- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 02-DPI engine configuration | 232.10 KB |
Configure a DPI application profile
Activating policy and rule settings for DPI service modules
Configuring action parameter profiles
Configuring a block source parameter profile
Configuring a capture parameter profile
Configuring a logging parameter profile
Configuring a redirect parameter profile
Configuring an anti-virus warning parameter profile
Configuring a warning parameter profile for URL filtering
Enabling inspection suspension upon excessive CPU usage
Configuring DPI engine inspection parameters
Configuring an inspection mode
Configuring stream fixed length inspection
Configuring file fixed length inspection
Configuring file decompression parameters
Setting the maximum number of file decompression operations
Setting the maximum number of NFS file names recorded
Configuring advanced features of the DPI engine
Enabling source port-based application identification
Specifying a proxy server for online DPI service signature update
Specifying the source address for the request packet for online DPI service signature update
Enabling IPS logging to record HTTP packet details
Disabling DPI engine from transparently transmitting DPI service traffic
Disabling the DPI engine for all protocols
Disabling the DPI engine for the specified protocols
Display and maintenance commands for DPI engine
Configuring DPI engine
About DPI engine
DPI engine is an inspection module shared by DPI service modules. DPI engine uses inspection rules to identify the application layer information, including the application layer protocol and behavior. DPI service modules process packets based on the inspection results.
DPI functions
DPI engine provides the following functions:
· Protocol parsing—Identifies the application layer protocols and analyzes the application layer information. Information analysis includes recognizing, normalizing, and uncompressing application layer fields.
· AC pattern matching—Matches packet payloads by the Aho-Corasick (AC) patterns in inspection rules. AC pattern matching is fast and it is the core function of the DPI engine.
· Option matching—Matches packet payloads by the options in the inspection rules whose AC patterns have been matched. Option matching is slower than AC pattern matching.
DPI engine inspection rules
DPI engine uses inspection rules to match packets. Inspection rules are transformed from the rules or signatures of the DPI service modules. The match criteria in an inspection rule can contain the following types:
· AC pattern—Criteria that identify packet signatures. An AC pattern is a character string that is three or more bytes long.
· Option—Criteria other than AC patterns. For example, an option can be the port number or protocol type.
An inspection rule can contain both AC patterns and options. A packet must match both the AC patterns and options to match the rule.
An inspection rule can also contain only options. A packet matches the rule if it matches the options in the rule.
DPI engine mechanism
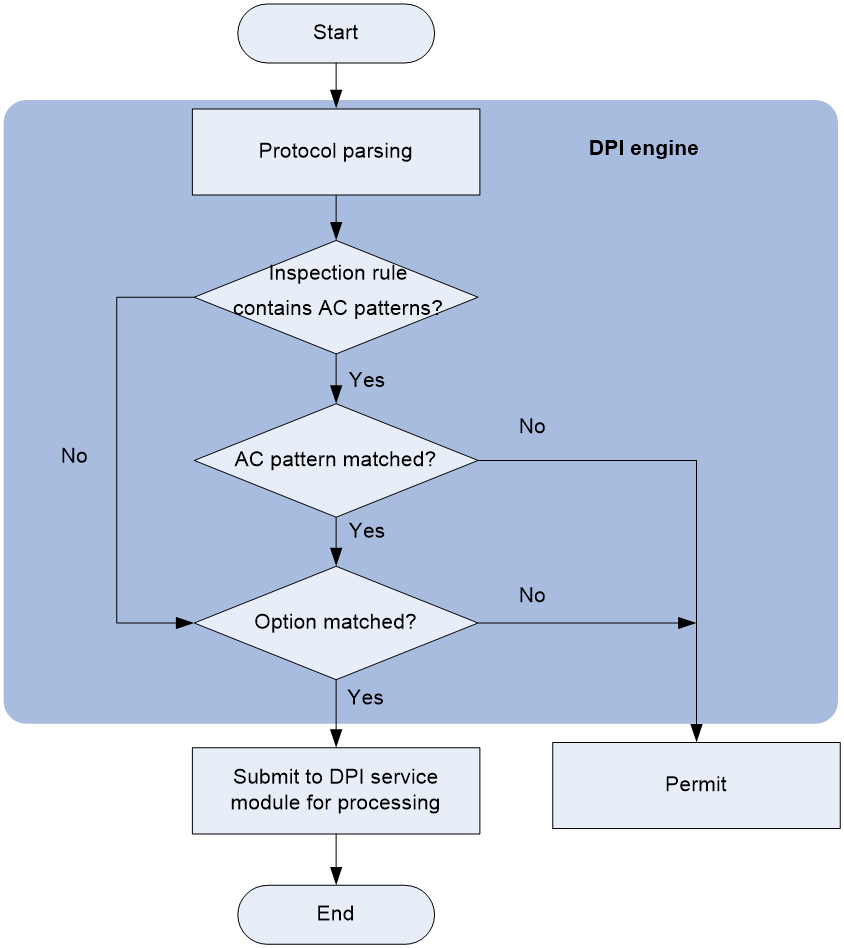
As shown in Figure 1, DPI engine works as follows:
1. The DPI engine performs protocol parsing for the packet and searches for applicable inspection rules according to the parsing results.
