- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 05-URL filtering configuration | 222.61 KB |
URL filtering whitelist/blacklist rule
URL filtering signature library management
URL filtering tasks at a glance
Configuring a URL filtering policy
About configuring a URL filtering policy
Configuring a category-based URL filtering policy
Configuring a whitelist-based URL filtering policy
Copying a URL filtering policy or category
Copying a URL filtering policy
Copying a URL filtering category
Applying a warning parameter profile to a URL filtering policy
Applying a URL filtering policy to a DPI application profile
Activating URL filtering policy and rule settings
Applying a DPI application profile to a security policy rule
Managing the URL filtering signature library
Scheduling automatic URL filtering signature library update
Triggering an immediate URL filtering signature update
Performing a URL filtering signature manual update
Rolling back the URL filtering signature library
Configuring URL filtering logging for resource access
About URL filtering logging for resource access
Logging access to only resources in the root directories of websites
Disabling logging for access to resources of specific types
Display and maintenance commands for URL filtering
URL filtering configuration examples
Example: Using a URL filtering policy in a security policy
Configuring URL filtering
About URL filtering
URL filtering controls access to the Web resources by filtering the URLs that the users visit.
URL
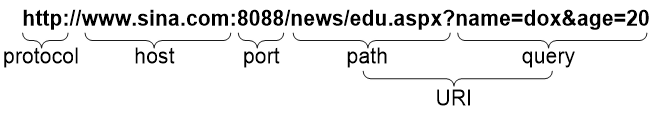
A URL is a reference to a resource that specifies the location of the resource on a network and a mechanism for retrieving it. The syntax of a URL is protocol://host [:port]/path/[;parameters][?query]#fragment. Figure 1 shows an example URL.
Table 1 describes the fields in a URL.
Table 1 URL field descriptions
|
Field |
Description |
|
protocol |
Transmission protocol, such as HTTP. |
|
host |
Domain name or IP address of the server where the indicated resource is located. |
|
[:port] |
Optional field that identifies the port number of the transmission protocol. If this field is omitted, the default port number of the protocol is used. |
|
/path/ |
String that identifies the directory or file where the indicated resource is stored. The path is a sequence of segments separated by zero or multiple forward slashes. |
|
[parameters] |
Optional field that contains special parameters. |
|
[?query] |
Optional field that contains parameters to be passed to the software for querying dynamic webpages. Each parameter is a <key>=<value> pair. Different parameters are separated by an ampersand (&). |
|
URI |
Uniform resource identifier that identifies a resource on a network. |
URL filtering rule
A URL filtering rule matches URLs based on the content in the URI or hostname field.
URL filtering rule type
URL filtering provides the following types of URL filtering rules:
· Predefined URL filtering rules—Signature-based URL filtering rules. The device automatically generates them based on the local URL filtering signatures. In most cases, the predefined rules are sufficient for URL filtering.
· User-defined URL filtering rules—Regular expression- or text-based URL filtering rules that are manfully configured.
URL filtering rule matching method
A URL filtering rule supports the following URL matching methods:
· Text-based matching—Matches the hostname and URI fields of a URL against text patterns.
When performing text-based matching for the hostname field of a URL, the device first determines if the text pattern contains the asterisk (*) wildcard character at the beginning or end.
¡ If the text pattern does not contain the asterisk (*) wildcard character at the beginning or end, the hostname matching succeeds if the hostname of the URL matches the text pattern.
¡ If the text pattern contains the asterisk (*) wildcard character at the beginning, the hostname matching succeeds if the hostname of the URL matches or ends with the text pattern without the wildcard character.
¡ If the text pattern contains the asterisk (*) wildcard character at the end, the hostname matching succeeds if the hostname of the URL matches or starts with the text pattern without the wildcard character.
¡ If the text pattern contains the asterisk (*) wildcard character at both the beginning and the end, the hostname matching succeeds if the hostname of the URL matches or includes the text pattern without the wildcard characters.
