd0c
IPv6 packet frame type: Ethernet II, hardware address: 3822-d666-bd0c
Media type is twisted pair, port hardware type is 1000_BASE_T
Port priority: 2
Unknown-speed mode, unknown-duplex mode
Link speed type is autonegotiation, link duplex type is autonegotiation
Flow-control is not enabled
Maximum frame length: 9216
Output queue - Urgent queuing: Size/Length/Discards 0/1024/0
Output queue - Protocol queuing: Size/Length/Discards 0/500/0
Output queue - FIFO queuing: Size/Length/Discards 0/75/0
Last link flapping: 6 hours 39 minutes 28 seconds
Last hardware down reason: PHY line side is down
Last clearing of counters: Never
Current system time:2019-01-08 14:50:06
Last time when physical state changed to up:2019-01-08 14:49:45
Last time when physical state changed to down:2019-01-08 14:49:45
Peak input rate: 0 bytes/sec, at 2013-07-07 16:07:11
Peak output rate: 0 bytes/sec, at 2013-07-07 16:07:11
Last 300 seconds input: 0 packets/sec 0 bytes/sec 0%
Last 300 seconds output: 0 packets/sec 0 bytes/sec 0%
Input (total): 0 packets, 0 bytes
0 unicasts, 0 broadcasts, 0 multicasts, - pauses
Input (normal): 0 packets, 0 bytes
0 unicasts, 0 broadcasts, 0 multicasts, 0 pauses
Input: 0 input errors, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overruns, - aborts
- ignored, - parity errors
Output (total): 0 packets, 0 bytes
0 unicasts, 0 broadcasts, 0 multicasts, - pauses
Output (normal): 0 packets, 0 bytes
0 unicasts, 0 broadcasts, 0 multicasts, 0 pauses
Output: 0 output errors, - underruns, - buffer failures
0 aborts, 0 deferred, 0 collisions, 0 late collisions
- lost carrier, - no carrier
4. Check whether the aggregate interface is in dynamic mode.
¡ If the aggregate interface is in dynamic mode, check whether the peer aggregate interface is also in dynamic mode. Execute the display link-aggregation verbose command in any view to check the aggregation mode of the aggregate interfaces at both ends of the link and ensure that the aggregation modes at both ends are the same.
Taking the Layer 3 aggregate interface as an example, when Aggregation Mode: Dynamic is displayed, the aggregation interface is in dynamic mode:
<Sysname> display link-aggregation verbose route-aggregation 10
Loadsharing Type: Shar -- Loadsharing, NonS -- Non-Loadsharing
Port Status: S -- Selected, U -- Unselected, I -- Individual
Port: A -- Auto port, M -- Management port, R -- Reference port
Flags: A -- LACP_Activity, B -- LACP_Timeout, C -- Aggregation,
D -- Synchronization, E -- Collecting, F -- Distributing,
G -- Defaulted, H -- Expired
Role: P -- Primary, S -- Secondary
Aggregate Interface: Route-Aggregation10
Creation Mode: Manual
Aggregation Mode: Dynamic
Loadsharing Type: Shar
Management VLANs: None
System ID: 0x8000, 000f-e267-6c6a
Local:
Port Status Priority Index Oper-Key Flag
XGE0/0/6 S 32768 61 2 {ACDEF}
XGE0/0/7 S 32768 62 2 {ACDEF}
XGE0/0/8 S 32768 63 2 {ACDEF}
Remote:
Actor Priority Index Oper-Key SystemID Flag
XGE0/0/6(R) 32768 111 2 0x8000, 000f-e267-57ad {ACDEF}
XGE0/0/7 32768 112 2 0x8000, 000f-e267-57ad {ACDEF}
XGE0/0/8 32768 113 2 0x8000, 000f-e267-57ad {ACDEF}
If the configuration is incorrect, change the aggregation interface of the remote end to dynamic aggregation. If the configuration is correct, execute the debugging link-aggregation lacp packet command to identify whether LACP packets are received and sent correctly.
