- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 05-PIM Troubleshooting Guide | 186.74 KB |
Troubleshooting multicast
PIM issues
PIM neighbor establishment failure
Symptom
The PIM neighbor relationship fails to be established.
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· The physical state of the interface is down.
· The primary IP address is not configured on the interface.
· The PIM function on the interface does not take effect.
· The interface is not enabled with PIM.
· The PIM-related configuration on the interface is incorrect.
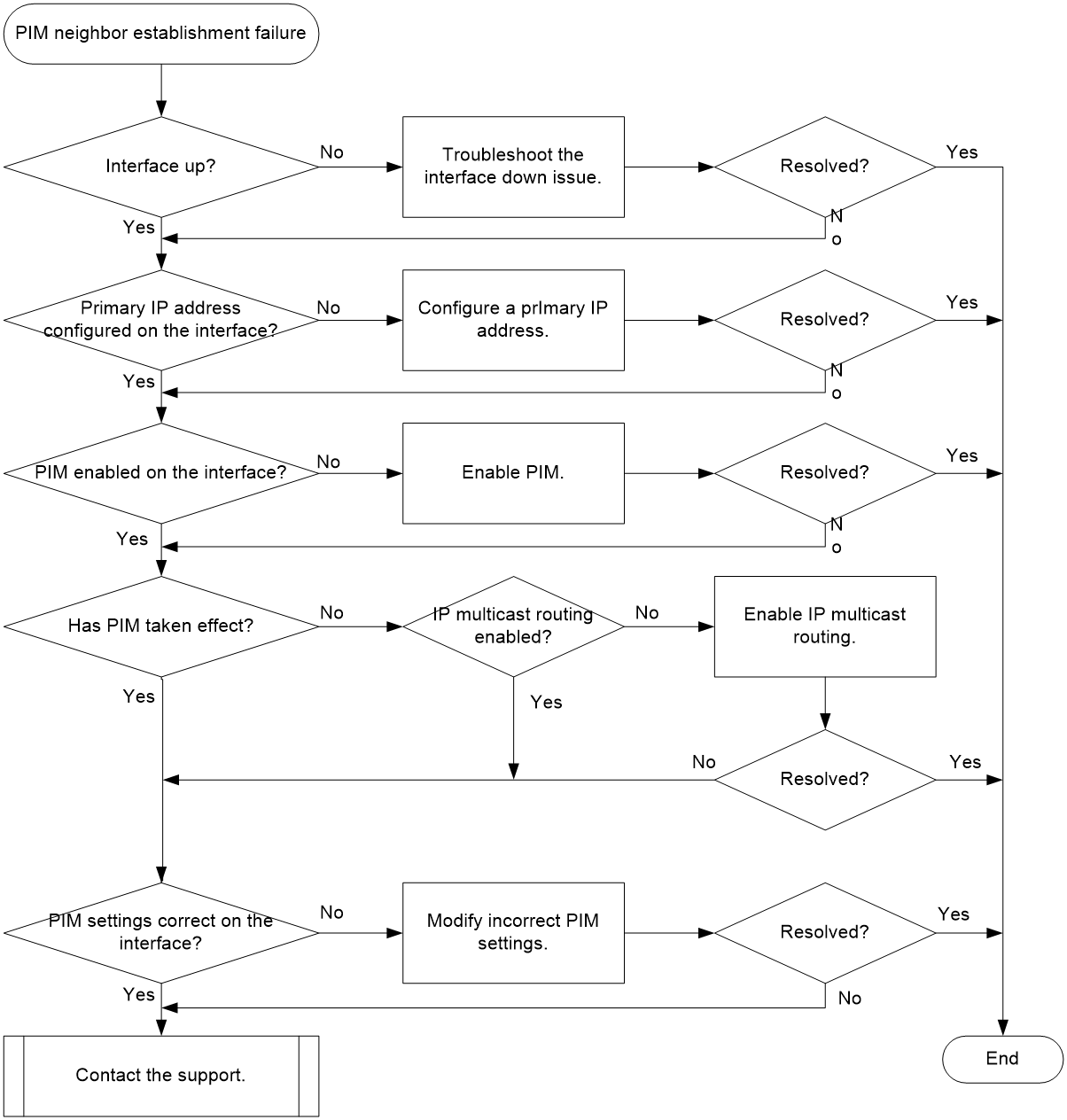
Troubleshooting flow
Figure 1 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 1 Flowchart for troubleshooting PIM neighbor establishment failure
Solution
1. Verify that the physical state of the interface is up.
Execute the display interface interface-type interface-number command, and check the Current state field for the physical state of the interface.