Text-based matching for the URI field works in the same way that text-based matching for the hostname field works.
· Regular expression-based matching—Matches the hostname and URI fields of a URL against regular expressions. For example, if you set the regular expression for hostname matching to sina.*cn, URLs that carry the news.sina.com.cn hostname will be matched.
URL category
URL filtering provides the URL categorization feature to facilitate filtering rule management.
You can classify multiple URL filtering rules to a URL category and specify an action for the category. If a matching rule is in multiple URL categories, the system takes the action for the category with the highest severity level.
URL filtering supports the following types of URL categories:
· Predefined URL categories.
The predefined URL categories contain the predefined URL filtering rules. Each predefined URL category has a unique severity level in the range of 1 to 999, and a category name that begins Pre-. Predefined URL categories cannot be modified.
The device supports two levels of predefined URL categories: child URL category and parent URL category.
A predefined parent URL category contains only predefined child URL categories.
· User-defined URL categories.
You can manually create URL categories and configure filtering rules for them. The severity level of a user-defined URL category is in the range of 1000 to 65535. You can edit the filtering rules and change the severity level for a user-defined URL category.
URL filtering whitelist/blacklist rule
The device supports using URL-based whitelist and blacklist rules to filter packets. If the URL in a packet matches a blacklist rule, the packet is dropped. If the URL matches a whitelist rule, the packet is permitted to pass through.
URL filtering policy
A URL filtering policy can contain the following settings:
· URL categories and filtering actions. URL filtering actions include drop, permit, block source, reset, redirect, and logging.
· URL filtering whitelist and blacklist rules.
You can also specify the default action on packets that do not match any filtering rules (including URL categories and URL filtering whitelist and blacklist rules) in the policy.
URL filtering mechanism
URL filtering takes effect after you apply a URL filtering policy to a DPI application profile and use the DPI application profile in a security policy rule.
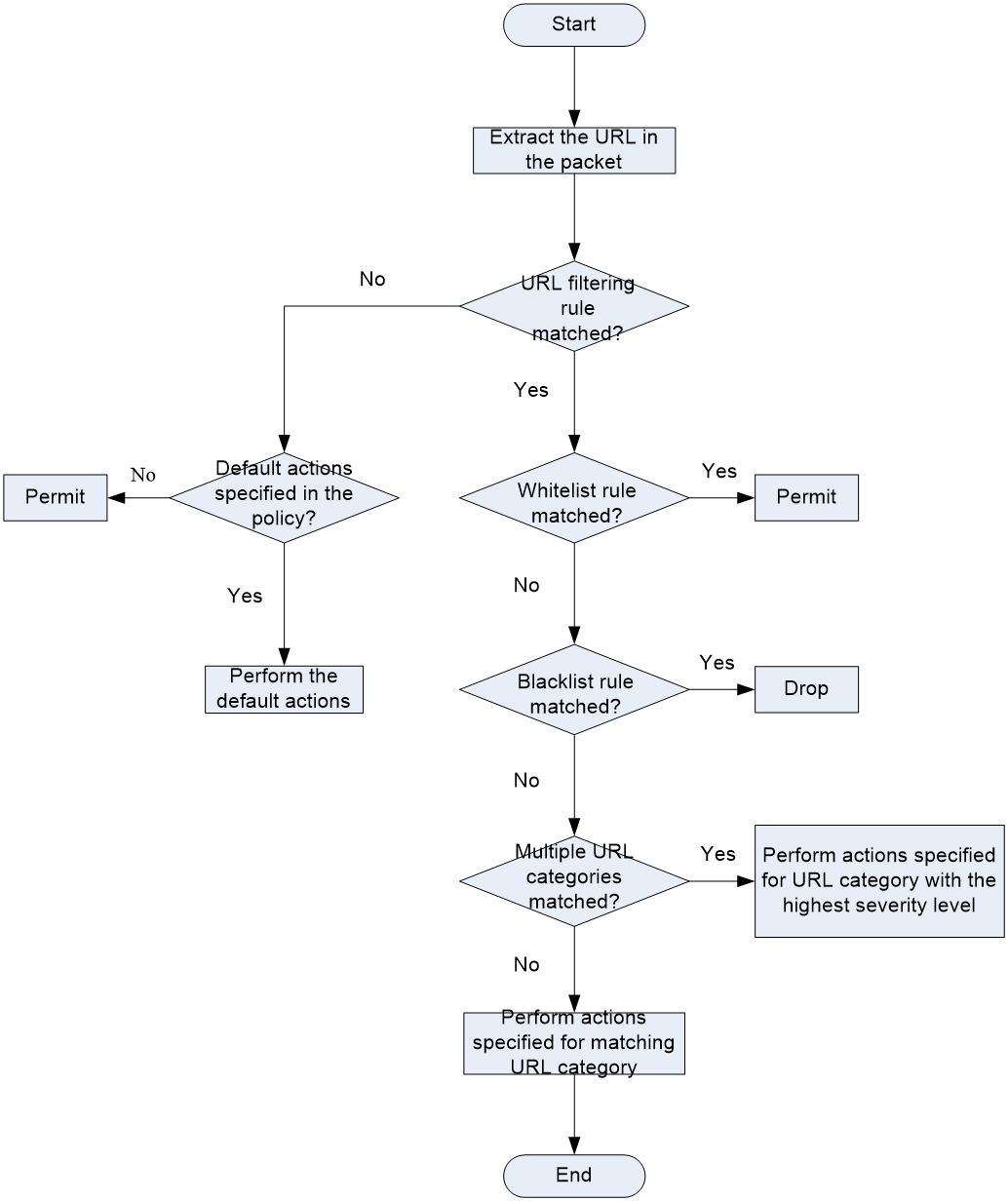
As shown in Figure 2, upon receiving a packet, the device performs the following operations:
1. The device compares the packet with the security policy rules.
