- Table of Contents
-
- 11-Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-System maintenance and debugging configuration
- 02-NQA configuration
- 03-iNQA configuration
- 04-NTP configuration
- 05-PoE configuration
- 06-SNMP configuration
- 07-RMON configuration
- 08-Event MIB configuration
- 09-NETCONF configuration
- 10-Ansible configuration
- 11-Puppet configuration
- 12-Chef configuration
- 13-SmartMC configuration
- 14-EPA configuration
- 15-ONVIF configuration
- 16-CWMP configuration
- 17-EAA configuration
- 18-Process monitoring and maintenance configuration
- 19-Sampler configuration
- 20-Mirroring configuration
- 21-NetStream configuration
- 22-IPv6 NetStream configuration
- 23-sFlow configuration
- 24-Information center configuration
- 25-Packet capture configuration
- 26-VCF fabric configuration
- 27-Cloud connection configuration
- 28-EPS agent configuration
- 29-eMDI configuration
- 30-SQA configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 22-IPv6 NetStream configuration | 187.67 KB |
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with IPv6 NetStream
IPv6 NetStream tasks at a glance
Specifying a working mode for a NetStream interface extension module
Specifying a working mode for a NetStream interface extension module
Configuring IPv6 NetStream sampling
Configuring the IPv6 NetStream data export format
Configuring the refresh rate for IPv6 NetStream version 9 or version 10 template
Configuring IPv6 NetStream flow aging
Configuring periodical flow aging
Configuring the IPv6 NetStream data export
Configuring the IPv6 NetStream traditional data export
Display and maintenance commands for IPv6 NetStream
IPv6 NetStream configuration examples
Example: Configuring IPv6 NetStream traditional data export
Configuring IPv6 NetStream
About IPv6 NetStream
IPv6 NetStream is an accounting technology that provides statistics on a per-flow basis. An IPv6 flow is defined by the following 8-tuple elements:
· Destination IPv6 address.
· Source IPv6 address.
· Destination port number.
· Source port number.
· Protocol number.
· Traffic class.
· Flow label.
· Input or output interface.
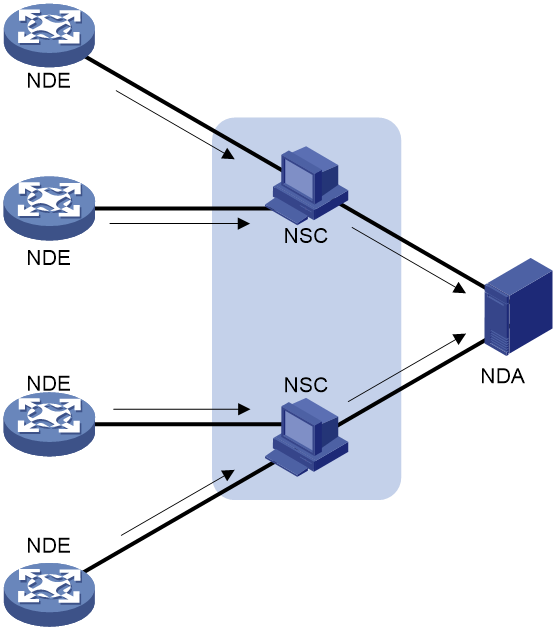
IPv6 NetStream architecture
A typical IPv6 NetStream system includes the following elements:
· NetStream data exporter—A device configured with IPv6 NetStream. The NDE provides the following functions:
¡ Classifies traffic flows by using the 8-tuple elements.
¡ Collects data from the classified flows.
¡ Exports the data to the NSC.
· NetStream collector—A program running in a Unix or Windows operating system. The NSC parses the packets received from the NDEs, and saves the data to its database.
· NetStream data analyzer—A network traffic analyzing tool. Based on the data in NSC, the NDA generates reports for traffic billing, network planning, and attack detection and monitoring. The NDA can collect data from multiple NSCs. Typically, the NDA features a Web-based system for easy operation.
NSC and NDA are typically integrated into a NetStream server.
Figure 1 IPv6 NetStream system
IPv6 NetStream flow aging
IPv6 NetStream uses flow aging to enable the NDE to export IPv6 NetStream data to NetStream servers. IPv6 NetStream creates an IPv6 NetStream entry for each flow for storing the flow statistics in the cache.