2. If an applicable inspection rule contains AC patterns, DPI engine performs AC pattern matching first. If an applicable inspection rule does not contain AC patterns, DPI engine directly performs option matching. The packet matches the rule if it matches the options.
3. If the packet matches an AC pattern in an applicable inspection rule, the DPI engine further compares the packet against the options associated with the AC pattern. The packet matches the rule if it matches the both the AC pattern and its associated options. If the packet matches an AC pattern but does not match its associated options, the DPI engine permits the packet to pass.
4. If the packet matches an inspection rule, the DPI engine submits the packet to the corresponding DPI service module for processing. If the packet does not match any rule, the DPI engine permits the packet to pass.
DPI engine tasks at a glance
To configure the DPI engine, perform the following tasks:
1. Configure a DPI application profile
2. Activating policy and rule settings for DPI service modules
3. Configuring action parameter profiles
4. (Optional.) Optimizing the DPI engine
5. (Optional.) Enabling inspection suspension upon excessive CPU usage
6. (Optional.) Configuring DPI engine inspection parameters
¡ Configuring an inspection mode
¡ Configuring stream fixed length inspection
¡ Configuring file fixed length inspection
¡ Configuring file decompression parameters
¡ Setting the maximum number of file decompression operations
¡ Setting the maximum number of NFS file names recorded
7. (Optional.) Configuring advanced features of the DPI engine
¡ Enabling source port-based application identification
¡ Specifying a proxy server for online DPI service signature update
¡ Specifying the source address for the request packet for online DPI service signature update
¡ Enabling IPS logging to record HTTP packet details
8. (Optional.) Disabling the DPI engine
Configure a DPI application profile
About this task
A DPI application profile includes a set of DPI service policies, such as a URL filtering policy. It can be applied to a security policy rule to specify the DPI service policy for packets that match the rule.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a DPI application profile and enter its view.
app-profile profile-name
3. Apply DPI service policies to the DPI application profile.
¡ Specify an IPS policy.
ips apply policy policy-name mode { protect | alert }
For more information about this command, see DPI Command Reference.
¡ Specify a URL filtering policy.
url-filter apply policy policy-name
For more information about this command, see DPI Command Reference.
¡ Specify a data filtering policy.
data-filter apply policy policyname
For more information about this command, see DPI Command Reference.
¡ Specify a file filtering policy.
file-filter apply policy policyname
For more information about this command, see DPI Command Reference.
¡ Specify an anti-virus policy.
anti-virus apply policy policyname mode { alert | protect }
For more information about this command, see DPI Command Reference.
By default, no DPI service policies are applied to a DPI application profile.