If the packet matches a rule that is associated with a URL filtering policy (through a DPI application profile), the device extracts the URL from the packet.
For more information about security policies, see Security Configuration Guide.
2. The device compares the extracted URL with the whitelist and blacklist rules in the URL filtering policy.
If both the whitelist and blacklist features are enabled, the device uses the following process to handle the packet:
a. If the URL matches a whitelist rule, the packet is permitted to pass through.
b. If the URL does not match a whitelist rule, the device identifies whether the URL matches a blacklist rule.
- If the URL matches a blacklist rule, the packet is dropped.
- If the URL does not match a blacklist rule, the device performs step 3.
If only the whitelist feature is enabled, the device handles the packet as follows:
¡ If the URL matches a whitelist rule, the packet is permitted to pass through.
¡ If the URL does not match a whitelist rule, the device drops the packet.
If both the whitelist and blacklist features are not enabled, the device performs step 3.
3. The device compares the extracted URL with the URL filtering rules in the URL filtering policy.
a. If the URL matches a URL filtering rule that belongs to a user-defined URL category, the devices takes the action specified for the URL category. If the URL filtering rule belongs to multiple user-defined URL categories, the action specified for the URL category with the highest severity level apply.
If no matching URL filtering rule belongs to a user-defined URL category, the device moves to step b.
b. If the URL matches a URL filtering rule that belongs to a predefined URL category, the devices takes the action specified for the URL category.
If the URL filtering rule belongs to multiple predefined URL categories, the action specified for the URL category with the highest severity level apply.
4. If the URL does not match any rule in the policy, the default action specified for the policy applies. If the default action is not configured, the device permits the packet to pass through.
Figure 2 URL filtering mechanism
URL filtering signature library management
The device uses the local URL filtering signature library to identify URLs in the HTTP packets.
You can update the device URL filtering signature library to the most up-to-date version or roll back the library to a version.
Updating the URL filtering signature library
The following methods are available for updating the URL filtering signature library on the device:
· Automatic update.
The device periodically accesses the company's website and automatically downloads the most up-to-date URL filtering signature file to update its local signature library.