When a flow is aged out, the NDE performs the following operations:
· Exports the summarized data to NetStream servers in a specific format.
· Clears IPv6 NetStream entry information in the cache.
IPv6 NetStream supports the following flow aging methods:
· Periodical aging.
· Forced aging.
Periodical aging
Periodical aging uses the following methods:
· Inactive flow aging—A flow is inactive if no packet arrives for the IPv6 NetStream entry within the inactive flow aging timer. When the timer expires, the following events occur:
¡ The inactive flow entry is aged out.
¡ The statistics of the flow are sent to NetStream servers and are cleared in the cache. The statistics can no longer be displayed by using the display ipv6 netstream cache command.
This method ensures that inactive flow entries are cleared from the cache in a timely manner so new entries can be cached.
· Active flow aging—A flow is active if packets arrive for the IPv6 NetStream entry within the active flow aging timer. When the timer expires, the statistics of the active flow are exported to NetStream servers. The device continues to collect its statistics, which can be displayed by using the display ipv6 netstream cache command.
The active flow aging method periodically exports the statistics of active flows to NetStream servers.
Forced aging
To implement forced aging, execute the reset ipv6 netstream statistics command to clear the IPv6 NetStream cache immediately and export the cached entries to NetStream servers.
IPv6 NetStream data export
Traditional data export
IPv6 NetStream collects the statistics of each flow and exports the statistics to NetStream servers.
This method consumes a lot of bandwidth and CPU usage, and requires a large cache size. In addition, you do not need all of the data in most cases.
IPv6 NetStream data export format
IPv6 NetStream exports data in the version 9 or version 10 format.
Both formats are template-based and support collecting statistics about BGP next hop.
The version 10 export format is compliant with the IPFIX standard.
IPv6 NetStream sampling
IPv6 NetStream sampling collects statistics on fewer packets and is useful when the network has a large amount of traffic. IPv6 NetStream on sampled traffic lessens the impact on the device's performance. For more information about sampling, see "Configuring samplers."
Protocols and standards
RFC 5101, Specification of the IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Protocol for the Exchange of IP Traffic Flow Information
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with IPv6 NetStream
IPv6 NetStream is supported only on the devices installed with H3C LSWM2FPGA or LSWM2FPGAB NetStream interface extension modules.
IPv6 NetStream tasks at a glance
To configure IPv6 NetStream, perform the following tasks:
1. Specifying a working mode for a NetStream interface extension module
Specifying a working mode for a NetStream interface extension module
About this task
A NetStream interface extension module supports the following working modes:
· 0—Normal mode. In this mode, IPv6 NetStream is not supported.
Restrictions and guidelines
Procedure
2. Set the working mode of a NetStream interface extension module to NetStream.
fpga-working-mode slot slot-number 1
Display and maintenance commands for NetStream interface extension modules
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Display the working mode of a NetStream interface extension module. |
2. (Optional.) Configuring IPv6 NetStream sampling
3. (Optional.) Configuring the IPv6 NetStream data export format
4. (Optional.) Configuring the refresh rate for IPv6 NetStream version 9 or version 10 template
5. (Optional.) Configuring IPv6 NetStream flow aging
¡ Configuring periodical flow aging
¡ Configuring forced flow aging
6. Configuring the IPv6 NetStream data export
a. Configuring the IPv6 NetStream traditional data export
Specifying a working mode for a NetStream interface extension module
About this task
You can install a NetStream interface extension module on the device to provide the IPv6 NetStream feature. After the device mirrors traffic to the NetStream interface extension module, the field programmable gate array (FPGA) chip in the module collects and analyzes traffic statistics and creates NetStream entries. This NetStream approach saves ACL resources, improves NetStream entry creation performance, and greatly reduces NetStream impact on the device forwarding performance.
A NetStream interface extension module supports the following working modes:
· 0—Normal mode. In this mode, IPv6 NetStream is not supported.
· 1—NetStream mode. The NetStream interface extension module works in the unidirectional NetStream mode.