Activating policy and rule settings for DPI service modules
About this task
By default, the system will detect whether another configuration change (such as creation, modification, or deletion) occurs within a 20-second interval after a configuration change for DPI service modules such as URL filtering:
· If no configuration change occurs within the interval, the system performs an activation operation at the end of the next interval to make the configuration take effect.
· If a configuration change occurs within the interval, the system continues to periodically check whether a configuration change occurs within the interval.
To activate the policy and rule configurations for DPI service modules immediately, you can execute the inspect activate command.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Activate policy and rule settings for DPI service modules.
inspect activate
By default, the creation, modification, and deletion of DPI service policies and rules will be activated automatically.
|
CAUTION: This command causes transient DPI service interruption. DPI-based services might also be interrupted. For example, security policies cannot control access to applications. |
Configuring action parameter profiles
Configuring a block source parameter profile
About this task
A block source parameter profile defines the block period for the block source action in DPI service modules.
Restrictions and guidelines
The block source action takes effect only after the blacklist feature is enabled.
With the blacklist feature is enabled, the device drops the matching packet and adds the packet's source IP address to the IP blacklist. Subsequent packets from the source IP address will be dropped directly during the block period.
For more information about the blacklist feature, see attack detection and prevention configuration in the Security Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a block source parameter profile and enter its view.
inspect block-source parameter-profile parameter-name
3. Set the block period during which a source IP address is blocked.
block-period period
The default setting is 1800 seconds.
Configuring a capture parameter profile
About this task
A capture parameter profile defines the following parameters for the capture action in DPI service modules:
· Maximum number of bytes that can be cached.
· Daily export time for cached packets.
· URL to which cached packets are exported (for example, tftp://192.168.100.100/upload).
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a capture parameter profile and enter its view.
inspect capture parameter-profile parameter-name
3. (Optional.) Configure a description for the capture parameter profile.
description text
By default, a capture parameter profile does not have a description.
4. Set the maximum volume of captured packets that can be cached.
capture-limit kilobytes
By default, the device can cache a maximum of 512 Kilobytes of captured packets.
5. Set the daily export time for cached captured packets.
export repeating-at time
By default, the cached captured packets are exported at 1:00 a.m. every day.
6. Specify the URL to which cached captured packets are exported.
export url url-string
By default, no URL is specified for exporting the cached captured packets.
Only FTP, TFTP, and HTTPS are supported for URLs.
Only IPS supports exporting captured packets to a URL through HTTPS.
7. Set the .zip export format for capture files.
capture-upload zip
By default, capture files are exported in .pcap format one by one.
This command enables the device to export capture files in ,zip format, enhancing exporting efficiency and facilitating security event tracking and analysis.
8. Configure the storage space limits for captured packets.
capture-storage { max-cache-percentage percent-number | max-session-size session-size } *
By default, the maximum storage space is 5% of the total memory size, and the maximum captured packet size for a single session is 64 KB.
Configuring a logging parameter profile
About this task
A logging parameter profile defines the log output method and log output language for the logging action in DPI service modules.
Restrictions and guidelines
After setting the IPS log language to Chinese, only the attack name field of the IPS logs supports displaying in Chinese.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a logging parameter profile and enter its view.
inspect logging parameter-profile parameter-name
3. Specify the log export method.
log syslog
By default, logs are exported to the information center.
4. Set the language for IPS log output to Chinese.
log language chinese
By default, IPS logs are output in English.
Configuring a redirect parameter profile
About this task
A redirect parameter profile defines the URL to which packets are redirected for the redirect action in DPI service modules.
Restrictions and guidelines
The URL to which packets are redirected must start with http:// or https://, for example, https://www.example.com.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a redirect parameter profile and enter its view.
inspect redirect parameter-profile parameter-name
3. Specify the URL to which packets are redirected.
redirect-url url-string
By default, no URL is specified for packet redirecting.