¡ If the physical state is up, proceed to step 2.
¡ If the physical state is down, troubleshoot the interface down issue.
2. Verify that the interface is configured with a primary IP address.
Execute the display this command on the interface, and check for the primary IP address.
¡ If the primary IP address is not configured, use the ip address command to configure it.
¡ If the primary IP address is configured, proceed to step 3.
3. Verify that the interface is enabled with PIM.
Execute the display current-configuration interface command to identify whether PIM is enabled on the interface.
¡ If PIM is not enabled, execute the pim dm or pim sm command on the interface.
¡ If PIM is enabled, proceed to step 4.
4. Verify that PIM has taken effect on the interface.
Execute the display pim interface command. If PIM information exists for the interface, PIM has taken effect on the interface.
¡ If PIM has not taken effect, execute the display current-configuration | include multicast command to identify whether IP multicast routing has been enabled.
- If IP multicast routing has not been enabled, execute the multicast routing command to enable it.
- If IP multicast routing has been enabled, proceed to step 5.
¡ If PIM has taken effect, proceed to step 5.
5. Verify that the PIM-related configuration on the interface is correct.
The following are the common configuration errors that can cause the PIM neighbor relationship to fail to be established:
¡ The IP addresses of the directly connected interfaces are not on the same network segment.
¡ A PIM hello policy is configured on the interface by using the pim neighbor-policy command, but the neighbor’s IP address is not permitted by the specified ACL and PIM hello messages from the neighbor are dropped. Identify whether a PIM hello policy is required.
- If yes, modify the ACL so that the IP address of the PIM neighbor can be permitted by the ACL.
- If no, execute the undo pim neighbor-policy command to delete it.
¡ The pim require-genid command is executed on the interface to drop the hello messages without generation ID options, and hello messages from the neighbor do not carry generation ID options. Identify whether hello messages without generation ID options must be dropped.
- If yes, proceed to step 6.
- If no, execute the undo pim require-genid command.
6. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact the support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
N/A
Layer 3 multicast traffic forwarding failure within a PIM domain
Symptom
After IP multicast routing is enabled, Layer 3 multicast traffic fails to be forwarded within the same PIM domain.
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· An interface for forwarding multicast data is not enabled with PIM.
· The PIM function on an interface does not take effect.
· The PIM neighboring relationship fails to be established.
· The interface connected to the hosts is not enabled with IGMP.
· In a PIM-SM or BIDIR-PIM network, the RP is not configured or the RP information is incorrect.
· No RPF route to the RP or multicast source exists.
· An interface for forwarding multicast data has been configured with a multicast forwarding boundary.
· In a PIM-SM or BIDIR-PIM network, an incorrect multicast source policy is configured.
· No multicast entry is generated.