· Triggered update.
The device downloads the most up-to-date URL filtering signature file from the company's website to update its local signature library immediately you trigger the operation.
· Manual update.
Use this method when the device cannot connect to the company's website.
You must manually download the most up-to-date URL filtering signature file from the company's website, and then use the file to update the signature library on the device.
Rolling back the URL filtering signature library
If filtering false alarms or filtering exceptions occur frequently, you can roll back the URL filtering signature library to the factory default version.
URL filtering tasks at a glance
To configure URL filtering:
1. (Optional.) Configuring a URL category
2. Configuring a URL filtering policy
3. (Optional.) Copying a URL filtering policy or category
4. (Optional.) Applying a warning parameter profile to a URL filtering policy
5. Applying a URL filtering policy to a DPI application profile
6. (Optional.) Activating URL filtering policy and rule settings
7. Applying a DPI application profile to a security policy rule
8. Managing the URL filtering signature library
9. (Optional.) Enabling DPI engine logging
10. (Optional.) Configuring URL filtering logging for resource access
Configuring a URL category
About this task
Perform this task to create a user-defined URL category and configure filtering rules for it to meet specific URL filtering requirements.
Restrictions and guidelines
When creating a URL category, you must assign a unique severity level in the range of 1000 to 65535 to the URL category. The larger the value, the higher the severity level.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a URL category and enter its view.
url-filter category category-name [ severity severity-level ]
By default, the device provides predefined URL categories with names starting with Pre-.
The name of a user-defined URL category cannot start with Pre-.
3. (Optional.) Configure a description for the URL category.
description text
4. Configure URL filtering rules for the URL category. Choose the options to configure as needed:
¡ Configure a URL filtering rule.
rule rule-id host { regex regex | text string } [ uri { regex regex | text string } ]
¡ (Optional.) Add the URL filtering rules of a predefined URL category to the URL category.
include pre-defined category-name
By default, a user-defined URL category does not contain the URL filtering rules of any predefined URL category.
Configuring a URL filtering policy
About configuring a URL filtering policy
The URL filtering is implemented by URL filtering polices.
To configure a URL filtering policy, perform either of the following tasks:
· Configuring a category-based URL filtering policy
A category-based URL filtering policy contains the following settings:
¡ URL category-to-action mappings.
¡ Default action.
¡ (Optional.) Whitelist and blacklist rules.
· Configuring a whitelist-based URL filtering policy
Restrictions and guidelines
If DRS is enabled, the name of a URL filtering policy cannot be drs to avoid unexpected configuration changes or other errors after reboot. To enable DRS, use the wlan drs enable command. For more information about DRS, see WLAN DRS configuration in WLAN Security Configuration Guide.
Configuring a category-based URL filtering policy
Restrictions and guidelines
The logging keyword enables the URL filtering module to log URL filtering events and use one of the following methods to send log messages:
· Fast log output—You must specify a log host to receive the log messages. Log messages are sent to the specified log host.
· Syslog output—Log messages are sent to the information center. With the information center, you can set log message filtering and output rules, including output destinations. The information center can output URL filtering syslogs to any destinations except the console and the monitor terminal. If you configure the console or monitor terminal as an output destination, the output destination setting will not take effect. To view URL filtering syslogs stored on the device, use the display logbuffer command. Make sure you do not disable log output to the log buffer, which is enabled by default. For more information about configuring the information center, see System Management Configuration Guide.
Syslog output might affect device performance. As a best practice, use fast log output. For more information about fast log output, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a URL filtering policy and enter its view.
url-filter policy policy-name
3. Specify the actions for a URL category.
category category-name action { block-source [ parameter-profile parameter-name ] | drop | permit | redirect parameter-profile parameter-name | reset } [ logging [ parameter-profile parameter-name ] ]
By default, no actions are specified for a URL category.
If a packet matches a rule that is in multiple URL categories, the system uses the actions for the category with the highest severity level.