Configuring an anti-virus warning parameter profile
About this task
An anti-virus warning parameter profile defines the parameters for the warning action in the anti-virus module. After you create a warning parameter profile, you can import a user-defined alarm message from a file.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create an anti-virus warning parameter profile and enter its view,.
inspect warning parameter-profile profile-name
3. Import a user-defined alarm message from a warning file.
import block warning-file file-path
By default, the device uses the alarm message "The site you are accessing has a security risk and thereby is blocked."
4. (Optional.) Restore the default alarm message.
reset block warning-file
This command clears the user-defined alarm message and restores the default alarm message.
Configuring a warning parameter profile for URL filtering
About this task
A warning parameter profile for URL filtering defines the parameters for the warning action in the URL filtering module. After you create a warning parameter profile, you can import a user-defined alarm message from a file.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a warning parameter profile for URL filtering and enter its view,.
inspect url-filter warning parameter-profile profile-name
3. Import a user-defined alarm message from a warning file.
import warning-file file-path
By default, the device uses the default alarm message in the warning file named uflt-xxx.html. The xxx in the file name is the profile name. For information about the contents of the default alarm message, see this command in DPI Configuration Guide.
4. (Optional.) Restore the default alarm message.
reset warning-file
This command clears the user-defined alarm message and restores the default alarm message.
Optimizing the DPI engine
About this task
The DPI engine includes a series of optimization features. For example, you can enable the DPI engine to uncompress or decode the compressed or encoded packets to identify the application information of the packets. The optimization features improve inspection and accuracy of the DPI engine, but consume more system resources.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the maximum number of payload-carrying packets to be inspected per data flow.
inspect packet maximum max-number
By default, the DPI engine can inspect a maximum of 32 payload-carrying packets per data flow.
3. Set the maximum number of options to be cached per TCP or UDP data flow.
inspect cache-option maximum max-number
By default, the DPI engine can cache a maximum of 32 options per TCP or UDP data flow.
4. Configure the TCP segment reassembly feature.
¡ Enable TCP segment reassembly.
inspect tcp-reassemble enable
By default, the TCP segment reassembly feature is disabled.
¡ Set the maximum number of TCP segments that can be cached for reassembly per TCP flow.
inspect tcp-reassemble max-segment max-number
By default, a maximum of 10 TCP segments can be cached for reassembly per TCP flow.
5. Enable SMB protocol packet reassembly.
inspect smb-reassemble enable
By default, SMB protocol packet reassembly is disabled.
6. (Optional.) Disable a DPI engine optimization feature.
inspect optimization [ chunk | no-acsignature | raw | uncompress | url-normalization ] disable
By default, all DPI engine optimization features are enabled.
You can disable DPI engine optimization features to improve the device performance as needed.
Enabling inspection suspension upon excessive CPU usage
About this task
Packet inspection of the DPI engine is a complex and resource-consuming process.
Inspection suspension upon excessive CPU usage works as follows:
· When the device's CPU usage rises to or above the CPU usage threshold, the DPI engine suspends packet inspection to guarantee the device performance.
· When the device's CPU usage drops to or below the CPU usage recovery threshold, the DPI engine resumes packet inspection.
For information about configuring the CPU usage thresholds, see system management in System Management Configuration Guide.
Restrictions and guidelines
Do not disable inspection suspension upon excessive CPU usage if the device's CPU usage is high.
When the device's CPU usage is low, you can disable this feature to improve inspection accuracy.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable inspection suspension upon excessive CPU usage.
undo inspect cpu-threshold disable
By default, inspection suspension upon excessive CPU usage is enabled.
Configuring DPI engine inspection parameters
Configuring an inspection mode
About this task
Select an inspection mode as required:
· Balanced mode—Applicable to most scenarios. This mode makes a tradeoff between the device performance and inspection coverage. The maximum length is 64 Kilobytes for FTP, HTTP, SMB, NFS, and email streams, and the maximum file length for MD5 inspection is 2048 Kilobytes. The maximum file length for other protocols and audio/video applications is not limited.
