- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 05-MAC authentication configuration | 171.78 KB |
Contents
Configuring MAC authentication
Restrictions and guidelines: MAC authentication configuration
MAC authentication tasks at a glance
Prerequisites for MAC authentication
Specifying a MAC authentication domain
Configuring the user account format
Configuring MAC authentication timers
Configuring a MAC authentication guest VLAN
Setting the maximum number of concurrent MAC authentication users on a port
Configuring MAC authentication delay
Configuring the keep-online feature
Display and maintenance commands for MAC authentication
Configuring MAC authentication
About MAC authentication
MAC authentication controls network access by authenticating source MAC addresses on a port. The feature does not require client software, and users do not have to enter a username and password for network access. The device initiates a MAC authentication process when it detects an unknown source MAC address on a MAC authentication-enabled port. If the MAC address passes authentication, the user can access authorized network resources. If the authentication fails, the device marks the MAC address as a silent MAC address, drops the packet, and starts a quiet timer. The device drops all subsequent packets from the MAC address within the quiet time. The quiet mechanism avoids repeated authentication during a short time.
User account policies
MAC authentication supports the following user account policies:
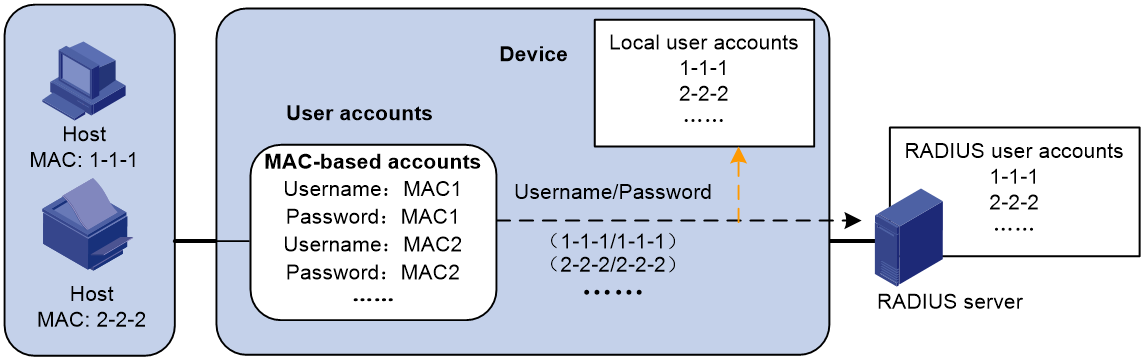
· One MAC-based user account for each user. As shown in Figure 1, the access device uses the source MAC addresses in packets as the usernames and passwords of users for MAC authentication. This policy is suitable for an insecure environment.
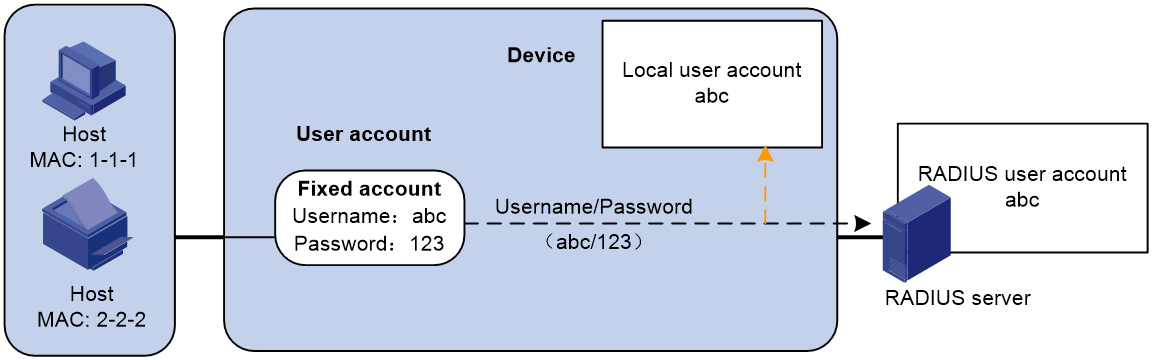
· One shared user account for all users. You specify one username and password, which are not necessarily a MAC address, for all MAC authentication users on the access device. This policy is suitable for a secure environment. See Figure 2.
Figure 1 MAC-based user account policy
Figure 2 Shared user account policy
Authentication methods
You can perform MAC authentication on the access device (local authentication) or through a RADIUS server.
For more information about configuring local authentication and RADIUS authentication, see "Configuring AAA."
RADIUS authentication
If MAC-based accounts are used, the access device sends the source MAC address of the packet as the username and password to the RADIUS server for authentication.
If a shared account is used, the access device sends the shared account username and password to the RADIUS server for authentication.
Local authentication
If MAC-based accounts are used, the access device uses the source MAC address of the packet as the username and password to search the local account database for a match.