Execute the debugging link-aggregation lacp packet command to view the Actor field in the send information and the Partner field in the receive information of the member port. If the sys-mac, key, and port-index fields are inconsistent, the LACP protocol packet transmission is abnormal. Check if the receiving or sending fiber is disconnected. If the sys-mac, key, and port-index fields are consistent, the LACP protocol packet transmission is normal, and proceed to step 5.
Enable the debugging switch for the LACP packets of the aggregation member port Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/6, and observe LACP packet receiving and sending on this port.
<Sysname> debugging link-aggregation lacp packet all interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/6
*Nov 2 15:51:21:15 2007 Sysname LAGG/7/Packet: PACKET.Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/6.send.
size=110, subtype =1, version=1
Actor: type=1, len=20, sys-pri=0x8000, sys-mac=00e0-fc02-0300, key=0x1, pri=0x8000, port-index=0x2, state=0xc5
Partner: type=2, len=20, sys-pri=0x0, sys-mac=0000-0000-0000, key=0x0, pri=0x0, port-index=0x0, state=0x32
Collector: type=3, len=16, col-max-delay=0x0
Terminator: type=0, len=0
*Nov 2 15:55:21:15 2007 Sysname LAGG/7/Packet: PACKET.Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/6.receive.
size=110, subtype =1, version=1
Actor: type=1, len=20, sys-pri=0x8000, sys-mac=00e0-fc00-0000, key=0x1, pri=0x8000, port-index=0x6, state=0xd
Partner: type=2, len=20, sys-pri=0x8000, sys-mac=00e0-fc02-0300, key=0x1, pri=0x8000, port-index=0x2, state=0xc5
Collector: type=3, len=16, col-max-delay=0x0
Terminator: type=0, len=0
¡ If the aggregate interface is in static mode, proceed to step 5.
5. Check whether the minimum number of selected ports for the aggregate interface affects the selection of member ports.
Execute the display this command in aggregate interface view. If the link-aggregation selected-port minimum command is configured, modify the minimum selected port limit to meet the selection requirement. If the number of selectable member ports are increased to the minimum number of selected member ports or a larger value, the status of these member ports will become selected, and the link state of the corresponding aggregate interface will also change to up.
If the minimum number of selected ports for the aggregation interface does not affect the selection of the member ports, proceed to step 6.
For example, the minimum number of selected ports for Layer 3 aggregate interface 1 is 2. The aggregation group of Layer 3 aggregation interface 1 has only one member port, so this member port is in unselected state.
[Sysname-Route-Aggregation1] display this
#
interface Route-Aggregation1
link-aggregation selected-port minimum 2
#
return
[Sysname-Route-Aggregation1] display link-aggregation verbose
Loadsharing Type: Shar -- Loadsharing, NonS -- Non-Loadsharing
Port Status: S -- Selected, U -- Unselected, I -- Individual
Port: A -- Auto port, M -- Management port, R -- Reference port
Flags: A -- LACP_Activity, B -- LACP_Timeout, C -- Aggregation,
D -- Synchronization, E -- Collecting, F -- Distributing,
G -- Defaulted, H -- Expired
Role: P -- Primary, S -- Secondary
Aggregate Interface: Route-Aggregation1
Aggregation Mode: Static
Loadsharing Type: Shar
Management VLANs: None
Port Status Priority Oper-Key
XGE0/0/6 U 32768 1
6. Check whether selected member ports exist in the aggregation group.
If no selected member port exists in the aggregation group, see "Unselection of aggregation member ports." If selected member ports exist in the aggregation group, proceed to step 7.
7. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
N/A
Uneven traffic load sharing on an aggregate interface
Symptom
When two devices are connected through a link aggregation, output from the display counters rate command shows that some member ports have extremely low rates or a rate of 0 in the outbound direction.
Common causes
The common cause is the incorrect configuration of the aggregation load sharing method.
Troubleshooting flow
To resolve this issue, identify the characteristics of the packets forwarded by the aggregate interface and check whether the aggregate load sharing mode matches the packet characteristics.