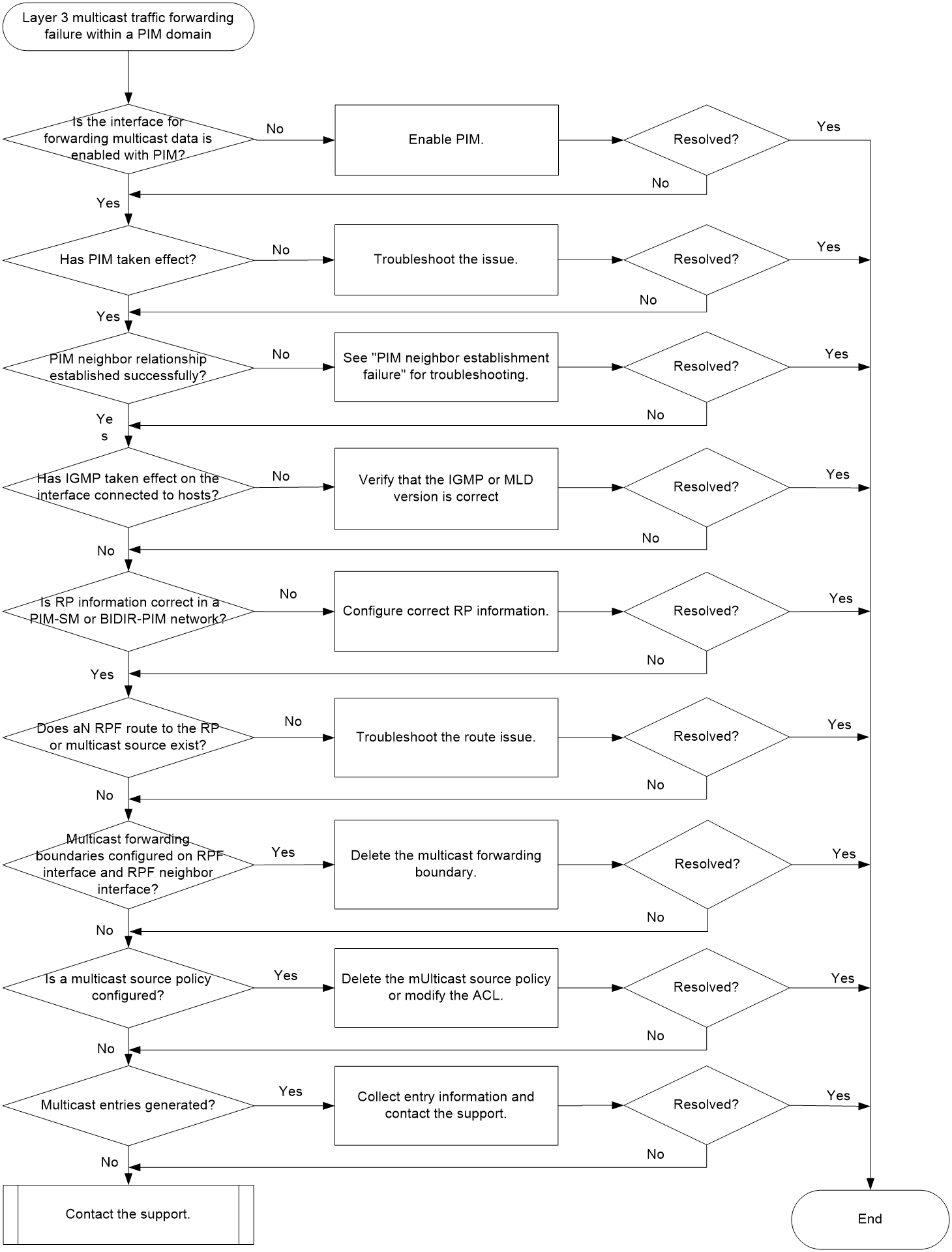
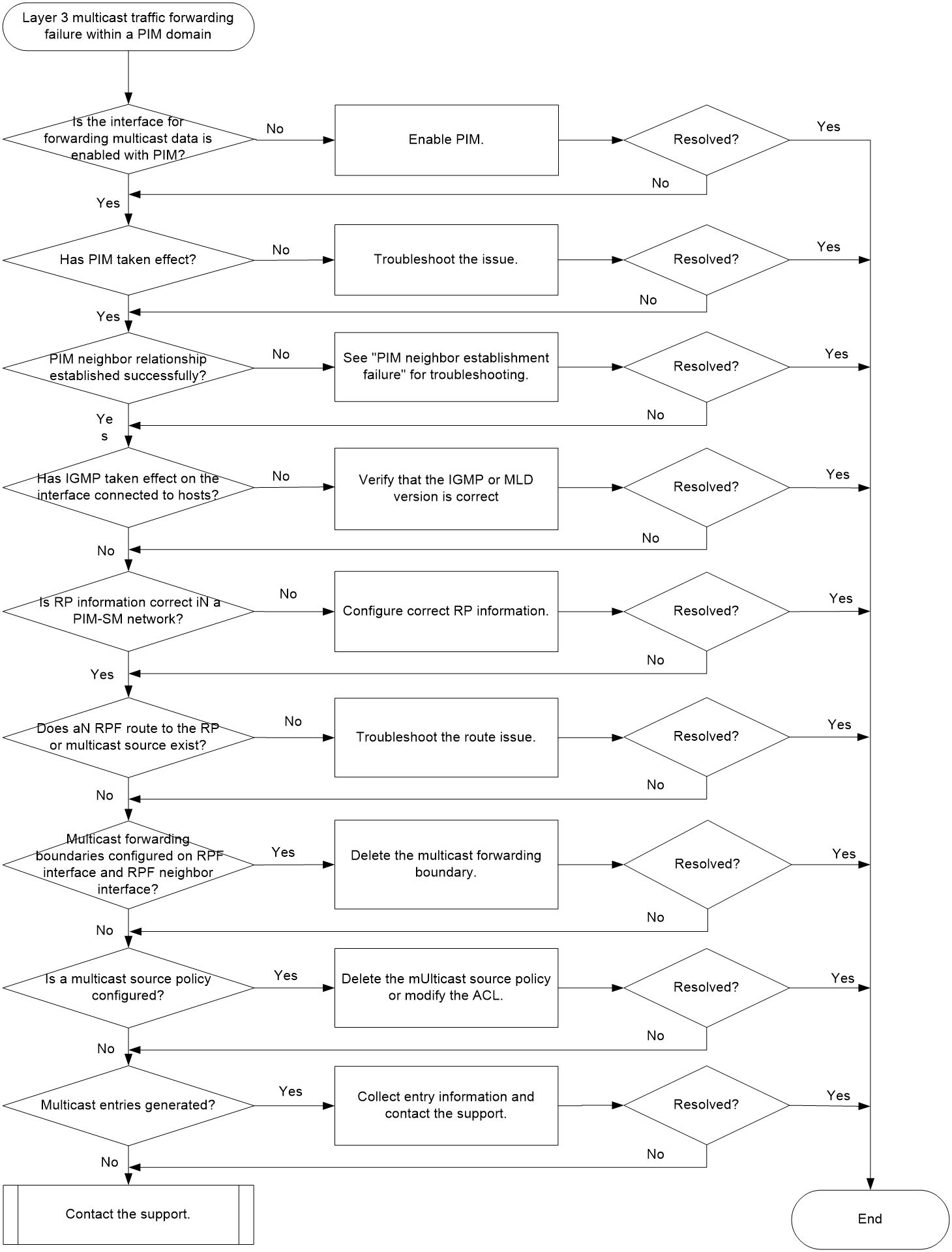
Troubleshooting flow
Figure 2 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Solution
1. Verify that the interface for forwarding multicast data is enabled with PIM.
Execute the display this command on the interface for forwarding multicast data, and identify whether the PIM-SM or PIM-DM configuration exists.
¡ If no, PIM is not enabled on the interface. Execute the pim sm or pim dm command on the interface. In the case of a BIDIR-PIM network, also execute the bidir-pim enable command to enable BIDIR-PIM.
¡ If yes, proceed to step 2.
2. Verify that PIM has taken effect on the interface.
Execute the display pim interface command. If PIM information exists for the interface, PIM has taken effect on the interface.
¡ If PIM has not taken effect, execute the display interface interface-type interface-number command, and check the Current state field for the physical state of the interface. If the physical state is down, troubleshoot the interface down issue.
¡ If PIM has taken effect, proceed to step 3.
3. Verify that the PIM neighbor relationship has been established successfully.
Execute the display pim neighbor command. If PIM neighbor information exists, the PIM neighbor relationship has been established successfully.
¡ If the PIM neighbor relationship fails to be established, see “PIM neighbor establishment failure” for troubleshooting.
¡ If the PIM neighbor relationship has been established successfully, proceed to step 4.
4. Verify that IGMP has taken effect on the interface connected to the subnet of hosts.
Execute the display igmp interface command. If IGMP information exists for the interface, IGMP has taken effect on the interface.
¡ If IGMP has not taken effect, execute the igmp enable command on the interface to enable IGMP.
¡ If IGMP has taken effect:
- For a PIM-SM or BIDIR-PIM network, proceed to step 5.
- For a PIM-DM network, proceed to step 7.
5. Verify that the RP information is correct in a PIM-SM or BIDIR-PIM network.
