- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 03-MSDP Troubleshooting Guide | 93.21 KB |
Troubleshooting multicast
MSDP issues
(S, G) entry creation failure
Symptom
The receiver-side MSDP peer fails to create (S, G) entries.
Common causes
The following are the common causes of this type of issue:
· The receiver-side MSDP peer fails to establish an MSDP peer relationship with the source-side MSDP peer.
· The receiver-side MSDP peer is not enabled with the SA message cache mechanism.
· The receiver-side MSDP peer does not receive SA messages from the source-side MSDP peer.
· The source-side MSDP peer is not created on the RP.
· Configuration errors exist, such as incorrect SA incoming policy, SA outgoing policy, or SA message creation policy.
Troubleshooting flow
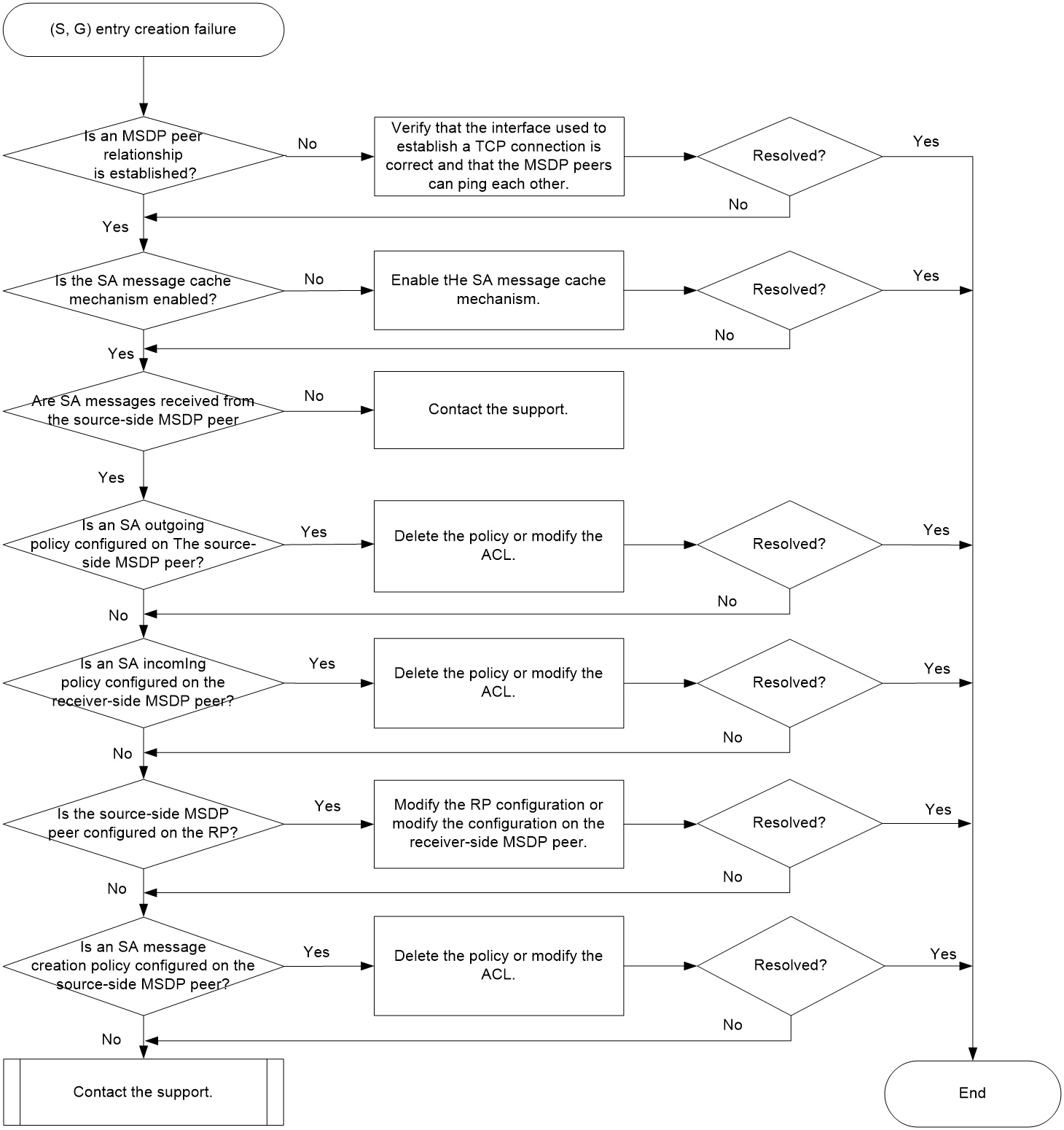
Figure 1 shows the troubleshooting flowchart.