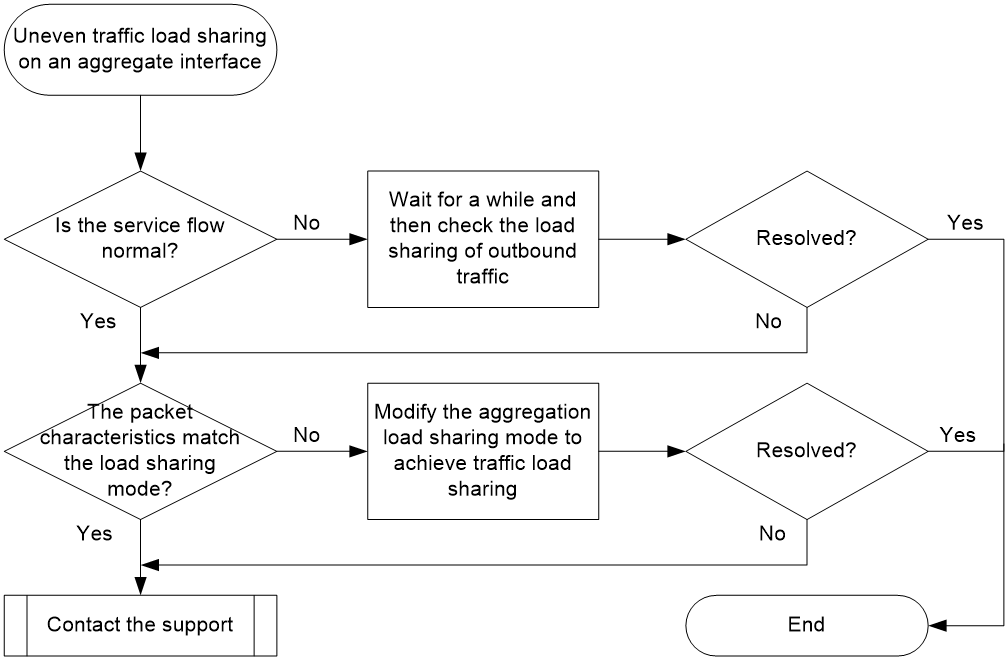
Figure 2 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 2 Flowchart for troubleshooting uneven traffic load sharing on an aggregate interface
Solution
1. Check whether the user service traffic is normal.
If the user service traffic is normal, wait for a while and then execute the display counters rate command to check the outbound traffic rate of the aggregation member ports. Check whether the traffic load sharing of the aggregation member ports has been restored.
¡ If load sharing has been restored, no action is required.
¡ If load sharing is not restored, proceed to step 2.
If the user service traffic is abnormal, proceed to step 2.
2. Check whether the aggregation load sharing mode matches the packet characteristics.
Check the type of aggregation load sharing by executing the display link-aggregation load-sharing modecommand. If it does not match the packet characteristics, adjust the mode of aggregation load sharing with the following command:
¡ Execute the link-aggregation global load-sharing mode command in system view to adjust the global load-sharing mode.
¡ Execute the link-aggregation load-sharing mode command in aggregate interface view to adjust the load sharing mode of the aggregate interface.
The load sharing mode adjustment varies by device model and service traffic type.
If the aggregation load sharing mode matches the characteristics of the packets, proceed to step 3.
3. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
N/A
Unselection of aggregation member ports
Symptom
When two devices are connected via link aggregation, the member ports of the aggregation group are in unselected state and the aggregation fails.
Common causes
The following are the common causes for this type of issue:
· Link connectivity fault.
· The operational key and attribute configurations are inconsistent between the local end and the peer end.
· The aggregation member port count is incorrect.
Troubleshooting flow
To resolve this issue:
1. Check if the member ports are up and eliminate physical faults on the port.
2. Use the debugging link-aggregation lacp packet command to view the LACP interaction on member ports of the dynamic aggregation group.