Execute the display pim rp-info command on each device in the network. Identify whether the RP information for the multicast group is the same on all devices.
¡ If the RP information is different and static RPs are used, execute the static-rp command on each device to configure the same static RP. To use dynamically elected RPs, proceed to step 6.
¡ If the RP information is the same on all devices, proceed to step 6.
6. Verify that an RPF route to the RP exists.
Execute the display multicast rpf-info command to check for the RPF route to the RP.
¡ If no RPF route to the RP exists, examine the unicast route configuration. Execute the ping command on both the device and the RP to identify whether they can ping each other successfully. If no, modify the unicast route configuration until they can ping each other successfully.
¡ If an RPF route to the RP exists, execute the display multicast rpf-info command, and check the Referenced route type field for the type of the referenced route.
- If the RPF route is a static multicast route, execute the display multicast routing-table static command to identify whether the static multicast route is correct.
- If the RPF route is a unicast route, execute the display ip routing-table command to identify whether the unicast route is the same as the RPF route.
If an RPF route to the RP exists and is correct, proceed to step 8.
7. Verify that an RPF route to the multicast source exists.
Execute the display multicast rpf-info command to check for the RPF route to the multicast source.
¡ If no RPF route to the multicast source exists, examine the unicast route configuration. Execute the ping command on both the device and the multicast source to identify whether they can ping each other successfully. If no, modify the unicast route configuration until they can ping each other successfully.
¡ If an RPF route to the multicast source exists, execute the display multicast rpf-info command, and check the Referenced route type field for the type of the referenced route.