Figure 1 Flowchart for troubleshooting (S, G) entry creation failure
Solution
1. Verify that the receiver-side MSDP peer have successfully established an MSDP peer relationship with the source-side MSDP peer.
Execute the display msdp brief command on the receiver-side MSDP peer, and check the State field. If the State field is Established, an MSDP peer relationship has been established successfully.
¡ If the State field is not Established, verify that the interface used to establish a TCP connection with the source-side MSDP peer is correct and that the MSDP peers can ping each other. If the MSDP peers cannot ping each other, troubleshoot the ping failure as described in "Ping failure."
¡ If an MSDP peer relationship has been established successfully, proceed to step 2.
2. Verify that the receiver-side MSDP peer is enabled with the SA message cache mechanism.
Execute the display this command in MSDP view on the receiver-side MSDP peer to identify whether the SA message cache mechanism is enabled.
¡ If no, execute the cache-sa-enable command.
¡ If yes, proceed to step 3.
3. Identify whether the receiver-side MSDP peer receives SA messages from the source-side MSDP peer.
Execute the display this command to display (S, G) entries in the SA cache. Identify whether SA messages from the source-side MSDP peer are received by examining the (S, G) entries.
¡ If no, proceed to step 4.
¡ If yes, proceed to step 8.
4. Identify whether the source-side MSDP peer is configured with an SA outgoing policy.
Execute the display this command on the source-side MSDP peer to identify whether an SA outgoing policy is configured.
¡ If yes, perform one of the following tasks depending on whether an ACL is specified:
- If no ACL is specified, the source-side MSDP peer discards all SA messages, and use the undo peer sa-policy export command to delete the SA outgoing policy.
- If an ACL is specified, the source-side MSDP peer forwards only SA messages that the ACL permits. Verify that the SA messages are permitted by the specified ACL. If the SA messages are not permitted, use the undo peer sa-policy export command to delete the SA outgoing policy or modify the ACL.
¡ If no, proceed to step 5.
5. Identify whether the receiver-side MSDP peer is configured with an SA incoming policy.
Execute the display this command on the receiver-side MSDP peer to identify whether an SA incoming policy is configured.
¡ If yes, perform one of the following tasks depending on whether an ACL is specified:
- If no ACL is specified, the receiver-side MSDP peer discards all SA messages, and use the undo peer sa-policy export command to delete the SA incoming policy.
- If an ACL is specified, the receiver-side MSDP peer receives only SA messages that the ACL permits. Verify that the SA messages are permitted by the specified ACL. If the SA messages are not permitted, use the undo peer sa-policy export command to delete the SA incoming policy or modify the ACL.
¡ If no, proceed to step 6.
6. Verify that the source-side MSDP peer is the RP.
Execute the display pim routing-table command on the source-side MSDP peer, and check the Flag field. If the Flag field is 2MSDP, the source-side MSDP peer is the RP.
¡ If the source-side MSDP peer is not the RP, modify the RP configuration or modify the configuration on the receiver-side MSDP peer.
¡ If the source-side MSDP peer is the RP, proceed to step 7.
7. Identify whether the source-side MSDP peer is configured with an SA message creation policy.
Execute the display this command on the source-side MSDP peer to identify whether an SA message creation policy is configured.
¡ If yes, perform one of the following tasks depending on whether an ACL is specified:
- If no ACL is specified, the source-side MSDP peer does not advertise any (S, G) entries when creating SA messages, and use the undo import-source command to delete the SA message creation policy.
- If an ACL is specified, the source-side MSDP peer advertises only the (S, G) entries that the ACL permits. Verify that the (S, G) entries are permitted by the specified ACL. If the (S, G) entries are not permitted, use the undo import-source command to delete the SA message creation policy or modify the ACL.
¡ If no, proceed to step 8.
8. If the issue persists, collect the following information and contact the support:
¡ Results of each step.
¡ The configuration file, log messages, and alarm messages.
Related alarm and log messages
Alarm messages
N/A
Log messages
N/A