- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 03-Appendix B Managed Hot Swapping of OCP Network Adapters | 381.62 KB |
Appendix B Managed hot swapping of OCP network adapters
Guidelines
Use the OS compatibility query tool at http://www.h3c.com/en/home/qr/default.htm?id=66 to obtain operating systems that support managed hot swapping of OCP network adapters.
Only the OCP network adapters of the same model support managed hot swapping.
Make sure the following software version requirements are met:
· HDM2 is 1.55 or later.
· CPLD is CPLD1_V003 or CPLD1_V003.
Performing hot swapping
This section uses an OCP network adapter in slot 23 as an example.
To perform hot swapping:
1. Access the operating system.
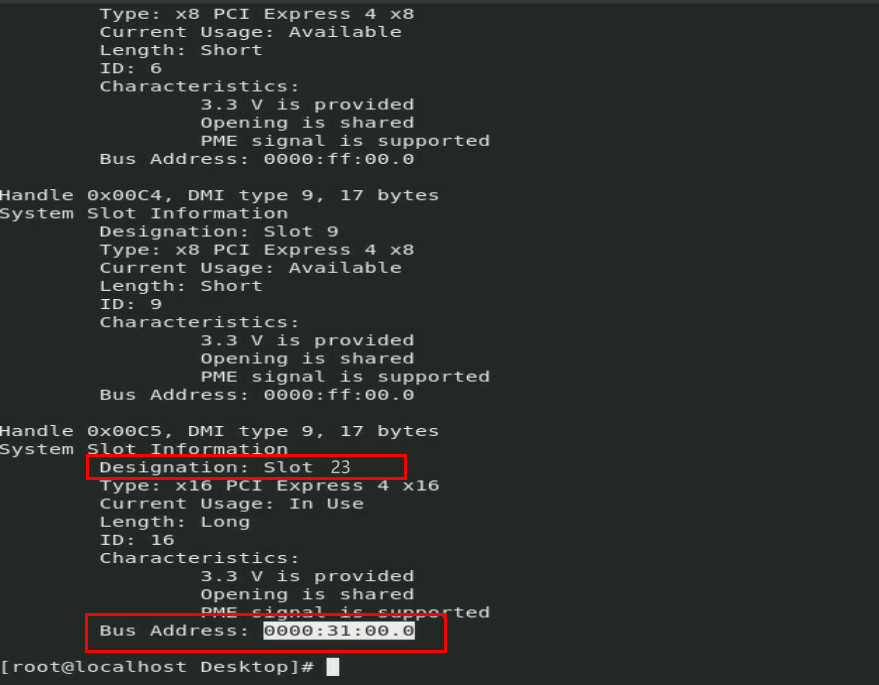
2. Execute the dmidecode -t 9 command to search for the bus address of the OCP network adapter. As shown in Figure 1, the bus address of the OCP network adapter in slot 23 is 0000:31:00.0.
Figure 1 Searching for the bus address of an OCP network adapter by slot number
3. Execute the echo 0 > /sys/bus/pci/slots/slot number/power command, where slot number represents the number of the slot where the OCP network adapter resides.
Figure 2 Executing the echo 0 > /sys/bus/pci/slots/slot number/power command
4. Identify whether the OCP network adapter has been disconnected:
¡ Observe the OCP network adapter LED. If the LED is off, the OCP network adapter has been disconnected.
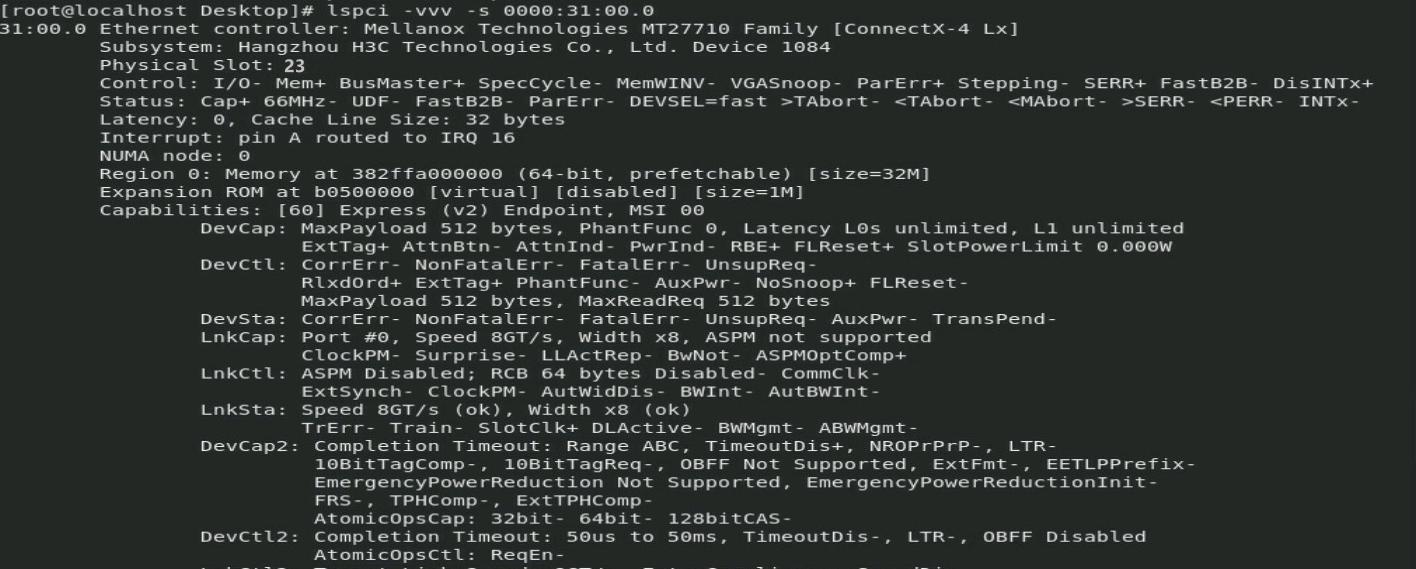
¡ Execute the lspci –vvv –s 0000:31:00.0 command. If no output is displayed, the OCP network adapter has been disconnected.
Figure 3 Identifying OCP network adapter status
5. Replace the OCP network adapter.
6. Identify whether the OCP network adapter has been connected:
¡ Observe the OCP network adapter LED. If the LED is on, the OCP network adapter has been connected.
¡ Execute the lspci –vvv –s 0000:31:00.0 command. If an output is displayed, the OCP network adapter has been connected.
Figure 4 Identifying OCP network adapter status
7. Identify whether any exception exists. If any exception occurred, contact Technical Support.