· Large coverage mode—Applicable to the scenarios that require large inspection coverage. This mode improves the inspection coverage at the cost of device performance. The maximum length is 128 Kilobytes for FTP, HTTP, SMB, NFS, and email streams, and the maximum file length for MD5 inspection is 5120 Kilobytes. The maximum file length for other protocols and audio/video applications is not limited.
· High performance mode—Applicable to the scenarios that require high device performance. This mode improves the device performance while ensuring a certain inspection coverage. The maximum length is 32 Kilobytes for FTP, HTTP, SMB, NFS, and email streams, and the maximum file length for MD5 inspection is 32 Kilobytes. The maximum file length for other protocols and audio/video applications is not limited.
· User-defined mode—Applicable to the scenarios that have specific requirements for inspection coverage and device performance. In this mode, you can execute the inspect stream-fixed-length command to set the maximum stream length for inspection.
The following rules apply when you change the inspection mode:
· When you change an inspection mode to the user-defined mode, the maximum lengths for stream inspection and MD5 inspection will not change.
· When you change the user-defined inspection mode to another inspection mode, the maximum length for MD5 inspection changes to the value of the new inspection mode. The maximum length for stream inspection varies by protocol type.
¡ For FTP, HTTP, SMB, NFS, and email protocols, the maximum length for stream inspection changes to the value of the new inspection mode.
¡ For other protocols and audio/video applications:
- If you change to the balanced mode, the maximum length for stream inspection of the user-defined inspection mode is clear, and the length for stream inspection is not limited.
- If you change to the large coverage or high performance mode, the maximum length for stream inspection of the user-defined inspection mode is retained.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure a DPI engine inspection mode.
inspect coverage { balanced | large-coverage | high-performance | user-defined }
By default, the DPI engine uses the balanced mode.
Configuring stream fixed length inspection
About this task
Perform this task to configure the DPI engine to inspect only a specified stream length for a protocol or an audio/video application. The remaining stream data is not inspected. Reducing the maximum length for stream inspection enhances the inspection efficiency.
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature can be configured only if the DPI engine inspection mode is user-defined mode.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the maximum length for stream inspection.
inspect stream-fixed-length { audio-video | dns | email | ftp | http | https | imaps | nfs | pop3s | rtmp | sip | smb | smtps | telnet | tftp } * length
By default, the maximum length is 32 Kilobytes for FTP, HTTP, NFS, SMB, SMTP, POP3, and email protocols (including SMTP, POP3, and IMAP). For audio/video applications and DNS, HTTPS, IMAPS, POP3S, RTMP, SIP, SMTPS, Telnet, and TFTP protocols, the length for stream inspection is not limited.
The longer the inspection data length, the lower the device throughput, and the higher the packet inspection accuracy.
3. (Optional.) Disable the stream maximum length inspection.
inspect stream-fixed-length disable
By default, the stream maximum length inspection is enabled.
Disable this function if your network requires high packet inspection accuracy.
Configuring file fixed length inspection
About this task
DPI engine inspects only the fixed-length data of files in each data stream. The remaining data of the file is not inspected. This is because virus signatures are typically embedded in the first half of a file. Narrowing the inspection scope enhances the file inspection efficiency.
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature can be configured only if the DPI engine inspection mode is user-defined mode.
Because files are transmitted in a data stream, the fixed length of files must not be longer than that of the data stream.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable the file fixed length inspection.
inspect file-fixed-length enable
By default, the file fixed length inspection is disabled.
3. Set the fixed length for file inspection.
inspect file-fixed-length { email | ftp | http | nfs | smb } * length-value
By default, the fixed length is 64 Kilobytes for FTP, HTTP, NFS, SMB, and email files.
If a data stream contains multiple files, this feature inspects only the fixed length data of each file.
Configuring file decompression parameters
About this task
After the device receives compressed files, DPI engine will decompress the files and match the decompressed files with signatures. You can set the following parameters for file decompression:
· Decompression data size limit—Maximum data size that can be decompressed in a file. DPI engine will not decompress the remaining file data and will match the remaining compressed file data with signatures.