3. Check the local and peer aggregate interface configurations to eliminate configuration faults.
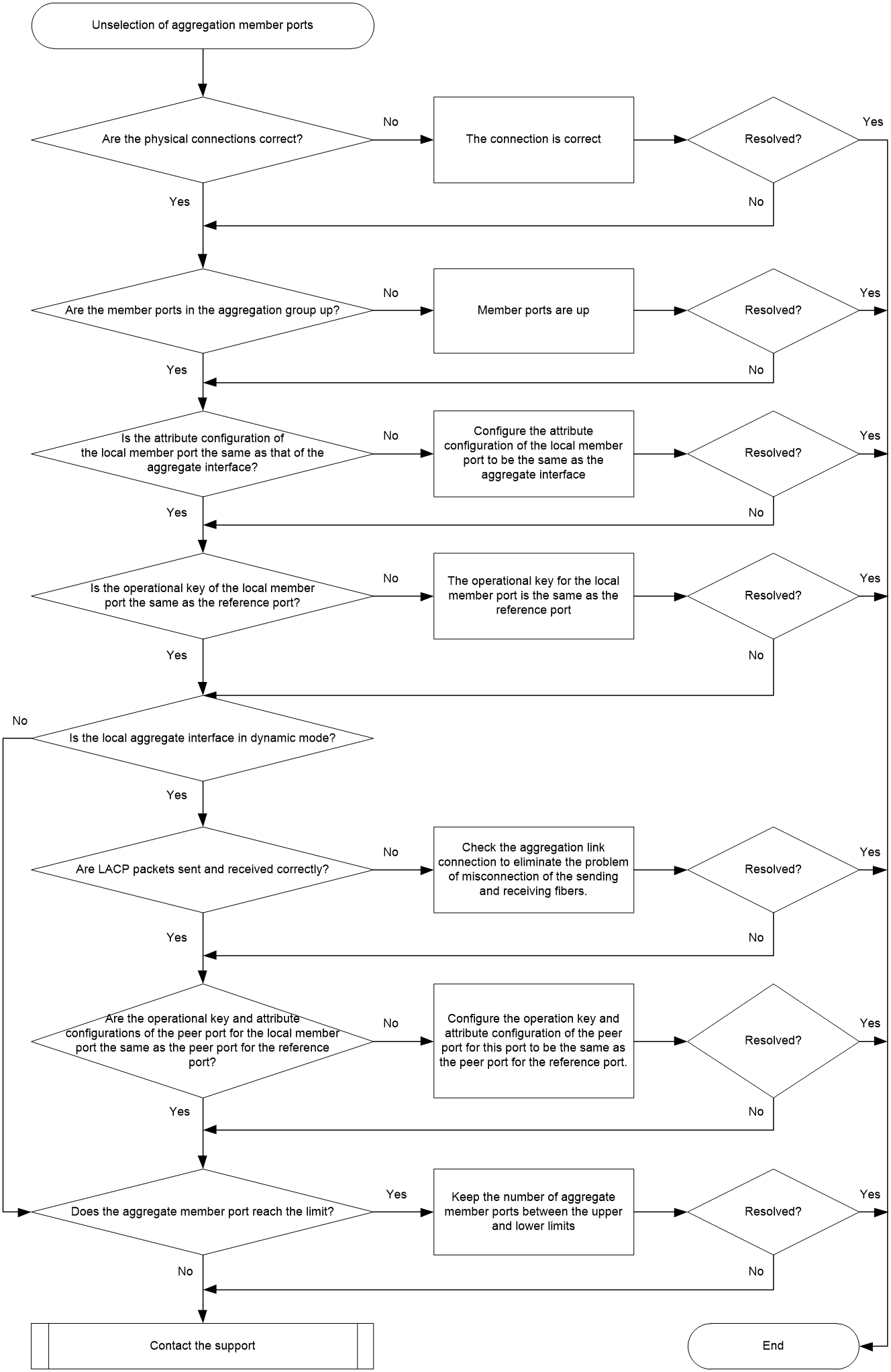
Figure 3 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 3 Flowchart for troubleshooting unselection of aggregation member ports
Solution
1. Check if the physical connections are correct.
Perform a link check according to the network plan of the aggregate interface, and identify whether the physical connections are connected as planned.
If the physical connections are correct, proceed to step 2.
2. Check whether the member ports in the aggregation group are up.
Use the display interface command to check if the member ports in the aggregation group are up. If they are not up, follow the troubleshooting procedure for the down interface issue.
If the member ports are up, proceed to step 3.