4. (Optional.) Specify the default action on packets that do not match any rule in the policy.
default-action { block-source [ parameter-profile parameter-name ] | drop | permit | redirect parameter-profile parameter-name | reset } [ logging [ parameter-profile parameter-name ] ]
5. (Optional.) Configure a whitelist or blacklist rule in the policy.
add { blacklist | whitelist } [ id ] host { regex host-regex | text host-name } [ uri { regex uri-regex | text uri-name } ]
6. (Optional.) Enable the referer whitelist.
referer-whitelist enable
By default, the referer whitelist is enabled. It allows an HTTP or HTTPS request to pass through if its referer header matches a whitelist rule.
7. (Optional.) Rename the URL filtering policy.
rename new-name
Configuring a whitelist-based URL filtering policy
About the task
This feature allows only the HTTP or HTTPS requests that match the whitelist rules to pass through. When you do not want to perform any other configurations, such as URL categories, URL filtering actions, and URL filtering policy default action, you can use this feature.
With this feature enabled, the device allows users to access only the Web resources added to the whitelist rules, and other Web resources are not allowed to access.
Restrictions and guidelines
After URL filtering whitelist is enabled, URL filtering supports only fast log output and does not support system log output. For more information on fast logs, see fast log output in Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a URL filtering policy and enter its view.
url-filter policy policy-name
3. Configure a whitelist rule in the policy.
add whitelist [ id ] host { regex host-regex | text host-name } [ uri { regex uri-regex | text uri-name } ]
4. (Optional.) Enable the referer whitelist.
referer-whitelist enable
By default, the referer whitelist is enabled. It allows an HTTP or HTTPS request to pass through if its referer header matches a whitelist rule.
5. Enable URL whitelist-only filtering.
whitelist-only enable
By default, URL whitelist-only filtering is disabled.
Copying a URL filtering policy or category
Copying a URL filtering policy
About this task
You can create a new URL filtering policy by copying an existing one.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a URL filtering policy and enter its view.
url-filter copy policy old-name new-name
Copying a URL filtering category
About this task
You can create a new URL category by copying an existing one.
Restrictions and guidelines
When you copy a URL category, be sure to assign a unique severity level to the new URL category.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Copy a URL category.
url-filter copy category old-name new-name severity severity-level
Applying a warning parameter profile to a URL filtering policy
About this task
If an endpoint user visits a website blocked by URL filtering, the device will display an alarm message on the user's browser. The alarm message is stored in the warning parameter profile applied to the URL filtering policy. For more information about configuring a warning parameter profile, see DPI engine configuration in DPI Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a URL filtering policy and enter URL filtering policy view.
url-filter policy policy-name
3. Apply a warning parameter profile to the URL filtering policy and enable sending the alarm message defined in the profile.
warning parameter-profile profile-name
By default, no warning parameter profile is applied to a URL filtering policy and the device sends the default alarm message to users. For more information about the default alarm message, see the usage guidelines for this URL filtering command in DPI Command Reference.
Applying a URL filtering policy to a DPI application profile
About this task
A URL filtering policy must be applied to a DPI application profile to take effect.
Restrictions and guidelines
A DPI application profile can use only one URL filtering policy. If you apply different URL filtering policies to the same DPI application profile, only the most recent configuration takes effect.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter DPI application profile view.
app-profile app-profile-name
For more information about this command, see DPI engine commands in DPI Command Reference.
3. Assign a URL filtering policy to the DPI application profile.
url-filter apply policy policy-name
By default, no URL filtering policy is applied to the DPI application profile.
Activating URL filtering policy and rule settings
About this task
By default, the system will detect whether another configuration change (such as creation, modification, or deletion) occurs within a 20-second interval after a change to the URL filtering policy and rule settings:
· If no configuration change occurs within the interval, the system will perform an activation operation at the end of the next 20-second interval to make the configuration take effect.
· If a configuration change occurs within the interval, the system continues to periodically detect whether configuration changes occur within next 20-second intervals.