If a shared account is used, the access device uses the shared account username and password to search the local account database for a match.
VLAN assignment
Authorization VLAN
The authorization VLAN controls the access of a MAC authentication user to authorized network resources. The device supports authorization VLANs assigned locally or by a remote server.
|
IMPORTANT: Only remote servers can assign tagged authorization VLANs. |
Remote VLAN authorization
In remote VLAN authorization, you must configure an authorization VLAN for a user on the remote server. After the user authenticates to the server, the server assigns authorization VLAN information to the device. Then, the device assigns the user access port to the authorization VLAN as a tagged or untagged member.
The device supports assignment of the following authorization VLAN information by the remote server:
· VLAN ID.
· VLAN name, which must be the same as the VLAN description on the access device.
· Astring of VLAN IDs and VLAN names.
In the string, some VLANs are represented by their IDs, and some VLANs are represented by their names.
· VLAN group name.
For more information about VLAN groups, see VLAN configuration in Network Connectivity Configuration Guide.
· VLAN ID with a suffix of t or u.
The t and u suffixes require the device to assign the access port to the VLAN as a tagged or untagged member, respectively. For example, 2u indicates assigning the port to VLAN 2 as an untagged member.
If a VLAN name or VLAN group name is assigned, the device converts the information into a VLAN ID before VLAN assignment.
|
IMPORTANT: For a VLAN represented by its VLAN name to be assigned successfully, you must make sure the VLAN has been created on the device. To assign VLAN IDs with suffixes, make sure the user access port is a hybrid or trunk port. |
To ensure a successful assignment, the authorization VLANs assigned by the remote server cannot be any of the following types:
· Dynamically learned VLANs.
· Reserved VLANs.
If the server assigns a group of VLANs, the access device selects a VLAN as described in Table 1.
Table 1 Authorization VLAN selection from a group of VLANs
|
VLAN information |
Authorization VLAN selection |
|
VLANs by IDs VLANs by names VLAN group name |
The device selects an authorization VLAN from the VLAN group for a user according to the following rules: On an access, trunk, or hybrid port: · If the port does not have online users, the device selects the VLAN with the lowest ID. · If the port has online users, the device examines the VLAN group for the VLAN of the online users. If the VLAN is found, the VLAN is assigned to the user as the authorization VLAN. If the VLAN is not found, VLAN authorization fails. |
|
VLAN IDs with suffixes |
1. The device selects the leftmost VLAN ID without a suffix, or the leftmost VLAN ID suffixed by u as an untagged VLAN, whichever is more leftmost. 2. The device assigns the untagged VLAN to the port as the PVID, and it assigns the remaining as tagged VLANs. If no untagged VLAN is assigned, the PVID of the port does not change. The port permits traffic from these tagged and untagged VLANs to pass through. For example, the authentication server sends the string 1u 2t 3 to the access device for a user. The device assigns VLAN 1 as an untagged VLAN and all remaining VLANs (including VLAN 3) as tagged VLANs. VLAN 1 becomes the PVID. |
Local VLAN authorization
To perform local VLAN authorization for a user, specify the VLAN ID in the authorization attribute list of the local user account for that user. For each local user, you can specify only one authorization VLAN ID. The user access port is assigned to the VLAN as an untagged member.
|
IMPORTANT: Local VLAN authorization does not support assignment of tagged VLANs. |
For more information about local user configuration, see "Configuring AAA."
Authorization VLAN manipulation on a MAC authentication-enabled port
Table 2 describes the way the network access device handles authorization VLANs (except for the VLANs specified with suffixes) for MAC authenticated users.
|
Port type |
VLAN manipulation |
|
· Access port · Trunk port · Hybrid port |
· The device assigns the port to the first authenticated user's authorization VLAN and sets the VLAN as the PVID if that authorization VLAN has the untagged attribute. · If the authorization VLAN has the tagged attribute, the device assigns the port to the authorization VLAN without changing its PVID. NOTE: The tagged attribute is supported only on trunk and hybrid ports. |
|
IMPORTANT: · If the users are attached to a port whose link type is access, make sure the authorization VLAN assigned by the server has the untagged attribute. VLAN assignment will fail if the server issues a VLAN that has the tagged attribute. · When you assign VLANs to users attached to a trunk port or a hybrid port, make sure there is only one untagged VLAN. If a different untagged VLAN is assigned to a subsequent user, the user cannot pass authentication. · As a best practice to enhance network security, do not use the port hybrid vlan command to assign a hybrid port to an authorization VLAN as a tagged member. |
For a MAC authenticated user to access the network on a hybrid port when no authorization VLAN is configured for the user, perform one of the following tasks:
· If the port receives tagged authentication packets from the user in a VLAN, use the port hybrid vlan command to configure the port as a tagged member in the VLAN.