3. Check whether the attribute configuration of the local member ports is the same as that of the aggregate interface.
a. Execute the display link-aggregation verbose command to view the unselected member ports on the local end.
Taking a Layer 3 aggregate interface as an example, when the Status field displays U, the member port is unselected.
<Sysname> display link-aggregation verbose route-aggregation 10
Loadsharing Type: Shar -- Loadsharing, NonS -- Non-Loadsharing
Port Status: S -- Selected, U -- Unselected, I -- Individual
Port: A -- Auto port, M -- Management port, R -- Reference port
Flags: A -- LACP_Activity, B -- LACP_Timeout, C -- Aggregation,
D -- Synchronization, E -- Collecting, F -- Distributing,
G -- Defaulted, H -- Expired
Role: P -- Primary, S -- Secondary
Aggregate Interface: Route-Aggregation10
Creation Mode: Manual
Aggregation Mode: Dynamic
Loadsharing Type: Shar
Management VLANs: None
System ID: 0x8000, 000f-e267-6c6a
Local:
Port Status Priority Index Oper-Key Flag
XGE0/0/6 S 32768 61 2 {ACDEF}
XGE0/0/7 S 32768 62 2 {ACDEF}
XGE0/0/8 U 32768 63 2 {ACDEF}
Remote:
Actor Priority Index Oper-Key SystemID Flag
XGE0/0/6(R) 32768 111 2 0x8000, 000f-e267-57ad {ACDEF}
XGE0/0/7 32768 112 2 0x8000, 000f-e267-57ad {ACDEF}
XGE0/0/8 32768 113 2 0x8000, 000f-e267-57ad {ACDEF}
b. Execute the display current-configuration interface command to check whether the attribute configuration (such as VLAN) of the unselected member port on the local end is the same as the aggregate interface. If not, modify the attribute configuration for consistent configuration.
For example, the member port Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/8 is in unselected state and has different attribute configuration from the reference port Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/6. This difference prevents the member port. You must modify the attribute configuration of the member port Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/8.
<Sysname> display current-configuration interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/6
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/6
port link-mode route
mtu 1500
port link-aggregation group 1
#
return
<Sysname> display current-configuration interface route-aggregation 1
#
interface Route-Aggregation1
mtu 2000
link-aggregation mode dynamic
#
return
If the attribute configuration of the local member port is the same as the aggregate interface, proceed to step 4.
4. Check whether the operational key of the member ports on the local end is the same as the reference port.
a. Execute the display link-aggregation verbose command to view the unselected member ports on the local end.
Taking the Layer 3 aggregate interface as an example, when the Status field displays U, the member port is unselected:
<Sysname> display link-aggregation verbose
Loadsharing Type: Shar -- Loadsharing, NonS -- Non-Loadsharing
Port Status: S -- Selected, U -- Unselected, I -- Individual
Port: A -- Auto port, M -- Management port, R -- Reference port
Flags: A -- LACP_Activity, B -- LACP_Timeout, C -- Aggregation,
D -- Synchronization, E -- Collecting, F -- Distributing,
G -- Defaulted, H -- Expired
Role: P -- Primary, S -- Secondary
Aggregate Interface: Route-Aggregation10
Creation Mode: Manual
Aggregation Mode: Dynamic
Loadsharing Type: Shar
Management VLANs: None
System ID: 0x8000, 000f-e267-6c6a
Local:
Port Status Priority Index Oper-Key Flag
XGE0/0/6 S 32768 1 1 {ACDEF}
XGE0/0/7 S 32768 2 1 {ACDEF}
XGE0/0/8 U 32768 3 2 {AC}
Remote:
Actor Priority Index Oper-Key SystemID Flag
XGE0/0/6(R) 32768 1 1 0x8000, 36f6-c0aa-0200 {ACDEF}
XGE0/0/7 32768 2 1 0x8000, 36f6-c0aa-0200 {ACDEF}
XGE0/0/8 32768 3 1 0x8000, 36f6-c0aa-0200 {AC}
b. Execute the display current-configuration interface command to check whether the operational key of the local member port in unselected state (including the port's speed and duplex mode) is the same as the reference port. If not, modify the configuration for consistency.