- If the RPF route is a static multicast route (the Referenced route type field is multicast static), execute the display multicast routing-table static command to identify whether the static multicast route is correct.
- If the RPF route is a unicast route (the Referenced route type field is igp, egp, unicast (direct), or unicast), execute the display ip routing-table command to identify whether the unicast route is the same as the RPF route.
¡ If an RPF route to the multicast source exists and is correct, proceed to step 8.
8. Verify that the RPF interface and the connected interface of the device's RPF neighbor have not been configured with a multicast forwarding boundary.
Execute the display multicast boundary command to check for the multicast forwarding boundary configuration.
¡ If an interface is configured with a multicast forwarding boundary, execute the undo multicast boundary command to delete it.
¡ If no interface is configured with a multicast forwarding boundary, proceed to step 9.
9. Verify that no multicast source policy is configured or multicast data is permitted by a multicast source policy.
Execute the display this command in PIM view to check for a multicast source policy (configured by using the source-policy command).
¡ If a multicast source policy has been configured, verify that it permits multicast data to be forwarded. If the multicast source policy denies multicast data, execute the undo source-policy command to delete it or modify the ACL so that it can permit the multicast data to pass through.
¡ If no multicast source policy is configured, proceed to step 10.
10. Verify that multicast entries have been generated.
¡ If multicast entries exist, collect entry information and proceed to 11.
¡ If no multicast entries exist., proceed to step 11.
Use the following commands to collect entry information:
¡ Execute the display pim routing-table command to check for PIM routing entries.
¡ Execute the display igmp group command to check for IGMP multicast group entries.
¡ Execute the display multicast routing-table command to check for multicast routing entries.
¡ Execute the display multicast forwarding-table command to check for multicast forwarding entries.
11. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact the support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
N/A
SPT forwarding failure in PIM-SM
Symptom
Multicast data fails to be forwarded through the SPT in a PIM-SM network. This section applies to only non-RP devices. If the faulty device is an RP, contact the support.
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· The interface connected to downstream devices does not receive PIM join messages.
· The interface is not enabled with PIM-SM.
· The RPF route to the multicast source is incorrect.
· Configuration errors exist, such as multicast forwarding boundary and multicast source policy.
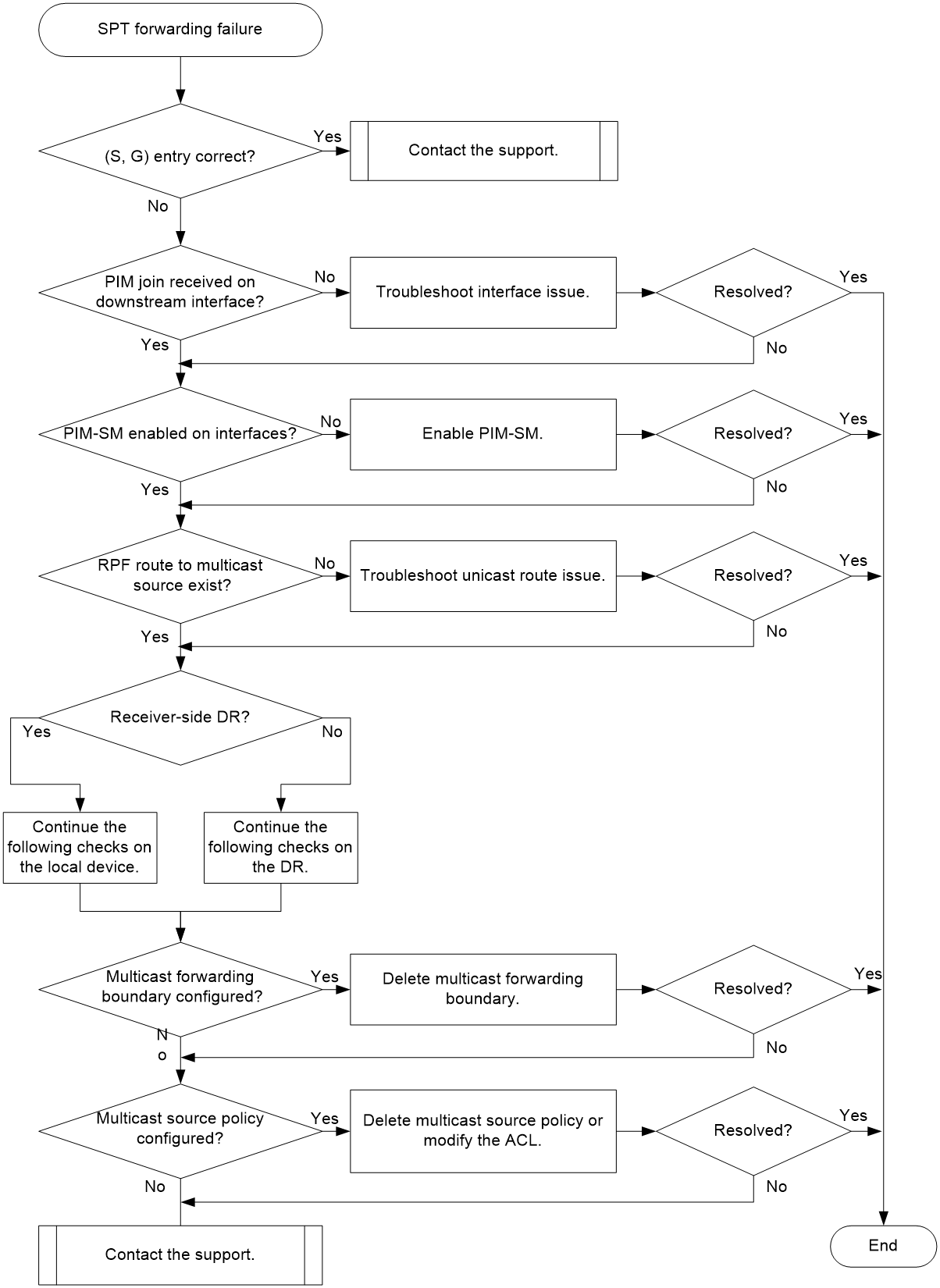
Troubleshooting flow
Figure 3 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 3 Flowchart for troubleshooting SPT forwarding failure in PIM-SM
Solution
1. Verify that a correct (S, G) entry exists in the PIM routing table.
Execute the display pim routing-table command to check for the correct (S, G) entry.
¡ If a correct (S, G) entry exists, execute the display multicast forwarding-table command at 15-second intervals, and check the Matched packets and Forwarded packets fields.