To immediately activate a configuration change, execute the inspect activate command.
For more information about activating DPI service module configuration, see "Configuring DPI engine."
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Activate URL filtering policy and rule settings.
inspect activate
By default, the system automatically activates changed URL filtering policy and rule settings for them to take effect.
|
CAUTION: This command can cause temporary outage for DPI services. Services based on the DPI services might also be interrupted. For example, security policies cannot control access to applications. |
Applying a DPI application profile to a security policy rule
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter security policy view.
security-policy { ip | ipv6 }
3. Enter security policy rule view.
rule { rule-id | [ rule-id ] name rule-name }
4. Set the rule action to pass.
action pass
The default rule action is drop.
5. Use a DPI application profile in the rule.
profile app-profile-name
By default, no DPI application profile is used in a security policy rule.
Managing the URL filtering signature library
You can update or roll back the version of the URL filtering signature library on the device.
Restrictions and guidelines
· Do not delete the /dpi/ folder in the root directory of the storage medium.
· Do not perform URL filtering signature update and rollback when the device's free memory is below the normal state threshold. For more information about device memory thresholds, see system management in System Management Configuration Guide.
· For successful automatic and immediate signature update, make sure the device can resolve the domain name of the company's website into an IP address through DNS. For more information about DNS, see DNS configuration in Network Connectivity Configuration Guide.
· Update only one signature library at a time. Do not perform signature library update until the existing signature library update is completed.
· The upgrade of the URL filtering signature library on the WSG1800X and WX2800X series requires a license to run on the device. If the license expires, you can still use the URL filtering functions but you can no longer upgrade the URL filtering signature library on the device. For more information about licenses, see License Management Configuration Guide.
Scheduling automatic URL filtering signature library update
About this task
You can schedule automatic URL filtering signature library update if the device can access the signature database services on the company's website. The device periodically obtains the latest signature file from the company's website to update its local signature library as scheduled.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable automatic URL filtering signature library update and enter automatic URL filtering signature library update configuration view.
url-filter signature auto-update
By default, automatic URL filtering signature library update is disabled.
3. Schedule the update time.
update schedule { daily | weekly { fri | mon | sat | sun | thu | tue | wed } } start-time time tingle minutes
By default, the device starts to update the URL filtering signature at a random time between 01:00:00 and 03:00:00 every day.
Triggering an immediate URL filtering signature update
About this task
Anytime you find a release of new signature version on the company's website, you can trigger the device to immediately update the local signature library.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Trigger an automatic URL filtering signature library update.
url-filter signature auto-update-now
Performing a URL filtering signature manual update
About this task
If the device cannot access the signature database services on the company's website, use one of the following methods to manually update the URL filtering signature library on the device:
· Local update—Updates the URL filtering signature library on the device by using the locally stored update URL filtering signature file.
· FTP/TFTP update—Updates the URL filtering signature library on the device by using the file stored on the FTP or TFTP server.
To specify the source IP of request packets to the TFTP or FTP server for manual signature library update, specify the source keyword in the url-filter signature update command. For example, if packets from the device must be translated by NAT before accessing the TFTP or FTP server, you must specify a source IP address complied with NAT rules for NAT translation. If NAT translation is performed by an independent NAT device, make sure the IP address specified by the url-filter signature update command can reach the NAT device at Layer 3.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Manually update the URL filtering signature library on the device.
url-filter signature update file-path [ source { ip | ipv6 } { ip-address | interface interface-type interface-number } ]
|
CAUTION: Select a signature file according to the memory size and software version of the device. H3C provides signature files separately for high-memory (equal to or higher than 8 GB) and low-memory (lower than 8 GB) devices and for different software versions. If you use a signature file applicable to high-memory devices to update the URL filtering signature library on a low-memory device, exceptions might occur on the low-memory device. As a best practice, use a signature file that is compatible with the software version and memory size of the device to update the URL filtering signature library on the device. |
Rolling back the URL filtering signature library
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Roll back the URL filtering signature library to the factory default version.
url-filter signature rollback factory
Enabling DPI engine logging
About this task
You can enable DPI engine logging for audit purposes. Log messages generated by DPI engine are output to the device information center. The information center then sends the messages to designated destinations based on log output rules. For more information about the information center, see System Management Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable DPI engine logging.
url-filter log enable
By default, DPI engine logging is disabled.