· If the port receives untagged authentication packets from the user in a VLAN, use the port hybrid vlan command to configure the port as an untagged member in the VLAN.
Guest VLAN
The MAC authentication guest VLAN on a port accommodates users that have failed MAC authentication for any reason other than server unreachable. For example, the VLAN accommodates users for which invalid passwords are entered.
You can deploy a limited set of network resources in the MAC authentication guest VLAN. For example, a software server for downloading software and system patches.
A hybrid port is always assigned to a MAC authentication guest VLAN as an untagged member. After the assignment, do not reconfigure the port as a tagged member in the VLAN.
The device reauthenticates users in the MAC authentication guest VLAN at a specific interval. Table 3 shows the way that the network access device handles guest VLANs for MAC authentication users.
|
Authentication status |
VLAN manipulation |
|
A user in the MAC authentication guest VLAN fails MAC authentication. |
The user is still in the MAC authentication guest VLAN. |
|
A user in the MAC authentication guest VLAN passes MAC authentication. |
The device remaps the MAC address of the user to the authorization VLAN assigned by the authentication server. If no authorization VLAN is configured for the user on the authentication server, the device remaps the MAC address of the user to the PVID of the port. |
Restrictions and guidelines: MAC authentication configuration
Do not change the link type of a port when the MAC authentication guest VLAN on the port has users.
If the MAC address that has failed authentication is a static MAC address or a MAC address that has passed any security authentication, the device does not mark the MAC address as a silent address.
MAC authentication tasks at a glance
To configure MAC authentication, perform the following tasks:
1. Enabling MAC authentication
2. Configure basic MAC authentication features
¡ Specifying a MAC authentication domain
¡ Configuring the user account format
¡ (Optional.) Configuring MAC authentication timers
3. (Optional.) Configuring MAC authentication VLAN assignment
¡ Configuring a MAC authentication guest VLAN
4. (Optional.) Configuring other MAC authentication features
¡ Setting the maximum number of concurrent MAC authentication users on a port
¡ Configuring MAC authentication delay
¡ Configuring the keep-online feature
Prerequisites for MAC authentication
Before you configure MAC authentication, complete the following tasks:
1. Make sure the port security feature is disabled. For more information about port security, see "Configuring port security."
2. Configure an ISP domain and specify an AAA method. For more information, see "Configuring AAA."
¡ For local authentication, you must also create local user accounts (including usernames and passwords) and specify the lan-access service for local users.
¡ For RADIUS authentication, make sure the device and the RADIUS server can reach each other and create user accounts on the RADIUS server. If you are using MAC-based accounts, make sure the username and password for each account are the same as the MAC address of each MAC authentication user.
Enabling MAC authentication
Restrictions and guidelines
For MAC authentication to take effect on a port, you must enable this feature globally and on the port.
You cannot enable MAC authentication on a port that is in a link aggregation group.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable MAC authentication globally.
mac-authentication
By default, MAC authentication is disabled globally.
3. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
4. Enable MAC authentication on the port.
mac-authentication
By default, MAC authentication is disabled on a port.
Specifying a MAC authentication domain
About this task
By default, MAC authentication users are in the system default authentication domain. To implement different access policies for users, you can use one of the following methods to specify authentication domains for MAC authentication users:
· Specify a global authentication domain in system view. This domain setting applies to all ports enabled with MAC authentication.
· Specify an authentication domain for an individual port in Layer 2 Ethernet interface view.
MAC authentication chooses an authentication domain for users on a port in this order: the port-specific domain, the global domain, and the default domain. For more information about authentication domains, see "Configuring AAA."
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify an authentication domain for MAC authentication users.
¡ In system view:
mac-authentication domain domain-name
¡ In Layer 2 Ethernet interface view:
interface interface-type interface-number
mac-authentication domain domain-name
By default, the system default authentication domain is used for MAC authentication users.
Configuring the user account format
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure the MAC authentication user account format.
¡ Use one MAC-based user account for each user.
mac-authentication user-name-format mac-address [ { with-hyphen [ six-section | three-section ] | without-hyphen } [ lowercase | uppercase ] ]
¡ Use one shared user account for all users.
mac-authentication user-name-format fixed [ account name ] [ password { cipher | simple } string ]
By default, the device uses the MAC address of a user as the username and password for MAC authentication. The MAC address is in hexadecimal notation without hyphens, and letters are in lower case.
Configuring MAC authentication timers
About this task
MAC authentication uses the following timers:
· Offline detect timer—Sets the interval that the device must wait for traffic from a user before the device determines that the user is idle. If the device has not received traffic from a user before the timer expires, the device logs off that user and requests the accounting server to stop accounting for the user.