Restrictions and guidelines
To make the configuration take effect, save the configuration and reboot the device. Before rebooting the device, evaluate the effect of the device reboot on the network.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the working mode of a NetStream interface extension module to NetStream.
fpga-working-mode slot slot-number 1
By default, a NetStream interface extension module works in mode 0 and the device does not support IPv6 NetStream.
Display and maintenance commands for NetStream interface extension modules
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display the working mode of a NetStream interface extension module. |
display fpga-working-mode status slot slot-number |
Enabling IPv6 NetStream
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable IPv6 NetStream on the interface.
ipv6 netstream { inbound | outbound }
By default, IPv6 NetStream is disabled on an interface.
Configuring IPv6 NetStream sampling
Restrictions and guidelines
By default, IPv6 NetStream collects all data of target flows. If the flow traffic is heavy, IPv6 NetStream is resource-consuming and can cause high CPU usage, which impacts the device forwarding performance. IPv6 NetStream sampling is helpful to decrease the IPv6 NetStream traffic volume. If the collected statistics can basically reflect the network status, you can enable this feature and set a proper sampling rate. The higher the sampling rate, the less impact on device performance.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a sampler.
sampler sampler-name mode { fixed | random } packet-interval n-power rate
For more information about samplers, see "Configuring samplers."
3. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
4. Configure IPv6 NetStream sampling.
ipv6 netstream { inbound | outbound } sampler sampler-name
By default, IPv6 NetStream sampling is disabled.
Configuring the IPv6 NetStream data export format
About this task
When you configure the IPv6 NetStream data export format, you can also specify the following settings:
· Whether or not to export the BGP next hop information.
· How to export the autonomous system (AS) information: origin-as or peer-as.
¡ origin-as—Records the original AS numbers for the flow source and destination.
¡ peer-as—Records the peer AS numbers for the flow source and destination.
For example, as shown in Figure 2, a flow starts at AS 20, passes AS 21 through AS 23, and then reaches AS 24. IPv6 NetStream is enabled on the device in AS 22.
· Specify the origin-as keyword to export AS 20 as the source AS and AS 24 as the destination AS.
· Specify the peer-as keyword to export AS 21 as the source AS and AS 23 as the destination AS.
Figure 2 Recorded AS information varies by different keyword configurations
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure the IPv6 NetStream data export format, and configure the AS and BGP next hop export attributes.
¡ Configure the version 9 format.
ipv6 netstream export version 9 { origin-as | peer-as } [ bgp-nexthop ]
¡ Configure the version 10 format.
ipv6 netstream export version 10 [ origin-as | peer-as ] [ bgp-nexthop ]
By default:
¡ The version 9 format is used to export IPv6 NetStream data.
¡ The peer AS numbers for the flow source and destination are exported.
¡ The BGP next hop information is not exported.
Configuring the refresh rate for IPv6 NetStream version 9 or version 10 template
About this task
Version 9 and version 10 are template-based and support user-defined formats. An IPv6 NetStream device must send the updated template to NetStream servers regularly, because the servers do not permanently save templates.
For a NetStream server to use the correct version 9 or version 10 template, configure the time-based or packet count-based refresh rate. If both settings are configured, the template is sent when either of the conditions is met.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure the refresh rate for the IPv6 NetStream version 9 or version 10 template.
ipv6 netstream export template refresh-rate { packet packets | time minutes }
By default, the packet count-based refresh rate is 20 packets, and the time-based refresh interval is 30 minutes.
Configuring IPv6 NetStream flow aging
Configuring periodical flow aging
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the aging timer for active flows.
ipv6 netstream timeout active minutes
By default, the aging timer for active flows is 5 minutes.
3. Set the aging timer for inactive flows.
ipv6 netstream timeout inactive seconds
By default, the aging timer for inactive flows is 300 seconds.
Configuring forced flow aging
1. Execute the following command in user view to clear the cache, including the cached IPv6 NetStream entries and the related statistics.
reset ipv6 netstream statistics
Configuring the IPv6 NetStream data export
Configuring the IPv6 NetStream traditional data export
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify a destination host for IPv6 NetStream traditional data export.
ipv6 netstream export host { ipv4-address | ipv6-address } udp-port [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
By default, no destination host is specified.