· Decompression layer limit—Maximum number of layers that can be decompressed in a file. DPI engine will not decompress the remaining layers and will match the remaining compressed file with signatures.
Restrictions and guidelines
DPI engine can decompress only .zip and .gzip files.
Set appropriate parameters for file decompression.
· Large limits might make DPI engine get stuck in decompressing a large file or a multi-layer compressed file, improving the identification of file content at the cost of the following aspects:
¡ Affect the decompression of subsequent files.
¡ Consume a large amount of the device memory.
¡ Affect the device forwarding performance.
· Small limits might make DPI engine unable to identify the original file content correctly, reducing the impact on the device forwarding performance but affecting the accuracy of the file inspection results for DPI services (such as anti-virus and data filtering).
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the maximum data size that can be decompressed in a file.
inspect file-uncompr-len max-size
By default, the device can decompress a maximum of 100 MB data in a file.
3. Set the maximum number of layers that can be decompressed in a file.
inspect file-uncompr-layer max-layer
By default, the device can decompress a maximum of three layers in a file. If the max-layer field value is 0, the file will not be decompressed.
Setting the maximum number of file decompression operations
About this task
The DPI engine consumes memory resources each time it performs a file decompression operation. A large number of file decompression operations might consume a large number of memory resources. Perform this task to limit the memory resources consumed by file decompression operations.
A small limit can reduce memory consumption but might reduce the detection success rate of the DPI engine. A great limit might improve the detection success rate of the DPI engine but degrade the device performance.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the maximum number of file decompression operations.
inspect uncompress maximum max-number
By default, the maximum number of file decompression operations is calculated according to the actual memory size of the device.
Setting the maximum number of NFS file names recorded
About this task
The DPI engine records file names during file detection for users to obtain file information in logs. The record process occupies memory resources. The more files detected, the more memory resources occupied. In an environment using NFS to transfer a large number of files, perform this task to limit the memory resources consumed by recording file names.
Restrictions and guidelines
In scenarios requiring high performance, you can set a small limit to reduce memory consumption. In scenarios not requiring high performance, you can set a great limit to enable users to obtain more file information.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the maximum number of NFS file names recorded.
inspect record-filename nfs maximum max-number
By default, the maximum number of NFS file names recorded is calculated according to the actual memory size of the device.
Configuring advanced features of the DPI engine
Enabling source port-based application identification
About this task
You can use this feature to identify traffic of applications that use fixed source ports when the following conditions are true:
· The types of traffic transmitted over networks are relatively unvaried and use fixed source ports.
· Destination port-based application identification or signature-based traffic content identification is not supported.
The application identification results produced by this feature might not be accurate. Configure this feature according to your live network as a best practice.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable source port-based application identification.
inspect source-port-identify enable
By default, source port-based application identification is disabled.
Specifying a proxy server for online DPI service signature update
About this task
The device must access the company's website for online signature update of DPI services (such as URL filtering). If direct connectivity is not available, the device can access the company's website through the specified proxy server. For more information about online signature update, see "Configuring URL filtering" and "Configuring anti-virus."
Restrictions and guidelines
If you specify a proxy server by domain name instead of IP address, make sure the device can resolve the domain name into an IP address through DNS. For more information about DNS, see Network Connectivity Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify a proxy server for online DPI service signature update
inspect signature auto-update proxy { domain domain-name | ip ip-address } [ port port-number ] [ user user-name password { cipher | simple } string ]
By default, the proxy server used by DPI services for online signature update is not specified.
Specifying the source address for the request packet for online DPI service signature update
About this task
You can perform this task to specify the source IP address for the request packet sent from the device to the library server for online DPI service signature update. For example, if the packet sent by the device must be NATed, you must specify a source IP address that matches the NAT rule. If the packet traverses an independent NAT device, the specified source IP address must be able to reach the NAT device.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify the source address for online DPI service signature update.
inspect signature auto-update source { ip | ipv6 } { ip-address | interface interface-type interface-number }
By default, the source address of the request packet is the IP address of the outgoing interface in the matching route.