· Quiet timer—Sets the interval that the device must wait before the device can perform MAC authentication for a user that has failed MAC authentication. All packets from the MAC address are dropped during the quiet time. This quiet mechanism prevents repeated authentication from affecting system performance.
· Server timeout timer—Sets the interval that the device waits for a response from a RADIUS server before the device determines that the RADIUS server is unavailable. If the timer expires during MAC authentication, the user cannot access the network.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure MAC authentication timers.
mac-authentication timer { offline-detect offline-detect-value | quiet quiet-value | server-timeout server-timeout-value }
By default, the offline detect timer is 300 seconds, the quiet timer is 60 seconds, and the server timeout timer is 100 seconds.
Configuring a MAC authentication guest VLAN
Restrictions and guidelines
When you configure the MAC authentication guest VLAN on a port, follow the guidelines in Table 4.
Table 4 Relationships of the MAC authentication guest VLAN with other security features
|
Feature |
Relationship description |
Reference |
|
Quiet feature of MAC authentication |
The MAC authentication guest VLAN feature has higher priority. When a user fails MAC authentication, the user can access the resources in the guest VLAN. The user's MAC address is not marked as a silent MAC address. |
|
|
Port intrusion protection |
The guest VLAN feature has higher priority than the block MAC action but lower priority than the shutdown port action of the port intrusion protection feature. |
See "Configuring port security." |
Prerequisites
Before you configure the MAC authentication guest VLAN on a port, complete the following tasks:
· Create the VLAN to be specified as the MAC authentication guest VLAN.
· Configure the port as a hybrid port, and configure the VLAN as an untagged member on the port.
For information about VLAN configuration, see Network Connectivity Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Specify the MAC authentication guest VLAN on the port.
mac-authentication guest-vlan guest-vlan-id
By default, no MAC authentication guest VLAN is specified on a port.
You can configure only one MAC authentication guest VLAN on a port. The MAC authentication guest VLANs on different ports can be different.
4. Set the authentication interval for users in the MAC authentication guest VLAN.
mac-authentication guest-vlan auth-period period-value
The default setting is 30 seconds.
Setting the maximum number of concurrent MAC authentication users on a port
About this task
Perform this task to prevent the system resources from being overused.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Set the maximum number of concurrent MAC authentication users on the port.
mac-authentication max-user max-number
The default setting is 4294967295.
Configuring MAC authentication delay
About this task
When both 802.1X authentication and MAC authentication are enabled on a port, you can delay MAC authentication so that 802.1X authentication is preferentially triggered.
If no 802.1X authentication is triggered or 802.1X authentication fails within the delay period, the port continues to process MAC authentication.
Restrictions and guidelines
Do not set the port security mode to mac-else-userlogin-secure or mac-else-userlogin-secure-ext when you use MAC authentication delay. The delay does not take effect on a port in either of the two modes. For more information about port security modes, see "Configuring port security."
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable MAC authentication delay and set the delay timer.
mac-authentication timer auth-delay time
By default, MAC authentication delay is disabled.
Configuring the keep-online feature
About this task
Periodic MAC reauthentication tracks the connection status of online users, and updates the authorization attributes assigned by the RADIUS server. The attributes include VLAN.
The device reauthenticates an online MAC authentication user periodically only after it receives the termination action Radius-request from the authentication server for this user. The Session-Timeout attribute (session timeout period) assigned by the server is the reauthentication interval. To display the server-assigned Session-Timeout and Termination-Action attributes, use the display mac-authentication connection command. Support for the server configuration and assignment of Session-Timeout and Termination-Action attributes depends on the server model.
The keep-online feature enables the device to keep the MAC authentication users online when no server is reachable for MAC reauthentication.
Restrictions and guidelines
In a fast-recovery network, you can use the keep-online feature to prevent MAC authentication users from coming online and going offline frequently.
Any modification to the MAC authentication domain or user account format setting does not affect the reauthentication of online MAC authentication users. The modified setting takes effect only on MAC authentication users that come online after the modification.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable the keep-online feature for authenticated MAC authentication users on the port.
mac-authentication re-authenticate server-unreachable keep-online
By default, the keep-online feature is disabled. The device logs off online MAC authentication users if no server is reachable for MAC reauthentication.
Display and maintenance commands for MAC authentication
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display MAC authentication information. |
display mac-authentication [ ap ap-name [ radio radio-id ] | interface interface-type interface-number ] |
|
Display MAC authentication connections. |
display mac-authentication connection [ ap ap-name [ radio radio-id ] | interface interface-type interface-number | user-mac mac-address | user-name user-name ] |
|
Clear MAC authentication statistics. |
reset mac-authentication statistics [ ap ap-name [ radio radio-id ] | interface interface-type interface-number ] |
|
Remove users from the MAC authentication guest VLAN on a port. |
reset mac-authentication guest-vlan interface interface-type interface-number [ mac-address mac-address ] |