Configuring URL filtering logging for resource access
About URL filtering logging for resource access
URL filtering logs user access to resources after you specify the logging action for a URL category or as a default action for a URL filtering policy.
You can use either of the following methods to configure URL filtering to log access to specific types of resources:
· Configure URL filtering to log access to only resources in the root directories of websites.
· Enable or disable URL filtering logging for access to resources of specific types.
Logging access to only resources in the root directories of websites
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure URL filtering to log only access to resources in the root directories of websites.
url-filter log directory root
By default, URL filtering logs access to Web resources in all directories.
Disabling logging for access to resources of specific types
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Disable URL filtering logging for access to resources of a specific resource type.
¡ Disable logging for access to resources of a predefined resource type.
url-filter log except pre-defined { css | gif | ico | jpg | js | png | swf | xml }
¡ Disable logging for access to resources of a user-defined resource type.
url-filter log except user-defined text
By default, URL filtering logs access to all resources except for resources of the predefined resource types (including CSS, GIF, ICO, JPG, JS, PNG, SWF, and XML resources).
Display and maintenance commands for URL filtering
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display URL category information. |
display url-filter { category | parent-category } [ verbose ] |
|
Display information about the URL filtering signature library. |
display url-filter signature library |
|
Display URL filtering statistics. |
display url-filter statistics |
|
Clear URL filtering statistics. |
reset url-filter statistics |
URL filtering configuration examples
Example: Using a URL filtering policy in a security policy
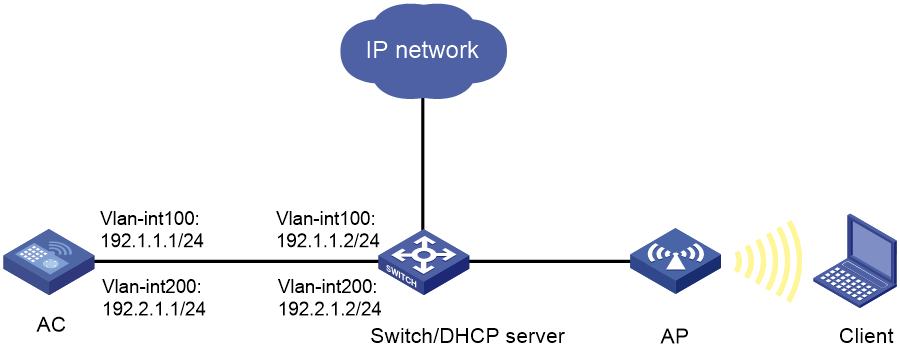
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 3, the switch acts as a DHCP server to assign IP addresses to the AP and client. The AP and AC establish CAPWAP tunnels in VLAN 100. The client accesses the wireless network in VLAN 200.
Configure a URL filtering policy on the AC so the AC performs the following operations:
· Permits the client to access website http://www.sina.com on the IP network.
· Drops and logs packets that match the Pre-Game URL category.
· Drops and logs packets that do not match any filtering rule in the URL filtering policy.
Procedure
1. Configure interfaces on the AC:
# Create VLAN 100 and VLAN-interface 100, and assign an IP address to the VLAN interface. The AP will obtain this IP address to establish CAPWAP tunnels with the AC.
<AC> system-view
[AC] vlan 100
[AC-vlan100] quit
[AC] interface vlan-interface 100
[AC-Vlan-interface100] ip address 192.1.1.1 24
[AC-Vlan-interface100] quit
# Create VLAN 200 and VLAN-interface 200, and assign an IP address to the VLAN interface. The client will access the wireless network in this VLAN.