- If no (S, G) entry exists in the forwarding table or the values of the Matched packets and Forwarded packets fields do not increase, proceed to step 8.
- If a (S, G) entry exists in the forwarding table and the values of the Matched packets and Forwarded packets fields increase, also proceed to step 8.
¡ If no correct (S, G) entry exists, proceed to step 2.
2. Verify that the interface connected to the downstream device has received PIM join messages.
Under the guidance of the support, use a packet capture tool such as Wireshark to capture packets on the interface to identify whether PIM join messages are received.
¡ If not, use the packet capture tool to capture packets on the interface connecting the downstream device to the device to identify whether the downstream device has sent PIM join messages. If not, troubleshoot the downstream device. If yes, the communication between the device and the downstream device is abnormal, and proceed to step 8.
¡ If the interface connected to the downstream device has received PIM join messages, and proceed to step 3.
3. Verify that the interface is enabled with PIM-SM.
Execute the display pim interface verbose command to identify whether the RPF interface, RPF neighbor interface, and interface connected to the subnet of hosts (downstream interface on the receiver-side DR) have been enabled with PIM-SM.
¡ If any of the interfaces is not enabled with PIM-SM, execute the pim sm command on the interface. Verify that IP multicast routing has been enabled by using the multicast routing command and that the neighbor relationship has been established successfully (displayed by using the display pim neighbor command).
¡ If all of the interfaces are enabled with PIM-SM, proceed to step 4.
4. Verify that an RPF route to the multicast source exists.
Execute the display multicast rpf-info command to check for the RPF route to the multicast source.
¡ If no route to the RP exists, examine unicast route configuration. Execute the ping command on both the device and the multicast source to identify whether they can ping each other successfully. If no, modify the unicast route configuration until they can ping each other successfully.
¡ If a route to the RP exists, execute the display multicast rpf-info command, and check the Referenced route type field for the type of the referenced route.
- If the RPF route is a static multicast route (the Referenced route type field is multicast static), execute the display multicast routing-table static command to identify whether the static multicast route is correct.
- If the RPF route is a unicast route (the Referenced route type field is igp, egp, unicast (direct), or unicast), execute the display ip routing-table command to identify whether the unicast route is the same as the RPF route.
¡ If an RPF route to the multicast source exists and is correct, proceed to step 5.
Execute the display pim interface command, and check the DR-Address field. If (local) is displayed after the DR address, the DR is the receiver-side DR.
¡ If the DR is not the receiver-side DR, locate the device where the DR resides and perform step 6 on the device.
¡ If the DR is the receiver-side DR, perform step 6 on the current device.
Execute the display multicast boundary command to check for the multicast forwarding boundary configuration.