Enabling IPS logging to record HTTP packet details
About this task
This feature enables the device to cache HOST, URI, and other fields and record them in IPS logs. For example, when an HTTP response matches an IPS policy, the device records the HOST field in the HTTP request and the status line and some header fields in the HTTP response.
If a large number of HTTP packets exist in the network, this feature can consume a large amount of memory and degrade the device performance. You can set the maximum memory size to limit the amount of memory used to store the fields in IPS logs. A smaller maximum memory size might cause fields in some IPS logs to fail to be displayed.
Restrictions and guidelines
This feature does not take effect on IPS logs generated before it is enabled.
To save memory resources, enable this feature only when necessary.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enabe IPS logging to record HTTP packet details.
inspect ips log-details enable
By default, this feature is disabled.
3. Set the maximum memory size for storing the HTTP fields in IPS logs.
inspect log-details max-size max-size-value
By default, the maximum memory size is calculated according to the device memory.
Disabling DPI engine from transparently transmitting DPI service traffic
About this task
When asymmetric traffic exists in the network environment (that is, the forward and backward paths are inconsistent for packets of the same flow), the forward and backward packets of the flow might be sent to different devices. As a result, DPI services might fail to be processed correctly. For example, antivirus services cannot detect virus files. To solve this problem, the DPI engine transparently transmits DPI service traffic between devices by default. This ensures that the forward and backward packets of the same flow are sent to the same device.
Transparent traffic transmission consumes device resources and reduces device performance. When the network environment requires high device performance and can accept the risk of losing some DPI service detection accuracy, you can disable the DPI engine from transparently transmitting DPI service traffic to reduce the impact on device performance.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Disable DPI engine from transparently transmitting DPI service traffic.
undo inspect transparent enable
By default, DPI engine is enabled to transparently transmitting DPI service traffic.
Disabling the DPI engine
Disabling the DPI engine for all protocols
About this task
Packet inspection in the DPI engine is a complex and resource-consuming process. When the CPU usage is too high, you can disable the DPI engine to guarantee the device performance.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Disable the DPI engine.
inspect bypass
By default, the DPI engine is enabled.
|
CAUTION: This command causes packets of any protocols not to be processed by DPI. DPI-based services might also be interrupted. For example, security policies cannot control access to applications. |
Disabling the DPI engine for the specified protocols
About this task
Perform this task in the following scenarios:
· Scenario 1: Inspection on packets of the specified protocols is not required. You can disable the DPI engine for the specified protocols to reduce the consumption of device resources and improve the device performance.
· Scenario 2: Inspection on packets of the specified protocols causes device reboot. You can specify the protocols to bypass the DPI engine to avoid device reboot caused by inspection error and ensure the inspection on packets of other protocols.
To disable the DPI engine for the specified protocols, you can use either of the following methods:
· Manual configuration—If the administrator knows the protocols to bypass, you can use this method. This method applies to scenario 1.
· Automatic configuration—This method applies to scenario 2. If you use this method, the device automatically identifies the protocols to bypass the DPI engine after device reboot.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Disable the DPI engine for the specified protocols.
¡ Manually disable the DPI engine for the specified protocols.
inspect bypass protocol { dns | ftp | ftp-data | http | https | ibm-db2 | imap | mongodb-protocol | ms-sql-s | mysql-protocol | nfs | pop3 | postgresql-protocol | rtmp | sip | smb | smtp | sqlnet | telnet | tftp } *
By default, the DPI engine inspects all supported protocols.
¡ Automatically disable the DPI engine for the specified protocols.
inspect auto-bypass enable
By default, automatic bypass of the DPI engine is disabled.
Display and maintenance commands for DPI engine
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display the SMB breakpoint resumption table. |
display inspect smb-breakpoint-resume table { ipv4 | ipv6 } |
|
Display the status of the DPI engine. |
display inspect status |
|
Clear the SMB breakpoint resumption table. |
reset inspect smb-breakpoint-resume table { ipv4 | ipv6 } |