3. (Optional.) Specify the source interface for IPv6 NetStream data packets sent to the NetStream servers.
ipv6 netstream export source interface interface-type interface-number
By default, no source interface is specified for IPv6 NetStream data packets. The packets take the IPv6 address of the output interface (interface that is connected to the NetStream server) as the source IPv6 address.
As a best practice, connect the management Ethernet interface to a NetStream server, and configure the interface as the source interface.
4. (Optional.) Limit the IPv6 NetStream data export rate.
ipv6 netstream export rate rate
By default, the data export rate is not limited.
Display and maintenance commands for IPv6 NetStream
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display IPv6 NetStream entry information. |
display ipv6 netstream cache [ verbose ] [ type { ip | ipl2 | l2 } ] [ destination destination-ipv6 | interface interface-type interface-number | source source-ipv6 ] * [ slot slot-number ] |
|
Display information about the IPv6 NetStream data export. |
display ipv6 netstream export |
|
Display IPv6 NetStream template information. |
display ipv6 netstream template [ slot slot-number ] display ipv6 netstream template |
|
Age out, export all IPv6 NetStream data, and clear the cache. |
reset ipv6 netstream statistics |
IPv6 NetStream configuration examples
Example: Configuring IPv6 NetStream traditional data export
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 3, configure IPv6 NetStream on the device to collect statistics on packets passing through the device.
· Enable IPv6 NetStream for incoming and outgoing traffic on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
· Configure the device to export the IPv6 NetStream traditional data to UDP port 5000 of the NetStream server.
Procedure
# Specify the NetStream mode for the NetStream interface extension module. Save the configuration and reboot the device. (Details not shown.)
# Assign an IP address to each interface, as shown in Figure 3. (Details not shown.)
# Enable IPv6 NetStream for incoming and outgoing traffic on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<Device> system-view
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ipv6 netstream inbound
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ipv6 netstream outbound
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Specify 40::1 as the IP address of the destination host and UDP port 5000 as the export destination port number.
[Device] ipv6 netstream export host 40::1 5000
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about IPv6 NetStream entries.
<Device> display ipv6 netstream cache
IPv6 NetStream cache information:
Active flow timeout : 5 min
Inactive flow timeout : 300 sec
Max number of entries : 1048576
IPv6 active flow entries : 2
MPLS active flow entries : 0
IPL2 active flow entries : 0
IPv6 flow entries counted : 10
MPLS flow entries counted : 0
IPL2 flow entries counted : 0
Last statistics resetting time : 01/01/2019 at 00:01:02
IPv6 packet size distribution (1103746 packets in total):
1-32 64 96 128 160 192 224 256 288 320 352 384 416 448 480
.249 .694 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000
512 544 576 1024 1536 2048 2560 3072 3584 4096 4608 >4608
.000 .000 .027 .000 .027 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000
Protocol Total Packets Flows Packets Active(sec) Idle(sec)
Flows /sec /sec /flow /flow /flow
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
TCP-Telnet 2656855 372 4 86 49 27
TCP-FTP 5900082 86 9 9 11 33
TCP-FTPD 3200453 1006 5 193 45 33
TCP-WWW 546778274 11170 887 12 8 32
TCP-other 49148540 3752 79 47 30 32
UDP-DNS 117240379 570 190 3 7 34
UDP-other 45502422 2272 73 30 8 37
ICMP 14837957 125 24 5 12 34
IP-other 77406 5 0 47 52 27
Type DstIP(Port) SrcIP(Port) Pro TC FlowLbl If(Direct) Pkts
DstMAC(VLAN) SrcMAC(VLAN)
TopLblType(IP/MASK)Lbl-Exp-S-List
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
IP 2001::1(1024) 2002::1(21) 6 0 0x0 GE1/0/1(I) 42996
IP 2002::1(21) 2001::1(1024) 6 0 0x0 GE1/0/1(O) 42996
# Display information about the IPv6 NetStream data export.
[Device] display ipv6 netstream export
IPv6 export information:
Flow source interface : Not specified
Flow destination VPN instance : Not specified
Flow destination IP address (UDP) : 40::1 (5000)
Version 9 exported flow number : 10
Version 9 exported UDP datagram number (failed) : 10 (0)