¡ If an interface is configured with a multicast forwarding boundary, execute the undo multicast boundary command to delete it.
¡ If no interface is configured with a multicast forwarding boundary, proceed to step 7.
Execute the display this command in PIM view to check for a multicast source policy.
¡ If a multicast source policy has been configured, verify that it permits multicast data to be forwarded. If the multicast source policy denies multicast data, execute the undo source-policy command to delete it or modify the ACL so that it can permit the multicast data to pass through.
¡ If no interface is configured with a multicast forwarding boundary, proceed to step 8.
8. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact the support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
N/A
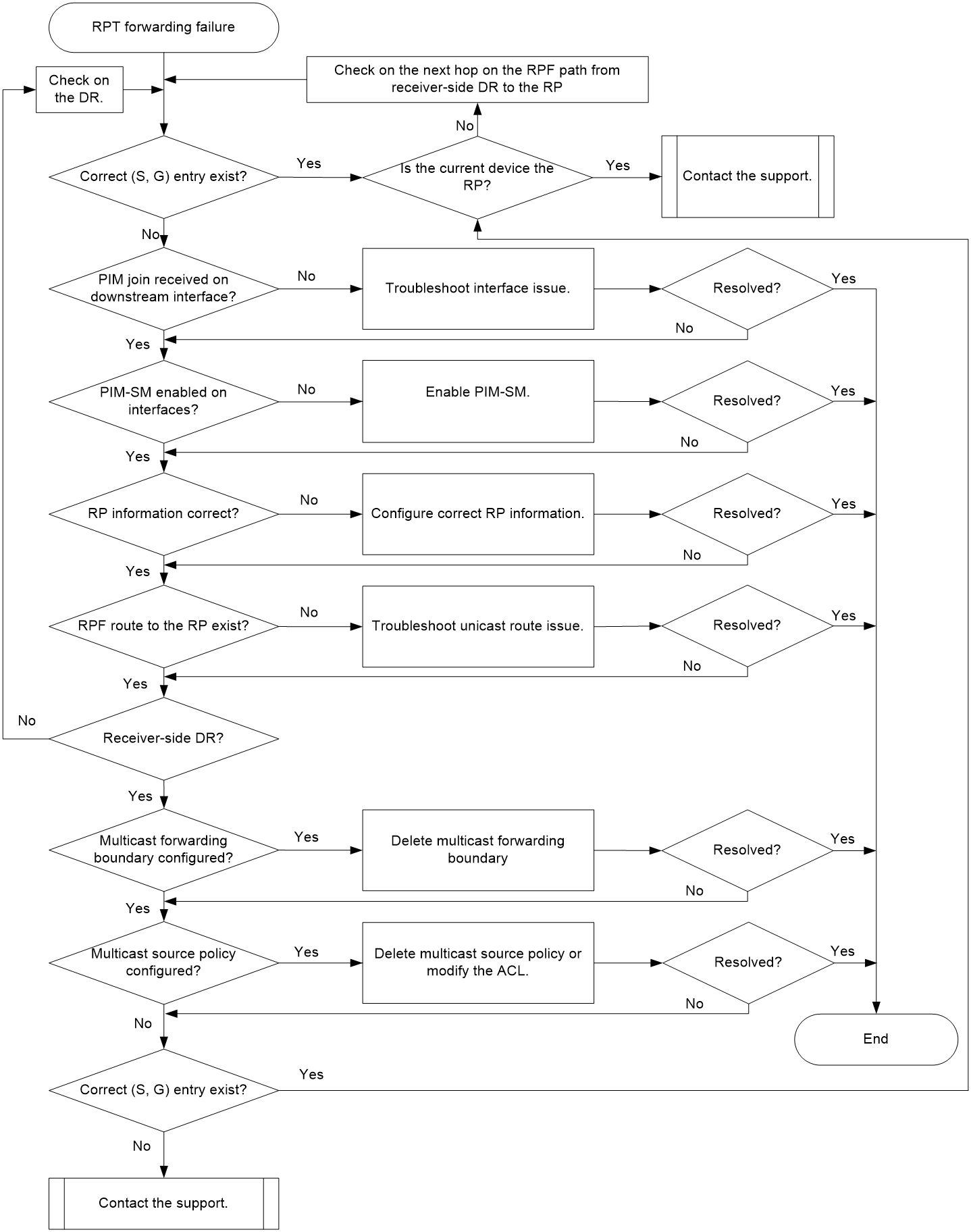
RPT forwarding failure in PIM-SM
Symptom
Multicast data fails to be forwarded through the RPT in a PIM-SM network. This section applies to only non-RP devices. If the faulty device is an RP, contact the support.