[AC] vlan 200
[AC-vlan200] quit
[AC] interface vlan-interface 200
[AC-Vlan-interface200] ip address 192.2.1.1 24
[AC-Vlan-interface200] quit
# Set the link type of GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 (the port connected to the switch) to trunk. Deny traffic from VLAN 1 from passing through the port and allow traffic from VLAN 100 and VLAN 200 to pass through the port. Set the PVID of the port to 100.
[AC] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[AC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[AC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] undo port trunk permit vlan 1
[AC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 100 200
[AC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port trunk pvid vlan 100
[AC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
2. Configure a wireless service:
# Create service template 1 and enter service template view.
[AC] wlan service-template 1
# Set the SSID to service.
[AC-wlan-st-1] ssid service
# Assign the client to VLAN 200 after it comes online.
[AC-wlan-st-1] vlan 200
# Enable the service template.
[AC-wlan-st-1] service-template enable
[AC-wlan-st-1] quit
3. Configure the AP:
# Create a manual AP named ap1, and specify the AP model.
[AC] wlan ap ap1 model WA6320
# Set the serial ID to 219801A28N819CE0002T.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] serial-id 219801A28N819CE0002T
# Enter the view of radio 1 and bind service template 1 to the radio.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] radio 1
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] service-template 1
# Enable radio 1.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-1] quit
# Enter the view of radio 2 and bind service template 1 to the radio.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] radio 2
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-2] service-template 1
# Enable radio 2.
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-2] radio enable
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1-radio-2] quit
[AC-wlan-ap-ap1] quit
4. Configure an IP address object group named urlfilter and specify subnet 192.2.1.0/24 for the object group.
[AC] object-group ip address urlfilter
[AC-obj-grp-ip-urlfilter] network subnet 192.2.1.0 24
[AC-obj-grp-ip-urlfilter] quit
5. Configure URL filtering:
# Create a URL category named news, set its severity level to 2000, and enter URL category view.
[AC] url-filter category news severity 2000
# Create URL filtering rule 1 to match HTTP packets that contain host name www.sina.com in the URL.
[AC-url-filter-category-news] rule 1 host text www.sina.com
[AC-url-filter-category-news] quit
# Create a URL filtering policy named urlnews and enter URL filtering policy view.
[AC] url-filter policy urlnews
# In the URL filtering policy, specify action permit for URL category news.
[AC-url-filter-policy-urlnews] category news action permit
# In the URL filtering policy, specify action drop for predefined URL category Pre-Games and enable logging for the matching packets.
[AC-url-filter-policy-urlnews] category Pre-Games action drop logging
# In the URL filtering policy, set the default actions to drop and logging
[AC-url-filter-policy-urlnews] default-action drop logging
[AC-url-filter-policy-urlnews] quit
6. Apply URL filtering policy urlnews to a DPI application profile and activate the IPS policy settings:
# Create a DPI application profile named sec and enter DPI application profile view.
[AC] app-profile sec
# Apply URL filtering policy urlnews to the DPI application profile.
[AC-app-profile-sec] url-filter apply policy urlnews
[AC-app-profile-sec] quit
# Activate the URL filtering policy and rule settings.
[AC] inspect activate
7. Configure a security policy:
# Enter IPv4 security policy view.
[AC] security-policy ip
# Create a rule named urlfilter to permit the traffic from IP address in IP address object group urlfilter and apply DPI application profile sec to the security policy.
[AC-security-policy-ip] rule name urlfilter
[AC-security-policy-ip-13-urlfilter] source-ip urlfilter
[AC-security-policy-ip-13-urlfilter] action pass
[AC-security-policy-ip-13-urlfilter] profile sec
[AC-security-policy-ip-13-urlfilter] quit
# Activate rule matching acceleration.
[AC-security-policy-ip] accelerate enhanced enable
[AC-security-policy-ip] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the client can access website http://www.sina.com on the IP network. (Details not shown.)
# Verify that the device drops and logs the client's HTTP requests to game resources. (Details not shown.)