For example, the operational key of the member port Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/8 in unselected state is different from that of the reference port Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/6. As a result, the member port cannot be selected and the port rate configuration must be modified.
<Sysname> display current-configuration interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/6
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/6
port link-mode route
port link-aggregation group 11
#
return
<Sysname> display current-configuration interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/8
port link-mode route
speed 100
port link-aggregation group 11
#
return
If the operational key of the local member port is the same as the reference port, proceed to step 5.
5. Check whether the local aggregate interface is in dynamic mode.
If it is in dynamic mode, proceed to step 6. If it is in static mode, proceed to step 8.
6. Check whether LACP packets are sent and received correctly.
Execute the debugging link-aggregation lacp packet command to check if LACP packets are sent and received correctly. Examine the Actor field in the send information and the Partner field in the receive information of the member port. If the sys-mac, key, and port-index fields are inconsistent, the LACP protocol packet transmission is abnormal. Check if the receiving or sending fiber is disconnected. If the sys-mac, key, and port-index fields are consistent, the LACP protocol packet transmission is normal, and proceed to step 7.
Enable the debugging switch for the LACP packets of the aggregation member port Ten-GigabitEthernet 0/0/6, and observe LACP packet receiving and sending on this port.
<Sysname> debugging link-aggregation lacp packet all interface ten-gigabitethernet 0/0/6
*Nov 2 15:51:21:15 2021 Sysname LAGG/7/Packet: PACKET.Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/6.send.
size=110, subtype =1, version=1
Actor: type=1, len=20, sys-pri=0x8000, sys-mac=00e0-fc02-0300, key=0x1, pri=0x8000, port-index=0x2, state=0xc5
Partner: type=2, len=20, sys-pri=0x0, sys-mac=0000-0000-0000, key=0x0, pri=0x0, port-index=0x0, state=0x32
Collector: type=3, len=16, col-max-delay=0x0
Terminator: type=0, len=0
*Nov 2 15:55:21:15 2021 Sysname LAGG/7/Packet: PACKET.Ten-GigabitEthernet0/0/6.receive.
size=110, subtype =1, version=1
Actor: type=1, len=20, sys-pri=0x8000, sys-mac=00e0-fc00-0000, key=0x1, pri=0x8000, port-index=0x6, state=0xd
Partner: type=2, len=20, sys-pri=0x8000, sys-mac=00e0-fc02-0300, key=0x1, pri=0x8000, port-index=0x2, state=0xc5
Collector: type=3, len=16, col-max-delay=0x0
Terminator: type=0, len=0
7. Check whether the operational key and attribute configuration of the peer port for the local member port are the same as the peer port for the reference port.
Execute the display current-configuration interface command on the device on the peer end of the local unselected port. Check if the operational key and attribute configuration of the peer end for the unselected port are the same as those on the peer port for the reference port. If not, modify the configuraiton for consistency.
If the operational key and attribute configuration of the peer port for the local member port are the same as those of the peer port for the reference port, proceed to step 8.
8. Check whether the number of aggregation member ports reaches the upper limit.
¡ The number of aggregation member ports reaches the upper limit.
Execute the link-aggregation selected-port maximum command in aggregate interface view to configure the maximum number of selected ports in the aggregation group. Use the display link-aggregation verbose command to check if the number of member ports in the aggregation group reaches the upper limit. If yes, the excess ports will be placed in unselected state. Selected ports are sorted in ascending order by port ID. Execute the undo port link-aggregation group command in member port view to remove undesired selected ports from the aggregation group for desired member ports to be selected.
¡ The number of aggregate member ports is below the lower limit.
Execute the link-aggregation selected-port minimum command in aggregate interface view to configure the minimum number of selected ports in the aggregation group. Execute the display link-aggregation verbose command to check whether the member ports in the aggregation group are lower than the lower limit. If they are lower than the lower limit, all member ports are in unselected state. Execute the link-aggregation selected-port minimum command to modify the minimum selected port count or add member ports to the aggregation group so that the minimum selection requirements are met.
If the number of aggregation member ports has not reached the limit of the aggregation group, proceed to step 9.
9. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact Technical Support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
N/A