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· The route to the RP is unreachable.
· The RP address is not the same on all devices in the PIM-SM network.
· The interface connected to downstream devices does not receive PIM join messages.
· The interface is not enabled with PIM-SM.
· The RPF route to the RP is incorrect.
· Configuration errors exist, such as multicast forwarding boundary and multicast source policy.
Troubleshooting flow
Figure 4 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 4 Flowchart for troubleshooting RPT forwarding failure in PIM-SM
Solution
1. Verify that a correct (S, G) entry exists in the PIM routing table.
Execute the display pim routing-table command to check for the correct (S, G) entry.
¡ If a correct (S, G) entry exists, execute the display multicast forwarding-table command at 15-second intervals, and identify whether the same (S, G) entry exists in the forwarding table and check the Matched packets and Forwarded packets fields.
- If no (S, G) entry exists in the forwarding table or the values of the Matched packets and Forwarded packets fields do not increase, proceed to step 9.
- If the same (S, G) entry exists in the forwarding table and the values of the Matched packets and Forwarded packets fields increase,, also proceed to step 9.
¡ If no correct (S, G) entry exists, proceed to step 2.
2. Verify that the interface connected to the downstream device has received PIM join messages.
Under the guidance of the support, use a packet capture tool such as Wireshark to capture packets on the interface to identify whether PIM join messages are received.
¡ If not, use the packet capture tool to capture packets on the interface connecting the downstream device to the device to identify whether the downstream device has sent PIM join messages. If not, troubleshoot the downstream device. If yes, the communication between the device and the downstream device is abnormal, and proceed to step 9.
¡ If the interface connected to the downstream device has received PIM join messages, and proceed to step 3.
3. Verify that the interface is enabled with PIM-SM.
Execute the display pim interface verbose command to identify whether the RPF interface, RPF neighbor interface, and interface connected to the subnet of hosts (downstream interface on the receiver-side DR) have been enabled with PIM-SM.
¡ If any of the interfaces is not enabled with PIM-SM, execute the pim sm command on the interface. Verify that IP multicast routing has been enabled by using the multicast routing command and that the neighbor relationship has been established successfully (displayed by using the display pim neighbor command).
¡ If all of the interfaces are enabled with PIM-SM, proceed to step 4.
4. Verify that the RP information is correct.
Execute the display pim rp-info command to check for the RP information, and identify whether all other devices in the PIM-SM domain has the same RP information.
¡ If the RP information is not the same and static RPs are used, execute the static-rp command on all devices to configure the same RP address. If dynamic RPs are used, proceed to step 9.
¡ If the RP information is the same, proceed to step 5.
5. Verify that an RPF route to the RP exists.
Execute the display multicast rpf-info command to check for the RPF route to the RP.
¡ If no route to the RP exists, examine unicast route configuration. Execute the ping command on both the device and the RP to identify whether they can ping each other successfully. If no, modify the unicast route configuration until they can ping each other successfully.
¡ If a route to the RP exists, execute the display multicast rpf-info command, and check the Referenced route type field for the type of the referenced route.
- If the RPF route is a static multicast route, execute the display multicast routing-table static command to identify whether the static multicast route is correct.
- If the RPF route is a unicast route, execute the display ip routing-table command to identify whether the unicast route is the same as the RPF route.
¡ If an RPF route to the RP exists and is correct, proceed to step 6.
6. Verify that the DR corresponding to the interface for forwarding multicast data is the receiver-side DR.
Execute the display pim interface command, and check the DR-Address field. If (local) is displayed after the DR address, the DR is the receiver-side DR.
¡ If the DR is not the receiver-side DR, locate the device where the DR resides and perform step 7 on the device.
¡ If the DR is the receiver-side DR, perform step 7 on the current device.
7. Verify that the RPF interface and the connected interface of the device's RPF neighbor have not been configured with a multicast forwarding boundary.
Execute the display multicast boundary command to check for the multicast forwarding boundary configuration.
¡ If an interface is configured with a multicast forwarding boundary, execute the undo multicast boundary command to delete it.
¡ If no interface is configured with a multicast forwarding boundary, proceed to step 8.
8. Verify that no multicast source policy is configured or multicast data is not denied by a multicast source policy.
Execute the display this command in PIM view to check for a multicast source policy.
¡ If a multicast source policy has been configured, verify that it permits multicast data to be forwarded. If the multicast source policy denies multicast data, execute the undo source-policy command to delete it or modify the ACL so that it can permit the multicast data to pass through.
¡ If no interface is configured with a multicast forwarding boundary, proceed to step 9.
9. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact the support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
N/A